日志导致线程Block的这些坑,你不得不防
Posted 美团技术团队
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了日志导致线程Block的这些坑,你不得不防相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
研发人员在项目开发中不可避免地要使用日志,通过它来记录信息和排查问题。Apache Log4j2提供了灵活且强大的日志框架,虽然上手比较快,但稍有不慎也非常容易踩“坑”。
本文介绍了美团统一API网关服务Shepherd在实践中所踩过的关于日志导致线程Block的那些“坑”,以及我们如何从日志框架源码层面进行分析和解决问题的过程,并在最后给大家分享一些关于日志避“坑”的实践经验,希望能给大家带来一些帮助。
1. 前言
日志对程序的重要性不言而喻。它很“大”,我们在项目中经常通过日志来记录信息和排查问题,相关代码随处可见。它也很“小”,作为辅助工具,日志使用简单、上手快,我们通常不会花费过多精力耗在日志上。但看似不起眼的日志也隐藏着各种各样的“坑”,如果使用不当,它不仅不能帮助我们,反而还可能降低服务性能,甚至拖垮我们的服务。
日志导致线程Block的问题,相信你或许已经遇到过,对此应该深有体会;或许你还没遇到过,但不代表没有问题,只是可能还没有触发而已。本文主要介绍美团统一API网关服务Shepherd(参见《百亿规模API网关服务Shepherd的设计与实现》一文)在实践中所踩过的关于日志导致线程Block的那些“坑”,然后再分享一些避“坑”经验。
2. 背景
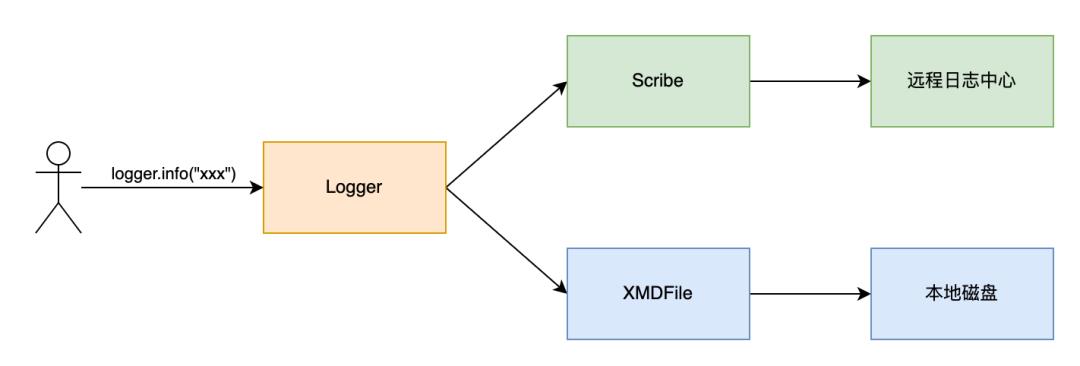
API网关服务Shepherd基于Java语言开发,使用业界大名鼎鼎的Apache Log4j2作为主要日志框架,同时使用美团内部的XMD-Log SDK和Scribe-Log SDK对日志内容进行处理,日志处理整体流程如下图1所示。业务打印日志时,日志框架基于Logger配置来决定把日志交给XMDFile处理还是Scribe处理。其中,XMDFile是XMD-Log内部提供的日志Appender名称,负责输出日志到本地磁盘,Scribe是Scribe-Log内部提供的日志Appender名称,负责上报日志到远程日志中心。
随着业务的快速增长,日志导致的线程Block问题愈发频繁。比如调用后端RPC服务超时,导致调用方大量线程Block;再比如,业务内部输出异常日志导致服务大量线程Block等,这些问题严重影响着服务的稳定性。因此,我们结合项目在过去一段时间暴露出来的各种由于日志导致的线程Block问题,对日志框架存在的稳定性风险因素进行了彻底的排查和修复,并在线下、线上环境进行全方位验证。在此过程中,我们总结了一些日志使用相关的实践经验,希望分享给大家。
在进入正文前,首先介绍项目当时的运行环境和日志相关配置信息。
-
JDK版本
java version "1.8.0_45"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_45-b14)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.45-b02, mixed mode)-
日志依赖版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.7</version>
</dependency>-
日志配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration status="warn">
<appenders>
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT" follow="true">
<PatternLayout pattern="%dyyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss.SSS %t [%p] %c1 (%F:%L) %msg%n" />
</Console>
<XMDFile name="ShepherdLog" fileName="shepherd.log"/>
<!--XMDFile异步磁盘日志配置示例-->
<!--默认按天&按512M文件大小切分日志,默认最多保留30个日志文件。-->
<!--注意:fileName前会自动增加文件路径,只配置文件名即可-->
<XMDFile name="LocalServiceLog" fileName="request.log"/>
<Scribe name="LogCenterSync">
<!-- 在指定日志名方面,scribeCategory 和 appkey 两者至少存在一种,且 scribeCategory 高于 appkey。-->
<!-- <Property name="scribeCategory">data_update_test_lc</Property> -->
<LcLayout/>
</Scribe>
<Async name="LogCenterAsync" blocking="false">
<AppenderRef ref="LogCenterSync"/>
</Async>
</appenders>
<loggers>
<AsyncLogger name="com.sankuai.shepherd" level="info" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="ShepherdLog" level="warn"/>
<AppenderRef ref="LogCenterAsync" level="info"/>
</AsyncLogger>
<root level="info">
<!--Console日志是同步、阻塞的,推荐只在本地调试时使用,线上将该配置去掉-->
<!--appender-ref ref="Console" /-->
<appender-ref ref="LocalServiceLog"/>
<appender-ref ref="LogCenterAsync"/>
</root>
</loggers>
</configuration>3. 踩过的坑
本章节主要记录项目过去一段时间,我们所遇到的一系列日志导致的线程Block问题,并逐个深入分析问题根因。
3.1 日志队列满导致线程Block
3.1.1 问题现场
收到“jvm.thread.blocked.count”告警后立刻通过监控平台查看线程监控指标,当时的线程堆栈如图2和图3所示。
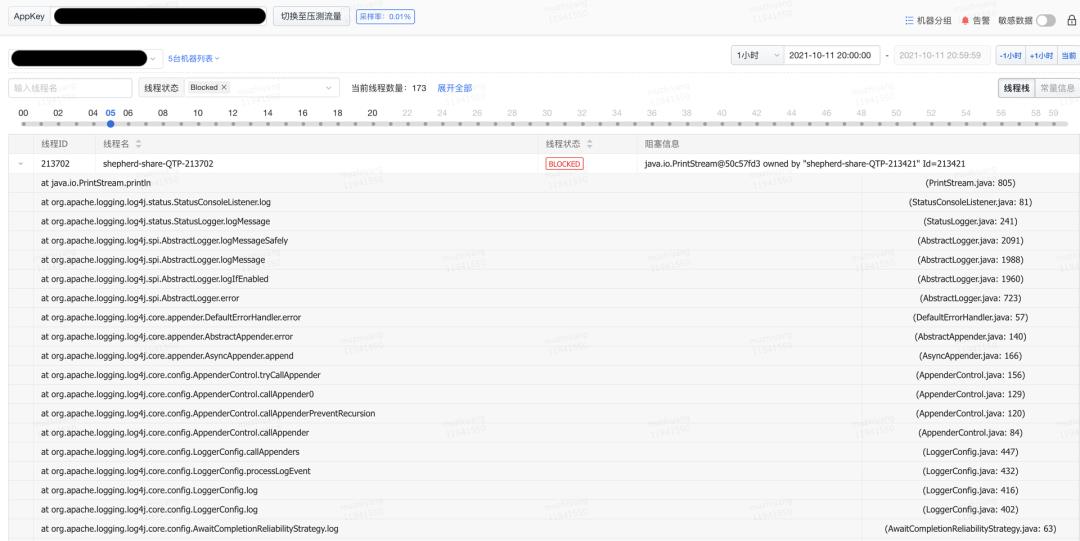


从Blocked线程堆栈不难看出这跟日志打印相关,而且是INFO级别的日志,遂即登陆机器查看日志是否有异样,发现当时日志量非常大,差不多每两分钟就写满一个500MB的日志文件。
那大量输出日志和线程Block之间会有怎样的关联呢?接下来本章节将结合如下图4所示的调用链路深入分析线程Block的根因。

3.1.2 为什么会Block线程?
从Blocked线程堆栈着手分析,查看PrintStream相关代码片段如下图5所示,可以看到被阻塞地方有synchronized同步调用,再结合上文发现每两分钟写满一个500MB日志文件的现象,初步怀疑是日志量过大导致了线程阻塞。

但上述猜测仍有一些值得推敲的地方:
-
如果仅仅因为日志量过大就导致线程Block,那日志框架也太不堪重用了,根本没法在高并发、高吞吐业务场景下使用。
-
日志配置里明明是输出日志到文件,怎么会输出到Console PrintStream?
3.1.3 为什么会输出到Console?
继续沿着线程堆栈调用链路分析,可以看出是AsyncAppender调用append方法追加日志时发生了错误,相关代码片段如下:
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.appender.AsyncAppender
// 内部维护的阻塞队列,队列大小默认是128
private final BlockingQueue<LogEvent> queue;
