小熊派LiteOS移植LVGL
Posted JeckXu666
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了小熊派LiteOS移植LVGL相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
小熊派LiteOS移植LVGL
一、移植前言
之前使用小熊派实现了鸿蒙动画的开机界面,具体使用的技术栈为 STM32 + LiteOS + LVGL + FATFS +DMA 方式实现,刷新效率非常高,预览视频如下:

关于这个的实现过程我会写一系列的教程分享出来,主要分为下面几个部分,本节为第二部分,基于 LiteOS 移植 LVGL 显示接口
- 小熊派移植华为 LiteOS-M(基于MDK):链接;
- 小熊派基于 LiteOS 移植 LVGL 显示接口:链接;
- 小熊派基于 LiteOS 移植 LVGL 文件系统:链接;
- 小熊派实现鸿蒙开机界面(LiteOS+LVGL):链接;
本节的教程就是先通过 STM32CubeMX 来配置 小熊派的 TFT 初始化代码,开启 DMA 加速(不开启会卡出翔),配置完成后获取 LVGL 的代码,移植到工程里面,然后将 TFT 驱动接口和 LVGL 接口对接,在运行 Demo 代码
二、配置 TFT
我们在上一节移植好 LiteOS 工程的基础上使用 CubeMX 配置 TFT 的 SPI 接口,具体 SPI 驱动接口可以参考这篇文章:小熊派 FreeRTOS+SPI+DMA 驱动 TFT-LCD
SPI 配置完成如下:
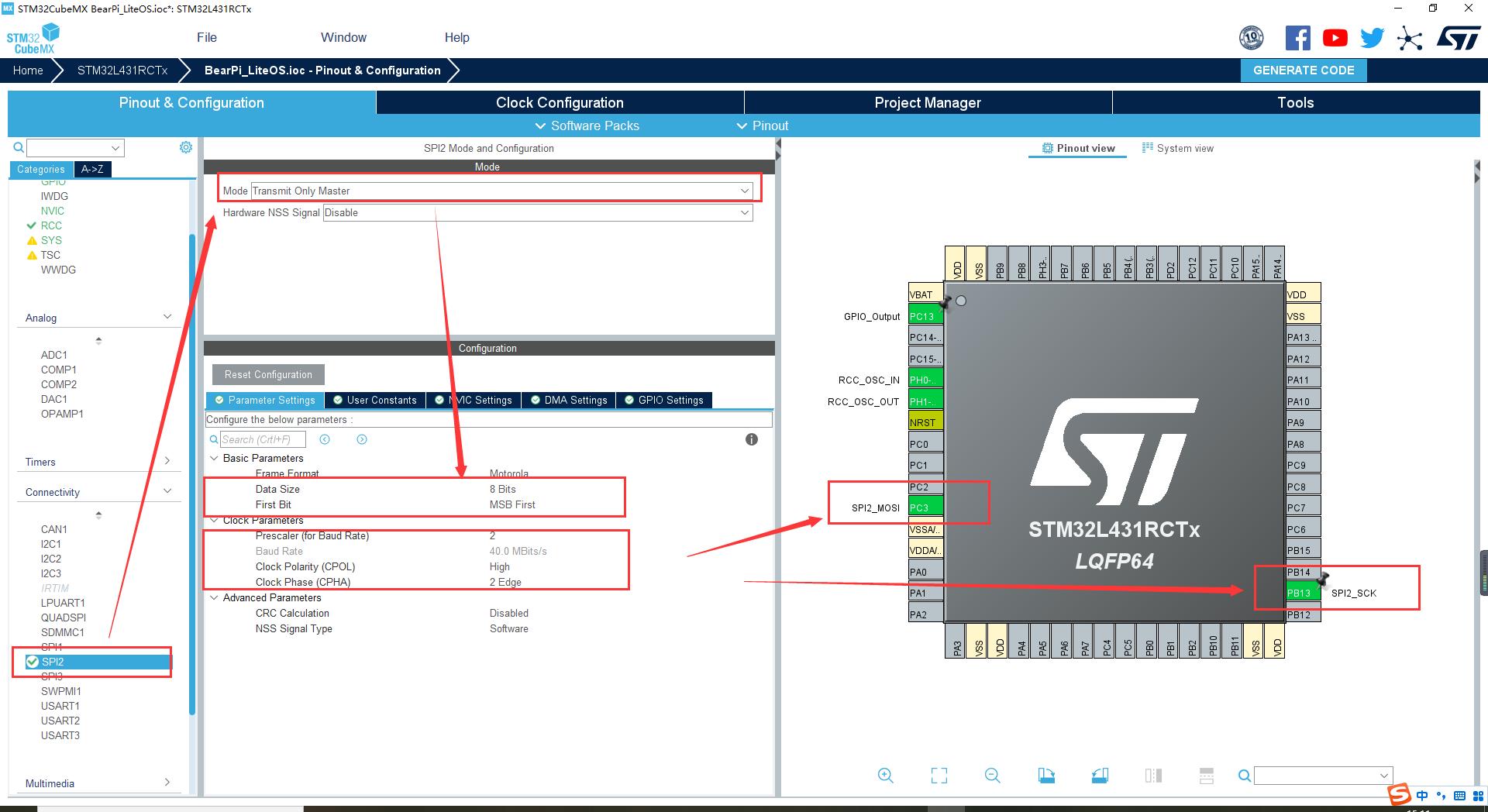
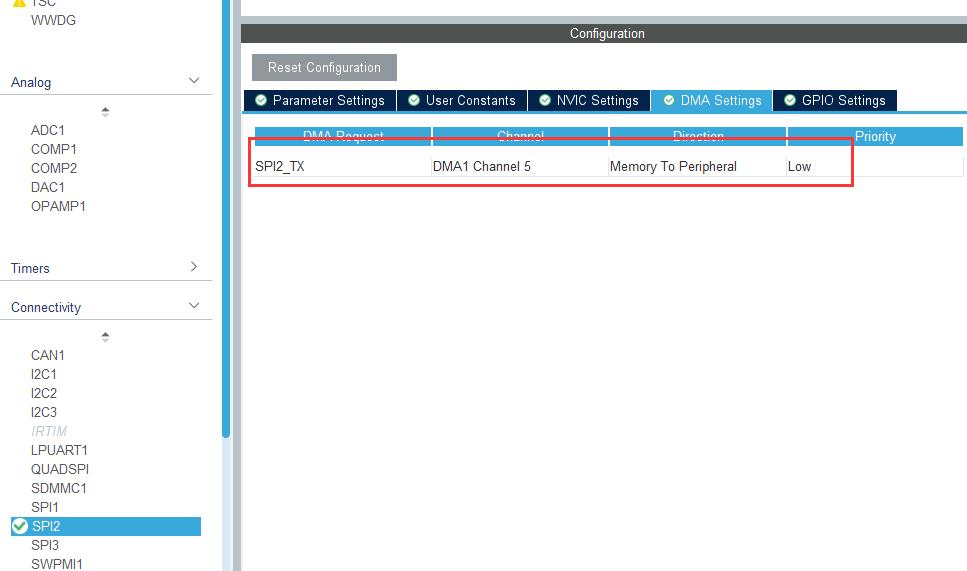
开启 DMA,并且在 NVIC 里面使能中断
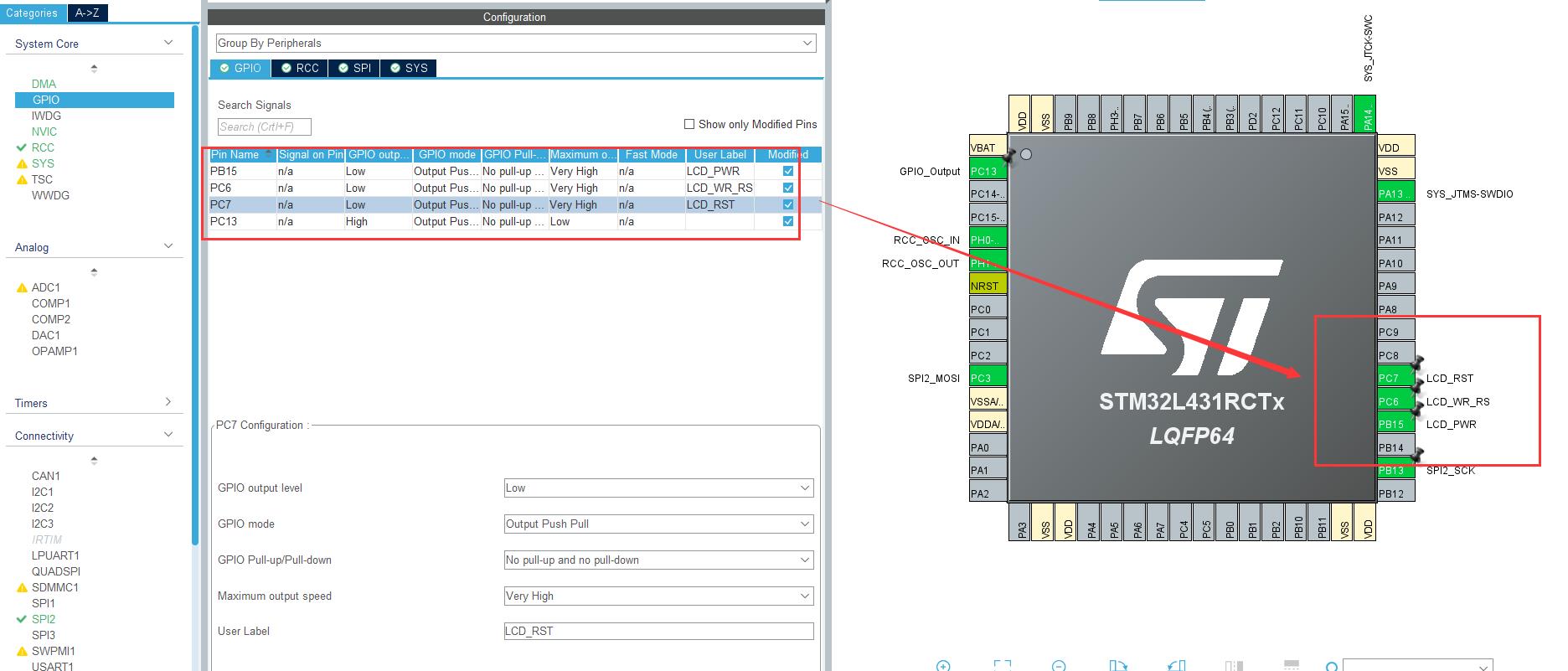
除了上面的 SPI 引脚还需要,配置 TFT 的其他控制引脚,关于引脚在参考文章中有写出来,配置完成如下:
在 MDK 工程根目录下创建 Hardware/LCD 文件夹用来存放驱动代码,驱动文件命名为 lcd.c 和 lcd.h
拷贝下面的代码进去
lcd.c
#include "lcd.h"
#include "gpio.h"
#include "spi.h"
#include "cmsis_os.h"
extern osSemaphoreId_t DMA_SemaphoreHandle;
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/**
* @brief SPI 发送字节函数
* @param TxData 要发送的数据
* @param size 发送数据的字节大小
* @return 0:写入成功,其他:写入失败
*/
uint8_t SPI_WriteByte(uint8_t *TxData,uint16_t size)
osStatus_t result;
//获取信号,如果上一个DMA传输完成
//信号就能获取到,没有传输完成任务就挂起
//等到传输完成再恢复
result = osSemaphoreAcquire(DMA_SemaphoreHandle,0xFFFF);
if(result == osOK)
