C/C++实现特征点提取算法——Harris角点提取
Posted nanke_yh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C/C++实现特征点提取算法——Harris角点提取相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Harris算法
1 原理步骤
Harris算子是目前较为经典的角点提取算子。其基本原理为:选取一个较小尺寸的检测窗口(尺寸大小依据源影像大小或者试验效果要求适当确定,一般是奇数行列,如:3×3、5×5等等),将检测窗口叠加在影像上并不断地移动,通过记录窗口中各像元间的灰度值变化来确定特征点。检测窗口在影像上滑动时,窗口中灰度值变化主要分为下图中显示的三种情况。
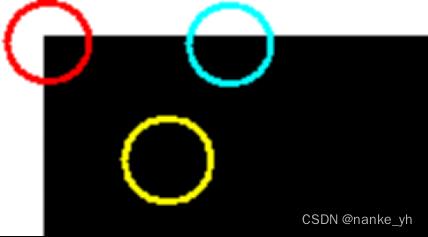
图中红黄蓝三种圆圈分别代表特征点、平坦区域和边缘区域。当出现图中红色圆圈的情况时,像素灰度的变化将会大于设定的阈值,此时检索窗口的中心点就是特征角点了。Harris理论详细介绍很多博主都有写,具体可参考:
【图像预处理】 Harris角点检测器原理及C++实现_Cai Yichao的博客-CSDN博客
Harris角点检测算法 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
OpenCV——角点检测原理分析(Harris,Shi-Tomasi、亚像素级角点检测) - 灰信网(软件开发博客聚合) (freesion.com)
具体的实现步骤如下:第一步:创建I、Ix、Ix2、Iy、Iy2、Ixy、cim、mx、corner等数组,分别是复制原图像矩阵I;水平、竖直方向sobel差分算子卷积获得的Ix、Iy;进而获得Ix2、Iy2、Ixy数组;另外Ix2_、Iy2_、Ixy_数组为高斯平滑后得到的数组;cim为响应函数R数组;mx为局部最大值数组(可不用)、corner为角点空间坐标标记数组(通过容器记录点坐标,数组可不用)。
//创建I、Ix、Ix2、Iy、Iy2、Ixy、cim、mx、corner数组
double *I = new double[width*height];
double *Ix = NULL;
double *Ix2 = new double[width*height];
double *Iy = NULL;
double *Iy2 = new double[width*height];
double *Ixy = new double[width*height];
double *Ix2_ = NULL;
double *Iy2_ = NULL;
double *Ixy_ = NULL;
double *cim = new double[width*height];
//double *mx = new double[width*height];
//bool *corner = new bool[width*height];
//memset(corner,0,width*height*sizeof(bool));
//将图像灰度值复制到I中
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
//将灰度图像转化为double型
I[i * width + j] = (double)buffer[i * width + j];
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第一步:利用差分算子对图像进行滤波
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//定义水平方向差分算子并求Ix
double dx[9] = -1,0,1,-1,0,1,-1,0,1;
Ix = mbys(I,width,height,dx,3,3);
//定义垂直方向差分算子并求Iy
double dy[9] = -1,-1,-1,0,0,0,1,1,1;
Iy = mbys(I,width,height,dy,3,3);
//计算Ix2、Iy2、Ixy矩阵
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
Ix2[i * width + j] = Ix[i * width + j]*Ix[i * width + j];
//Ix2[i * width + j] = pow(Ix[i * width + j],2);
Iy2[i * width + j] = Iy[i * width + j]*Iy[i * width + j];
Ixy[i * width + j] = Ix[i * width + j]*Iy[i * width + j];
第二步:计算各个像元的相关矩阵M:
 (1)
(1)
式中, 为权重比例,Ix和Iy是x,y方向上的一阶导数。
为权重比例,Ix和Iy是x,y方向上的一阶导数。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第二步:对Ix2/Iy2/Ixy进行高斯平滑,以去除噪声
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//本例中使用5×5的高斯模板
//计算模板参数
// const int GaussWindow=5;
// const double GaussSigma=0.08;
double *g = new double[GaussWindow * GaussWindow];
