SpringMVC从request到controller过程详解
Posted 轩辕223
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringMVC从request到controller过程详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
例行推广一下我的博客,喜欢这篇文章的朋友可以关注我的博客http://zwgeek.com
1. 背景
之前一篇文章 SpringMVC对象绑定时自定义名称对应关系 讲了如何去把request中的请求参数指定到对象的某个属性上。但文中只讲了一下做法,没有讲原理,因为这个原理涉及到SpringMVC时怎么处理Request的复杂过程。这篇文章就来和大家扒一扒这件事,SpringMVC是怎么把一个request的请求最终映射到Controller的方法的。这是正向的,对于Spring来说,其实还负责把Controller的返回结果通过一些处理展现给用户,这是后话,这篇文章我们只说正向的请求,也就是从request到Controller的过程。
首先,来一张SpringMVC处理请求的整个过程,图是来自《Spring实战》5.1.1章,我觉得总结的非常到位,几个大的过程都画出来了。
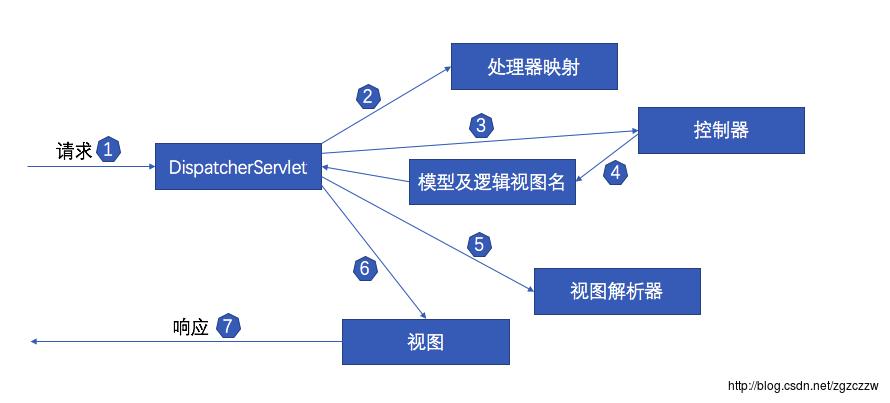
我们这篇文章要说的其实就是1,2,3这三个阶段的实现原理。后面4,5,6,7可能会再开一篇文章来说,如果我的懒癌治好了的话。过程1是第二部分请求到DispatcherServlet,过程2和过程3可以总结为DispatcherServlet处理请求,也就是本文的第三部分。
2. 请求到DispatcherServlet
那我们按照顺序先来说一下过程1,熟悉SpringMVC的同学肯定都知道DispatcherServlet这个类,这个类是整个SpringMVC的入口。那在这个类之前做工作的其实是J2EE,不是我们重点关注的对象。只简单说一下:
首先一个WEB程序的入口其实是web.xml,一个请求过来,J2EE会先来这个文件中寻找合适的servlet-mapping,找到了就交给对应的Servlet处理。SpringMVC也需要在这里配一个Servlet,并且声明处理一些请求,简单点来说,我们都会让SpringMVC处理所有的请求,所以请求映射的地方就会写‘/*’,比如下面这样。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Spring web</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/web-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Spring web</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>这样配置一下,所有的请求就都会交给DispatcherServlet来处理了,也就是交给SpringMVC来处理了。1的过程就这么简单,想看代码实现的话可以翻翻Tomcat的代码。好,那接下来我们这篇文章重点,过程2和过程3的实现原理,也就是DispatcherServlet的处理过程。
DispatcherServlet作为一个标准的Servlet,生命周期也是有三个,初始化,处理请求和销毁,分别对应Servlet接口的三个方法,init(), service()和destroy()。
public interface Servlet
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
这里我们重点关注init和service的过程,destroy是service之后的过程了,可以暂时忽略不看。
2.1 DispatcherServlet初始化
这里先放一张DispatcherServlet的继承关系吧

左边这条线就是Servlet的线,HttpServlet以及之上就是J2EE部分的代码,关注的是对请求的处理,比如doGet,doPost这些。下面HttpServletBean获取环境变量以方便子类使用。然后FrameworkServlet主要维护了自己的上下文对象webApplicationContext。我们知道一般的Servlet是不维护上下文对象的,而DispatcherServlet就是因为继承了FrameworkServlet,所以拥有了自己的上下文。简单来说大概就是这样,后面分析DispatcherServlet的工作过程的时候,还会追踪到它的这几个父类中来,到时候我们再细说。
首先我们先从init方法来分析DispatcherServlet的的初始化过程,这是Servlet接口中init的方法签名。
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;这个带参的init方法出现在GenericServlet中
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException
this.config = config;
this.init();
public void init() throws ServletException
接收了一个J2EE环境传过来的配置对象config,然后提供了一个无参的init方法供子类初始化。这个无参的init方法在HttpServletBean中。
public final void init() throws ServletException
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\'");
try
//获取配置文件,就是web.xml中contextConfigLocation的值
HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues ex = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
//将Servlet包装成一个bean
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//获取服务器信息
ServletContextResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
//初始化Bean
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
//设置配置文件到bean
bw.setPropertyValues(ex, true);
//其实以上部分没用到,因为在DispatcherServlet里initBeanWrapper没有被实现
catch (BeansException var4)
this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\'", var4);
throw var4;
//供子类初始化
this.initServletBean();
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Servlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\' configured successfully");
