设计模式结构型模式
Posted weixin_42412601
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式结构型模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
结构型模式:解决的是,怎么让我们的软件更加的有伸缩性、扩展性。
1、适配器模式
基本介绍:
1)适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)将某个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口表示,主的目的是兼容性,让原本因接口不匹配不能一起工作的两个类可以协同工作。其别名为包装器(Wrapper)
2)适配器模式属于结构型模式
3)主要分为三类:类适配器模式、对象适配器模式、接口适配器模式
类适配器模式
被适配者:220V电压
public class Voltage220V
//输出220v电压
public int output220V()
int src=220;
System.out.println("电压="+src+"伏");
return src;
适配接口:5V电压
public interface IVoltage5V
int output5V();
适配器:将220V电压转成5V,以便手机适配,能够进行充电
public class VoltageAdapter extends Voltage220V implements IVoltage5V
@Override
public int output5V()
//获取到220V电压
int i = output220V();
System.out.println("适配器正在将220V电压转为5V");
//转成5V电压
return i/44;
手机:
public class Phone
//充电
public void charging(IVoltage5V iVoltage5V)
if (iVoltage5V.output5V()==5)
System.out.println("电压5V,可以充电");
else
System.out.println("电压不等于5V,不能充电");
使用者:
public static void main(String[] args)
Phone phone = new Phone();
phone.charging(new VoltageAdapter());
类适配器模式注意事项和细节
1)Java 是单继承机制,所以类适配器需要继承src[被适配者]类这一点算是一个缺点, 因为这要求dst[适配者]必须是接口,有一定局限性;
2)src 类的方法在 Adapter 中都会暴露出来,也增加了使用的成本。
3)由于其继承了 src 类,所以它可以根据需求重写 src 类的方法,使得 Adapter 的灵活性增强了。
对象适配器模式
对象适配器就是对类适配器模式的改进。
使用关联关系(聚合)来替代继承关系,遵循的是合成复用原则。
适配器
public class VoltageAdapter implements IVoltage5V
private Voltage220V voltage220V;
public VoltageAdapter(Voltage220V voltage220V)
this.voltage220V = voltage220V;
@Override
public int output5V()
//获取到220V电压
int i = voltage220V.output220V();
System.out.println("适配器正在将220V电压转为5V");
//转成5V电压
return i/44;
使用者:
public static void main(String[] args)
Phone phone = new Phone();
phone.charging(new VoltageAdapter(new Voltage220V()));
接口适配器模式
- 核心思路:当不需要全部实现接口提供的方法时,可先设计一个抽象类实现接口,并为该接口中每个方法提供一个默认实现(空方法),那么该抽象类的子类可有选择地覆盖父类的某些方法来实现需求
- 适用于一个接口不想使用其所有的方法的情况。
接口:
public interface Interface4
void m1();
void m2();
void m3();
void m4();
适配器:
public abstract class AbsAdapter implements Interface4
@Override
public void m1()
@Override
public void m2()
@Override
public void m3()
@Override
public void m4()
使用:
public static void main(String[] args)
AbsAdapter absAdapter = new AbsAdapter()
//只需要去覆盖我们 需要使用的接口方法
@Override
public void m1()
System.out.println("使用了 m1 的方法");
;
absAdapter.m1();
适配器模式在 SpringMVC 框架应用的源码剖析
1)SpringMvc 中的 HandlerAdapter, 就使用了适配器模式
2)SpringMVC 处理请求的流程回顾
3)使用 HandlerAdapter 的原因分析:
可以看到处理器的类型不同,有多重实现方式,那么调用方式就不是确定的,如果需要直接调用 Controller 方法,需要调用的时候就得不断是使用 if else 来进行判断是哪一种子类然后执行。那么如果后面要扩展 Controller, 就得修改原来的代码,这样违背了 OCP 原则。
4)代码分析+Debug 源码

2、桥接模式
1、手机操作问题
现在对不同手机类型的不同品牌实现操作编程(比如:开机、关机、上网、打电话等),如图:

2、传统方案解决收集操作问题
传统方法对应的类图

扩展性极差(会产生类爆炸),如果我们再增加手机的类型,就需要增加各个品牌手机的类,同样如果我们增加一个手机品牌,也要在各个手机样式类下增加,违反了单一职责原则,增加了代码维护成本。
3、桥接模式解决收集操作问题
使用桥接模式改进传统方式,让程序具有更好的扩展性,利用程序维护