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < GaussWindow;j++)
g[i * GaussWindow + j] = exp(-((i - int(GaussWindow/2))*(i - int(GaussWindow/2)) + (j - int(GaussWindow/2)) * (j - int(GaussWindow/2)))/(2 * GaussSigma));
//g[i * GaussWindow + j] = exp(-(pow(double(i - int(GaussWindow/2)),2) + pow(double(j - int(GaussWindow/2)),2))/(2 * GaussSigma ));
//归一化:使模板参数之和为1(其实此步可以省略)
// 高斯函数前的常数可以不用计算,会在归一化的过程中给消去
double total = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow * GaussWindow;i++)
total += g[i];//将所有的值进行相加
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < GaussWindow;j++)
g[i * GaussWindow + j] /= total;//进行归一化
//进行高斯平滑smoothing,加入权重w(x,y)
Ix2_ = mbys(Ix2,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);
Iy2_ = mbys(Iy2,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);
Ixy_ = mbys(Ixy,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);第三步:根据Harris矩阵可计算出矩阵的特征值λ1、λ2,进而计算出角度响应R值:
 (2)
(2)
式中,k为一个常数,取值范围一般为[0.04,0.06],k的取值不同,提取的特征点效果也会不同。在实际应用中,为了减少k值选取时带来的随机性,常常采用公式(3)来计算响应函数R,式中ε为任意小的正数。
 (3)
(3)
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第三步:计算角点量
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//用来求得响应函数R
//计算cim:即cornerness of image,我们把它称做‘角点量’
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
//注意:要在分母中加入一个极小量以防止除数为零溢出
cim[i * width + j] = (Ix2_[i * width + j]*Iy2_[i * width + j] - Ixy_[i * width + j]*Ixy_[i * width + j])/(Ix2_[i * width + j] + Iy2_[i * width + j] + FLT_EPSILON);
第四步:进行非极大值抑制,在检测窗口范围内寻找R的极大值,当极值点R值大于特定阈值时,则视作特征点。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第四步:进行局部非极大值抑制以获得最终角点
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//注意进行局部极大值抑制的思路
const int size = 5;
int r = size/2;//局部半径
double max = -10000;//最大值
double dmax;//局部最大值
Pt object;
for(int i = 0; i < width*height; i++)
if(cim[i] > max)
max = cim[i];//统计最大值
int nRow = 0,nCol = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
dmax = 0;
for (int n = -r;n <= r;n++)
for (int m = -r;m <= r;m++)
//越界限制
nRow = i + n < height ? i + n : height - 1;
nRow = nRow > 0 ? nRow : 0;
nCol = j + m < width ? j + m : width - 1;
nCol = nCol > 0 ? nCol: 0;
if (cim[nRow * width + nCol] > dmax)
dmax = cim[nRow * width + nCol];//局部最大
if(dmax > thresh && cim[i * width + j] == dmax)
object.x = j;
object.y = i;
corners.push_back(object);
//corner[i * width + j] = 1;
Harris算法优点在于:实现简单,特征点提取均匀合理,影像的亮度、旋转、噪声以及视点变化对算法影响小,稳定性强;其缺点在于:不具备尺度不变特性,特征点的定位精度低,坐标为像素级。
以上也可参考基于自适应三角剖分的DMZ Ⅱ相机影像配准融合技术研究 - 中国知网 (cnki.net)
2 测试效果
