基础IO流javaSe
Posted Al_tair
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基础IO流javaSe相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基础IO流
大家好呀!我是小笙!我学习了韩顺平老师的类和对象的知识,收获颇丰!现在来和大家分享笔记!
文件
文件就是保存数据的地方
文件流
文件在程序中是以流的方式来操作的

常见文件的操作
// 构造器
File(File parent, String child) // 从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的File实例
// 代码实现
File parentFile = new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad");
String fileName = "w.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
file.createNewFile();
File(String pathname) // 通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的File实例
// 代码实现
String filePath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\w.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
file.createNewFile();
File(String parent, String child) // 从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的File实例
// 代码实现
String parentFile = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad";
String fileName = "w.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
file.createNewFile();
常见文件信息
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
// 目录可以理解为文件夹
String filePath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\w.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
System.out.println("文件名: "+file.getName()); // 文件名: w.txt
System.out.println("绝对路劲: "+file.getAbsolutePath()); // 绝对路劲: C:\\Users\\Ushop\\Desktop\\JavaLoad\\w.txt
System.out.println("父级路径: "+file.getParent()); // 父级路径: C:\\Users\\Ushop\\Desktop\\JavaLoad
System.out.println("文件大小: "+file.length()); // 0
System.out.println("文件是否存在: "+file.exists()); // false
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件是否存在: "+file.exists()); // true
文件夹的使用
// 注意文件和文件夹的细微区别
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
String filePath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test";
File file = new File(filePath);
file.createNewFile(); // 创建文件
file.mkdir(); // 创建单极目录文件夹
file.mkdirs(); // 创建多级目录的文件夹
// 删除文件或者文件夹
if(file.exists())
if(file.delete())
System.out.println("删除成功");
else
System.out.println("删除失败");
else
System.out.println("该文件不存在");
IO流原理及流的分类

IO流用于处理数据传输,如读写文件或者网络通讯
流的分类(流的本质就是运输者:运输文件数据)
-
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8bit),字符流(按字符)
-
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流和输出流
-
按流的角色不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流
抽象基类 字节流 字符流 输入流 InputStream Reader 输出流 OutputStream Writer
IO体系图中的常用类
字节流
InputStream:字节输入流
FileInputStream

// 文件输入流输入以字节的方式
// 当前存在问题:无法解决中文乱码的问题
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int data = 0;
while((data = fis.read()) != -1)
System.out.print((char)data);
fis.close();
// 优化后: 读取速度加快
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int readLen = 0;
// 字节数组 一次读取8字节
byte[] bytes = new byte[8];
// 读入缓冲区的总字节数,如果没有更多数据,则返回-1
while((readLen = fis.read(bytes)) != -1)
System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,readLen));
fis.close();
// 读操作是本地方法
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
BufferedInputStream
// 图片的拷贝
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\3.png");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\4.png");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1)
bos.write(b,0,len);
bis.close();
bos.close();
ObjectInputStream
反序列化:在恢复数据时,恢复数据的值和数据类型
class ObjectInputStream_
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
// 传入文件不管后缀是什么,都会以特点的文件格式存储
String filePath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
// 反序列化的顺序和原文件数据顺序需要一致
System.out.println( ois.readByte());
System.out.println( ois.readUTF());
System.out.println( ois.readFloat());
// 需要能访问到自己的类,访问不到将会出现异常 ClassNotFoundException
System.out.println(ois.readObject().toString());
ois.close();
class car implements Serializable
String name;
int age;
public car(String name, int age)
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
@Override
public String toString()
return "name: "+ name + " age: " + age;

OutputStream:字节输出流
FileOutputStream
构造方法


写操作

String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
// 得到文件输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
// 写操作
// 如果找到文件则进行写操作,否则将创建该文件
fos.write('a');
fos.close();
// 性能优化 写字符串
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
// 得到文件输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
// 写操作
// 如果找到文件则进行写操作,否则将创建该文件
String fileContent = "我又回来了大家!!";
fos.write(fileContent.getBytes());
fos.close();
读写操作
用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream流进行txt文件读写
// 从hello.txt读出内容
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int len = 0;
byte[] reader = new byte[1024];
String copyContent = "";
while((len = fis.read(reader)) != -1)
copyContent += new String(reader,0,len);
// 将读出的内容写入到copyFile.txt
String outFileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\copyFile.txt";
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outFileName);
fos.write(copyContent.getBytes());
fis.close();
fos.close();
// 优化代码:边读边写,防止一次性读入过大文件导致内存溢出
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
String outFileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\copyFile.txt";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outFileName);
int len = 0;
byte[] reader = new byte[9];
while((len = fis.read(reader)) != -1)
fos.write(new String(reader,0,len).getBytes());
fis.close();
fos.close();
用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream流进行图片文件读写
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\1.png";
String outFileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\2.png";
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outFileName);
int len = 0;
byte[] reader = new byte[1024];
while((len = fis.read(reader)) != -1)
fos.write(reader,0,len);
fis.close();
fos.close();
BufferedOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream是字节流,实现缓冲的输出流,可以将多个字节写入底层输出流,而不必对每个字节的写入都调用底层
// 拷贝视频
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\1.avi");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\2.avi");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1)
bos.write(b,0,len);
bis.close();
bos.close();
ObjectOutputStream
序列化:保存时,保存数据的值和数据类型
// 代码实现
public class ObjectOutputStream_
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
// 传入文件不管后缀是什么,都会以特点的文件格式存储
String filePath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello";
ObjectOutputStream obs = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
obs.writeByte(100);
obs.writeChars("100");;
obs.writeFloat(100.0f);
obs.writeObject(new car("小黄",18));
obs.close();
class car implements Serializable
String name;
int age;
public car(String name, int age)
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
@Override
public String toString()
return super.toString();

