目标检测一文干翻xml文件的读取
Posted 大气层煮月亮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了目标检测一文干翻xml文件的读取相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
在目标检测中xml文件的读取非常常见,常常要用到labelimg、labelme等标注软件, 打标时往往需要打开xml文件,但奈何一直没找到一篇完整的文章,故自己打算手写一篇。下面介绍利用python解析xml文件的方法。
【目标检测】一文搞定xml文件的读取
.xml实例
这是一个在目标检测中十分常见的.xml文件,今天我们就以它来作为例子!
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2007</folder>
<filename>000001.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2007 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
<flickrid>341012865</flickrid>
</source>
<owner>
<flickrid>Fried Camels</flickrid>
<name>Jinky the Fruit Bat</name>
</owner>
<size>
<width>353</width>
<height>500</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>dog</name>
<pose>Left</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>48</xmin>
<ymin>240</ymin>
<xmax>195</xmax>
<ymax>371</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>person</name>
<pose>Left</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>8</xmin>
<ymin>12</ymin>
<xmax>352</xmax>
<ymax>498</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
.py实战中得真知:
tree = ET.parse(xml_path) 读取xml文档 root = tree.getroot() 获取根节点
解析:ET.parse()将xml文件读入到dom,返回一个etree对象,可以通过etree的getroot()、find()等函数对树的根节点和某个子节点进行访问。如findall("object")则返回所有的object节点,还可以通过.text访问节点的文本属性。
1、获取根节点<filename>标签中的文本。
.py
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def get_JPGImgName(xmlpath):
dom=ET.parse(xmlpath)
root=dom.getroot()
#print(root.find('filename').text)
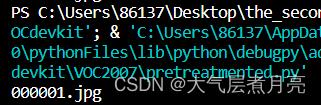
return root.find('filename').text
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(get_JPGImgName(r'VOC2007_Annotations\\000001.xml'))vscode.output
2、获取<object>标签中的子节点<name>的属性(多个)。
.py
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from xml.etree.ElementTree import Element
'''
ET.parse()将xml文件读入到dom,返回一个etree对象,可以通过etree的getroot()、find()等函数对树的根节点和某个子节点进行访问。如findall("object")则返回所有的object节点,还可以通过.text()访问节点的文本属性。
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
xml_path = r'VOC2007_Annotations\\000001.xml'
dom=ET.parse(xml_path)
root=dom.getroot()
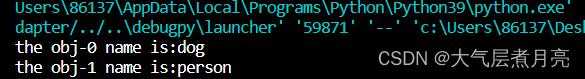
allobj=root.findall("object")
for i, obj in enumerate(allobj):
print('the obj name is:', obj.find('name').text)vscode.output
打包好一个函数用于获取object.name。
.py
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from xml.etree.ElementTree import Element
def get_objectName(xmlpath):
dom=ET.parse(xmlpath)
root=dom.getroot()
allobj=root.findall("object")
xmlNames = []
for i, obj in enumerate(allobj):
xmlNames.append(obj.find('name').text))
# print('the obj- name is:'.format(i,obj.find('name').text))
return xmlNames
番外阅读
XML是可扩展标记语言 ,标记数据、定义数据类型,是一种允许用户对自己的标记语言进行定义的源语言。其中有且只有一个根节点,如上例中根节点为annotations,<></>是一个标签对,标签对内可以有该节点的子节点及其标签对;标签对的内容是可以自定义的。
在用于标注数据的xml文件中,如一般根节点为annotations,包含size、folder、filename、object等多个子节点,object子结点中为bbox的信息。
完毕!
是不是超级简单呢?如果方便的话,欢迎大家点赞+关注!
以上是关于目标检测一文干翻xml文件的读取的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章