//获取成功
return HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi2,TxData,size);
else
//获取失败
return 1;
//DMA 传输完成后会调用 SPI传输完成回调函数
//在该函数中我们释放信号
void HAL_SPI_TxCpltCallback(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi)
if(hspi->Instance == hspi2.Instance)
osSemaphoreRelease(DMA_SemaphoreHandle);
/**
* @brief 写命令到LCD
* @param cmd —— 需要发送的命令
* @return none
*/
static void LCD_Write_Cmd(uint8_t cmd)
LCD_WR_RS(0);
SPI_WriteByte(&cmd, 1);
/**
* @brief 写数据到LCD
* @param dat —— 需要发送的数据
* @return none
*/
static void LCD_Write_Data(uint8_t dat)
LCD_WR_RS(1);
SPI_WriteByte(&dat, 1);
/**
* @breif 打开LCD显示背光
* @param none
* @return none
*/
void LCD_DisplayOn(void)
LCD_PWR(1);
/**
* @brief 关闭LCD显示背光
* @param none
* @return none
*/
void LCD_DisplayOff(void)
LCD_PWR(0);
/**
* @brief 设置数据写入LCD显存区域
* @param x1,y1 —— 起点坐标
* @param x2,y2 —— 终点坐标
* @return none
*/
void LCD_Address_Set(uint16_t x1, uint16_t y1, uint16_t x2, uint16_t y2)
/* 指定X方向操作区域 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x2a);
LCD_Write_Data(x1 >> 8);
LCD_Write_Data(x1);
LCD_Write_Data(x2 >> 8);
LCD_Write_Data(x2);
/* 指定Y方向操作区域 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x2b);
LCD_Write_Data(y1 >> 8);
LCD_Write_Data(y1);
LCD_Write_Data(y2 >> 8);
LCD_Write_Data(y2);
/* 发送该命令,LCD开始等待接收显存数据 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x2C);
/**
* @brief 以一种颜色清空LCD屏
* @param color —— 清屏颜色(16bit)
* @return none
*/
void LCD_Clear(uint16_t color)
uint16_t i;
