Elasticsearch:Runtime fields 及其应用
Posted Elastic 中国社区官方博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Elasticsearch:Runtime fields 及其应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这是继上一篇文章 “Elasticsearch:Runtime fields 及其应用(一)” 的续篇。
索引运行时字段
运行时字段由它们运行的上下文定义。 例如,你可以在搜索查询的上下文中或在索引映射的运行时部分中定义运行时字段。 如果你决定索引运行时字段以获得更高的性能,只需将完整的运行时字段定义(包括脚本)移动到索引映射的上下文中。 Elasticsearch 自动使用这些索引字段来驱动查询,从而实现快速响应时间。 此功能意味着你只能编写一次脚本,并将其应用于支持运行时字段的任何上下文。
注意:当前不支持对 composite 运行时字段进行索引
然后,你可以使用运行时字段来限制 Elasticsearch 需要为其计算值的字段数量。 将索引字段与运行时字段结合使用可为你索引的数据以及如何为其他字段定义查询提供灵活性。
重要:索引运行时字段后,你无法更新包含的脚本。 如果你需要更改脚本,请使用更新的脚本创建一个新字段。
例如,假设你的公司想要更换一些旧的压力阀。 连接的传感器只能报告真实读数的一小部分。 你决定根据报告的读数计算值,而不是为压力阀配备新的传感器。 根据报告的数据,您在 my-index-5 的映射中定义以下字段:
PUT my-index-5
"mappings":
"properties":
"timestamp":
"type": "date"
,
"temperature":
"type": "long"
,
"voltage":
"type": "double"
,
"node":
"type": "keyword"
然后,你可以批量索引来自传感器的一些样本数据。 该数据包括每个传感器的电压读数:
POST my-index-5/_bulk?refresh=true
"index":
"timestamp": 1516729294000, "temperature": 200, "voltage": 5.2, "node": "a"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516642894000, "temperature": 201, "voltage": 5.8, "node": "b"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516556494000, "temperature": 202, "voltage": 5.1, "node": "a"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516470094000, "temperature": 198, "voltage": 5.6, "node": "b"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516383694000, "temperature": 200, "voltage": 4.2, "node": "c"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516297294000, "temperature": 202, "voltage": 4.0, "node": "c"在与几位现场工程师交谈后,你意识到传感器报告的值至少应该是当前值的两倍,但可能更高。 你创建一个名为 voltage_corrected 的运行时字段,该字段检索当前电压并将其乘以 2:
PUT my-index-5/_mapping
"runtime":
"voltage_corrected":
"type": "double",
"script":
"source": """
emit(doc['voltage'].value * params['multiplier'])
""",
"params":
"multiplier": 2
你可以使用 _search API 上的 fields 参数检索计算值:
GET my-index-5/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"fields": [
"voltage_corrected",
"node"
],
"size": 2
上面的响应返回值为:
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-5",
"_id" : "LmsDcIEBD_ZocgsvAosw",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : 1516729294000,
"temperature" : 200,
"voltage" : 5.2,
"node" : "a"
,
"fields" :
"node" : [
"a"
],
"voltage_corrected" : [
10.4
]
,
"_index" : "my-index-5",
"_id" : "L2sDcIEBD_ZocgsvAosw",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : 1516642894000,
"temperature" : 201,
"voltage" : 5.8,
"node" : "b"
,
"fields" :
"node" : [
"b"
],
"voltage_corrected" : [
11.6
]
]
从上面的结果中,我们可以看出来 voltage_corrected 是 _source 中的 voltage 的两倍。
在查看传感器数据并运行一些测试后,你确定报告的传感器数据的乘数应该是 4。为了获得更高的性能,你决定使用新的乘数参数来索引 voltage_corrected 运行时字段。
在名为 my-index-5 的新索引中,将 voltage_corrected 运行时字段定义复制到新索引的映射中。 就是这么简单! 你可以添加一个名为 on_script_error 的可选参数,该参数确定脚本在索引时抛出错误时是否拒绝整个文档(默认)。