基于以上内容,进行的Harris特征点提取算法实现。其中主要的参数设置有:高斯平滑滤波参数GaussWindow为5,GaussSigma为0.08,这两个参数设计有外部输入接口,可调。阈值参数thresh外部接口输入(也可根据最大响应函数值来百分比设置)。默认参数差分滤波窗口3*3,抑制最大值的局部窗口5*5。
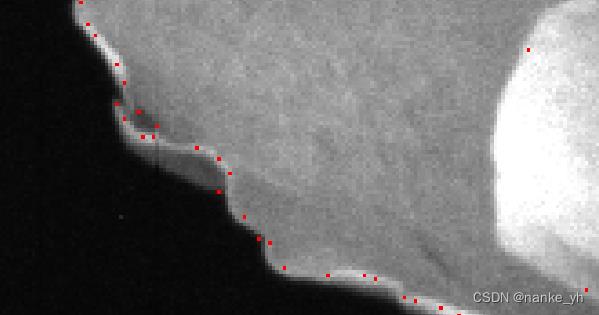
由于算法实现全为c/c++语言,特征点的显示就是通过多波段彩色叠加给特征点坐标位置处赋值为(255,0,0)。由于只是显示一个像素位置,那么在图上显示会特别小,直接看可能不容易发现特征点位置,故放了局部图以供查看。
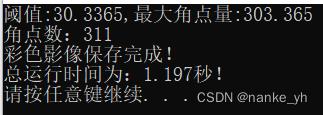
| Harris角点分布图 | 局部图 | 输出信息 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 小结
- 针对简单的图像,提取的角点较为准确,但是获得的点坐标均为整数,会存在误差,后续可以采用最小二乘等方法处理获得亚像素精度的点坐标。
- 对于复杂图像,提取的角点数量多但也存在错误点,这个需要调整和设置具体的参数值。
- 对于算法中出现的参数设置,相对比较难控制。文中主要控制阈值,阈值越大,得到的点越少,角点也越准确,但这需要根据具体图像设置。
4 完整代码
在以上内容中涉及到的代码和函数有:
1.差分算子卷积函数mbys
/*****************************************************
*function description: 滤波处理
*
*input parameter: double * ptImg,int width,int height 输入影像
* double *filterBuf,int winW,int winH 滤波器
*return: 滤波后影像
*
******************************************************/
double * mbys(double * ptImg,int width,int height,double *filterBuf,int winW,int winH)
if (ptImg == NULL || filterBuf == NULL)
return NULL;
//由于mbys函数中内存释放问题,内部不释放,外部会新创建内存可能导致内存错误
double * result = new double[width * height];
memset(result, 0, width * height * sizeof(double));
int fbw = winW/2;
int fbh = winH/2;
int twidth = width - fbw;
int theight = height - fbh;
//这里winH/2是为了不把图像边界算进去
for(int i = fbh;i < theight;i++)
for(int j = fbw;j < twidth;j++)
double a = 0;
for(int m = 0;m < winH;m++)
for(int n = 0;n < winW;n++)
int ph = i + m - fbh;
int pw = j + n - fbw;
a += ptImg[ph*width+pw]*filterBuf[m*winW+n];//每个元素和窗体函数遍历相加
//赋值
result[i*width+j] = a;
return result;
2.Harris特征点提取函数
/*****************************************************
*function description:提取图像harris特征点
*
*input parameter:ImgTyp*buffer,int width,int height 输入影像
* int GaussWindow,double GaussSigma 高斯参数
* double thresh,vector<Pt>&corners 阈值和角点
*return: int
******************************************************/
int Harris(ImgTyp*buffer,int width,int height,int GaussWindow,double GaussSigma,double thresh,vector<Pt>&corners)
if (buffer == NULL)
return -1;
//创建I、Ix、Ix2、Iy、Iy2、Ixy、cim、mx、corner数组
double *I = new double[width*height];
double *Ix = NULL;
double *Ix2 = new double[width*height];
double *Iy = NULL;
double *Iy2 = new double[width*height];
double *Ixy = new double[width*height];
double *Ix2_ = NULL;
double *Iy2_ = NULL;
double *Ixy_ = NULL;
double *cim = new double[width*height];
//double *mx = new double[width*height];
//bool *corner = new bool[width*height];
//memset(corner,0,width*height*sizeof(bool));
