Java算法 -- 单链表的反转单链表实现栈和队列以及双端队列K 个一组翻转链表
Posted CodeJiao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java算法 -- 单链表的反转单链表实现栈和队列以及双端队列K 个一组翻转链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 单链表的反转
单链表的反转即把原来的单链表的指针顺序倒置。如下图所示:
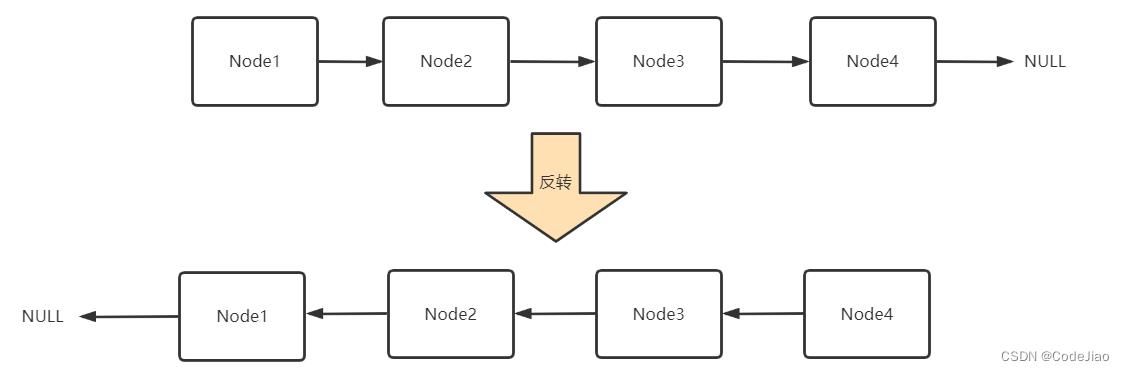
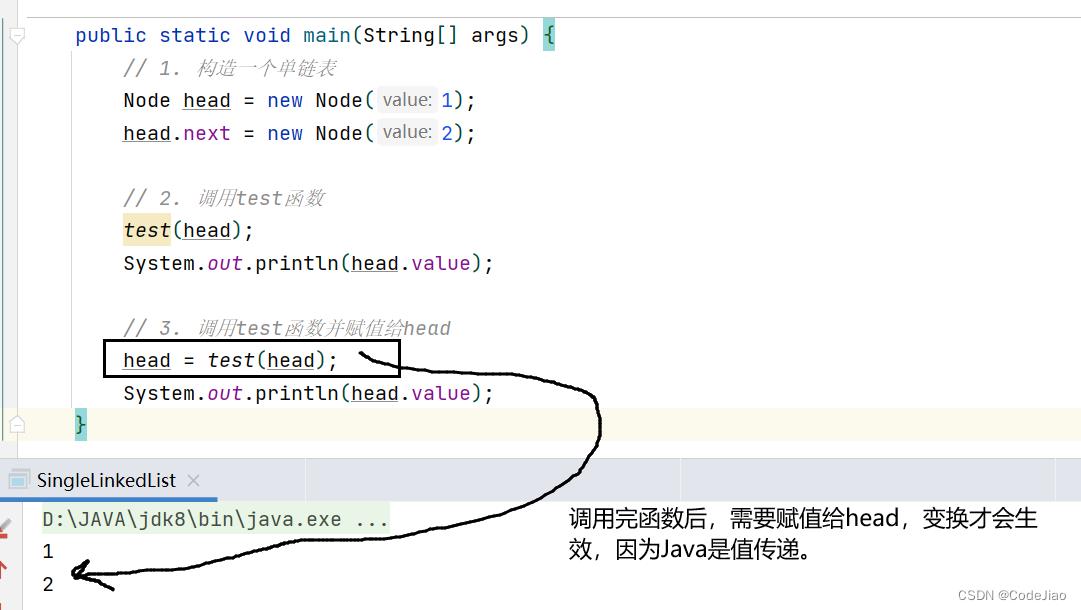
需要注意的点是,Java中是值(传递引用也可以认为是特殊的值传递)传递,函数在改变完值后记得赋值给原来的值,变化才会生效。
详细请看这篇文章(总的来说就是如果不改变传递进来的引用副本的值,那么更改引用相关的属性是可以生效的。如果改变了引用副本的值,那么对原引用的相关属性的更改是不生效的。)
示例代码:
static class Node
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int value)
this.value = value;
public static Node test(Node head)
head = head.next;
return head;
public static void main(String[] args)
// 1. 构造一个单链表
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
// 2. 调用test函数
test(head);
System.out.println(head.value);
// 3. 调用test函数并赋值给head
head = test(head);
System.out.println(head.value);
运行结果:
下面我们就可以正式的编写反转单链表的代码了:
static class Node
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int value)
this.value = value;
public static void main(String[] args)
// 1. 构造一个单链表
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head = reverseSingleList(head);
while (head != null)
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
/**
* 反转单链表
*
* @param head head是头结点
* @return 反转后的单链表的头结点
*/
public static Node reverseSingleList(Node head)
Node pre = null, next = null;
while (head != null)
// next是为了可以往后继续遍历
next = head.next;
// head的next指向pre
head.next = pre;
// pre指向head
pre = head;
// head指向next
head = next;
return pre;
运行结果:

下面我们来解释原理:
初始状态:
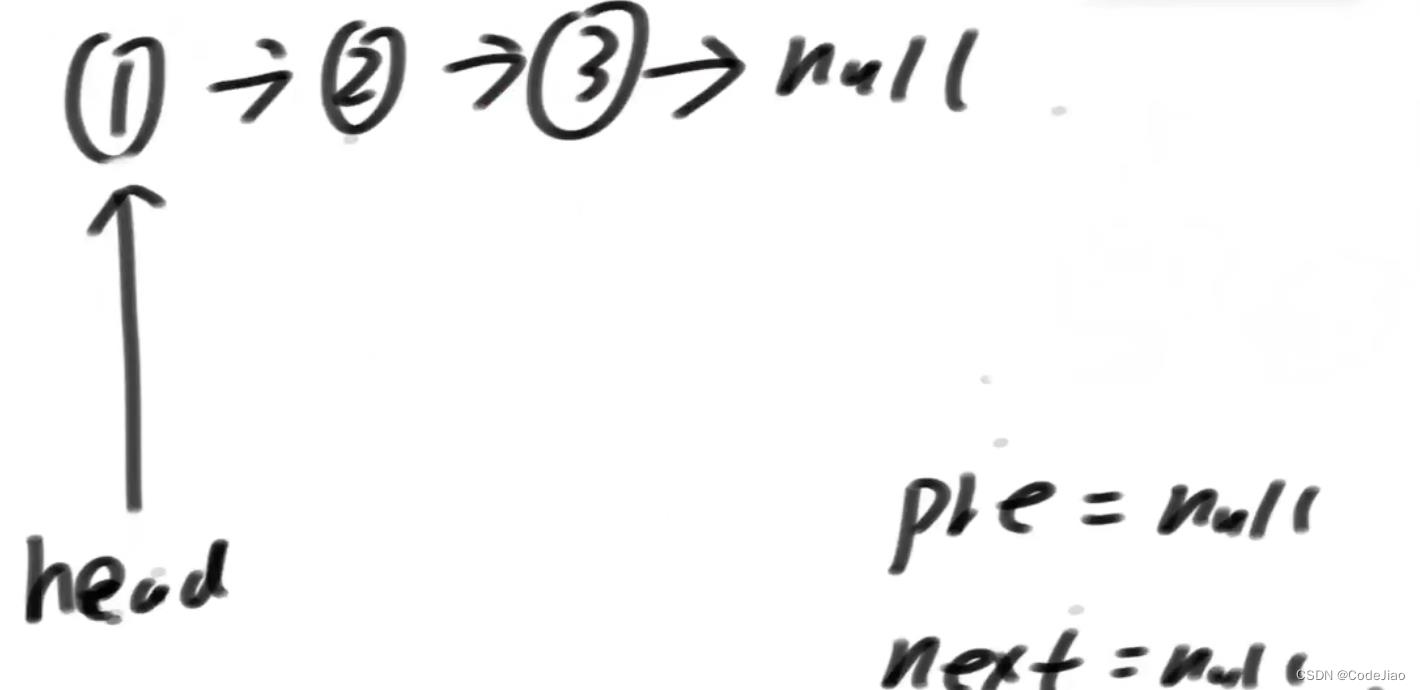
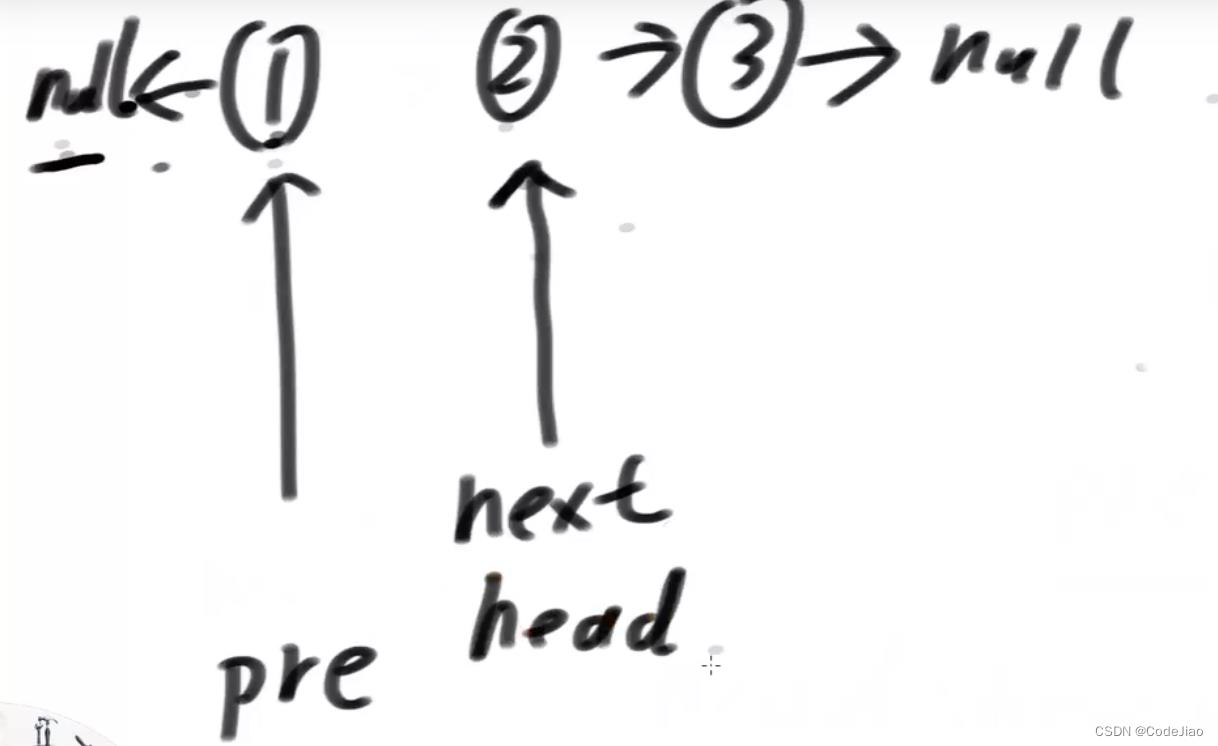
第一次循环结束后的状态:
第二次循环结束后的状态:
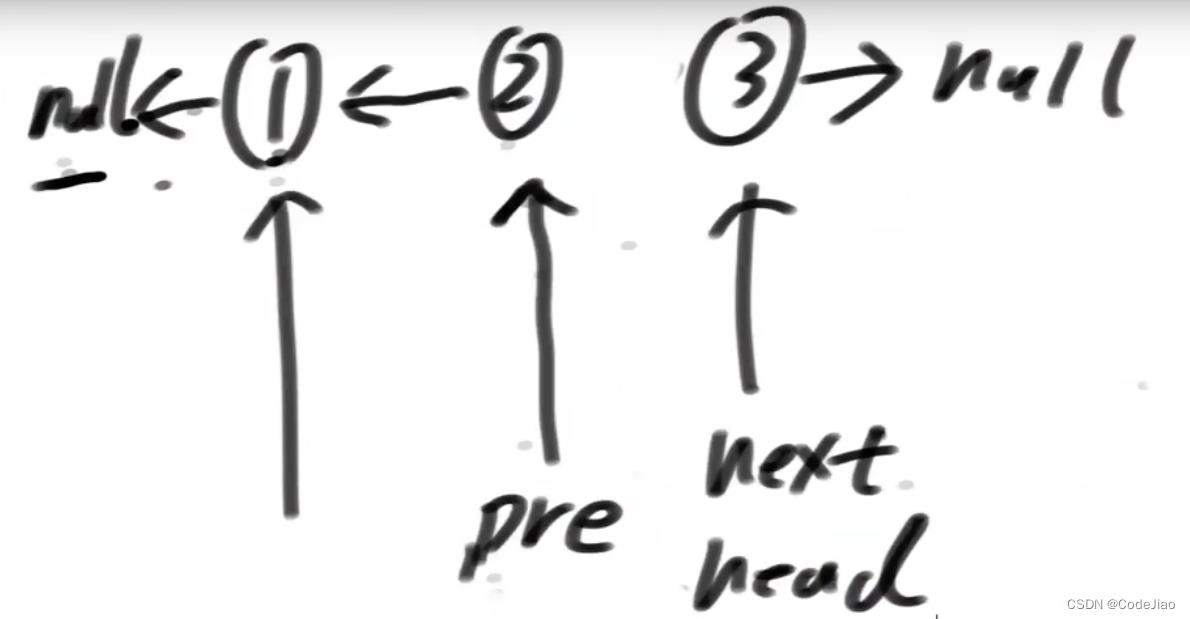
第三次循环结束后的状态:因为第三次循环结束后head == null,不满足head != null,所有循环结束,返回pre。
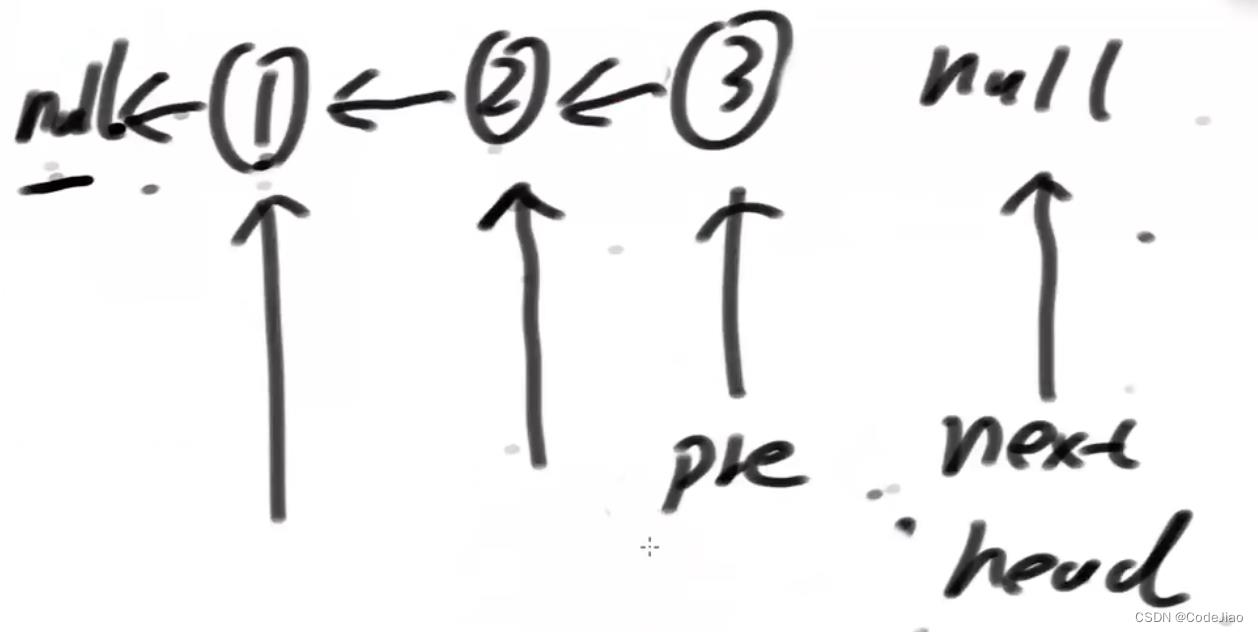