品牌接口:
public interface Brand
void open();
void close();
void call();
public class XiaoMi implements Brand
@Override
public void open()
System.out.println("小米手机开机");
@Override
public void close()
System.out.println("小米手机关机");
@Override
public void call()
System.out.println("小米手机打电话");
public class Vivo implements Brand
@Override
public void open()
System.out.println("Vivo手机开机");
@Override
public void close()
System.out.println("Vivo手机关机");
@Override
public void call()
System.out.println("Vivo手机打电话");
手机抽象类:
public abstract class Phone
//聚合品牌
Brand brand;
public Phone(Brand brand)
this.brand = brand;
public void open()
brand.open();
public void close()
brand.close();
public void call()
brand.call();
public class FoldedPhone extends Phone
public FoldedPhone(Brand brand)
super(brand);
@Override
public void open()
super.open();
System.out.println("折叠样式手机");
@Override
public void close()
super.close();
System.out.println("折叠样式手机");
@Override
public void call()
super.call();
System.out.println("折叠样式手机");
使用方:
public class Client
public static void main(String[] args)
Brand xiaoMi = new XiaoMi();
Phone phone = new FoldedPhone(xiaoMi);
phone.open();
phone.call();
phone.close();
4、桥接模式在 JDBC 的源码剖析
Jdbc 的 Driver 接口,如果从桥接模式来看,Driver 就是一个接口,下面可以有 mysql 的 Driver,Oracle 的
Driver,这些就可以当做实现接口类
与桥接模式不完全相同

3、装饰者模式(也叫包装模式)
装饰者模式:动态的将新功能附加到对象上。在对象功能扩展方面,它比继承更有弹性,装饰者模式也体现了开闭原则(ocp)
主要解决:一般的,我们为了扩展一个类经常使用继承方式实现,由于继承为类引入静态特征,并且随着扩展功能的增多,子类会很膨胀。
比如:
1)咖啡种类/单品咖啡:Espresso(意大利浓咖啡)、ShortBlack、LongBlack(美式咖啡)、Decaf(无因咖啡)
2)调料:Milk、Soy(豆浆)、Chocolate
3)要求在扩展新的咖啡种类时,具有良好的扩展性、改动方便、维护方便
使用继承的方式来实现:

每种单品咖啡都有对应调料,这样每种咖啡就会有很多与调料组成的子类,比如:加奶的咖啡,巧克力咖啡…
并且以后新出了一种咖啡,这个咖啡对应的与调料组成的子类也会很多。
问题:这样设计,会有很多类,当我们增加一个单品咖啡,或者一个新的调料,类的数量就会倍增,就会出现类爆炸
这种情况就可以使用装饰者模式解决,在不想增加很多子类的情况下扩展类功能。
例如:
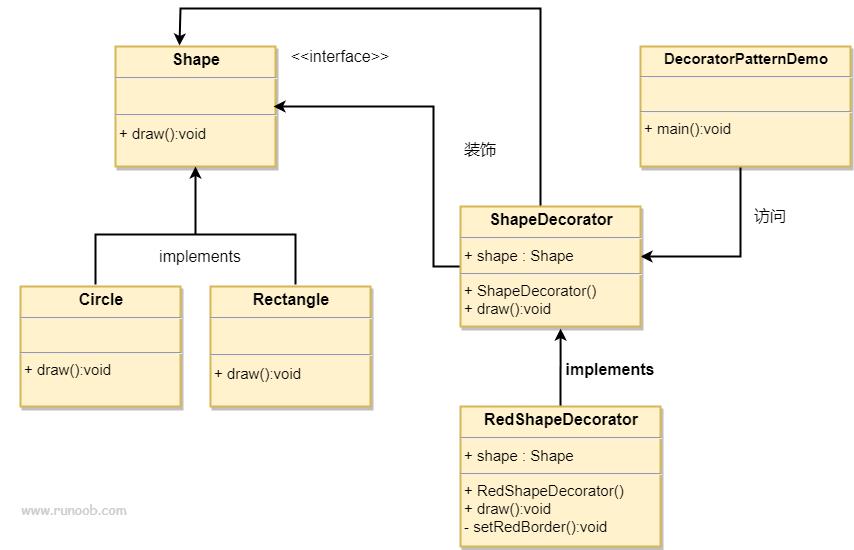
1、被装饰者:
public interface Shape
void draw();
public class Circle implements Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("draw circle");