//将图像灰度值复制到I中
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
//将灰度图像转化为double型
I[i * width + j] = (double)buffer[i * width + j];
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第一步:利用差分算子对图像进行滤波
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//定义水平方向差分算子并求Ix
double dx[9] = -1,0,1,-1,0,1,-1,0,1;
Ix = mbys(I,width,height,dx,3,3);
//定义垂直方向差分算子并求Iy
double dy[9] = -1,-1,-1,0,0,0,1,1,1;
Iy = mbys(I,width,height,dy,3,3);
//计算Ix2、Iy2、Ixy矩阵
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
Ix2[i * width + j] = Ix[i * width + j]*Ix[i * width + j];
//Ix2[i * width + j] = pow(Ix[i * width + j],2);
Iy2[i * width + j] = Iy[i * width + j]*Iy[i * width + j];
Ixy[i * width + j] = Ix[i * width + j]*Iy[i * width + j];
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第二步:对Ix2/Iy2/Ixy进行高斯平滑,以去除噪声
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//本例中使用5×5的高斯模板
//计算模板参数
// const int GaussWindow=5;
// const double GaussGaussSigma=0.08;
double *g = new double[GaussWindow * GaussWindow];
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < GaussWindow;j++)
g[i * GaussWindow + j] = exp(-((i - int(GaussWindow/2))*(i - int(GaussWindow/2)) + (j - int(GaussWindow/2)) * (j - int(GaussWindow/2)))/(2 * GaussSigma));
//g[i * GaussWindow + j] = exp(-(pow(double(i - int(GaussWindow/2)),2) + pow(double(j - int(GaussWindow/2)),2))/(2 * GaussSigma ));
//归一化:使模板参数之和为1(其实此步可以省略)
// 高斯函数前的常数可以不用计算,会在归一化的过程中给消去
double total = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow * GaussWindow;i++)
total += g[i];//将所有的值进行相加
for(int i = 0;i < GaussWindow;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < GaussWindow;j++)
g[i * GaussWindow + j] /= total;//进行归一化
//进行高斯平滑smoothing,加入权重w(x,y)
Ix2_ = mbys(Ix2,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);
Iy2_ = mbys(Iy2,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);
Ixy_ = mbys(Ixy,width,height,g,GaussWindow,GaussWindow);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第三步:计算角点量
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//用来求得响应函数R
//计算cim:即cornerness of image,我们把它称做‘角点量’
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
//注意:要在分母中加入一个极小量以防止除数为零溢出
cim[i * width + j] = (Ix2_[i * width + j]*Iy2_[i * width + j] - Ixy_[i * width + j]*Ixy_[i * width + j])/(Ix2_[i * width + j] + Iy2_[i * width + j] + FLT_EPSILON);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 第四步:进行局部非极大值抑制以获得最终角点
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//注意进行局部极大值抑制的思路
