基于C++11实现的高效线程池及工作原理
Posted linux大本营
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于C++11实现的高效线程池及工作原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简介
线程池(thread pool):一种线程的使用模式,线程过多会带来调度开销,进而影响缓存局部性和整体性能。而线程池维护着多个线程,等待着监督管理者分配可并发执行的任务。这避免了在处理短时间任务时创建与销毁线程的代价。线程池不仅能够保证内核的充分利用,还能防止过分调度。可用线程数量应该取决于可用的并发处理器、处理器内核、内存、网络sockets等的数量。
线程池的组成
1、线程池管理器
创建一定数量的线程,启动线程,调配任务,管理着线程池。
本篇线程池目前只需要启动(start()),停止方法(stop()),及任务添加方法(addTask).
start()创建一定数量的线程池,进行线程循环.
stop()停止所有线程循环,回收所有资源.
addTask()添加任务.
2、工作线程
线程池中线程,在线程池中等待并执行分配的任务.
本篇选用条件变量实现等待与通知机制.
3、任务接口,
添加任务的接口,以供工作线程调度任务的执行。
4、任务队列
用于存放没有处理的任务。提供一种缓冲机制
同时任务队列具有调度功能,高优先级的任务放在任务队列前面;本篇选用priority_queue 与pair的结合用作任务优先队列的结构.
线程池工作的四种情况.
假设我们的线程池大小为3,任务队列目前不做大小限制.
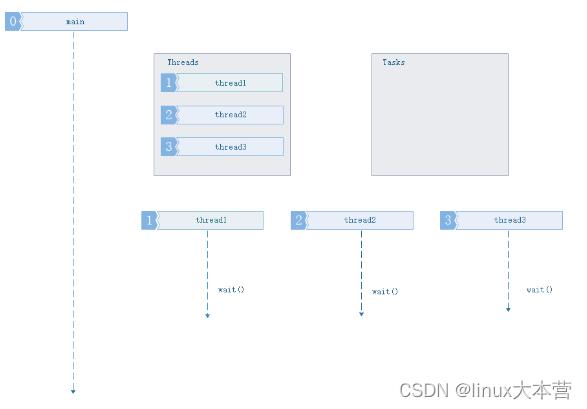
1、主程序当前没有任务要执行,线程池中的任务队列为空闲状态.
此情况下所有工作线程处于空闲的等待状态,任务缓冲队列为空.
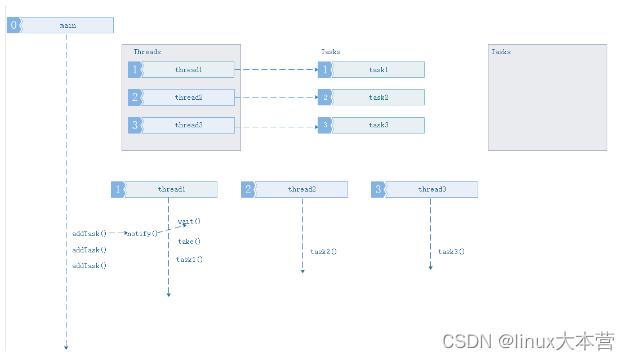
2、主程序添加小于等于线程池中线程数量的任务.
此情况基于情形1,所有工作线程已处在等待状态,主线程开始添加三个任务,添加后通知(notif())唤醒线程池中的线程开始取(take())任务执行. 此时的任务缓冲队列还是空。
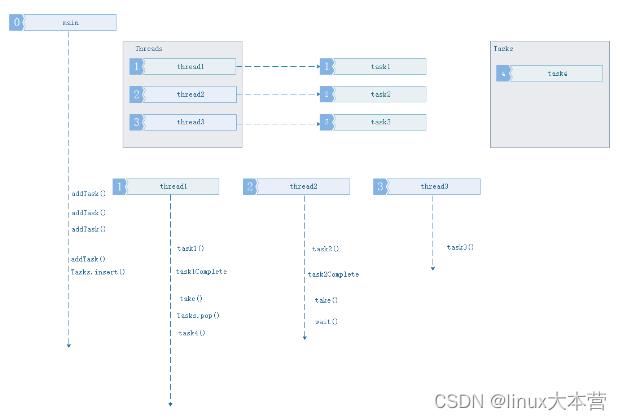
3、主程序添加任务数量大于当前线程池中线程数量的任务.
此情况发生情形2后面,所有工作线程都在工作中,主线程开始添加第四个任务,添加后发现现在线程池中的线程用完了,于是存入任务缓冲队列。工作线程空闲后主动从任务队列取任务执行.
