数论中的各种定理(待更新)
Posted queuelovestack
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数论中的各种定理(待更新)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本篇博客仅仅是搜罗各种数论中的定理便于日常使用,具体的证明还需从网络中获得,特此告知
1.费马小定理
内容:假如a是整数,p是质数,且a,p互质(即两者最大公约数为1),那么a的(p-1)次方除以p的余数恒等于1
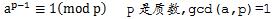


2.欧拉定理(其实包含了费马小定理)

3.威尔逊定理



4.中国剩余定理(孙子定理)
一元线性同余方程组
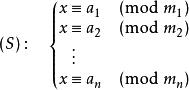
模板:
/*Sherlock and Watson and Adler*/
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<complex>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#define eps 1e-8
#define LL long long
#define bitnum(a) __builtin_popcount(a)
using namespace std;
const int N = 105;
const int M = 100005;
const int inf = 1000000007;
const int mod = 1000000007;
int group;
LL n[N],a[N];
LL Egcd(LL a,LL b,LL &x,LL &y)
if(b==0)
x=1,y=0;
return a;
LL d,tp;
d=Egcd(b,a%b,x,y);
tp=x;
x=y;
y=tp-a/b*y;
return d;
LL solve()
int i;
bool flag = false;
LL n1 = n[0], n2, b1 = a[0], b2, bb, d, t, k, x, y;
for (i = 1; i < group; i++)
n2 = n[i], b2 = a[i];
bb = b2 - b1;
d = Egcd (n1, n2, x, y);
if (bb % d) //模线性解k1时发现无解
flag = true;
break;
k = bb / d * x; //相当于求上面所说的k1【模线性方程】
t = n2 / d;
if (t < 0) t = -t;
k = (k % t + t) % t; //相当于求上面的K`
b1 = b1 + n1*k;
n1 = n1 / d * n2;
if(flag)
return -1; //无解
/******************求正整数解******************/
if(b1==0) //如果解为0,而题目要正整数解,显然不行
b1=n1; //n1刚好为所有ni的最小公倍数,就是解了
/******************求正整数解******************/
return b1; //形成的解:b1, b1+n1, b1+2n1,..., b1+xni...
int main()
int i;
scanf("%d",&group);
for(i=0;i<group;i++)
//X mod n[i] = a[i] ,n[i]两两之间不一定互质做法
scanf ("%lld%lld",&n[i],&a[i]);
a[i]%=n[i];
printf ("%lld\\n",solve());
return 0;
以上是关于数论中的各种定理(待更新)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章