const int size = 5;
int r = size/2;//局部半径
double max = -10000;//最大值
double dmax;//局部最大值
Pt object;
for(int i = 0; i < width*height; i++)
if(cim[i] > max)
max = cim[i];
if (thresh > max)
thresh = max*0.1;
if (thresh < max*0.1)
thresh = max*0.1;
int nRow = 0,nCol = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < width; j++)
dmax = 0;
for (int n = -r;n <= r;n++)
for (int m = -r;m <= r;m++)
//越界限制
nRow = i + n < height ? i + n : height - 1;
nRow = nRow > 0 ? nRow : 0;
nCol = j + m < width ? j + m : width - 1;
nCol = nCol > 0 ? nCol: 0;
if (cim[nRow * width + nCol] > dmax)
dmax = cim[nRow * width + nCol];//局部最大
if(dmax > thresh && cim[i * width + j] == dmax)
object.x = j;
object.y = i;
corners.push_back(object);
//corner[i * width + j] = 1;
cout<<"阈值:"<<thresh<<",最大角点量:"<<max<<endl;
delete []g; g=NULL;
delete []I; I=NULL;
delete []Ix; Ix=NULL;
delete []Ix2; Ix2=NULL;
delete []Iy; Iy=NULL;
delete []Iy2; Iy2=NULL;
delete []Ixy; Ixy=NULL;
delete []Ix2_; Ix2_=NULL;
delete []Iy2_; Iy2_=NULL;
delete []Ixy_; Ixy_=NULL;
delete []cim; cim=NULL;
//delete []mx; mx=NULL;
//delete []corner;corner=NULL;
return 0;
3.测试函数(调用函数)
void HarrisTest(const char* fileName,char* savepath)
if (fileName == NULL)
cout<<"Error:输入的图像地址为空,请检查后运行!"<<endl;
return;
int width,height;
ImgTyp* srcImg = OpenImage(fileName,width,height);
vector<Pt>points;
points.clear();
int rect = Harris(srcImg,width,height,5,0.08,500,points);//Harris角点提取参数可设置
int num = points.size();
if (num > 0)
ImgTyp** resultImg = new ImgTyp*[3];//为了输出显示,三波段彩色构造
for (int n = 0;n < 3;n++)
resultImg[n] = new ImgTyp[width*height];
memcpy(resultImg[n],srcImg,sizeof(ImgTyp)*width*height);
cout<<"角点数:"<<num<<endl;
for (int i = 0 ;i < num;i++)
int x = points.at(i).x;
int y = points.at(i).y;
//cout<<"第"<<i<<"个:"<<x<<","<<y<<endl;
resultImg[0][y*width+x] = 255;
resultImg[1][y*width+x] = 0;
resultImg[2][y*width+x] = 0;//红色点标记角点位置
SaveImage(resultImg,savepath,width,height,3);
points.clear();
for (int j = 0 ; j < 3;j++)
delete[] resultImg[j];
resultImg[j] = NULL;
delete[] resultImg;
resultImg = NULL;
delete[]srcImg;srcImg=NULL;
其中坐标点结构体Pt:
struct Pt
int x;
int y;
;以上是关于C/C++实现特征点提取算法——Harris角点提取的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
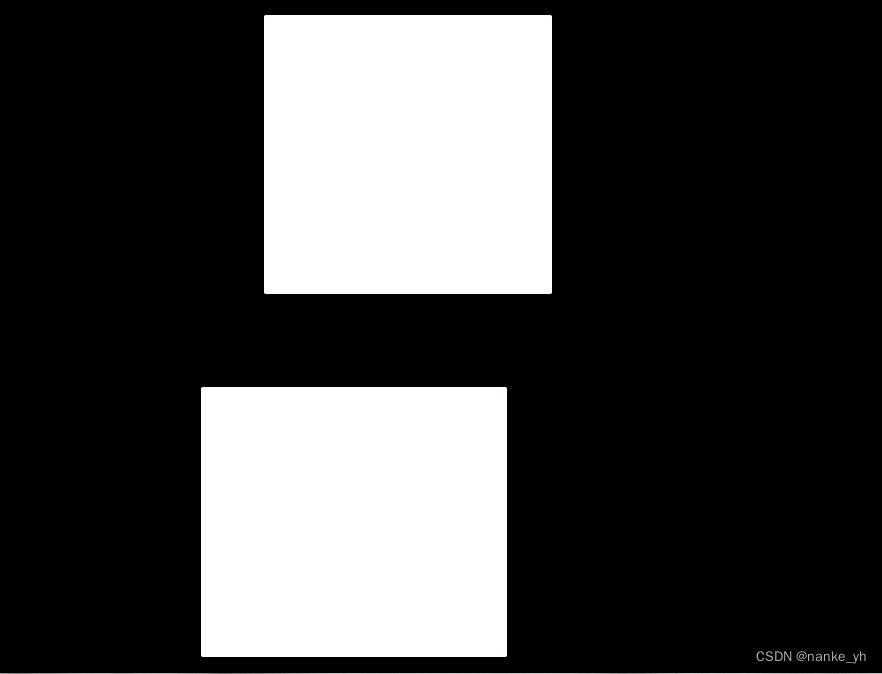
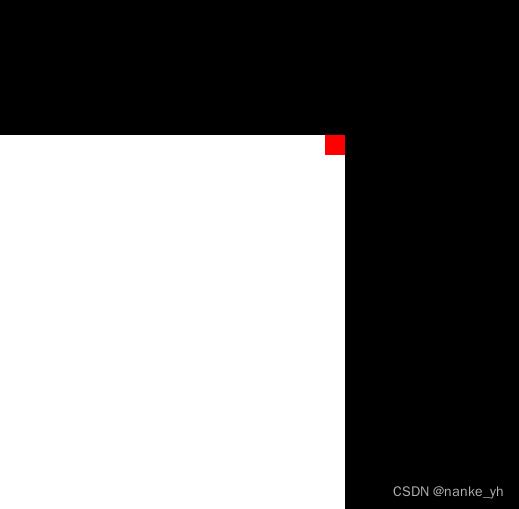
 8个角点提取位置在两个矩形各个顶角。
8个角点提取位置在两个矩形各个顶角。 

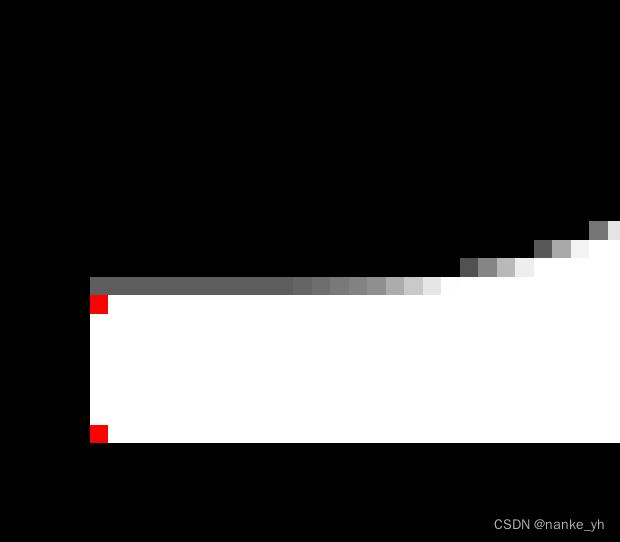
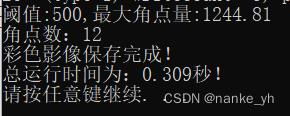 12个角点提取位置在“T”字的各个顶角上。
12个角点提取位置在“T”字的各个顶角上。