Java8之Stream常用操作方式
Posted 学无止境小奇
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java8之Stream常用操作方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
👏👏👏
哈喽!大家好,我是【学无止境小奇】,一位热爱分享各种技术的博主!😍😍😍
⭐【学无止境小奇】的创作宗旨:每一条命令都亲自执行过,每一行代码都实际运行过,每一种方法都真实实践过,每一篇文章都良心制作过。✊✊✊
⭐【学无止境小奇】的博客中所有涉及命令、代码的地方,除了提供图片供大家参考,另外会在图片下方提供一份纯文本格式的命令或者代码方便大家粘贴复制直接执行命令或者运行代码。🤝🤝🤝
⭐如果你对技术有着浓厚的兴趣,欢迎关注【学无止境小奇】,欢迎大家和我一起交流。😘😘😘
❤️❤️❤️感谢各位朋友接下来的阅读❤️❤️❤️
文章目录
一、前期准备
1、创建对象
1.1、Student
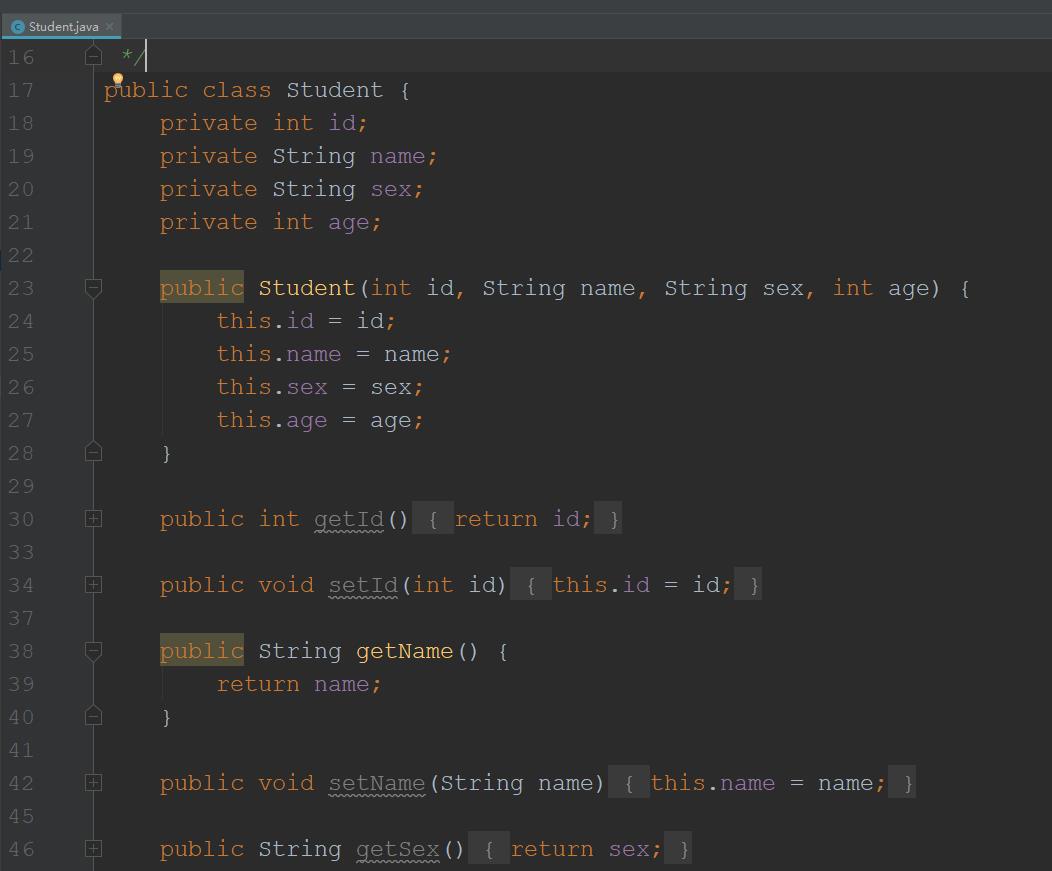
public class Student
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public Student(int id, String name, String sex, int age)
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
public int getId()
return id;
public void setId(int id)
this.id = id;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public String getSex()
return sex;
public void setSex(String sex)
this.sex = sex;
public int getAge()
return age;
public void setAge(int age)
this.age = age;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Student" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\\'' +
", age=" + age +
'';
2、初始化数据
2.1、初始化集合
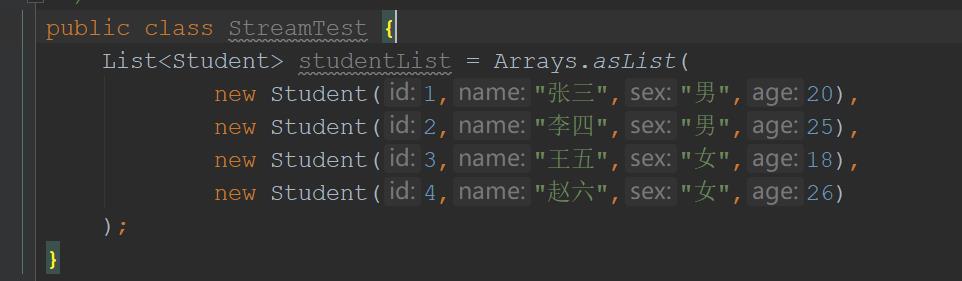
public class StreamTest
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(
new Student(1,"张三","男",20),
new Student(2,"李四","男",25),
new Student(3,"王五","女",18),
new Student(4,"赵六","女",26)
);
二、Stream常用操作方式
1、筛选
1.1、filter
filter从集合中过滤某些元素,例如查询集合中年龄大于20的数据集合