补充:单链表介绍
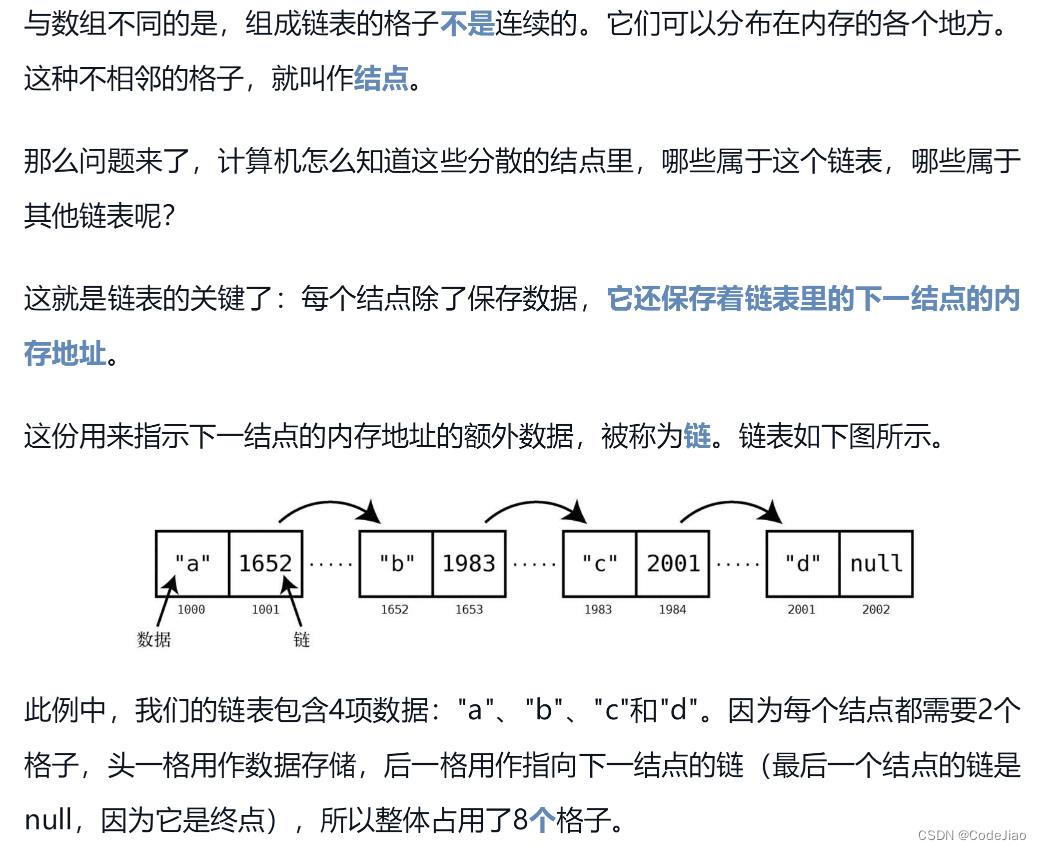
2. 双链表的反转
双链表的反转即把原来的双链表的指针顺序倒置。如下图所示:
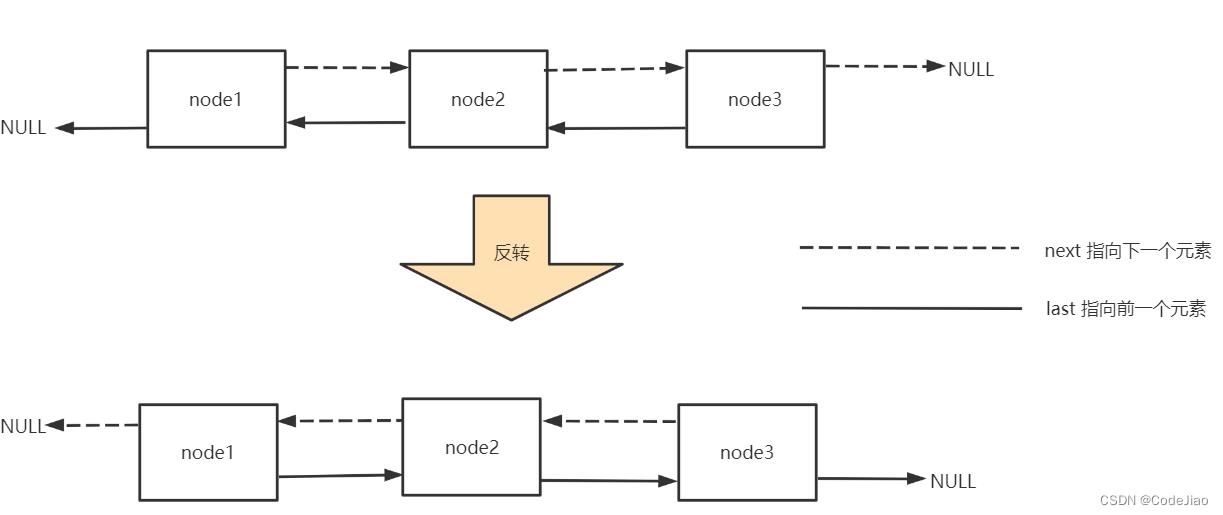
编写双链表的反转的代码:
public class DoubleLinkedList
public static class DoubleNode
public char value;
// next 指向下一个元素,last指向前一个元素
public DoubleNode next, last;
public DoubleNode(char value)
this.value = value;
/**
* 反转双向链表
*
* @param head 双向链表的头结点
* @return 反转后双向链表的头结点
*/
public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head)
DoubleNode pre = null, next = null;
while (head != null)
// next是为了可以往后继续遍历
next = head.next;
// head的next指向pre
head.next = pre;
// head的last指向next
head.last = next;
// pre指向head
pre = head;
// head指向next
head = next;
return pre;
// 测试代码
public static void main(String[] args)
DoubleNode node1 = new DoubleNode('a');
DoubleNode node2 = new DoubleNode('b');
DoubleNode node3 = new DoubleNode('c');
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node2.last = node1;