uint8_t data[2] = 0; //color是16bit的,每个像素点需要两个字节的显存
/* 将16bit的color值分开为两个单独的字节 */
data[0] = color >> 8;
data[1] = color;
LCD_Address_Set(0, 0, LCD_Width - 1, LCD_Height - 1);
LCD_WR_RS(1);
for(i=0;i<((LCD_Width)*(LCD_Height));i++)
SPI_WriteByte(data, 2);
/**
* @brief LCD初始化
* @param none
* @return none
*/
void LCD_Init(void)
/* 复位LCD */
LCD_PWR(0);
LCD_RST(0);
osDelay(100);
LCD_RST(1);
osDelay(120);
/* 关闭睡眠模式 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x11);
osDelay(120);
/* 开始设置显存扫描模式,数据格式等 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x36);
LCD_Write_Data(0x00);
/* RGB 5-6-5-bit格式 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x3A);
LCD_Write_Data(0x65);
/* porch 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xB2);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0C);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0C);
LCD_Write_Data(0x00);
LCD_Write_Data(0x33);
LCD_Write_Data(0x33);
/* VGH设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xB7);
LCD_Write_Data(0x72);
/* VCOM 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xBB);
LCD_Write_Data(0x3D);
/* LCM 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xC0);
LCD_Write_Data(0x2C);
/* VDV and VRH 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xC2);
LCD_Write_Data(0x01);
/* VRH 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xC3);
LCD_Write_Data(0x19);
/* VDV 设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xC4);