@Override
public void append(final LogEvent logEvent)
if (!isStarted())
throw new IllegalStateException("AsyncAppender " + getName() + " is not active");
if (!Constants.FORMAT_MESSAGES_IN_BACKGROUND) // LOG4J2-898: user may choose
logEvent.getMessage().getFormattedMessage(); // LOG4J2-763: ask message to freeze parameters
final Log4jLogEvent memento = Log4jLogEvent.createMemento(logEvent, includeLocation);
// 日志事件转入异步队列
if (!transfer(memento))
// 执行到这里说明队列满了,入队失败,根据是否blocking执行具体策略
if (blocking)
// 阻塞模式,选取特定的策略来处理,策略可能是 "忽略日志"、"日志入队并阻塞"、"当前线程打印日志"
// delegate to the event router (which may discard, enqueue and block, or log in current thread)
final EventRoute route = asyncQueueFullPolicy.getRoute(thread.getId(), memento.getLevel());
route.logMessage(this, memento);
else
// 非阻塞模式,交由 ErrorHandler 处理失败日志
error("Appender " + getName() + " is unable to write primary appenders. queue is full");
logToErrorAppenderIfNecessary(false, memento);
private boolean transfer(final LogEvent memento)
return queue instanceof TransferQueue
? ((TransferQueue<LogEvent>) queue).tryTransfer(memento)
: queue.offer(memento);
public void error(final String msg)
handler.error(msg);
AsyncAppender顾名思义是个异步Appender,采用异步方式处理日志,在其内部维护了一个BlockingQueue队列,每次处理日志时,都先尝试把Log4jLogEvent事件存入队列中,然后交由后台线程从队列中取出事件并处理(把日志交由AsyncAppender所关联的Appender处理),但队列长度总是有限的,且队列默认大小是128,如果日志量过大或日志异步线程处理不及时,就很可能导致日志队列被打满。
当日志队列满时,日志框架内部提供了两种处理方式,具体如下:
-
如果blocking配置为true,会选择相应的处理策略,默认是SYNCHRONOUS策略,可以在log4j2.component.properties文件中,通过log4j2.AsyncQueueFullPolicy参数配置日志框架提供的其他策略或自定义策略。
-
DISCARD策略,直接忽略日志。
-
SYNCHRONOUS策略,当前线程直接发送日志到Appender。
-
ENQUEUE策略,强制阻塞入队。
-
-
如果blocking配置为false,则由ErrorHandler和ErrorAppender处理失败日志。日志框架提供了默认的ErrorHandler实现,即DefaultErrorHandler,目前暂不支持业务在XML、JSON等日志配置文件里自定义ErrorHandler。日志框架默认不提供ErrorAppender,业务如有需要可在XML、JSON等日志配置文件里自定义error-ref配置。
在本项目的日志配置文件中可以看到,AsyncAppender设置了blocking为false,且没有配置error-ref,下面具体分析DefaultErrorHandler。
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.appender.DefaultErrorHandler
private static final Logger LOGGER = StatusLogger.getLogger();
private static final int MAX_EXCEPTIONS = 3;
// 5min 时间间隔
private static final long EXCEPTION_INTERVAL = TimeUnit.MINUTES.toNanos(5);
private int exceptionCount = 0;
private long lastException = System.nanoTime() - EXCEPTION_INTERVAL - 1;
public void error(final String msg)
final long current = System.nanoTime();
// 当前时间距离上次异常处理时间间隔超过5min 或者异常处理数小于3次
if (current - lastException > EXCEPTION_INTERVAL || exceptionCount++ < MAX_EXCEPTIONS)
// StatusLogger 负责处理
LOGGER.error(msg);
lastException = current;
DefaultErrorHandler内部在处理异常日志时增加了条件限制,只有下述两个条件任一满足时才会处理,从而避免大量异常日志导致的性能问题。
-
两条日志处理间隔超过5min。
-
异常日志数量不超过3次。
但项目所用日志框架版本的默认实现看起来存在一些不太合理的地方:
-
lastException用于标记上次异常的时间戳,该变量可能被多线程访问,无法保证多线程情况下的线程安全。
-
exceptionCount用于统计异常日志次数,该变量可能被多线程访问,无法保证多线程情况下的线程安全。
所以,在多线程场景下,可能有大量异常日志同时被DefaultErrorHandler处理,带来线程安全问题。值得一提的是,该问题已有相关Issue: DefaultErrorHandler can not share values across threads反馈给社区,并在2.15.0版本中进行了修复。
从上述DefaultErrorHandler代码中可以看到,真正负责处理日志的是StatusLogger,继续跟进代码进入logMessage方法,方法执行逻辑如下:
-
如果StatusLogger内部注册了StatusListener,则由对应的StatusListener负责处理日志。
-
否则由SimpleLogger负责处理日志,直接输出日志到System.err输出流。
// org.apache.logging.log4j.status.StatusLogger
private static final StatusLogger STATUS_LOGGER = new StatusLogger(StatusLogger.class.getName(),
ParameterizedNoReferenceMessageFactory.INSTANCE);
// StatusListener
private final Collection<StatusListener> listeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private final SimpleLogger logger;
private StatusLogger(final String name, final MessageFactory messageFactory)