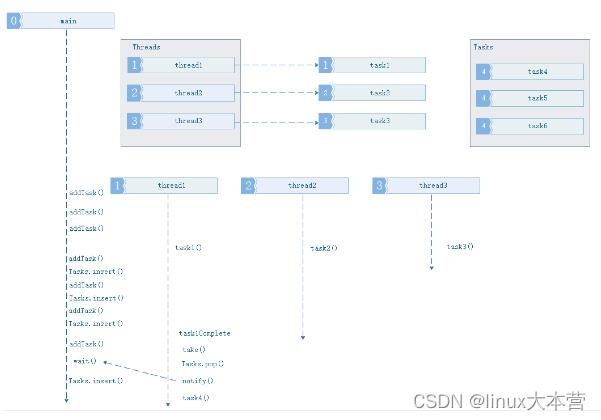
4、主程序添加任务数量大于当前线程池中线程数量的任务,且任务缓冲队列已满.
此情况发生情形3且设置了任务缓冲队列大小后面,主程序添加第N个任务,添加后发现池子中的线程用完了,任务缓冲队列也满了,于是进入等待状态、等待任务缓冲队列中的任务腾空通知。
但是要注意这种情形会阻塞主线程,本篇暂不限制任务队列大小,必要时再来优化.
相关视频推荐
【文章福利】需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加群812855908(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,内核,nginx,ZeroMQ,mysql,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等)
实现
等待通知机制通过条件变量实现,Logger和CurrentThread,用于调试,可以无视.
#ifndef _THREADPOOL_HH
#define _THREADPOOL_HH
#include <vector>
#include <utility>
#include <queue>
#include <thread>
#include <functional>
#include <mutex>
#include "Condition.hh"
class ThreadPool
public:
static const int kInitThreadsSize = 3;
enum taskPriorityE level0, level1, level2, ;
typedef std::function<void()> Task;
typedef std::pair<taskPriorityE, Task> TaskPair;
ThreadPool();
~ThreadPool();
void start();
void stop();
void addTask(const Task&);
void addTask(const TaskPair&);
private:
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool&);//禁止复制拷贝.
const ThreadPool& operator=(const ThreadPool&);
struct TaskPriorityCmp
bool operator()(const ThreadPool::TaskPair p1, const ThreadPool::TaskPair p2)
return p1.first > p2.first; //first的小值优先
;
void threadLoop();
Task take();
typedef std::vector<std::thread*> Threads;
typedef std::priority_queue<TaskPair, std::vector<TaskPair>, TaskPriorityCmp> Tasks;
Threads m_threads;
Tasks m_tasks;
std::mutex m_mutex;
Condition m_cond;
bool m_isStarted;
;
#endif
//Cpp
#include <assert.h>
#include "Logger.hh" // debug
#include "CurrentThread.hh" // debug
#include "ThreadPool.hh"
ThreadPool::ThreadPool()
:m_mutex(),
m_cond(m_mutex),
m_isStarted(false)
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool()
if(m_isStarted)
stop();
void ThreadPool::start()
assert(m_threads.empty());
m_isStarted = true;
m_threads.reserve(kInitThreadsSize);
for (int i = 0; i < kInitThreadsSize; ++i)
m_threads.push_back(new std::thread(std::bind(&ThreadPool::threadLoop, this)));
void ThreadPool::stop()
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::stop() stop.";
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
m_isStarted = false;
m_cond.notifyAll();
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::stop() notifyAll().";
for (Threads::iterator it = m_threads.begin(); it != m_threads.end() ; ++it)
(*it)->join();
delete *it;
m_threads.clear();
void ThreadPool::threadLoop()
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : " << CurrentThread::tid() << " start.";
while(m_isStarted)
Task task = take();
if(task)
task();
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : " << CurrentThread::tid() << " exit.";
void ThreadPool::addTask(const Task& task)
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
/*while(m_tasks.isFull())
//when m_tasks have maxsize
cond2.wait();
*/
TaskPair taskPair(level2, task);
m_tasks.push(taskPair);
m_cond.notify();
void ThreadPool::addTask(const TaskPair& taskPair)
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
/*while(m_tasks.isFull())
//when m_tasks have maxsize
cond2.wait();
*/
m_tasks.push(taskPair);
m_cond.notify();
ThreadPool::Task ThreadPool::take()
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
//always use a while-loop, due to spurious wakeup
while(m_tasks.empty() && m_isStarted)
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::take() tid : " << CurrentThread::tid() << " wait.";
m_cond.wait(lock);
LOG_TRACE << "ThreadPool::take() tid : " << CurrentThread::tid() << " wakeup.";
Task task;
Tasks::size_type size = m_tasks.size();
if(!m_tasks.empty() && m_isStarted)
task = m_tasks.top().second;
m_tasks.pop();
assert(size - 1 == m_tasks.size());
/*if (TaskQueueSize_ > 0)
cond2.notify();
*/
return task;
测试程序
start() 、stop()
测试线程池基本的创建退出工作,及检测资源是否正常回收.