public class Rectangle implements Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("draw rectangle");
希望能够对被装饰者进行增强,但不是仅仅通过增加子类的方式去实现,因为可能会引起类爆炸的问题。
2、装饰者:实现被装饰者,聚合被装饰者
public abstract class ShapeWrapper implements Shape
protected Shape shape;
public ShapeWrapper(Shape shape)
this.shape = shape;
@Override
public void draw()
shape.draw();
3、装饰者的具体实现类,即子类
主要是对被装饰者的增强
public class RedShapeWrapper extends ShapeWrapper
public RedShapeWrapper(Shape shape)
super(shape);
//对被装饰者的draw方法进行增强
@Override
public void draw()
shape.draw();
//具体的增强
setRedBorder(shape);
private void setRedBorder(Shape decoratedShape)
System.out.println("Border Color: Red");
4、使用
public static void main(String[] args)
RedShapeWrapper redShapeWrapper = new RedShapeWrapper(new Circle());
redShapeWrapper.draw();
draw circle
Border Color: Red
对被装饰者的增强,仅仅只需要在外面,再包一下,即可,这样就不用去添加更多的子类,来达到这个效果了。
3.1、装饰者模式在 JDK 应用的源码分析
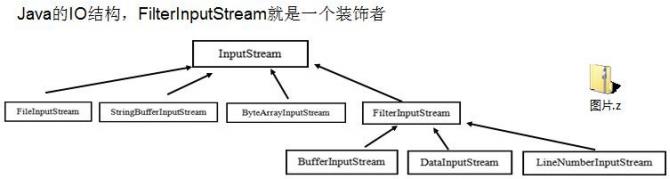
FilterInputStream聚合了InputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
//new FileInputStream是一个被装饰者
//DataInputStream是一个装饰者,对FileInputStream进行功能上的增强
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\\\\abc.txt"));
System.out.println(dis.read());
dis.close();
4、组合模式
1、基本介绍
1)组合模式(Composite Pattern),又叫部分整体模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构,将对象组合成树状结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次关系。
2)组合模式依据树形结构来组合对象,用来表示部分以及整体层次。
3)这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式。
4)组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的访问具有一致性,即:组合能让客户以一致的方式处理个别对象以及组合对象
2、编写程序展示一个学校院系结构:需求是这样,要在一个页面中展示出学校的院系组成,一个学校有多个学院, 一个学院有多个系
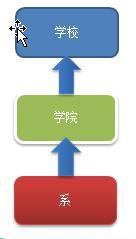
传统方案解决学校院系展示存在的问题分析
1)将学院看做是学校的子类,系是学院的子类,这样实际上是站在组织大小来进行分层次的
2)实际上我们的要求是 :在一个页面中展示出学校的院系组成,一个学校有多个学院,一个学院有多个系, 因
此这种方案,不能很好实现的管理的操作,比如对学院、系的添加,删除,遍历等
3)解决方案:把学校、院、系都看做是组织结构,他们之间没有继承的关系,而是一个树形结构,可以更好的实现管理操作。 => 组合模式
3、组合模式原理类图:

1)Component :这是组合中对象声明接口,在适当情况下,实现所有类共有的接口默认行为,用于访问和管理
Component 子部件, Component 可以是抽象类或者接口
2)Leaf : 在组合中表示叶子节点,叶子节点没有子节点
3)Composite :非叶子节点, 用于存储子部件, 在 Component 接口中实现 子部件的相关操作,比如增加(add), 删除。
4、组合模式解决学校院系展示的应用实例:

5、代码实现
Component:
@Getter
@Setter
public abstract class OrganizationComponent
//名称
private String name;
//描述
private String desc;
public OrganizationComponent(String name, String desc)
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
//默认实现,因为子节点,不能add
public void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
//默认实现,因为子节点,不能add
public void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
//方法 print, 做成抽象的, 子类都需要实现
protected abstract void print();
Composite非叶子节点:
//University 就是 Composite , 可以管理 College
public class UniversityComposite extends OrganizationComponent
//大学管理多个College
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents=new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
public UniversityComposite(String name, String desc)
super(name, desc);
//添加学院
@Override
public void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
//删除学院
@Override
public void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
// print 方法,就是输出 University 包含的学院
@Override
protected void print()
System.out.println("--------------" + getName() + "--------------");
//遍历 organizationComponents
for (OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : organizationComponents)
organizationComponent.print();
//College 就是 Composite , 可以管理Department
public class College extends OrganizationComponent
//List中存放的 Department
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents=new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
public College(String name, String desc)
super(name, desc);
//添加系Department
@Override
public void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
//删除系Department
@Override
public void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent)
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
// print 方法,就是输出College包含的系
@Override
protected void print()
System.out.println("--------------" + getName() + "--------------");
//遍历 organizationComponents
for (OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : organizationComponents)
organizationComponent.print();
//Department就是Composite
public class Department extends OrganizationComponent
//系已经是最小的了,没有下一层了,它自己就是叶子节点
//所以没有集合了
public Department(String name, String desc)
super(name, desc);
//add , remove 就不用写了,因为他是叶子节点
@Override
protected void print()
System.out.println(getName());
使用者:
public static void main(String[] args)
//从大到小创建对象,大学
OrganizationComponent universityComposite = new UniversityComposite("清华大学","清华大学描述xxx");
//创建学院
OrganizationComponent computerCollege = new College("计算机学院","计算机学院描述xxx");
OrganizationComponent infoEngineerCollege = new College("信息工程学院","信息工程学院描述xxx");
//创建计算机学院下面的系并添加到学院里
computerCollege.add(new Department("软件工程","软件工程不错"));
computerCollege.add(new Department("网络工程","网络工程不错"));
computerCollege.add(new Department("计算机科学与技术", " 计算机科学与技术是老牌的专业 "));
//创建信息工程学院下面的系并添加到学院里
infoEngineerCollege.add(new Department("通用工程","通用工程xxx"));
infoEngineerCollege.add(new Department("信息工程","信息工程好学"));
//将学院加入到学校
universityComposite.add(computerCollege);
universityComposite.add(infoEngineerCollege);
//查看大学里的信息
universityComposite.print();
System.out.println("=======================================");
//查看某个学院的信息
computerCollege.print();
4.1、组合模式在 JDK 集合的源码分析
Java 的集合类-HashMap 就使用了组合模式
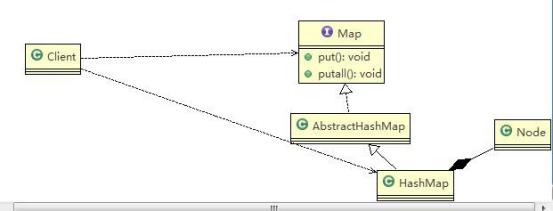
- Map/AbstractHashMap就是一个抽象的构建(相当于component)
- HashMap是一个中间的构建(Composite),实现/继承了相关方法put/putall
- Node是HashMap的静态内部类,类似leaf叶子节点,这里就没有put/putall
5、外观模式(门面模式)
基本介绍
1)外观模式(Facade),也叫“过程模式:外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用
2)外观模式通过定义一个一致的接口,用以屏蔽内部子系统的细节,使得调用端只需跟这个接口发生调用,而无需关心这个子系统的内部细节
主要解决:降低访问复杂系统的内部子系统时的复杂度,简化客户端与之的接口。
例如:

接口和实现类:
public interface Shape
void draw();
public class Rectangle implements Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("Rectangle::draw()");
public class Square implements Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("Square::draw()");
public class Circle implements Shape
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("Circle::draw()");
创建一个外观类。
public class ShapeMaker
private Shape circle;
private Shape rectangle;
private Shape square;
public ShapeMaker()
circle = new Circle();
rectangle = new Rectangle();
square = new Square();
public void drawCircle()
circle.draw();
public void drawRectangle()
rectangle.draw();
public void drawSquare()
square.draw();
使用者:使用者直接使用外观类,无需关心内部子系统是如何实现的。
public static void main(String[] args)
ShapeMaker shapeMaker = new ShapeMaker();
shapeMaker.drawCircle();
shapeMaker.drawRectangle();
shapeMaker.drawSquare();
5.1、外观模式在 MyBatis 框架应用的源码分析
Configuration相当于外观类:

DefaultReflectorFactory、DefaultObjectFactory、DefaultObjectWrapperFactory是组合在外观类中的子系统。
Configuration外观类提供了newMetaObject方法供客户端使用,屏蔽了内部对子系统的细节,降低了客户端对子系统使用的复杂性


6、享元模式
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)主要用于减少创建对象的数量,以减少内存占用和提高性能。
主要解决:在有大量对象时,有可能会造成内存溢出,我们把其中共同的部分抽象出来,如果有相同的业务请求,直接返回在内存中已有的对象,避免重新创建。
使用场景: 1、系统有大量相似对象。 2、需要缓冲池的场景。
应用实例: 1、JAVA 中的 String,如果有则返回,如果没有则创建一个字符串保存在字符串缓存池里面。 2、数据库的数据池。

接口和实现类:
public interface Shape
void draw();
public class Circle implements Shape
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color)
this.color = color;
public void setX(int x)
this.x = x;
public void setY(int y)
this.y = y;
public void setRadius(int radius)
this.radius = radius;
@Override
public void draw()
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color
+", x : " + x +", y :" + y +", radius :" + radius);
工厂类:
public class ShapeFactory
//用于缓存大量相似对象
private static final Map<String,Shape> circleMap=new HashMap<>();
//获取对象
public static Shape getCircle(String color)
Circle circle = (Circle) circleMap.get(color);
if (circle==null)
circle=new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color,circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
return circle;
使用:
public class FlyweightPatternDemo
private static final String colors[] =
"Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" ;
public static void main(String[] args)
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i)
Circle circle =
(Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
private static String getRandomColor()
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
private static int getRandomX()
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
private static int getRandomY()
return (int)(Math.random()*100以上是关于设计模式结构型模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章