node3.last = node2;
node1 = reverseDoubleList(node1);
while (node1 != null)
System.out.print(node1.value + " ");
node1 = node1.next;
运行结果:
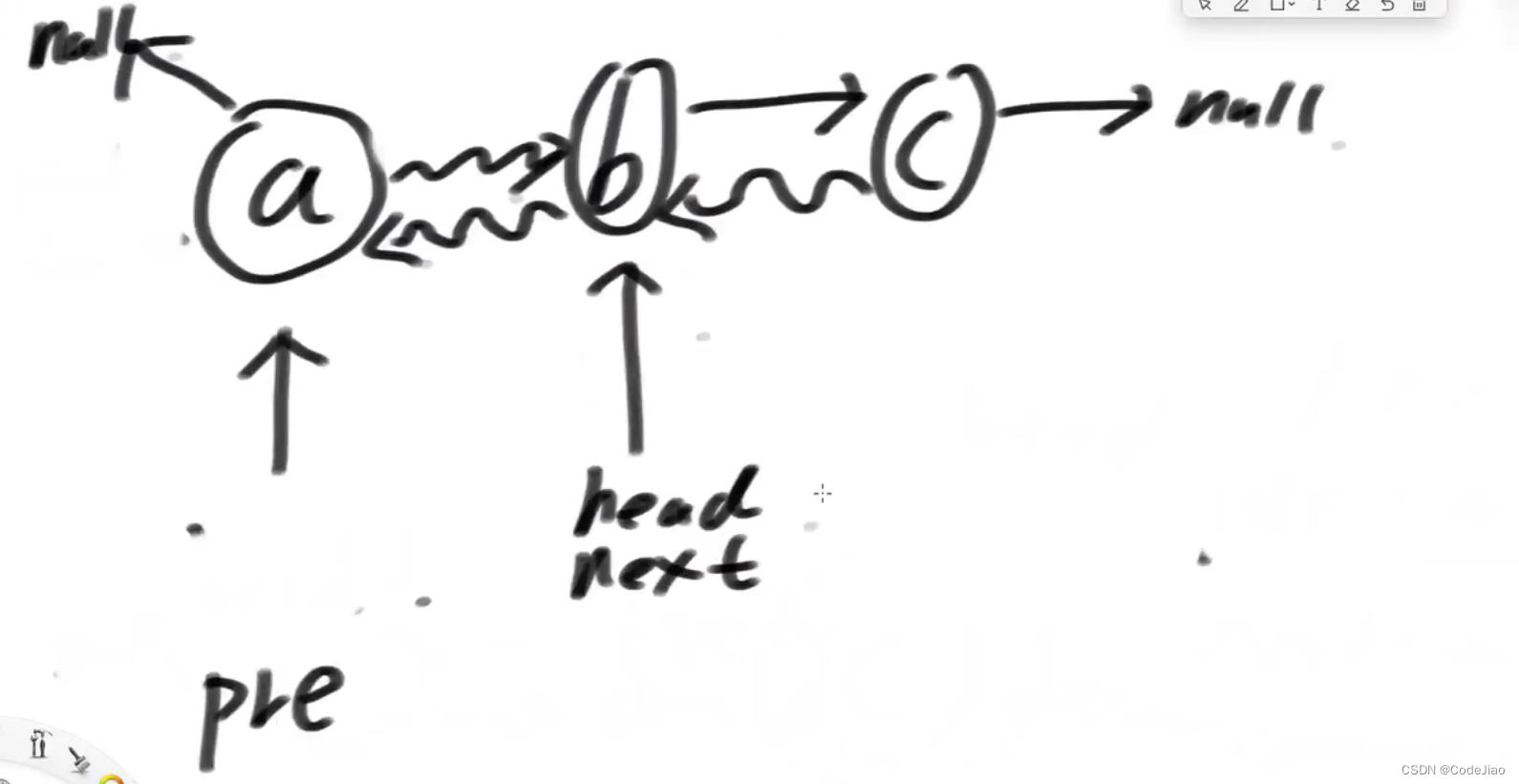
下面我们来解释原理:
初始状态:这里用曲线表示last指针,直线表示next指针。

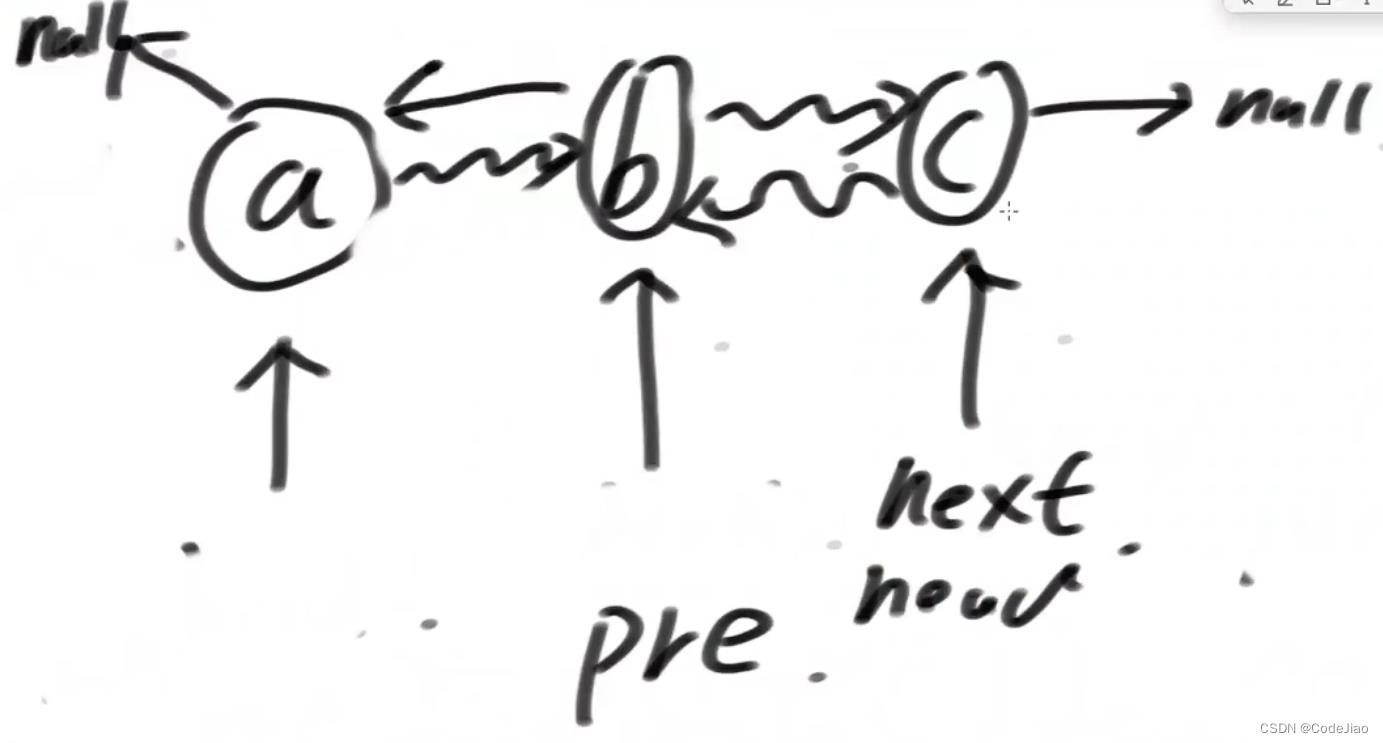
第一次循环结束后的状态:
第二次循环结束后的状态:
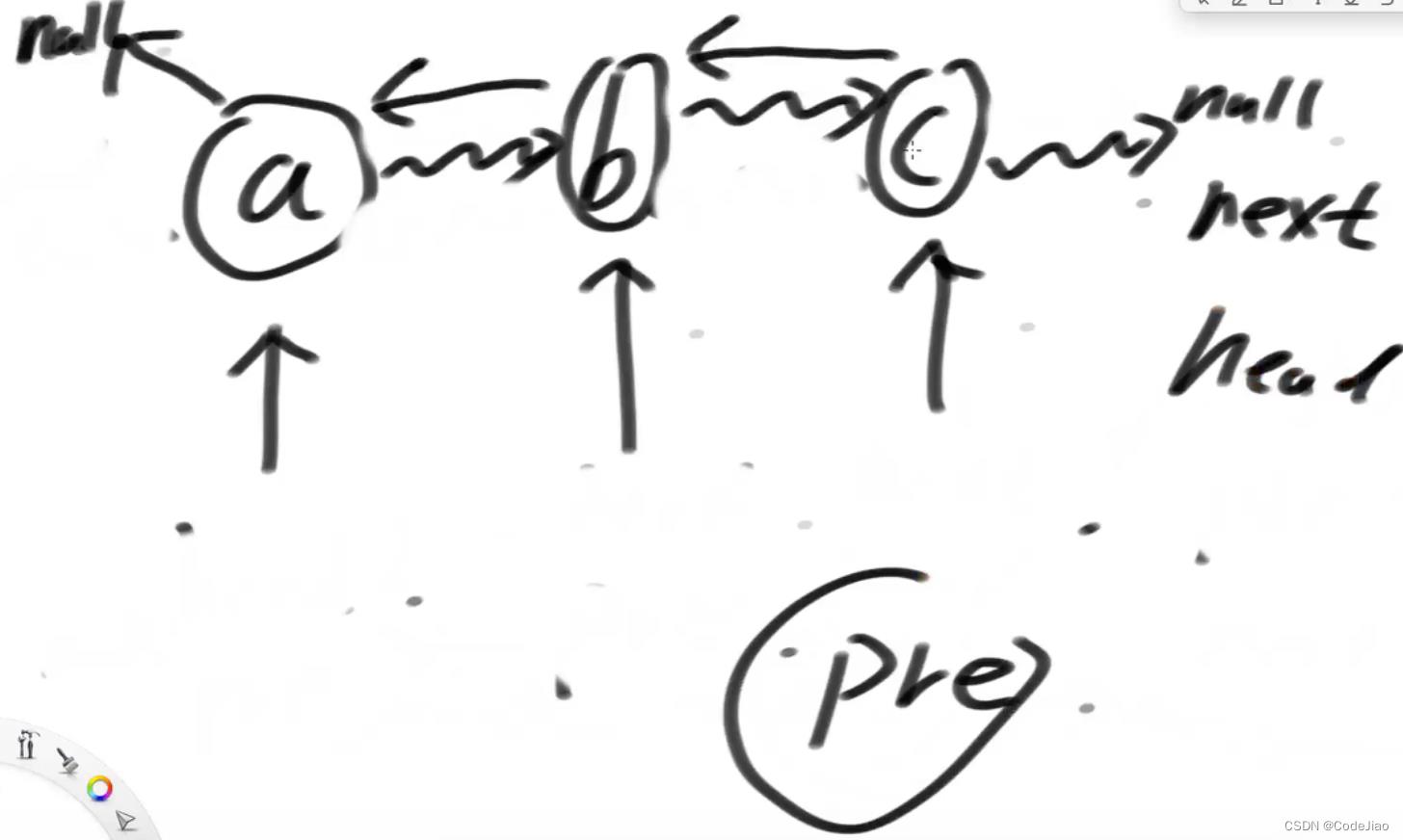
第三次循环结束后的状态:
补充:双向链表介绍
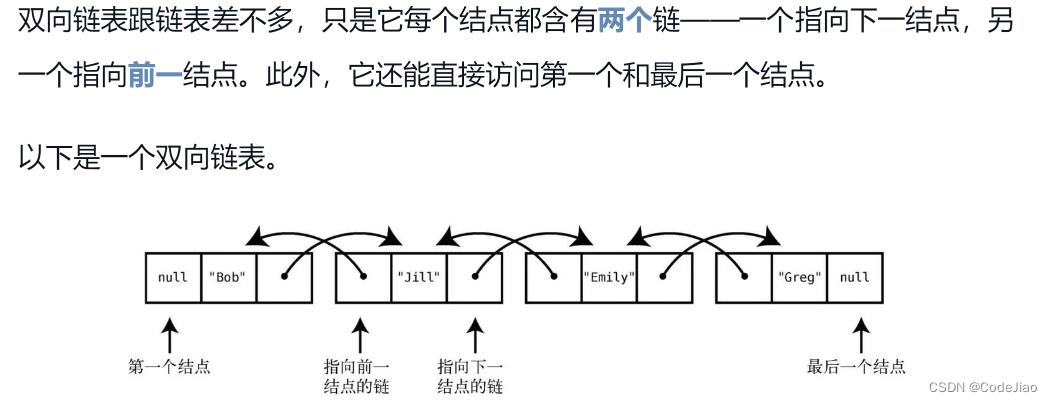
3. 单链表实现栈
栈介绍:

单链表实现栈:
public class MyStack<V>
private Node<V> head;
private int size;
public MyStack(int size)
this.size = size;
public boolean isEmpty()
return size == 0;
public int size()
return size;
// 入栈
public void push(V value)
Node<V> currentNode = new Node<>(value);
if (head != null)
currentNode.next = head;
head = currentNode;
size++;
// 出栈
public V pop()
if (head != null)
V result = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
return result;