super(name, messageFactory);
this.logger = new SimpleLogger("StatusLogger", Level.ERROR, false, true, false, false, Strings.EMPTY,
messageFactory, PROPS, System.err);
this.listenersLevel = Level.toLevel(DEFAULT_STATUS_LEVEL, Level.WARN).intLevel();
/**
* Retrieve the StatusLogger.
*
* @return The StatusLogger.
*/
public static StatusLogger getLogger()
return STATUS_LOGGER;
@Override
public void logMessage(final String fqcn, final Level level, final Marker marker, final Message msg,
final Throwable t)
StackTraceElement element = null;
if (fqcn != null)
element = getStackTraceElement(fqcn, Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace());
final StatusData data = new StatusData(element, level, msg, t, null);
msgLock.lock();
try
messages.add(data);
finally
msgLock.unlock();
if (listeners.size() > 0)
// 如果系统注册了 listener,由 StatusConsoleListener 处理日志
for (final StatusListener listener : listeners)
if (data.getLevel().isMoreSpecificThan(listener.getStatusLevel()))
listener.log(data);
else
// 否则由 SimpleLogger 处理日志,直接输出到 System.err
logger.logMessage(fqcn, level, marker, msg, t);
从上述Blocked线程堆栈来看,是StatusConsoleListener负责处理日志,而StatusConsoleListener是StatusListener接口的实现类,那么StatusConsoleListener是如何被创建的?
3.1.4 StatusConsoleListener是怎么来的?
通常来说,每个项目都会有一个日志配置文件(如log4j2.xml),该配置对应Log4j2日志框架中的Configuration接口,不同的日志配置文件格式有不同的实现类:
-
XmlConfiguration,即XML格式日志配置
-
JsonConfiguration,即JSON格式日志配置
-
XMDConfiguration,即美团内部日志组件XMD-Log定义的日志配置(XML格式)
-
......
log4j2.xml 示例配置(仅做示例,请勿实际项目中使用该配置)。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="debug" name="RoutingTest">
<Properties>
<Property name="filename">target/rolling1/rollingtest-$$sd:type.log</Property>
</Properties>
<ThresholdFilter level="debug"/>
<Appenders>
<Console name="STDOUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="%m%n"/>
<ThresholdFilter level="debug"/>
</Console>
<Routing name="Routing">
<Routes pattern="$$sd:type">
<Route>
<RollingFile name="Rolling-$sd:type" fileName="$filename"
filePattern="target/rolling1/test1-$sd:type.%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout>
<pattern>%d %p %c1. [%t] %m%n</pattern>
</PatternLayout>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="500" />
</RollingFile>
</Route>
<Route ref="STDOUT" key="Audit"/>
</Routes>
</Routing>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Logger name="EventLogger" level="info" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Routing"/>
</Logger>
<Root level="error">
<AppenderRef ref="STDOUT"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>Log4j2在启动时会加载并解析log4j2.xml配置文件,由对应的ConfigurationFactory创建具体Configuration实例。
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.xml.XmlConfiguration
public XmlConfiguration(final LoggerContext loggerContext, final ConfigurationSource configSource)
super(loggerContext, configSource);
final File configFile = configSource.getFile();
byte[] buffer = null;
try
final InputStream configStream = configSource.getInputStream();
try
buffer = toByteArray(configStream);
finally
Closer.closeSilently(configStream);
final InputSource source = new InputSource(new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer));
source.setSystemId(configSource.getLocation());
final DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = newDocumentBuilder(true);
Document document;
try
// 解析 xml 配置文件
document = documentBuilder.parse(source);
catch (final Exception e)
// LOG4J2-1127
final Throwable throwable = Throwables.getRootCause(e);
if (throwable instanceof UnsupportedOperationException)
LOGGER.warn(
"The DocumentBuilder does not support an operation: ."