LCD_Write_Data(0x20);
/* 普通模式下显存速率设置 60Mhz */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xC6);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0F);
/* 电源控制 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xD0);
LCD_Write_Data(0xA4);
LCD_Write_Data(0xA1);
/* 电压设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xE0);
LCD_Write_Data(0xD0);
LCD_Write_Data(0x04);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0D);
LCD_Write_Data(0x11);
LCD_Write_Data(0x13);
LCD_Write_Data(0x2B);
LCD_Write_Data(0x3F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x54);
LCD_Write_Data(0x4C);
LCD_Write_Data(0x18);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0D);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0B);
LCD_Write_Data(0x1F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x23);
/* 电压设置 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0xE1);
LCD_Write_Data(0xD0);
LCD_Write_Data(0x04);
LCD_Write_Data(0x0C);
LCD_Write_Data(0x11);
LCD_Write_Data(0x13);
LCD_Write_Data(0x2C);
LCD_Write_Data(0x3F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x44);
LCD_Write_Data(0x51);
LCD_Write_Data(0x2F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x1F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x1F);
LCD_Write_Data(0x20);
LCD_Write_Data(0x23);
/* 显示开 */
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x21);
LCD_Write_Cmd(0x29);
/*打开显示*/
LCD_PWR(1);
lcd.h
#include "main.h"