return null;
// 查看栈顶元素(不弹出)
public V peek()
return head == null ? null : head.value;
static class Node<V>
public V value;
public Node<V> next;
public Node(V value)
this.value = value;
4. 单链表实现队列
队列介绍:
单链表实现队列:
public class MyQueue<V>
// 指向队列头
private Node<V> head;
// 指向队列尾
private Node<V> tail;
// 队列大小
private int size;
public MyQueue(int size)
this.size = size;
public boolean isEmpty()
return size == 0;
public int size()
return size;
// 网队列尾部插入一个元素
public void offer(V value)
Node<V> currentNode = new Node<>(value);
if (tail == null)
head = currentNode;
else
// 让链表链接下去 保证结点可达
tail.next = currentNode;
// 让队列的尾部指针指向新结点
tail = currentNode;
// 弹出当前队列头的元素
public V poll()
V result = null;
if (head != null)
result = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
else
tail = null;
return result;
// 获取当前队列头的元素(不弹出)
public V peek()
if (head != null)
return head.value;
return null;
class Node<V>
public V value;
public Node<V> next;
public Node(V value)
this.value = value;
5. 用双向链表实现双端队列
双端队列相对于普通队列,双端队列的入队和出队操作在两端都可进行。

public class MYDoubleEndedQueue<V>
// 双端队列头
private DoubleNode<V> head;
// 双端队列尾
private DoubleNode<V> tail;
private int size;
public MYDoubleEndedQueue(int size)
this.size = size;
public boolean isEmpty()
return size == 0;
public int size()
return size;
// 头部插入元素
public void pushHead(V value)
DoubleNode<V> currentNode = new DoubleNode<>(value);
if (head == null)
tail = currentNode;
else
currentNode.next = head;
head.last = currentNode;
head = currentNode;
size++;
// 尾部插入元素
public void pushTail(V value)
DoubleNode<V> currentNode = new DoubleNode<>(value);
if (head == null)
head = currentNode;
else
tail.next = currentNode;
currentNode.last = tail;
tail = currentNode;
size++;
// 头部取出元素
public V pollHead()
if (head == null)
return null;
V result = head.value;