+ "Trying again without XInclude...",
documentBuilder, e);
document = newDocumentBuilder(false).parse(source);
else
throw e;
rootElement = document.getDocumentElement();
// 处理根节点属性配置,即 <Configuration></Configuration> 节点
final Map<String, String> attrs = processAttributes(rootNode, rootElement);
// 创建 StatusConfiguration
final StatusConfiguration statusConfig = new StatusConfiguration().withVerboseClasses(VERBOSE_CLASSES)
.withStatus(getDefaultStatus());
for (final Map.Entry<String, String> entry : attrs.entrySet())
final String key = entry.getKey();
final String value = getStrSubstitutor().replace(entry.getValue());
// 根据配置文件中的 status 属性值,来设置 StatusConfiguration 的 status level
if ("status".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
statusConfig.withStatus(value);
// 根据配置文件中的 dest 属性值,来设置 StatusConfiguration 的日志输出 destination
else if ("dest".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
statusConfig.withDestination(value);
else if ("shutdownHook".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
isShutdownHookEnabled = !"disable".equalsIgnoreCase(value);
else if ("verbose".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
statusConfig.withVerbosity(value);
else if ("packages".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
pluginPackages.addAll(Arrays.asList(value.split(Patterns.COMMA_SEPARATOR)));
else if ("name".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
setName(value);
else if ("strict".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
strict = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
else if ("schema".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
schemaResource = value;
else if ("monitorInterval".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
final int intervalSeconds = Integer.parseInt(value);
if (intervalSeconds > 0)
getWatchManager().setIntervalSeconds(intervalSeconds);
if (configFile != null)
final FileWatcher watcher = new ConfiguratonFileWatcher(this, listeners);
getWatchManager().watchFile(configFile, watcher);
else if ("advertiser".equalsIgnoreCase(key))
createAdvertiser(value, configSource, buffer, "text/xml");
// 初始化 StatusConfiguration
statusConfig.initialize();
catch (final SAXException | IOException | ParserConfigurationException e)
LOGGER.error("Error parsing " + configSource.getLocation(), e);
if (getName() == null)
setName(configSource.getLocation());
// 忽略以下内容
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.status.StatusConfiguration
private static final PrintStream DEFAULT_STREAM = System.out;
private static final Level DEFAULT_STATUS = Level.ERROR;
private static final Verbosity DEFAULT_VERBOSITY = Verbosity.QUIET;
private final Collection<String> errorMessages = Collections.synchronizedCollection(new LinkedList<String>());
// StatusLogger
private final StatusLogger logger = StatusLogger.getLogger();
private volatile boolean initialized = false;
private PrintStream destination = DEFAULT_STREAM;
private Level status = DEFAULT_STATUS;
private Verbosity verbosity = DEFAULT_VERBOSITY;
public void initialize()
if (!this.initialized)
if (this.status == Level.OFF)
this.initialized = true;
else
final boolean configured = configureExistingStatusConsoleListener();
if (!configured)
// 注册新 StatusConsoleListener
registerNewStatusConsoleListener();
migrateSavedLogMessages();
private boolean configureExistingStatusConsoleListener()
boolean configured = false;
for (final StatusListener statusListener : this.logger.getListeners())
if (statusListener instanceof StatusConsoleListener)
final StatusConsoleListener listener = (StatusConsoleListener) statusListener;
// StatusConsoleListener 的 level 以 StatusConfiguration 的 status 为准
listener.setLevel(this.status);
this.logger.updateListenerLevel(this.status);
if (this.verbosity == Verbosity.QUIET)
listener.setFilters(this.verboseClasses);
configured = true;
return configured;
private void registerNewStatusConsoleListener()
// 创建 StatusConsoleListener,级别以 StatusConfiguration 为准
// 默认 status 是 DEFAULT_STATUS 即 ERROR
// 默认 destination 是 DEFAULT_STREAM 即 System.out
final StatusConsoleListener listener = new StatusConsoleListener(this.status, this.destination);
if (this.verbosity == Verbosity.QUIET)
listener.setFilters(this.verboseClasses);
this.logger.registerListener(listener);
// org.apache.logging.log4j.status.StatusConsoleListener
private Level level = Level.FATAL; // 级别
private String[] filters;
private final PrintStream stream; // 输出流
public StatusConsoleListener(final Level level, final PrintStream stream)
if (stream == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must provide a stream to use for this listener.");
this.level = level;
this.stream = stream;
以XmlConfiguration为例,分析上述日志配置解析代码片段可以得知,创建XmlConfiguration时,会先创建StatusConfiguration,随后在初始化StatusConfiguration时创建并注册StatusConsoleListener到StatusLogger的listeners中,日志配置文件中<Configuration>标签的属性值通过XmlConfiguration->StatusConfiguration->StatusConsoleListener这样的关系链路最终影响StatusConsoleListener的行为。
日志配置文件中的<Configuration>标签可以配置属性字段,部分字段如下所示:
-
status,可选值包括OFF、FATAL、ERROR、WARN、INFO、DEBUG、TRACE、ALL,该值决定StatusConsoleListener级别,默认是ERROR。
-
dest,可选值包括out、err、标准的URI路径,该值决定StatusConsoleListener输出流目的地,默认是System.out。
在本项目的日志配置文件中可以看到并没有设置Configuration的dest属性值,所以日志直接输出到System.out。
3.1.5 StatusLogger有什么用?
上文提到StatusConsoleListener是注册在StatusLogger中,StatusLogger在交由StatusListener处理日志前,会判断日志级别,如果级别条件不满足,则忽略此日志,StatusConsoleListener的日志级别默认是ERROR。
// org.apache.logging.log4j.status.StatusLogger
@Override
public void logMessage(final String fqcn, final Level level, final Marker marker, final Message msg,
final Throwable t)
StackTraceElement element = null;
if (fqcn != null)
element = getStackTraceElement(fqcn, Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace());
final StatusData data = new StatusData(element, level, msg, t, null);
msgLock.lock();
try
messages.add(data);
finally
msgLock.unlock();
// 系统注册了 listener,由 StatusConsoleListener 处理日志
if (listeners.size() > 0)
for (final StatusListener listener : listeners)
// 比较当前日志的 leve 和 listener 的 level
if (data.getLevel().isMoreSpecificThan(listener.getStatusLevel()))
listener.log(data);
else
logger.logMessage(fqcn, level, marker, msg, t);
我们回头再来看下StatusLogger,StatusLogger采用单例模式实现,它输出日志到Console(如System.out或System.err),从上文分析可知,在高并发场景下非常容易导致线程Block,那么它的存在有什么意义呢?