//查询年龄大于20的数据集合
List<Student> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
1.2、limit
limit,和mysql中的limit类似,返回指定数量的数据
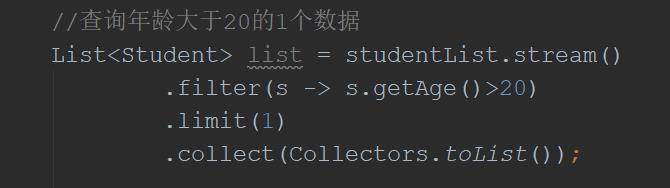
//查询年龄大于20的1个数据
List<Student> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.limit(1)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
1.3、skip
skip,跳过元素,返回一个跳过前n个元素的集合
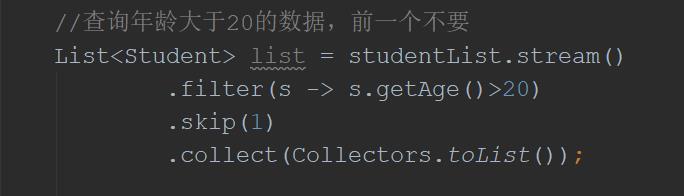
//查询年龄大于20的数据,前一个不要
List<Student> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.skip(1)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
1.4、distinct
distinct,筛选,通过元素的hashCode()和equals()去除重复元素
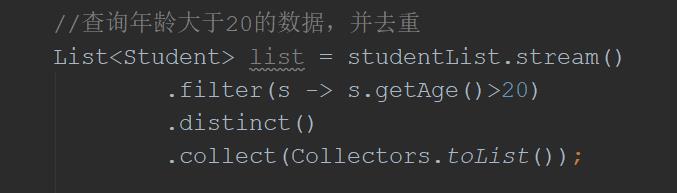
//查询年龄大于20的数据,并去重
List<Student> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
2、映射
2.1、map
map,将集合元素转换成其他形式返回,接收一个函数作为参数,该函数作用到每一个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素