HttpServletBean中提供了两个供子类重写的初始化方法initBeanWrapper和initServletBean,其中initBeanWrapper没有使用,DispatcherServlet使用了initServletBean来初始化接下来的工作。
initServletBean在FrameworkServlet中。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException
this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\'");
if(this.logger.isInfoEnabled())
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\': initialization started");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try
//初始化上下文对象
this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext();
//提供给子类初始化
this.initFrameworkServlet();
catch (ServletException var5)
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var5);
throw var5;
catch (RuntimeException var6)
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var6);
throw var6;
if(this.logger.isInfoEnabled())
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
initFrameworkServlet是提供给子类复写的初始化方法,但是DispatcherServlet也没有用,而是用了initWebApplicationContext中的refresh方法,任性啊。initWebApplicationContext是用来初始化上下文对象的,具体逻辑如下
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext()
//前面检查ApplicationContext是否被初始化过,如果有就直接拿来用
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if(this.webApplicationContext != null)
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if(wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext attrName = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac;
if(!attrName.isActive())
if(attrName.getParent() == null)
attrName.setParent(rootContext);
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(attrName);
if(wac == null)
wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();
if(wac == null)
wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
//Servlet自己的初始化方法
if(!this.refreshEventReceived)
this.onRefresh(wac);
//将上下文对象保存起来
if(this.publishContext)
String attrName1 = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName1, wac);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName1 + "]");
return wac;
这个方法前半部分是检查之前有没有创建过ApplicationContext对象,如果有,就直接拿过来用。如果没有,则初始化一个,onRefresh则是Servlet将自己的配置加到上下文对象中的方法,DispatcherServlet也是用了这个方法来初始化各种Bean。追了一堆,init方法终于到DispatcherServlet内部了。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context)
this.initStrategies(context);
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context)
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
看,上面就是DispatcherServlet的一堆初始化方法。
来自http://blog.csdn.net/snail_bi/article/details/50578371
MultipartResolver:
http://exceptioneye.iteye.com/blog/1314958
–> CommonsMultipartResolver 文件上传解析器LocalResolver: 支持国际化,区域解析器。每DispatcherServlet只能注册一个区域解析器
http://blog.csdn.NET/rj042/article/details/23354225
–> AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 它通过检验HTTP请求的accept-language头部来解析区域。由用户的web浏览器根据底层操作系统的区域设置进行设定。
–> SessionLocaleResolver 它通过检验用户会话中预置的属性来解析区域。如果该会话属性
不存在,它会根据accept-language HTTP头部确定默认区域。
–> CookieLocaleResolver来解析区域。如果Cookie不存在,它会根据accept-language HTTP头部确定默认区域。
–> FixedLocaleResolver 一直使用固定的Local, 不支持Local改变 。
修改用户的区域
除了显式调用LocaleResolver.setLocale()来修改用户的区域之外,还可以将LocaleChangeInterceptor拦截器应用到处理程序映射中,它会发现当前HTTP请求中出现的特殊参数。其中的参数名称可以通过拦截器的paramName属性进行自定义。如果这种参数出现在当前请求中,拦截器就会根据参数值来改变用户的区域。ThemeSource 动态更换样式的支持(主题)
http://starscream.iteye.com/blog/1075855
–> FixedThemeResolver:固定格式的theme,不能在系统运行时动态更改theme.