DELETE my-index-5
PUT my-index-5
"mappings":
"properties":
"timestamp":
"type": "date"
,
"temperature":
"type": "long"
,
"voltage":
"type": "double"
,
"node":
"type": "keyword"
,
"voltage_corrected":
"type": "double",
"on_script_error": "fail",
"script":
"source": """
emit(doc['voltage'].value * params['multiplier'])
""",
"params":
"multiplier": 4
在上面,我们使用了 on_script_error。我们设置它为 fail,表示当脚本在索引时抛出一个错误信息后,整个文档将被拒绝。将值设置为 ignore 将在文档的 _ignored 元数据字段中注册该字段并继续索引。
将传感器中的一些样本数据批量索引到 my-index-5 索引中:
POST my-index-5/_bulk?refresh=true
"index":
"timestamp": 1516729294000, "temperature": 200, "voltage": 5.2, "node": "a"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516642894000, "temperature": 201, "voltage": 5.8, "node": "b"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516556494000, "temperature": 202, "voltage": 5.1, "node": "a"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516470094000, "temperature": 198, "voltage": 5.6, "node": "b"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516383694000, "temperature": 200, "voltage": 4.2, "node": "c"
"index":
"timestamp": 1516297294000, "temperature": 202, "voltage": 4.0, "node": "c"你现在可以在搜索查询中检索计算值,并根据精确值查找文档。 以下范围查询返回计算得到的 voltage_corrected 大于或等于 16 但小于或等于 20 的所有文档。同样,使用 _search API 上的 fields 参数来检索你想要的字段:
POST my-index-5/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"query":
"range":
"voltage_corrected":
"gte": 16,
"lte": 20,
"boost": 1.0
,
"fields": ["voltage_corrected", "node"]
根据所包含脚本的计算值,响应包括与范围查询匹配的文档的 voltage_corrected 字段:
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-5",
"_id" : "SmsQcIEBD_Zocgsv9IsJ",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : 1516383694000,
"temperature" : 200,
"voltage" : 4.2,
"node" : "c"
,
"fields" :
"node" : [
"c"
],
"voltage_corrected" : [
16.8
]
,
"_index" : "my-index-5",
"_id" : "S2sQcIEBD_Zocgsv9IsJ",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : 1516297294000,
"temperature" : 202,
"voltage" : 4.0,
"node" : "c"
,
"fields" :
"node" : [
"c"
],
"voltage_corrected" : [
16.0
]
]
使用运行时字段探索你的数据
考虑要从中提取字段的大量日志数据。 索引数据非常耗时并且占用大量磁盘空间,你只想探索数据结构而不预先定义模式(schema)。
你知道你的日志数据包含你要提取的特定字段。 在这种情况下,我们希望专注于 @timestamp 和 message 字段。 通过使用运行时字段,你可以定义脚本以在搜索时计算这些字段的值。
定义索引字段为起点
你可以从一个简单的示例开始,将 @timestamp 和 message 字段添加到 my-index-6 映射作为索引字段。 为了保持灵活性,请使用 wildcard 作为 message 的字段类型:
PUT my-index-6
"mappings":
"properties":
"@timestamp":
"format": "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_second",
"type": "date"
,
"message":
"type": "wildcard"
摄取一些数据
映射你要检索的字段后,将日志数据中的一些记录索引到 Elasticsearch。 以下请求使用批量 API 将原始日志数据索引到 my-index-6。 你可以使用一个小样本来试验运行时字段,而不是索引所有日志数据。
最终文档不是有效的 Apache 日志格式,但我们可以在脚本中考虑这种情况。
POST /my-index-6/_bulk?refresh