#define LCD_PWR(n) (n?\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_PWR_GPIO_Port,LCD_PWR_Pin,GPIO_PIN_SET):\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_PWR_GPIO_Port,LCD_PWR_Pin,GPIO_PIN_RESET))
#define LCD_WR_RS(n) (n?\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_WR_RS_GPIO_Port,LCD_WR_RS_Pin,GPIO_PIN_SET):\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_WR_RS_GPIO_Port,LCD_WR_RS_Pin,GPIO_PIN_RESET))
#define LCD_RST(n) (n?\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_RST_GPIO_Port,LCD_RST_Pin,GPIO_PIN_SET):\\
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_RST_GPIO_Port,LCD_RST_Pin,GPIO_PIN_RESET))
//LCD屏幕分辨率定义
#define LCD_Width 240
#define LCD_Height 240
//颜色定义
#define WHITE 0xFFFF //白色
#define YELLOW 0xFFE0 //黄色
#define BRRED 0XFC07 //棕红色
#define PINK 0XF81F //粉色
#define RED 0xF800 //红色
#define BROWN 0XBC40 //棕色
#define GRAY 0X8430 //灰色
#define GBLUE 0X07FF //兰色
#define GREEN 0x07E0 //绿色
#define BLUE 0x001F //蓝色
#define BLACK 0x0000 //黑色
uint8_t SPI_WriteByte(uint8_t *TxData,uint16_t size);
static void LCD_Write_Cmd(uint8_t cmd);
static void LCD_Write_Data(uint8_t dat);
void LCD_DisplayOn(void);
void LCD_DisplayOff(void);
void LCD_Address_Set(uint16_t x1, uint16_t y1, uint16_t x2, uint16_t y2);
void LCD_Clear(uint16_t color);
void LCD_Init(void);
代码和文件添加完成后不要忘记添加文件路径,然后我们在主函数中创建一个用于 lcd 显示的任务,初始化 LCD 同时将屏幕初始化为蓝色
osThreadId_t lcd_taskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t lcd_task_attributes =