看官方介绍大意是说,在日志初始化完成前,也有打印日志调试的需求,StatusLogger就是为了解决这个问题而生。
Troubleshooting tip for the impatient:
From log4j-2.9 onward, log4j2 will print all internal logging to the console if system property log4j2.debug is defined (with any or no value).
Prior to log4j-2.9, there are two places where internal logging can be controlled:
Before a configuration is found, status logger level can be controlled with system property org.apache.logging.log4j.simplelog.StatusLogger.level.
After a configuration is found, status logger level can be controlled in the configuration file with the "status" attribute, for example: <Configuration status="trace">.
Just as it is desirable to be able to diagnose problems in applications, it is frequently necessary to be able to diagnose problems in the logging configuration or in the configured components. Since logging has not been configured, "normal" logging cannot be used during initialization. In addition, normal logging within appenders could create infinite recursion which Log4j will detect and cause the recursive events to be ignored. To accomodate this need, the Log4j 2 API includes a StatusLogger.
3.1.6 问题小结
日志量过大导致AsyncAppender日志队列被打满,新的日志事件无法入队,进而由ErrorHandler处理日志,同时由于ErrorHandler存在线程安全问题,导致大量日志输出到了Console,而Console在输出日志到PrintStream输出流时,存在synchronized同步代码块,所以在高并发场景下导致线程Block。
3.2 AsyncAppender导致线程Block
3.2.1 问题现场
收到“jvm.thread.blocked.count”告警后立刻通过监控平台查看线程监控指标,当时的线程堆栈如下图6和图7所示。
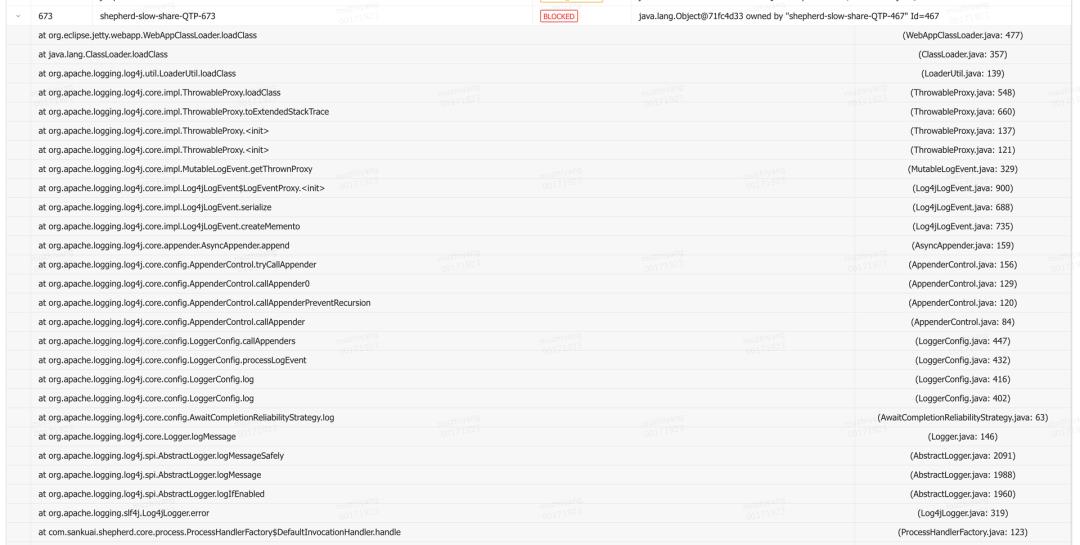

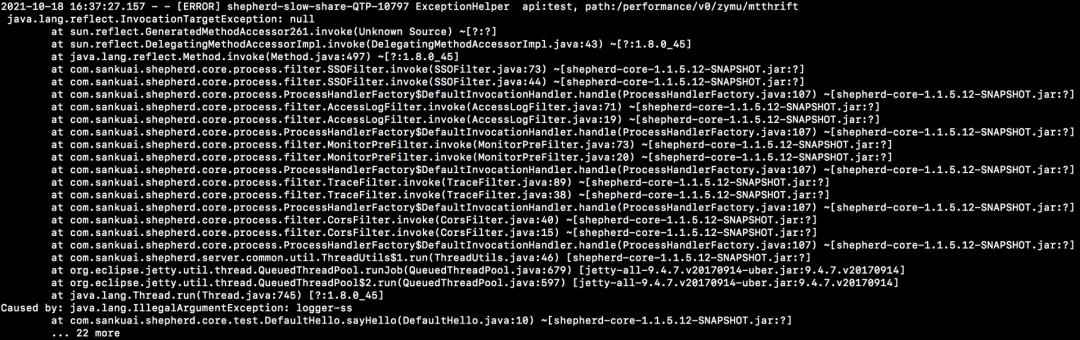
从Blocked线程堆栈不难看出是跟日志打印相关,由于是ERROR级别日志,查看具体报错日志,发现有两种业务异常,分别如下图8和图9所示:

这些业务异常会是导致线程Block的幕后元凶吗?接下来本章节将结合如下图10所示的调用链路深入分析线程Block的根因。

3.2.2 为什么会Block线程?