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:30:17-05:00","message":"40.135.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:30:17 -0500] \\"GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0\\" 200 24736"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:30:53-05:00","message":"232.0.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:30:53 -0500] \\"GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0\\" 200 24736"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:31:12-05:00","message":"26.1.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:12 -0500] \\"GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0\\" 200 24736"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:31:19-05:00","message":"247.37.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:19 -0500] \\"GET /french/splash_inet.html HTTP/1.0\\" 200 3781"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:31:22-05:00","message":"247.37.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:22 -0500] \\"GET /images/hm_nbg.jpg HTTP/1.0\\" 304 0"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:31:27-05:00","message":"252.0.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:27 -0500] \\"GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0\\" 200 24736"
"index":
"timestamp":"2020-04-30T14:31:28-05:00","message":"not a valid apache log"此时,你可以查看 Elasticsearch 如何存储您的原始数据。
GET my-index-6该映射包含两个字段:@timestamp 和 message。
"my-index-6" :
"aliases" : ,
"mappings" :
"properties" :
"@timestamp" :
"type" : "date",
"format" : "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_second"
,
"message" :
"type" : "wildcard"
,
"timestamp" :
"type" : "date"
,
"settings" :
"index" :
"routing" :
"allocation" :
"include" :
"_tier_preference" : "data_content"
,
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"provided_name" : "my-index-6",
"creation_date" : "1655443040323",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "y5O2QukeRkuGfthJou5kag",
"version" :
"created" : "8020099"
使用 grok 模式定义运行时字段
如果要检索包含 clientip 的结果,可以将该字段添加为映射中的运行时字段。 以下运行时脚本定义了从文档中的单个文本字段中提取结构化字段的 grok 模式。 grok 模式就像一个支持可重用的别名表达式的正则表达式。
该脚本匹配 %COMMONAPACHELOG 日志模式,该模式了解 Apache 日志的结构。 如果模式匹配,脚本会发出匹配 IP 地址的值。 如果模式匹配(clientip != null),脚本只会返回字段值而不会崩溃。
PUT my-index-6/_mappings
"runtime":
"http.client_ip":
"type": "ip",
"script": """
String clientip=grok('%COMMONAPACHELOG').extract(doc["message"].value)?.clientip;
if (clientip != null) emit(clientip);
"""
在上面,我们通过检查 clientip != null 来确保即使 message的模式不匹配,脚本也不会崩溃。
或者,你可以在搜索请求的上下文中定义相同的运行时字段。 运行时定义和脚本与之前在索引映射中定义的完全相同。 只需将该定义复制到 runtime_mappings 部分下的搜索请求中,并包含与运行时字段匹配的查询。 此查询返回的结果与你在索引映射中为 http.clientip 运行时字段定义搜索查询时返回的结果相同,但仅在此特定搜索的上下文中:
GET my-index-6/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"runtime_mappings":
"http.clientip":
"type": "ip",
"script": """
String clientip=grok('%COMMONAPACHELOG').extract(doc["message"].value)?.clientip;
if (clientip != null) emit(clientip);
"""
,
"query":