int main()
ThreadPool threadPool;
threadPool.start();
getchar();
getchar();
return 0;
./test.out
2021-10-11 16:50:36.054805 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:53] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3680 start.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.054855 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:72] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3680 wait.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055633 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:53] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3679 start.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055676 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:72] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3679 wait.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055641 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:53] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3681 start.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055701 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:72] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3681 wait.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055736 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:53] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3682 start.
2021-10-11 16:50:36.055746 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:72] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3682 wait.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.411792 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:36] [stop] ThreadPool::stop() stop.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.411863 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:39] [stop] ThreadPool::stop() notifyAll().
2021-10-11 16:51:01.411877 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:76] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3680 wakeup.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.411883 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:62] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3680 exit.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.412062 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:76] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3682 wakeup.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.412110 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:62] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3682 exit.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.413052 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:76] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3679 wakeup.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.4130982021-10-11 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:62] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3679 exit.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.413112 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:76] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 3681 wakeup.
2021-10-11 16:51:01.413141 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:62] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 3681 exit.addTask()、PriorityTaskQueue
测试添加任务接口,及优先任务队列.
主线程首先添加了5个普通任务、 1s后添加一个高优先级任务,当前3个线程中的最先一个空闲后,会最先执行后面添加的priorityFunc().
std::mutex g_mutex;
void priorityFunc()
for (int i = 1; i < 4; ++i)
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex);
LOG_DEBUG << "priorityFunc() [" << i << "at thread [ " << CurrentThread::tid() << "] output";// << std::endl;
void testFunc()
// loop to print character after a random period of time
for (int i = 1; i < 4; ++i)
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex);
LOG_DEBUG << "testFunc() [" << i << "] at thread [ " << CurrentThread::tid() << "] output";// << std::endl;
int main()
ThreadPool threadPool;
threadPool.start();
for(int i = 0; i < 5 ; i++)
threadPool.addTask(testFunc);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
threadPool.addTask(ThreadPool::TaskPair(ThreadPool::level0, priorityFunc));
getchar();
return 0;
./test.out
2021-10-11 18:24:20.886837 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:56] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4121 start.
2021-10-11 18:24:20.886893 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4121 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:20.887580 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:56] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4120 start.
2021-10-11 18:24:20.887606 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4120 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:20.887610 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:56] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4122 start.
2021-10-11 18:24:20.887620 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4122 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:21.887779 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [1] at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:21.887813 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [1] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:21.888909 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [1] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:22.888049 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [2] at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:22.888288 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [2] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:22.889978 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [2] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:23.888467 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [3] at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:23.888724 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4120 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:23.888778 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [3] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:23.888806 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4122 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:23.890413 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [3] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:23.890437 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4121 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:24.889247 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:92] [priorityFunc] priorityFunc() [1at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:24.891187 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [1] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:24.893163 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [1] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:25.889567 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:92] [priorityFunc] priorityFunc() [2at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:25.891477 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [2] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:25.893450 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [2] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:26.890295 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:92] [priorityFunc] priorityFunc() [3at thread [ 4120] output
2021-10-11 18:24:26.890335 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:99] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4120 wait.
2021-10-11 18:24:26.892265 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [3] at thread [ 4121] output
2021-10-11 18:24:26.892294 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:99] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4121 wait.
2021-10-11 18:24:26.894274 [DEBUG] [main.cpp:104] [testFunc] testFunc() [3] at thread [ 4122] output
2021-10-11 18:24:26.894299 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:99] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4122 wait.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359003 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:37] [stop] ThreadPool::stop() stop.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359043 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:42] [stop] ThreadPool::stop() notifyAll().
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359061 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4120 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359067 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:65] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4120 exit.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359080 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4122 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359090 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:65] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4122 exit.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359123 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:103] [take] ThreadPool::take() tid : 4121 wakeup.
2021-10-11 18:24:35.359130 [TRACE] [ThreadPool.cpp:65] [threadLoop] ThreadPool::threadLoop() tid : 4121 exit.以上是关于基于C++11实现的高效线程池及工作原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Spring使用ThreadPoolTaskExecutor自定义线程池及实现异步调用