从Blocked线程堆栈中可以看出,线程阻塞在类加载流程上,查看WebAppClassLoader相关代码片段如下图11所示,发现加载类时确实会根据类名来加synchronized同步块,因此初步猜测是类加载导致线程Block。
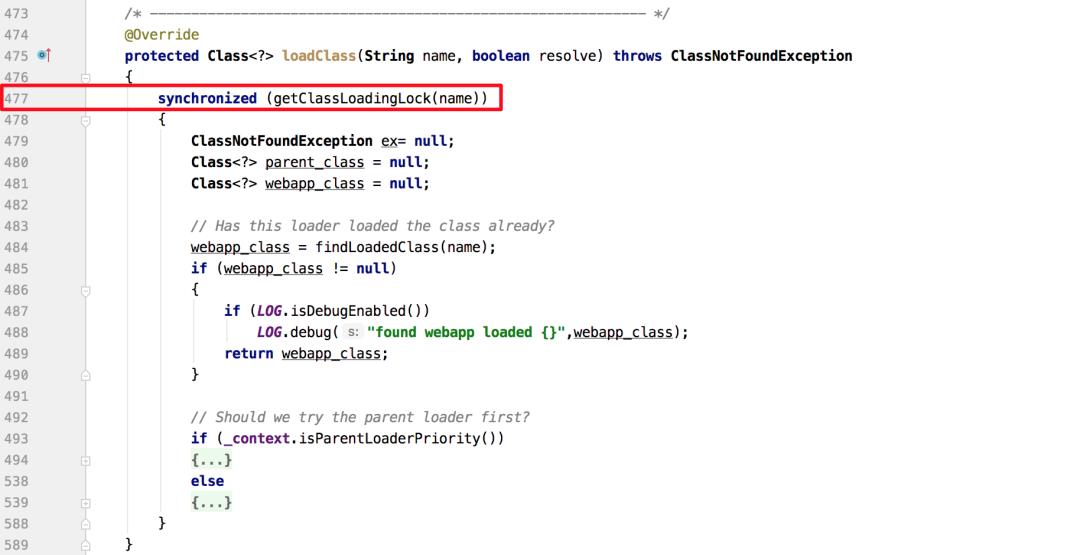
但上述猜测还有一些值得推敲的地方:
-
项目代码里只是普通地输出一条ERROR日志而已,为何会触发类加载?
-
通常情况下类加载几乎不会触发线程Block,不然一个项目要加载成千上万个类,如果因为加载类就导致Block,那项目就没法正常运行了。
3.2.3 为什么会触发类加载?
继续从Blocked线程堆栈着手分析,查看堆栈中的ThrowableProxy相关代码,发现其构造函数会遍历整个异常堆栈中的所有堆栈元素,最终获取所有堆栈元素类所在的JAR名称和版本信息。具体流程如下:
-
首先获取堆栈元素的类名称。
-
再通过loadClass的方式获取对应的Class对象。
-
进一步获取该类所在的JAR信息,从CodeSource中获取JAR名称,从Package中获取JAR版本。
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy
private ThrowableProxy(final Throwable throwable, final Set<Throwable> visited)
this.throwable = throwable;
this.name = throwable.getClass().getName();
this.message = throwable.getMessage();
this.localizedMessage = throwable.getLocalizedMessage();
final Map<String, CacheEntry> map = new HashMap<>();
final Stack<Class<?>> stack = ReflectionUtil.getCurrentStackTrace();
// 获取堆栈扩展信息
this.extendedStackTrace = this.toExtendedStackTrace(stack, map, null, throwable.getStackTrace());
final Throwable throwableCause = throwable.getCause();
final Set<Throwable> causeVisited = new HashSet<>(1);
this.causeProxy = throwableCause == null ? null : new ThrowableProxy(throwable, stack, map, throwableCause,
visited, causeVisited);
this.suppressedProxies = this.toSuppressedProxies(throwable, visited);
ExtendedStackTraceElement[] toExtendedStackTrace(final Stack<Class<?>> stack, final Map<String, CacheEntry> map,
final StackTraceElement[] rootTrace,
final StackTraceElement[] stackTrace)
int stackLength;
if (rootTrace != null)
int rootIndex = rootTrace.length - 1;
int stackIndex = stackTrace.length - 1;
while (rootIndex >= 0 && stackIndex >= 0 && rootTrace[rootIndex].equals(stackTrace[stackIndex]))
--rootIndex;
--stackIndex;
this.commonElementCount = stackTrace.length - 1 - stackIndex;
stackLength = stackIndex + 1;
else
this.commonElementCount = 0;
stackLength = stackTrace.length;
final ExtendedStackTraceElement[] extStackTrace = new ExtendedStackTraceElement[stackLength];
Class<?> clazz = stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.peek();
ClassLoader lastLoader = null;
for (int i = stackLength - 1; i >= 0; --i)
// 遍历 StackTraceElement
final StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = stackTrace[i];
// 获取堆栈元素对应的类名称
final String className = stackTraceElement.getClassName();
// The stack returned from getCurrentStack may be missing entries for java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
// and its implementation. The Throwable might also contain stack entries that are no longer
// present as those methods have returned.
ExtendedClassInfo extClassInfo;
if (clazz != null && className.equals(clazz.getName()))
final CacheEntry entry = this.toCacheEntry(stackTraceElement, clazz, true);
extClassInfo = entry.element;
lastLoader = entry.loader;
stack.pop();
clazz = stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.peek();
else
// 对加载过的 className 进行缓存,避免重复加载
final CacheEntry cacheEntry = map.get(className);
if (cacheEntry != null)
final CacheEntry entry = cacheEntry;
extClassInfo = entry.element;
if (entry.loader != null)
lastLoader = entry.loader;
else
// 通过加载类来获取类的扩展信息,如 location 和 version 等
final CacheEntry entry = this.toCacheEntry(stackTraceElement,
// 获取 Class 对象
this.loadClass(lastLoader, className), false);
extClassInfo = entry.element;
map.put(stackTraceElement.toString(), entry);
if (entry.loader != null)
lastLoader = entry.loader;
extStackTrace[i] = new ExtendedStackTraceElement(stackTraceElement, extClassInfo);
return extStackTrace;
/**
* Construct the CacheEntry from the Class's information.
*
* @param stackTraceElement The stack trace element
* @param callerClass The Class.
* @param exact True if the class was obtained via Reflection.getCallerClass.
* @return The CacheEntry.