"match":
"http.clientip": "40.135.0.0"
,
"fields" : ["http.clientip"]
上面搜索返回的结果是:
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-6",
"_id" : "TGsbcIEBD_Zocgsv_YvB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : "2020-04-30T14:30:17-05:00",
"message" : """40.135.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:30:17 -0500] "GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0" 200 24736"""
,
"fields" :
"http.clientip" : [
"40.135.0.0"
]
]
定义 composite 运行时字段
你还可以定义复合运行时字段以从单个脚本发出多个字段。 你可以定义一组类型化的子字段并 emit map 值。 在搜索时,每个子字段都会检索与其在 map 中的名称相关联的值。 这意味着你只需要指定一次 grok 模式并且可以返回多个值:
PUT my-index-6/_mappings
"runtime":
"http":
"type": "composite",
"script": "emit(grok(\\"%COMMONAPACHELOG\\").extract(doc[\\"message\\"].value))",
"fields":
"clientip":
"type": "ip"
,
"verb":
"type": "keyword"
,
"response":
"type": "long"
为了能够理解上面在做什么,我们还是借助 Kibana 中的 Grok debugger 来进行展示:
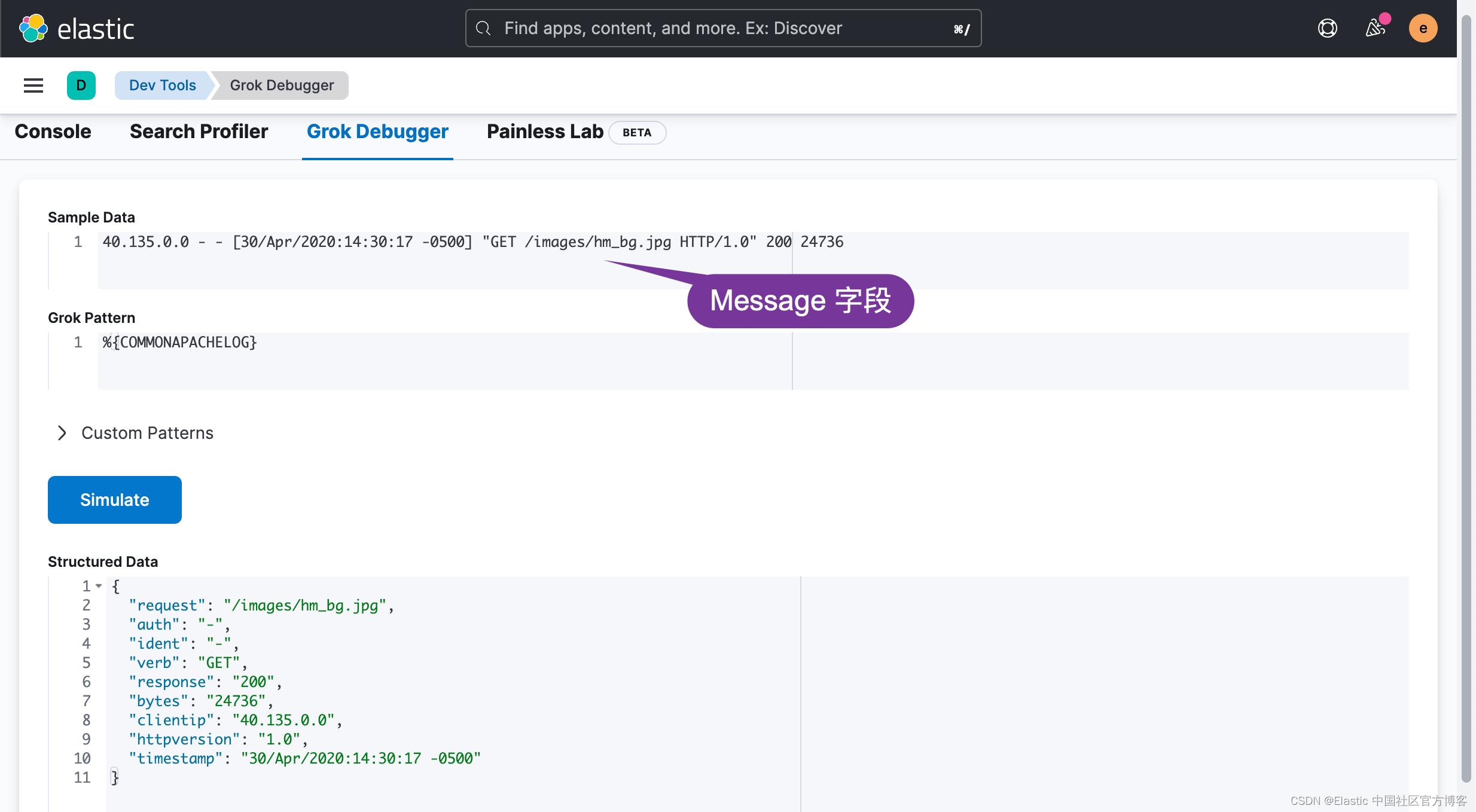
在上面,我们把 message 字段粘贴过来,并使用 %COMMONAPACHELOG grok pattern 来做测试。我们可以看到如上所示的字段。在 Structured Data 里,我们可以看到 clientip,verb 及 response 字段。
运行完上面的指令后,我们重新查看 my-index-6 的 mapping:
GET my-index-6/_mapping
"my-index-6" :
"mappings" :
"runtime" :
"http" :
"type" : "composite",
"script" :
"source" : """emit(grok("%COMMONAPACHELOG").extract(doc["message"].value))""",
"lang" : "painless"
,
"fields" :
"response" :
"type" : "long"
,
"clientip" :
"type" : "ip"
,
"verb" :
"type" : "keyword"
,
"http.client_ip" :
"type" : "ip",
"script" :
"source" : """
String clientip=grok('%COMMONAPACHELOG').extract(doc["message"].value)?.clientip;
if (clientip != null) emit(clientip);
""",
"lang" : "painless"
,
"properties" :
"@timestamp" :
"type" : "date",
"format" : "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_second"
,
"message" :
"type" : "wildcard"
,
"timestamp" :
"type" : "date"
搜索一个特定的 IP 地址
使用 http.clientip 运行时字段,你可以定义一个简单的查询来运行对特定 IP 地址的搜索并返回所有相关字段:
GET my-index-6/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"query":
"match":
"http.clientip": "40.135.0.0"
,
"fields" : ["*"]
上面的 API 返回以下结果。 因为 http 是一个复合运行时字段,所以响应包括字段下的每个子字段,包括与查询匹配的任何关联值。 无需提前构建数据结构,你可以以有意义的方式搜索和探索数据,以试验并确定要索引的字段。
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-6",
"_id" : "TGsbcIEBD_Zocgsv_YvB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : "2020-04-30T14:30:17-05:00",
"message" : """40.135.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:30:17 -0500] "GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0" 200 24736"""
,
"fields" :
"http.verb" : [
"GET"
],
"http.clientip" : [
"40.135.0.0"
],
"http.response" : [
200
],
"message" : [
"""40.135.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:30:17 -0500] "GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0" 200 24736"""
],
"http.client_ip" : [
"40.135.0.0"
],
"timestamp" : [
"2020-04-30T19:30:17.000Z"
]
]
另外,还记得脚本中的 if 语句吗?
