Android View 的scroll相关方法属性 以及Scroller弹性滑动原理
Posted 薛瑄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android View 的scroll相关方法属性 以及Scroller弹性滑动原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近在修改fragmentation 的bug时,其中SwipeBackLayout 的实现使用是ViewDragHelper ,而ViewDragHelper 使用的是OverScroller,OverScroller 在大部分时候是可以取代Scroller的。所以先从Scroller来分析,这些知识用到好几次,经常忘记,也算做个笔记。
android开发中,但在这些api的实际使用过程中,开发人员很容易在移动方向、移动距离上产生迷惑,本文通过图例总结了这四种方法的区别和联系。
很多文章中介绍Scroller的弹性滑动的时候,经常把view的方法和Scroller类的方法,混在一起,为了方便理解,下面将分开介绍View的scroll方法和Scroller类的方法
一、View的scroll相关方法
注意下面这些方法,是View的方法
在自定义控件的时候,如果涉及到滑动事件,经常需要使用View提供的诸如scrollTo()、scrollBy()、getScrollX()、getScrollY()等方法。
滑动对象
scrollTo和scrollBy用于滑动View的内容,而不是改变View本身所处的位置。所以,单独的View滑动很少见,更多的是ViewGroup调用scroll方法滑动子控件的位置。比如,使用TextView对象调用scrollTo或者ScrollBy方法,会发现TextView里面的文本内容的位置发生改变,而TextView本身所处的位置没有变化,也就是说Textview的点击事件位置没有变化。(View动画,关于其位置的变化,可阅读这篇文章)
getScrollX()和getScrollY()
返回值mScrollX和mScrollY分别表示距离起始View位置的X轴或Y轴方向上的偏移量,而不是View在X轴或Y轴方向上的坐标值,用于记录偏移增量的两个变量。所以,mScrollX和mScrollY的初始值为0和0。
/**
* Return the scrolled left position of this view. This is the left edge of
* the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels
* farther left, since those are outside of the frame of your view on
* screen.
*
* @return The left edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
*/
public final int getScrollX()
return mScrollX;
/**
* Return the scrolled top position of this view. This is the top edge of
* the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels above
* it, since those are outside of the frame of your view on screen.
*
* @return The top edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
*/
public final int getScrollY()
return mScrollY;
scrollTo()和 scrollBy()
返回值mScrollX和mScrollY分别表示距离起始View位置的X轴或Y轴方向上的偏移量,而不是View在X轴或Y轴方向上的坐标值,用于记录偏移增量的两个变量。所以,mScrollX和mScrollY的初始值为0和0。
/**
* Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* @link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int) and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the x position to scroll to
* @param y the y position to scroll to
*/
参数 x,y,表示要移动到的位置,赋值给mScrollX和mScrollY
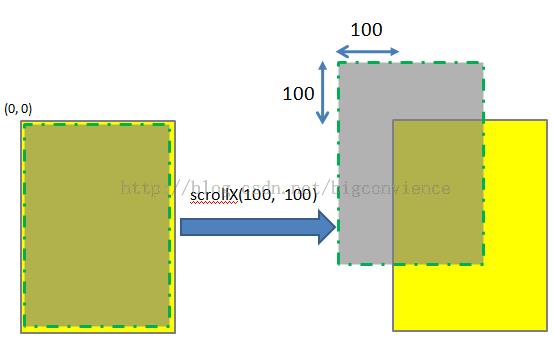
比如,我想移动到(100,100)这个位置,那么偏移量就是(0,0)-(100,100)=(-100,-100),所以调用的时候就是view.scrollTo(-100, -100),这样才能达到我们想要的偏移效果。
这个方法,已经能够实现view的位置移动,看上去是一瞬间完成的,没有动画效果。
public void scrollTo(int x, int y)
if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y)
int oldX = mScrollX;
int oldY = mScrollY;
mScrollX = x;
mScrollY = y;
invalidateParentCaches();
onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY);
if (!awakenScrollBars())
postInvalidateOnAnimation();
/**
* Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* @link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int) and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally
* @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically
*/
参数 x,y,表示相对于mScrollX和mScrollY要移动的偏移量,
public void scrollBy(int x, int y)
// scrollBy实际是调用了scrollTo方法:scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y)
scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
关于移动的正负值和方向的关系,参考下面这张图,图是网上找的
/**
* Called by a parent to request that a child update its values for mScrollX
* and mScrollY if necessary. This will typically be done if the child is
* animating a scroll using a @link android.widget.Scroller Scroller
* object.