//查询年龄大于20的数据,只获取姓名集合
List<String> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.map(Student::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
3、排序
3.1、sorted()
sorted()自然排序
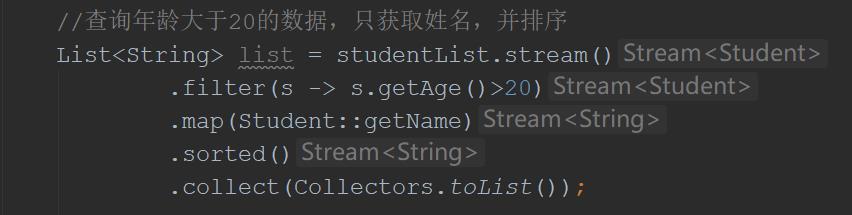
//查询年龄大于20的数据,只获取姓名,并排序
List<String> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.map(Student::getName)
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
3.2、sorted(Comparator com)定制排序
sorted(Comparator com)定制排序,定制输入排序规则
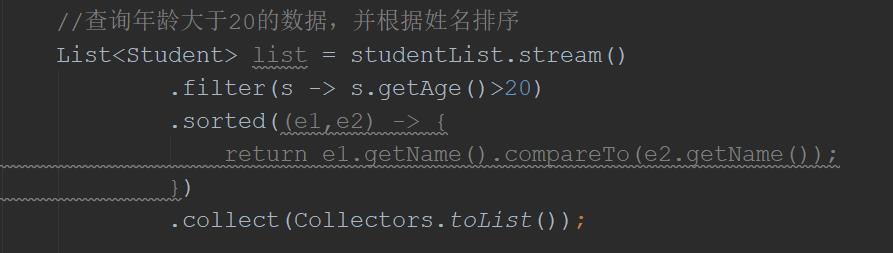
//查询年龄大于20的数据,并根据姓名排序
List<Student> list = studentList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.getAge()>20)
.sorted((e1,e2) ->
return e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
4、查找与匹配
4.1、allMatch
allMatch检查是否匹配所有元素
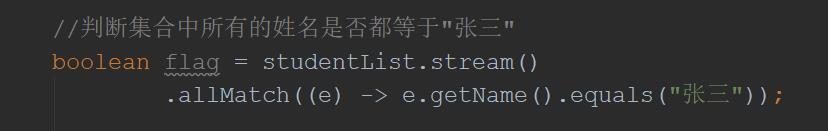
//判断集合中所有的姓名是否都等于"张三"
boolean flag = studentList.stream()
.allMatch((e) -> e.getName().equals("张三"));
4.2、anyMatch
anyMatch是否匹配至少一个元素
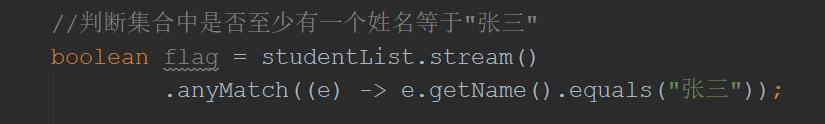
//判断集合中是否至少有一个姓名等于"张三"
boolean flag = studentList.stream()
.anyMatch((e) -> e.getName().equals("张三"));
4.3、noneMatch
noneMatch检查是否没有匹配所有元素
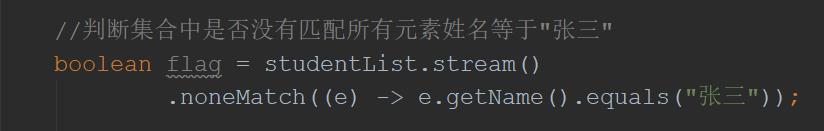
//判断集合中是否没有匹配所有元素姓名等于"张三"
boolean flag = studentList.stream()
.noneMatch((e) -> e.getName().equals("张三"));
4.4、findFirst
findFirst返回第一个元素

//返回集合中第一个元素
Optional<Student> student = studentList.stream()
.findFirst();
4.5、findAny
findAny返回当前集合中的任意元素

//返回集合中任意一个元素
Optional<Student> student = studentList.stream()
.findAny();
4.6、conut
conut返回流中元素的总个数

//返回集合的数量
long num = studentList.stream()
.count();
4.7、max
返回流中最大值
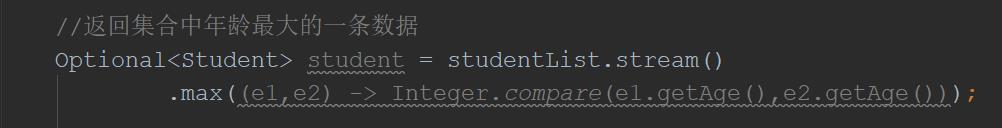
//返回集合中年龄最大的一条数据
Optional<Student> student = studentList.stream()
.max((e1,e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge()));
4.8、min
返回流中最小值
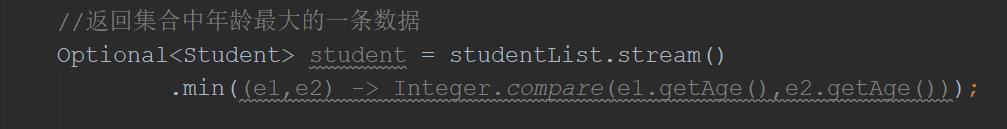
//返回集合中年龄最大的一条数据
Optional<Student> student = studentList.stream()
.min((e1,e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge()));
以上是关于Java8之Stream常用操作方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章