–> SessionThemeResolver:theme name存放在session中key值为 org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.SessionThemeResolver.THEME 的session attribute中。可在运行中通过更改session中的相应的key值来动态调整theme的值。
–> CookieThemeResolver:theme name存放在cookie中key值为 org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.CookieThemeResolver.THEME 中。可在运行中通过更改cookie中的相应的key值来动态调整theme的值。HandlerMapping
http://blog.csdn.Net/sunxing007/article/details/4584748
http://blog.csdn.net/prince2270/article/details/5894456
–>BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping: 查找spring容器中和请求的url同名的bean.
–>BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping :通过对比url和bean的name找到对应的对象
–>SimpleUrlHandlerMapping :也是直接配置url和对应bean,比BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping功能更多
–>DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping : 主要是针对注解配置@RequestMapping的,已过时
–>RequestMappingHandlerMapping :取代了上面一个
–> 还有很多 ,请看源码HandlerAdapter
–> SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
–> SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
–> RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
–> HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
–> AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapterHandlerExceptionResolver
RequestToViewNameTranslator 用于直接将请求转换为逻辑视图名。
http://sishuok.com/forum/blogPost/list/0/5514.html
http://haohaoxuexi.iteye.com/blog/1774603
–> DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
[
http://localhost:9080/web上下文/list ——-> 逻辑视图名为list
http://localhost:9080/web上下文/list.html ——-> 逻辑视图名为list(默认删除扩展名)
http://localhost:9080/web上下文/user/list.html ——-> 逻辑视图名为user/list
]ViewResolver 视图解析器:定义了如何通过view 名称来解析对应View实例的行为
http://blog.csdn.net/prince2270/article/details/5891085
http://www.iteye.com/problems/76107 多视图问题的解决
http://my.oschina.net/HeliosFly/blog/221392FlashMapManager
http://www.oschina.net/translate/spring-mvc-flash-attribute-example
–> SessionFlashMapManager
以上就是SpringMVC在初始化的时候加入的各种处理器,对于请求到Controller的映射,比较重要的是HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter,HandlerMapping是用来查找处理请求的对象,HandlerAdapter是用来处理请求参数。这里以HandlerAdapter来举个例子,看一下initHandlerAdapters方法。
·private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context)
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if(this.detectAllHandlerAdapters)
Map ex = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if(!ex.isEmpty())
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList(ex.values());
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
else
try
HandlerAdapter ex1 = (HandlerAdapter)context.getBean("handlerAdapter", HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ex1);
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var3)
;
if(this.handlerAdapters == null)
this.handlerAdapters = this.getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("No HandlerAdapters found in servlet \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\': using default");
上面的逻辑是这样的
1)如果detectAllHandlerAdapters属性为true(默认为true),根据类型匹配(HandlerAdapter)机制查找上下文及父Spring容器中所有匹配的Bean,将它们作为该类型组件;
2)如果detectAllHandlerAdapters属性为false,查找名为handlerAdapter类型为HandlerAdapter的Bean作为该类型组件;
3)如果通过以上方式都找不到,使用DispatcherServlet.properties配置文件中指定的三个实现类分别创建一个适配器,添加到适配器列表中。
DispatcherServlet.properties和DispatcherServlet在同一个包下,定义了一些默认的类,内容如下。
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager我们看到HandlerAdapter是有三个默认类,如果程序从上下文中找不到任何HandlerAdapter,就会把这三个加载进来。
DispatcherServlet结束了onRefresh的一系列方法,初始化过程就结束了。接下来就是一个请求到来的时候的处理工作了。
3. Dispatcher处理请求
3.1 预处理请求
请求到来的时候,J2EE会调用相应Servlet的onService方法,对于DispatcherServlet来说,这个onService在FrameworkServlet里,代码如下
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
String method = request.getMethod();
if(method.equalsIgnoreCase(RequestMethod.PATCH.name()))
this.processRequest(request, response);
else
super.service(request, response);
这个方法补充了对PATCH请求类型的处理,其他请求类型如GET,PUT,调用了super的service方法,也就是在HttpServlet的service方法(HttpServletBean中没有复写)。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
String method = req.getMethod();
long errMsg;
if(method.equals("GET"))
errMsg = this.getLastModified(req);
if(errMsg == -1L)
this.doGet(req, resp);
else
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if(ifModifiedSince < errMsg / 1000L * 1000L)
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, errMsg);
this.doGet(req, resp);
else
resp.setStatus(304);
else if(method.equals("HEAD"))
errMsg = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, errMsg);
this.doHead(req, resp);
else if(method.equals("POST"))
this.doPost(req, resp);
else if(method.equals("PUT"))