*/
private CacheEntry toCacheEntry(final StackTraceElement stackTraceElement, final Class<?> callerClass,
final boolean exact)
String location = "?";
String version = "?";
ClassLoader lastLoader = null;
if (callerClass != null)
try
// 获取 jar 文件信息
final CodeSource source = callerClass.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource();
if (source != null)
final URL locationURL = source.getLocation();
if (locationURL != null)
final String str = locationURL.toString().replace('\\\\', '/');
int index = str.lastIndexOf("/");
if (index >= 0 && index == str.length() - 1)
index = str.lastIndexOf("/", index - 1);
location = str.substring(index + 1);
else
location = str.substring(index + 1);
catch (final Exception ex)
// Ignore the exception.
// 获取类所在 jar 版本信息
final Package pkg = callerClass.getPackage();
if (pkg != null)
final String ver = pkg.getImplementationVersion();
if (ver != null)
version = ver;
lastLoader = callerClass.getClassLoader();
return new CacheEntry(new ExtendedClassInfo(exact, location, version), lastLoader);
从上述代码中可以看到,ThrowableProxy#toExtendedStackTrace方法通过Map<String, CacheEntry>缓存当前堆栈元素类对应的CacheEntry,来避免重复解析CacheEntry,但是由于Map缓存put操作使用的key来自于StackTraceElement.toString方法,而get操作使用的key却来自于StackTraceElement.getClassName方法,即使对于同一个StackTraceElement而言,其toString和getClassName方法对应的返回结果也不一样,所以此map形同虚设。
// java.lang.StackTraceElement
public String getClassName()
return declaringClass;
public String toString()
return getClassName() + "." + methodName +
(isNativeMethod() ? "(Native Method)" :
(fileName != null && lineNumber >= 0 ?
"(" + fileName + ":" + lineNumber + ")" :
(fileName != null ? "("+fileName+")" : "(Unknown Source)")));
该问题已有相关Issue: fix the CacheEntry map in ThrowableProxy#toExtendedStackTrace to be put and gotten with same key反馈给社区,并在2.11.1版本中修复了该问题。虽然通过让get/put方法使用同一个key来修复缓存的有效性问题,但由于ThrowableProxy对每个Throwable都会创建一个全新的Map,而不是使用全局Map,因此其缓存也仅仅对单个Throwable生效,作用范围非常有限,食之无味,弃之可惜。
言归正传,通常情况下一个类加载器对于一个类只会加载一次,类加载器内部保存有类缓存,无需重复加载,但目前的现象却是由于类加载而导致线程大量Block,因此必然是有些类加载不了,且不断重复尝试加载,那到底是什么类无法加载呢?
3.2.4 到底什么类加载不了?
要找到具体是什么类无法加载,归根结底还是要分析业务异常的具体堆栈。


对比如图12和图13所示的两份业务异常堆栈,我们可以看到两份堆栈基本相似,且大多数类都是很普通的类,但是唯一不同的地方在于:
-
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl(参见图12)。
-
sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor261(参见图13)。
从字面信息中不难猜测出这与反射调用相关,但问题是这两份堆栈对应的其实是同一份业务代码,为什么会产生两份不同的异常堆栈?
查阅相关资料得知,这与JVM反射调用相关,JVM对反射调用分两种情况:
-
默认使用native方法进行反射操作。
-
一定条件下会生成字节码进行反射操作,即生成sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor<N>类,它是一个反射调用方法的包装类,代理不同的方法,类后缀序号递增。
JVM反射调用的主要流程是获取MethodAccessor,并由MethodAccessor执行invoke调用,相关代码如下:
// java.lang.reflect.Method
@CallerSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
if (!override)
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers))
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null)
// 获取 MethodAccessor
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
// 通过 MethodAccessor 调用
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor()
MethodAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();
if (tmp != null)
methodAccessor = tmp;
else
// 通过 ReflectionFactory 创建 MethodAccessor
tmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);
setMethodAccessor(tmp);
return tmp;
当noInflation为false(默认为false)或者反射方法所在类是VM匿名类(类名中包括斜杠“/”)的情况下,ReflectionFactory会返回一个MethodAccessor代理类,即DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl。
// sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method)
// 通过启动参数获取并解析 noInflation 和 inflationThreshold 值
// noInflation 默认为 false
// inflationThreshold 默认为15
checkInitted();
if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass()))
return new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
else
NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc =
new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res =
new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);
acc.setParent(res);
// 返回代理 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl
return res;
private static void checkInitted()
if (initted) return;
AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Void>()
public Void run()
// Tests to ensure the system properties table is fully
// initialized. This is needed because reflection code is
// called very early in the initialization process (before
// command-line arguments have been parsed and therefore
// these user-settable properties installed.) We assume that
// if System.out is non-null then the System class has been
// fully initialized and that the bulk of the startup code
// has been run.