.name = "lcd_task",
.stack_size = 512 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityNormal1,
;
void Lcd_Task(void *argument);
void Lcd_Task(void *argument)
LCD_Init();
LCD_Clear(BLUE);
while(1)
osDelay(1000);
添加 DMA 信号量
osSemaphoreId_t DMA_SemaphoreHandle;
const osSemaphoreAttr_t DMA_Semaphore_attributes =
.name = "DMA_Semaphore"
;
初始化信号和 LiteOS:
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
osKernelInitialize();
/* creation of uart_task */
DMA_SemaphoreHandle = osSemaphoreNew(1, 1, &DMA_Semaphore_attributes);
led_taskHandle = osThreadNew(Led_Task, NULL, &led_task_attributes);
lcd_taskHandle = osThreadNew(Lcd_Task, NULL, &lcd_task_attributes);
osKernelStart();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
编译烧写程序,观察现象,屏幕清屏为蓝色,驱动程序跑通了,可以进行下一步:
三、LVGL 源码获取
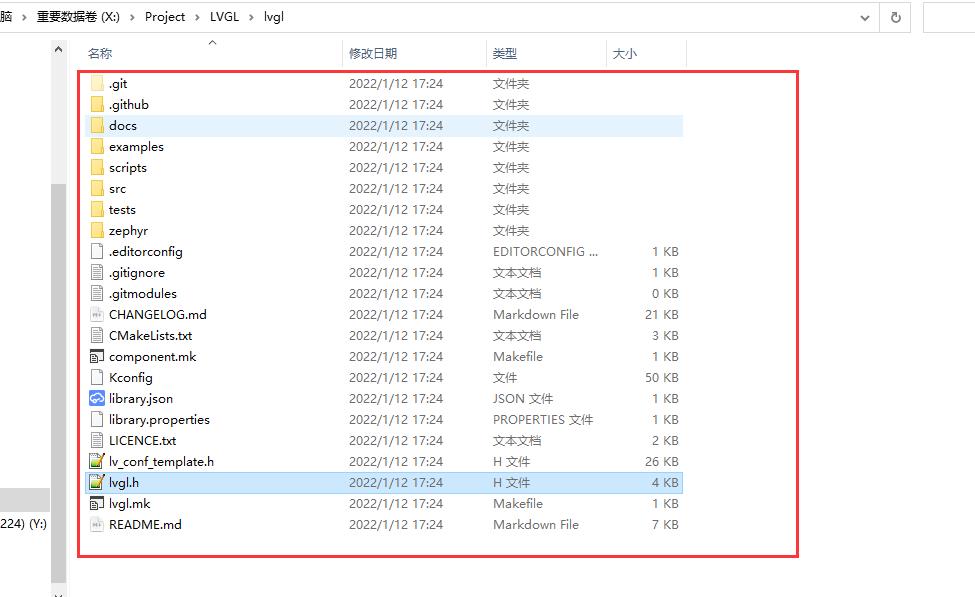
获取 lvgl 7.0 版本的源码
git clone -b release/v7 https://github.com/lvgl/lvgl.git
拉取后代码
下面我们在 MDK 工程目录按照下面的格式建立文件夹
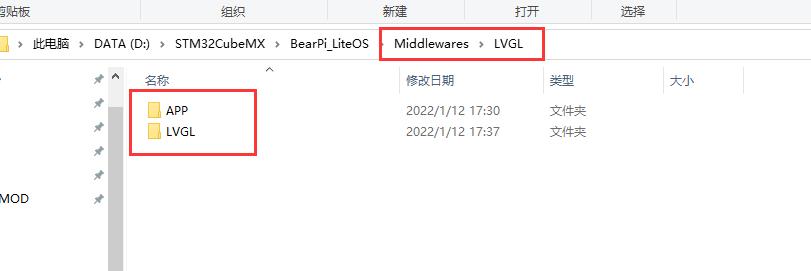
APP 文件夹用来存放我们编写的 lvgl 应用代码,LVGL 文件夹用来存放 lvgl 的源码,以及接口代码
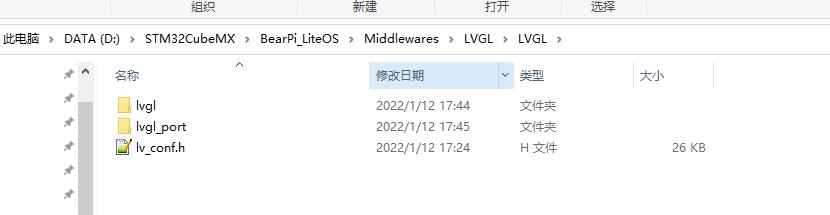
然后我们将刚刚 github 下载的源码拷贝到 LVGL 中,然后把里面 lvgl\\examples\\porting 文件夹复制到同一目录下,改名为 lvgl_port 文件夹,同时将 lvgl\\lv_conf_template.h 也复制到同一目录,并且改名为 lv_conf.h,修改结果如下:
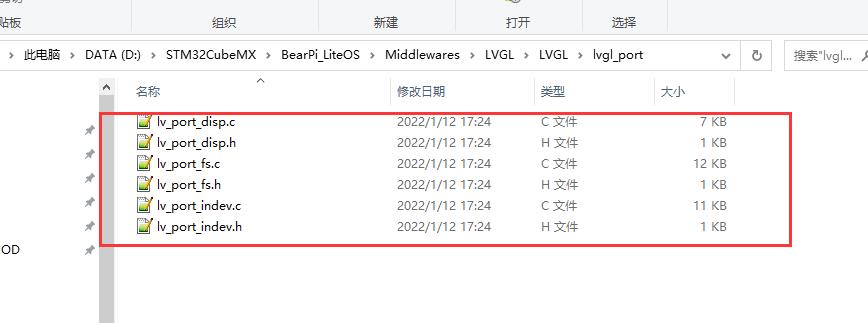
然后将 lvgl_port 下面的文件也修改名称为下面的格式:
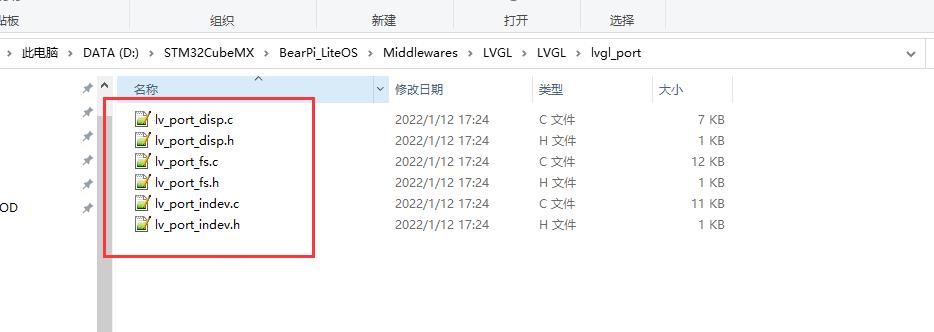
这6个文件是 lvgl 的接口文件,disp 是显示接口、fs 是文件系统接口、indev 是输入接口,下面我们在 MDK 工程里面添加文件和文件路径,添加路径如下:
..\\Middlewares\\LVGL\\APP