this.doPut(req, resp);
else if(method.equals("DELETE"))
this.doDelete(req, resp);
else if(method.equals("OPTIONS"))
this.doOptions(req, resp);
else if(method.equals("TRACE"))
this.doTrace(req, resp);
else
String errMsg1 = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]method;
errMsg1 = MessageFormat.format(errMsg1, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg1);
这个方法也很简单,根据不同的请求类型调用不同的方法,这里我们假设请求是个GET请求,那就会去执行子类的doGet方法,在FrameworkServlet里。
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
this.processRequest(request, response);
也没做什么,交给了processRequest处理,其实其他请求最后也都转给processRequest这个方法处理了,因为处理参数的逻辑是一样的。
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object failureCause = null;
//获取之前的位置信息,最后finally时恢复之前配置
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = this.buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = this.buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
//注册Interceptor,没理解干嘛的
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new FrameworkServlet.RequestBindingInterceptor(null));
//将请求中的位置信息记入
this.initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try
//做事情
this.doService(request, response);
catch (ServletException var18)
failureCause = var18;
throw var18;
catch (IOException var19)
failureCause = var19;
throw var19;
catch (Throwable var20)
failureCause = var20;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", var20);
finally
//恢复之前配置
this.resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if(requestAttributes != null)
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
if(failureCause != null)
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", (Throwable)failureCause);
else if(asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
this.logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
else
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
//发布事件 this.publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, (Throwable)failureCause);
先说下发布事件,Spring在请求处理结束后会发布一个ServletRequestHandledEvent类型的事件,可以通过ApplicationListener接收。
这个方法前面和后面做的工作是保留现场,请求处理结束后恢复现场。真正处理请求的方法是doService。这个方法在DispatcherServlet中。
话语权终于到DispatcherServlet中了。
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
String attributesSnapshot = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult()?" resumed":"";
this.logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\'" + attributesSnapshot + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
HashMap attributesSnapshot1 = null;
//处理include类型的request,用不到
if(WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request))
attributesSnapshot1 = new HashMap();
Enumeration inputFlashMap = request.getAttributeNames();
label113:
while(true)
String attrName;
do
if(!inputFlashMap.hasMoreElements())
break label113;
attrName = (String)inputFlashMap.nextElement();
while(!this.cleanupAfterInclude && !attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet"));
attributesSnapshot1.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
//将现在的各种参数加到Request中
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, this.getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap1 = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if(inputFlashMap1 != null)
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap1));
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try
//做事情
this.doDispatch(request, response);
finally
if(WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
return;
if(attributesSnapshot1 != null)
this.restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot1);
这个方法主要是把现在有的一些参数比如上下文对象加到Request中,然后转发到doDispatch方法去处理,终于到了最关键的方法了。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try
try
ModelAndView err = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
//获取Hanlder
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if(mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null)
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
//获取Adapter
HandlerAdapter ex = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if(isGet || "HEAD".equals(method))
long lastModified = ex.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
if((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet)
return;
//执行preHandle方法
if(!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response))
return;
//执行Handle方法
try
err = ex.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
finally
if(asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
return;
//处理默认的ViewName
this.applyDefaultViewName(request, err);
//执行PostHandle
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, err);