注意事项
- 序列化数据读写顺序需要一致
- 要求序列化的对象必须实现了Serializable
- 序列化的类中添加SerialVersionUID,为了提高版本的兼容性
- 序列化对象时,默认将对象里面所有属性进行序列化,但除了static或transient修饰的成员
- 序列化对象时,要求对象里面的属性(比如其他对象)必须也要序列化,数据才会被保存
- 序列化具备可继承性,当父类实现了串行化接口,该父类的所有子类默认实现了序列化
常见其他字节流

printstream : 打印流
默认输出到显示屏,可以通过setOut方法修改显示地址

字符流
节点流和处理流的区别
- 节点流是底层流,直接跟数据源相接
- 处理流包装节点流,既可以消除不同节点流的实现差异,也可以提供更方便的方法来完成输入输出
- 处理流采用了修饰器设计模式,不会直接与数据源相连
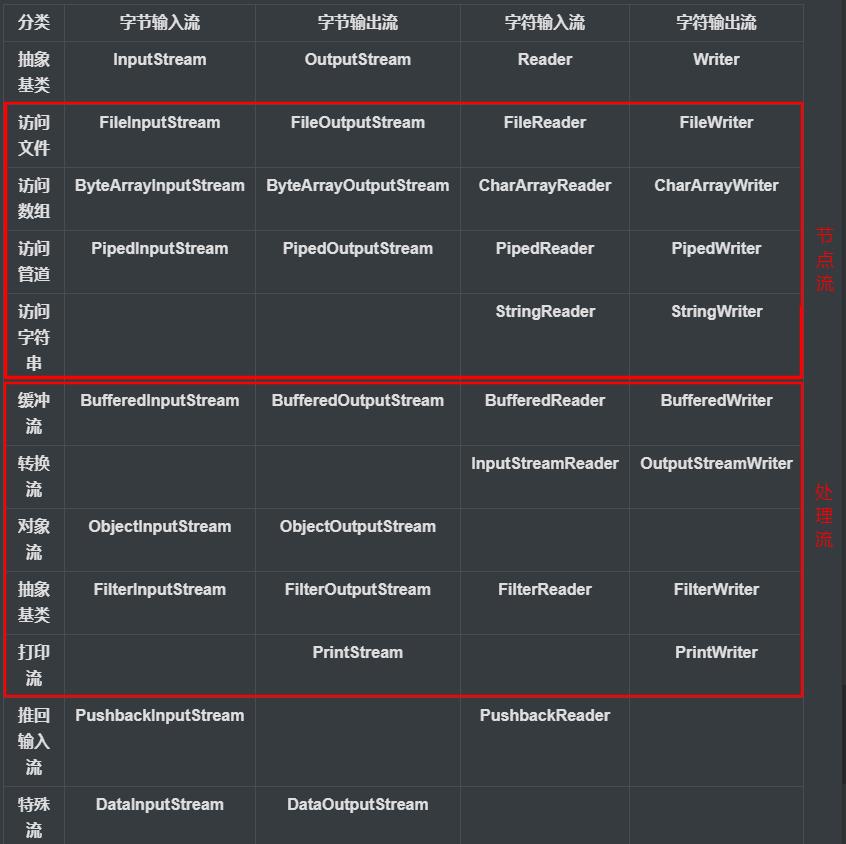
(备注:推回输入流和特殊流也属于处理流)
节点流
节点就是可以从一个指定的数据源进行读写数据
FileReader:字符输入流
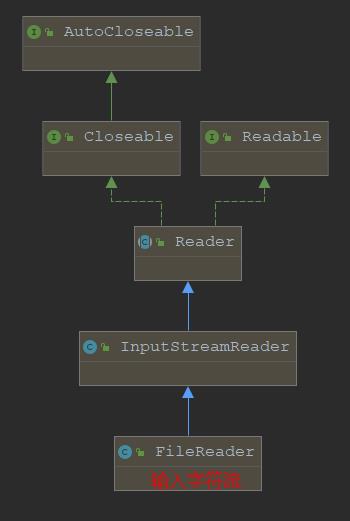
构造器

// 读操作
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(fileName);
char c = ' ';
// 寻换读取 使用read
while((c = (char)fileReader.read()) != (char)-1 )
System.out.print(c);
// 优化读取的一次性的量 字符 => 字符数组
String fileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\hello.txt";
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(fileName);
char[] c = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
// 寻换读取 使用read
while((len = (char)fileReader.read(c)) != (char)-1 )
System.out.print(new String(c,0,len));
// 注意String 和char数组的转换
new String(char[]);
new String(char[],off,len) // 将索引从off开始len个字符的转换成字符串
FileWriter:字符输出流

构造器

注意:FileWriter使用,必须要关闭(close)或者 刷新(flush),否则写入不到指定的文件!
// 写操作 : 输出字符串到文件
String writerFileName = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Ushop\\\\Desktop\\\\JavaLoad\\\\test\\\\copyFile.txt";
String content = "嘿嘿,打我呀!!";
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(writerFileName);
fileWriter.write(content);
fileWriter.flush();
fileWriter.close();
// 字符输出流为什么要关闭或者刷新才可以真正的写入文件中
// 源码解读:都调用writeBytes()方法来真正的输出
private void writeBytes() throws IOException
bb.flip();
int lim = bb.limit();
int pos = bb.position();
assert (pos <= lim);
int rem = (pos <= lim ? lim - pos : 0);
if (rem > 0)
if (ch != null)
if (ch.write(bb)