*/
public void computeScroll()
computeScroll
View的computeScroll () 是个空方法,从注释来看,这个方法是为了配合Scroller ,来实现动画移动,也就是弹性滑动,而诞生的一个方法。
这个方法会在View的四个地方被调用:
- draw() 一般都是因为这个方法的调用,触发了computeScroll ()方法
- updateDisplayListIfDirty()
- buildDrawingCacheImpl() 调用这个方法的方法,已经被废弃
- createSnapshot()
在介绍弹性滑动前,先来了解一下Scroller的相关方法
二、Scroller
在实现弹性滑动中,只使用到两个方法:
- startScroll
- computeScrollOffset
弹性滑动的实现
下面的代码中,直接调用的函数,都是View的函数。调用smoothScroll() 就可以实现弹性滑动
Scroller mScroller = new Scroller(mContext);
//自定义的函数
private void smoothScroll(int destX, int destY)
int scrollX = getScrollX();
int deltaX = destX - scrollX;
mScroller.startScroll(scrollX, 0, deltaX, 0, 500);
invalidate();
@Override
public void computeScroll()
super.computeScroll();
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset())
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
invalidate();
下面来分析一下这两个函数的源码:
public void startScroll(int startX, int startY, int dx, int dy, int duration)
mMode = SCROLL_MODE;
mFinished = false;
mDuration = duration;
mStartTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
mStartX = startX;
mStartY = startY;
mFinalX = startX + dx;
mFinalY = startY + dy;
mDeltaX = dx;
mDeltaY = dy;
mDurationReciprocal = 1.0f / (float) mDuration;
原来startScroll()方法只是进行相关参数的初始化,其中startX、startY代表滑动的起点,dx、dy代表需要滑动的距离,duration代表整个滑动需要的时间。
这段代码,并没有设置view移动的代码,那是如何实现弹性滑动的呢?
奥秘就是smoothScroll() 调用了 invalidate()->draw()-> computeScroll(),在computeScroll()函数中,调用scrollTo() 来改变view的位置,然后又调用了invalidate()。这样就会不断的调用scrollTo() 移动view,实现滑动动画。
在computeScroll()中 调用computeScrollOffset()函数 ,来判断要不要进行移动,以及下一次要移动到的位置
下面看一下,computeScrollOffset()函数的源码,代码很简单,注释写了一些说明
/**
* Call this when you want to know the new location. If it returns true,
* the animation is not yet finished.
* 如果返回True,表示动画未完成。返回false,表示动画完成
*/
public boolean computeScrollOffset()
//判断动画是否完成
if (mFinished)
return false;
//距离动画开始的时间,用这个时间差,配合插值器,计算出下一个动画的位置
int timePassed = (int)(AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis() - mStartTime);
if (timePassed < mDuration)
switch (mMode)
case SCROLL_MODE:
//滑动模式,手指还在屏幕上,配合插值器,计算出下一个动画的位置
final float x = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(timePassed * mDurationReciprocal);
mCurrX = mStartX + Math.round(x * mDeltaX);
mCurrY = mStartY + Math.round(x * mDeltaY);
break;
case FLING_MODE:
//抛模式,手指滑动离开屏幕,离开屏幕的那一点,手指具有速度
final float t = (float) timePassed / mDuration;
final int index = (int) (NB_SAMPLES * t);
float distanceCoef = 1.f;
float velocityCoef = 0.f;
if (index < NB_SAMPLES)
final float t_inf = (float) index / NB_SAMPLES;
final float t_sup = (float) (index + 1) / NB_SAMPLES;
final float d_inf = SPLINE_POSITION[index];
final float d_sup = SPLINE_POSITION[index + 1];
velocityCoef = (d_sup - d_inf) / (t_sup - t_inf);
distanceCoef = d_inf + (t - t_inf) * velocityCoef;
//计算出当前的速度
mCurrVelocity = velocityCoef * mDistance / mDuration * 1000.0f;
mCurrX = mStartX + Math.round(distanceCoef * (mFinalX - mStartX));
// Pin to mMinX <= mCurrX <= mMaxX
mCurrX = Math.min(mCurrX, mMaxX);
mCurrX = Math.max(mCurrX, mMinX);
mCurrY = mStartY + Math.round(distanceCoef * (mFinalY - mStartY));
// Pin to mMinY <= mCurrY <= mMaxY
mCurrY = Math.min(mCurrY, mMaxY);
mCurrY = Math.max(mCurrY, mMinY);
if (mCurrX == mFinalX && mCurrY == mFinalY)
mFinished = true;
break;
else
mCurrX = mFinalX;
mCurrY = mFinalY;
mFinished = true;
return true;
至此,弹性滑动的原理就算是介绍完了
以上是关于Android View 的scroll相关方法属性 以及Scroller弹性滑动原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章