if (clientip != null) emit(clientip);如果脚本不包含此条件,则查询将在任何与模式不匹配的分片上失败。 通过包含此条件,查询将跳过与 grok 模式不匹配的数据。
搜索特定范围内的文档
你还可以运行对时间戳 timestamp 字段进行操作的 range query。 以下查询返回时间戳大于或等于 2020-04-30T14:31:27-05:00 的任何文档:
GET my-index-6/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"query":
"range":
"timestamp":
"gte": "2020-04-30T14:31:27-05:00"
响应包括日志格式不匹配的文档,但 timestamp 在定义的范围内。
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-6",
"_id" : "UWsbcIEBD_Zocgsv_YvB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : "2020-04-30T14:31:27-05:00",
"message" : """252.0.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:27 -0500] "GET /images/hm_bg.jpg HTTP/1.0" 200 24736"""
,
"_index" : "my-index-6",
"_id" : "UmsbcIEBD_Zocgsv_YvB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : "2020-04-30T14:31:28-05:00",
"message" : "not a valid apache log"
]
使用 dissect 模式定义运行时字段
如果你不需要正则表达式的强大功能,你可以使用 dissect 模式而不是 grok 模式。 Dissect 模式匹配固定分隔符,但通常比 grok 快。
你可以使用 dissect 来获得与使用 grok 模式解析 Apache 日志相同的结果。 你不是匹配日志模式,你需要包含要丢弃的字符串部分。 特别注意要丢弃的字符串部分将有助于构建成功的 dissect 模式。
PUT my-index-6/_mappings
"runtime":
"http.client.ip":
"type": "ip",
"script": """
String clientip=dissect('%clientip %ident %auth [%@timestamp] "%verb %request HTTP/%httpversion" %status %size').extract(doc["message"].value)?.clientip;
if (clientip != null) emit(clientip);
"""
在上面,我们把所有的字段都添加上,尽管有些部分是我们不需要的。
同样,你可以定义 dissect 模式来提取 HTTP response code:
PUT my-index-6/_mappings
"runtime":
"http.responses":
"type": "long",
"script": """
String response=dissect('%clientip %ident %auth [%@timestamp] "%verb %request HTTP/%httpversion" %response %size').extract(doc["message"].value)?.response;
if (response != null) emit(Integer.parseInt(response));
"""
然后,你可以运行查询以使用 http.responses 运行时字段检索特定的 HTTP 响应。 使用 _search 请求的 fields 参数来指示您要检索哪些字段:
GET my-index-6/_search?filter_path=**.hits
"query":
"match":
"http.responses": "304"
,
"fields" : ["http.client_ip","timestamp","http.verb"]
响应包括一个文档,其中 HTTP 响应为 304:
"hits" :
"hits" : [
"_index" : "my-index-6",
"_id" : "UGsbcIEBD_Zocgsv_YvB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" :
"timestamp" : "2020-04-30T14:31:22-05:00",
"message" : """247.37.0.0 - - [30/Apr/2020:14:31:22 -0500] "GET /images/hm_nbg.jpg HTTP/1.0" 304 0"""
,
"fields" :
"http.verb" : [
"GET"
],
"http.client_ip" : [
"247.37.0.0"
],
"timestamp" : [
"2020-04-30T19:31:22.000Z"
]
]
以上是关于Elasticsearch:Runtime fields 及其应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章