if (head == tail)
head = null;
tail = null;
else
head = head.next;
head.last = null;
size--;
return result;
// 尾部取出元素
public V pollTail()
if (head == null)
return null;
V result = tail.value;
if (head == tail)
head = null;
tail = null;
else
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
size--;
return result;
class DoubleNode<V>
public V value;
public DoubleNode<V> last;
public DoubleNode<V> next;
public DoubleNode(V value)
this.value = value;
6. K 个一组翻转链表
题目要求:力扣题目链接

代码实现:
public class ReverseNodesInKGroup
// 不要提交这个类
public static class ListNode
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public static ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k)
ListNode start = head;
ListNode end = getKGroupEnd(start, k);
if (end == null)
return head;
// 第一组凑齐了!
head = end;
reverse(start, end);
// 上一组的结尾节点
ListNode lastEnd = start;
while (lastEnd.next != null)
start = lastEnd.next;
end = getKGroupEnd(start, k);
if (end == null)
return head;
reverse(start, end);
lastEnd.next = end;
lastEnd = start;
return head;
// 返回从start开始后的第k个节点 ...a,b,c,d,e... 比如调用getKGroupEnd(a,5) 返回e
public static ListNode getKGroupEnd(ListNode start, int k)
while (--k != 0 && start != null)
start = start.next;
return start;
public static void reverse(ListNode start, ListNode end)
end = end.next;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = start;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != end)
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
start.next = end;
思路:
初始状态:假设k = 3
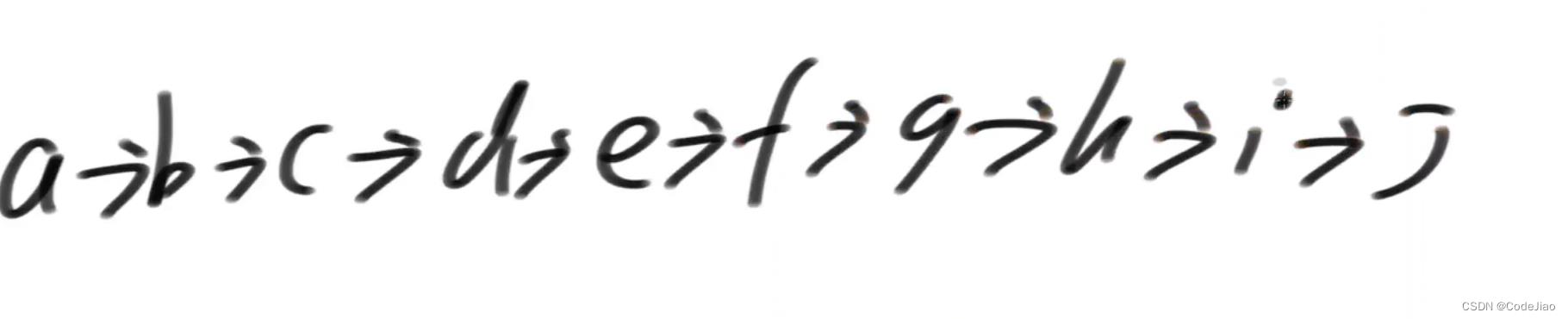
翻转第一小组链表
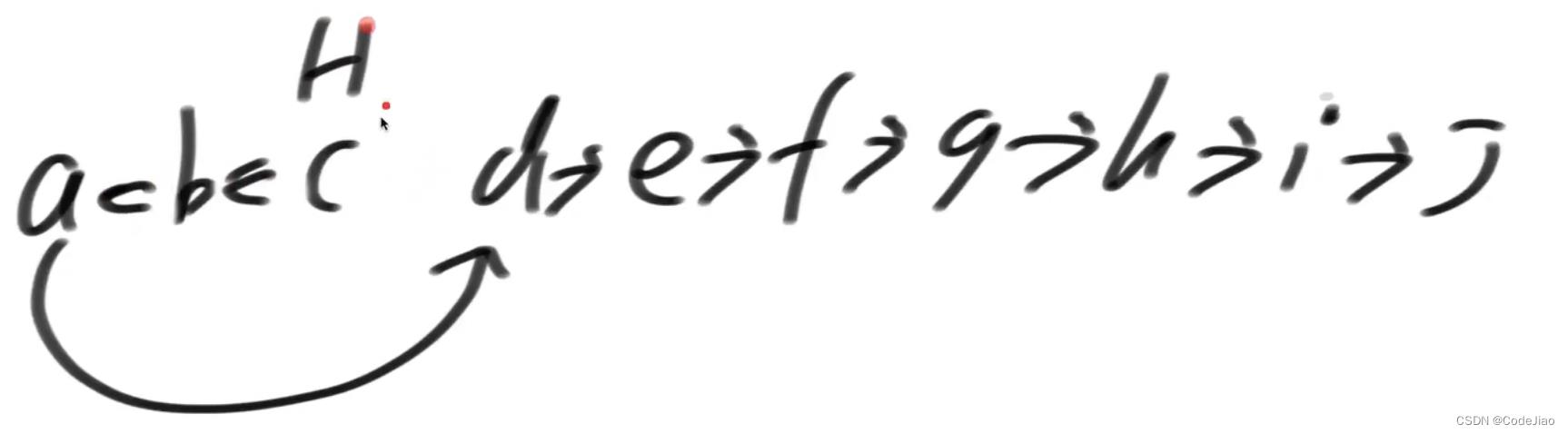
翻转第二小组链表
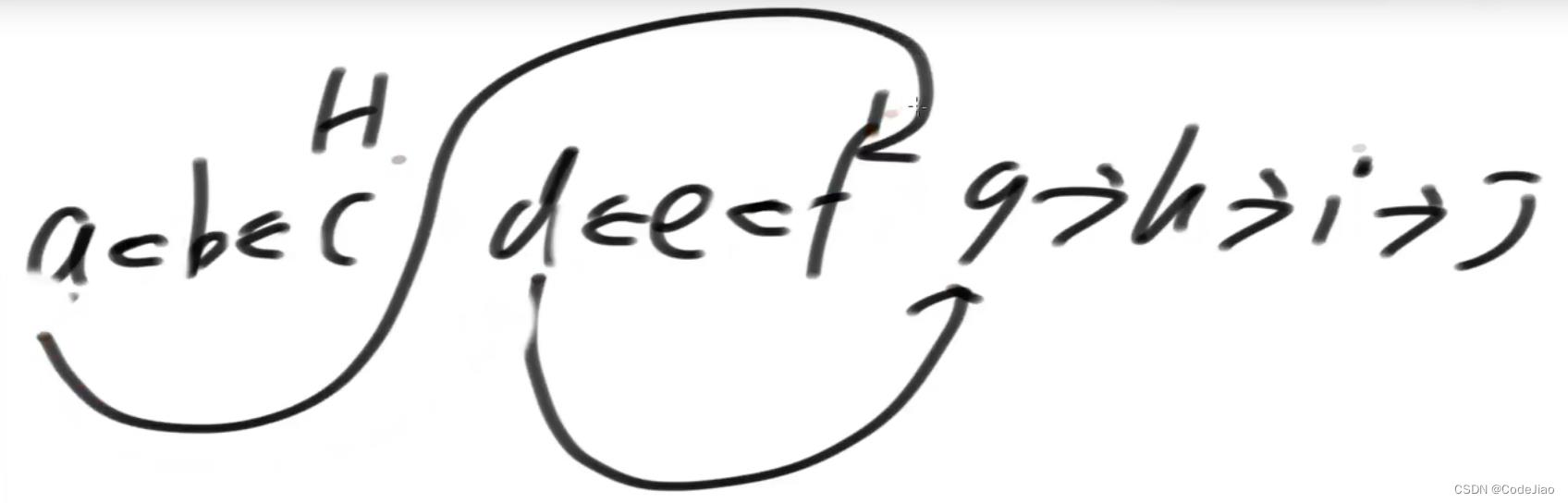
翻转第三小组链表
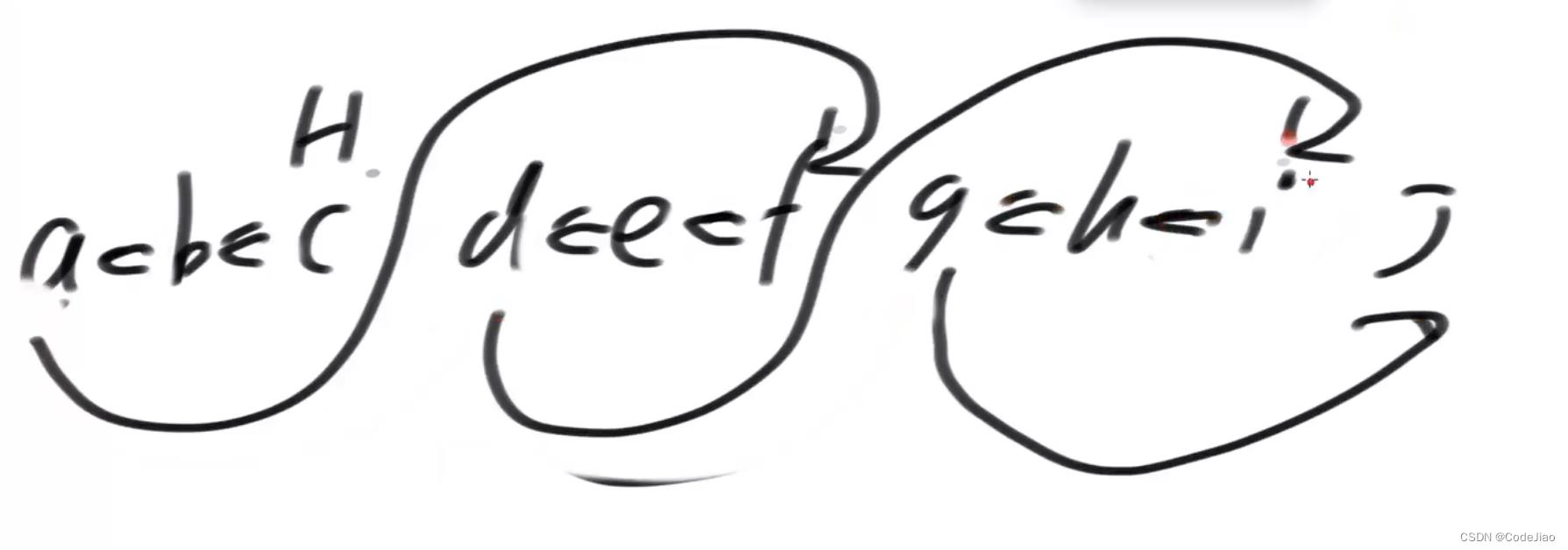
以上是关于Java算法 -- 单链表的反转单链表实现栈和队列以及双端队列K 个一组翻转链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章