catch (Exception var27)
dispatchException = var27;
//处理返回结果,绘制View
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err, dispatchException);
catch (Exception var28)
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var28);
catch (Error var29)
this.triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var29);
finally
if(asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
return;
else
if(multipartRequestParsed)
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
虽然这个方法可以说是整个SpringMVC中最重要的方法,但是整个流程缺及其简单,可以说这一切都归功于Spring框架高度的抽象。我们来梳理一下这个doDispatch方法的流程。
- 获取Handler
- 获取Adapter
- 执行preHandle方法
- 执行Handle方法
- 执行PostHandle
- 处理返回结果
5和6是Controller请求处理结束后的操作,本文中我们只讨论1-2-3-4这四个步骤。1-2-3-4这四个步骤对应了一开始提到的SpringMVC的七大步中的第二步请求到处理器映射和第三步请求到控制器。其中1-2是请求到处理器映射,3-4是请求到控制器。下面我们一步一步的来看。
3.2 根据请求获取Handler
首先第一步是根据request,获取合适的Handler。
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest, false);这里返回的结果是HandlerExecutionChain类型的,从名字我们知道这是一个执行链,里面包含了这个Handler所有相关的信息。下面我们来看下getHandler方法。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
Iterator i$ = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
HandlerExecutionChain handler;
do
if(!i$.hasNext())
return null;
HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)i$.next();
if(this.logger.isTraceEnabled())
this.logger.trace("Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name \\'" + this.getServletName() + "\\'");
handler = hm.getHandler(request);
while(handler == null);
return handler;
遍历HandlerMappings,然后依次调用每个HandlerMappings的getHandler方法,如果有返回就交给该Handler处理。
这个HandlerMappings是DispatcherServlet初始化的时候加入的,在initHandlerMapping方法里。我们看下系统默认的HandlerMapping都有哪些。
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping我的项目自定义了一个HandlerMappings,也是基于注解的
<!--配置注解式处理器映射器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>我们来看一下他是怎么工作的。getHandler方法。这个方法在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类AbstractHandlerMapping中
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
Object handler = this.getHandlerInternal(request);
if(handler == null)
handler = this.getDefaultHandler();
if(handler == null)
return null;
else
if(handler instanceof String)
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
return this.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
Spring框架一贯的套路,父类定义流程,开一个方法供子类去实现,比如这里的getHandlerInternal,返回了Handler之后,再用HandlerExecutionChain包装一下。那先来看下getHandlerInternal方法是怎么获取Handler的。这个方法依然在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中。
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
String lookupPath = this.getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
if(handlerMethod != null)
this.logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
else
this.logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
return handlerMethod != null?handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean():null;
两个重要的方法,getLookupPathForRequest和lookupHandlerMethod,这里我就不贴代码了,说一下实现原理吧,其实RequestMappingHandlerMapping在初始化的时候已经将系统中所有的@RequestMapping注解解析了,放在一个Map里面。实现过程如下。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,在Bean设置完参数后会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,而它在这个方法里面做了初始化的工作。
public void afterPropertiesSet()
this.initHandlerMethods();
protected void initHandlerMethods()
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + this.getApplicationContext());
String[] beanNames = this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts?BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.getApplicationContext(), Object.class):this.getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
String[] arr$ = beanNames;
int len$ = beanNames.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$)
String beanName = arr$[i$];
//判断类中是否含有RequestMapping注释
if(this.isHandler(this.getApplicationContext().getType(beanName)))
//解析方法
this.detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
this.handlerMethodsInitialized(this.getHandlerMethods());
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler)
Class handlerType = handler instanceof String?this.getApplicationContext().getType((String)handler):handler.getClass();
final IdentityHashMap mappings = new IdentityHashMap();
final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Set methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter()
public boolean matches(Method method)
Object mapping = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
if(mapping != null)
mappings.put(method, mapping);
return true;
else
return 以上是关于SpringMVC从request到controller过程详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章