if (System.out == null)
// java.lang.System not yet fully initialized
return null;
String val = System.getProperty("sun.reflect.noInflation");
if (val != null && val.equals("true"))
noInflation = true;
val = System.getProperty("sun.reflect.inflationThreshold");
if (val != null)
try
inflationThreshold = Integer.parseInt(val);
catch (NumberFormatException e)
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to parse property sun.reflect.inflationThreshold", e);
initted = true;
return null;
);
默认情况下DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl代理了NativeMethodAccessorImpl,但是随着反射调用次数的增加,当一个方法被反射调用的次数超过一定的阀值时(inflationThreshold,默认值是15),NativeMethodAccessorImpl会通过字节码生成技术,自动生成MethodAccessorImpl实现类,并修改DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl的内部代理对象指向字节码生成类实例,从而改变后续反射调用逻辑。
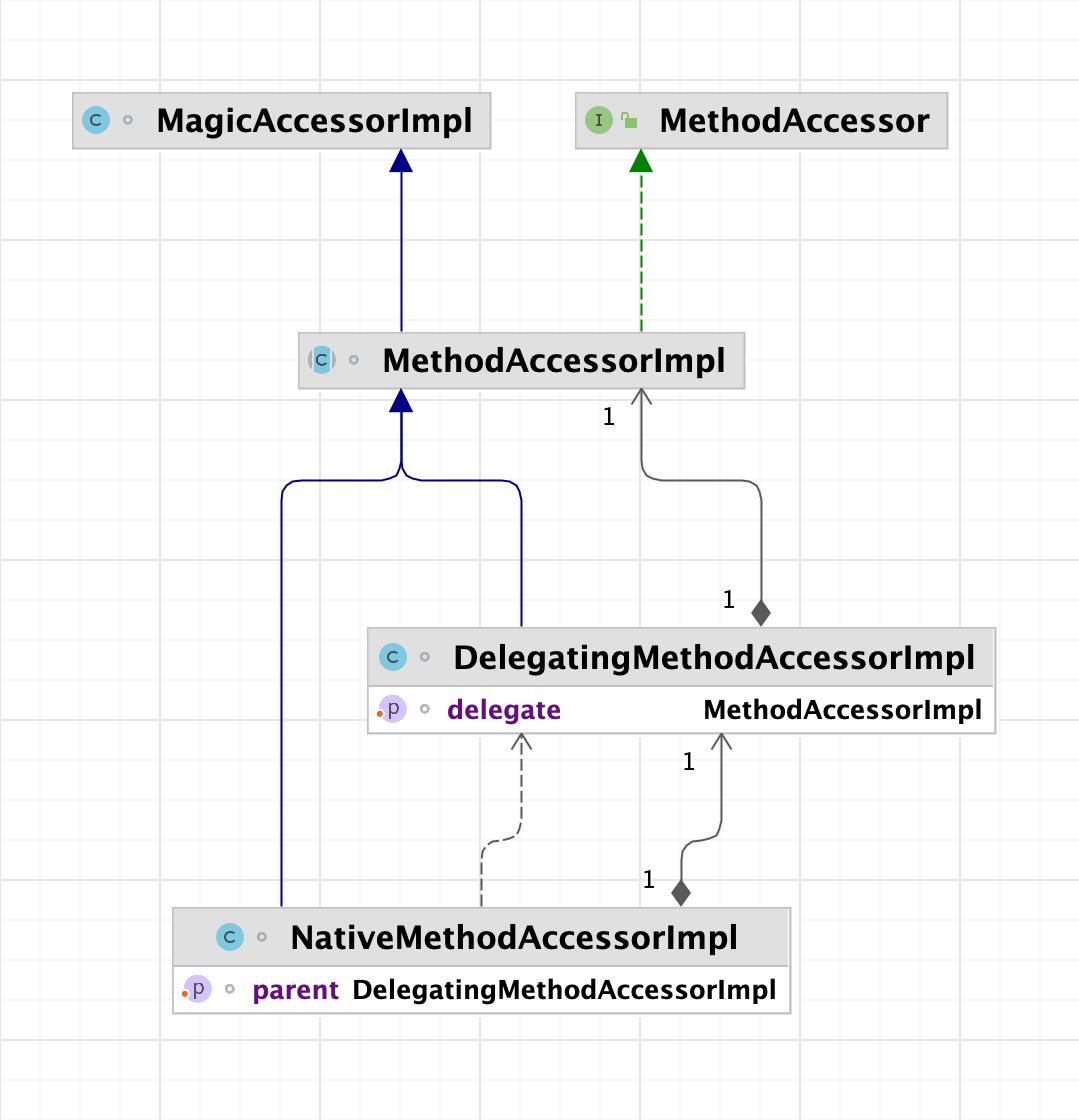
// sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl
// 内部代理 MethodAccessorImpl
private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl delegate)
setDelegate(delegate);
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
return delegate.invoke(obj, args);
void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl delegate)
this.delegate = delegate;
// sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl
private final Method method;
private DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent;
private int numInvocations;
NativeMethodAccessorImpl(Method method)
this.method = method;
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
// We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because
// that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be
// found from the generated bytecode.
// 每次调用时 numInvocations 都会自增加1,如果超过阈值(默认是15次),就会修改父类的代理对象,从而改变调用链路
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()
&& !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass()))
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
// 动态生成字节码,优化反射调用速度
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
// 修改父代理类的代理对象
parent.setDelegate(acc);
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
void setParent(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent)
this.parent = parent;
private static native Object invoke0(Method m, Object obj, Object[] args);
从MethodAccessorGenerator#generateName方法可以看到,字节码生成的类名称规则是sun.reflect.GeneratedConstructorAccessor<N>,其中N是从0开始的递增数字,且生成类是由DelegatingClassLoader类加载器定义,所以其他类加载器无法加载该类,也就无法生成类缓存数据,从而导致每次加载类时都需要遍历JarFile,极大地降低了类查找速度,且类加载过程是synchronized同步调用,在高并发情况下会更加恶化,从而导致线程Block。
// sun.reflect.MethodAccessorGenerator
public MethodAccessor generateMethod(Class<?> declaringClass,
String name,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Class<?> returnType,
Class<?>[] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers)
return (MethodAccessor) generate(declaringClass,
name,
parameterTypes,
returnType,
checkedExceptions,
modifiers,
false,
false,
null);
private MagicAccessorImpl generate(final Class<?> declaringClass,
String name,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Class<?> returnType,
Class<?>[] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers,
boolean isConstructor,
boolean forSerialization,
Class<?> serializationTargetClass)
final String generatedName = generateName(isConstructor, forSerialization);
// 忽略以上代码
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<MagicAccessorImpl>()
public MagicAccessorImpl run()
try
return (MagicAccessorImpl)
ClassDefiner.defineClass
(generatedName,
bytes,
0,
bytes.length,
declaringClass.getClassLoader()).newInstance();
catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e)
throw new InternalError(e);
);
// 生成反射类名,看到了熟悉的 sun.reflect.GeneratedConstructorAccessor<N>
private static synchronized String generateName(boolean isConstructor, boolean forSerialization)
if (isConstructor)
if (forSerialization)
int num = ++serializationConstructorSymnum;
return "sun/reflect/GeneratedSerializationConstructorAccessor" + num;
else
int num = ++constructorSymnum;
return "sun/reflect/GeneratedConstructorAccessor" + num;
else
int num = ++methodSymnum;
return "sun/reflect/GeneratedMethodAccessor" + num;
// sun.reflect.ClassDefiner
static Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] bytes, int off, int len,
final ClassLoader parentClassLoader)
ClassLoader newLoader = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<ClassLoader>()
以上是关于日志导致线程Block的这些坑,你不得不防的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章