..\\Middlewares\\LVGL\\LVGL\\lvgl_port
..\\Middlewares\\LVGL\\LVGL\\lvgl\\src
添加文件如下:

src 放的文件是下面文件夹的所有 c 文件
config 放的是 lvgl 配置头文件:

port 放的是 lvgl 的硬件接口文件
文件添加完成后我们先配置 lvgl 下的 lv_conf.h 文件,做一些配置,不然直接编译的话会有一堆报错
lv_conf.h 文件修改:
修改屏幕尺寸适配小熊派:
/* Maximal horizontal and vertical resolution to support by the library.*/
#define LV_HOR_RES_MAX (240)
#define LV_VER_RES_MAX (240)
设置屏幕颜色深度,以及颜色存放格式(适配 ST7789芯片):
/* Color depth:
* - 1: 1 byte per pixel
* - 8: RGB332
* - 16: RGB565
* - 32: ARGB8888
*/
#define LV_COLOR_DEPTH 16
/* Swap the 2 bytes of RGB565 color.
* Useful if the display has a 8 bit interface (e.g. SPI)*/
#define LV_COLOR_16_SWAP 1
设置调节界面缩放比例:
/* Dot Per Inch: used to initialize default sizes.
* E.g. a button with width = LV_DPI / 2 -> half inch wide
* (Not so important, you can adjust it to modify default sizes and spaces)*/
#define LV_DPI 60 /*[px]*/
设置动态内存大小:
/* Size of the memory used by `lv_mem_alloc` in bytes (>= 2kB)*/
# define LV_MEM_SIZE (16U * 1024U)
关闭使用 GPU:
/* 1: Enable GPU interface*/
#define LV_USE_GPU 0 /*Only enables `gpu_fill_cb` and `gpu_blend_cb` in the disp. drv- */
#define LV_USE_GPU_STM32_DMA2D 0
暂时先关闭文件系统:
/* 1: Enable file system (might be required for images */
#define LV_USE_FILESYSTEM 0
编译一下,有一些警告
..\\Middlewares\\LVGL\\LVGL\\lvgl\\src\\lv_draw\\lv_draw_mask.c(350): warning: #111-D: statement is unreachable
这些警告没有任何影响,可以把警告给屏蔽掉,切换到 C/C++选项卡,在 Misc Controls 中填入
--diag_suppress=111 把它屏蔽掉如下图所示:
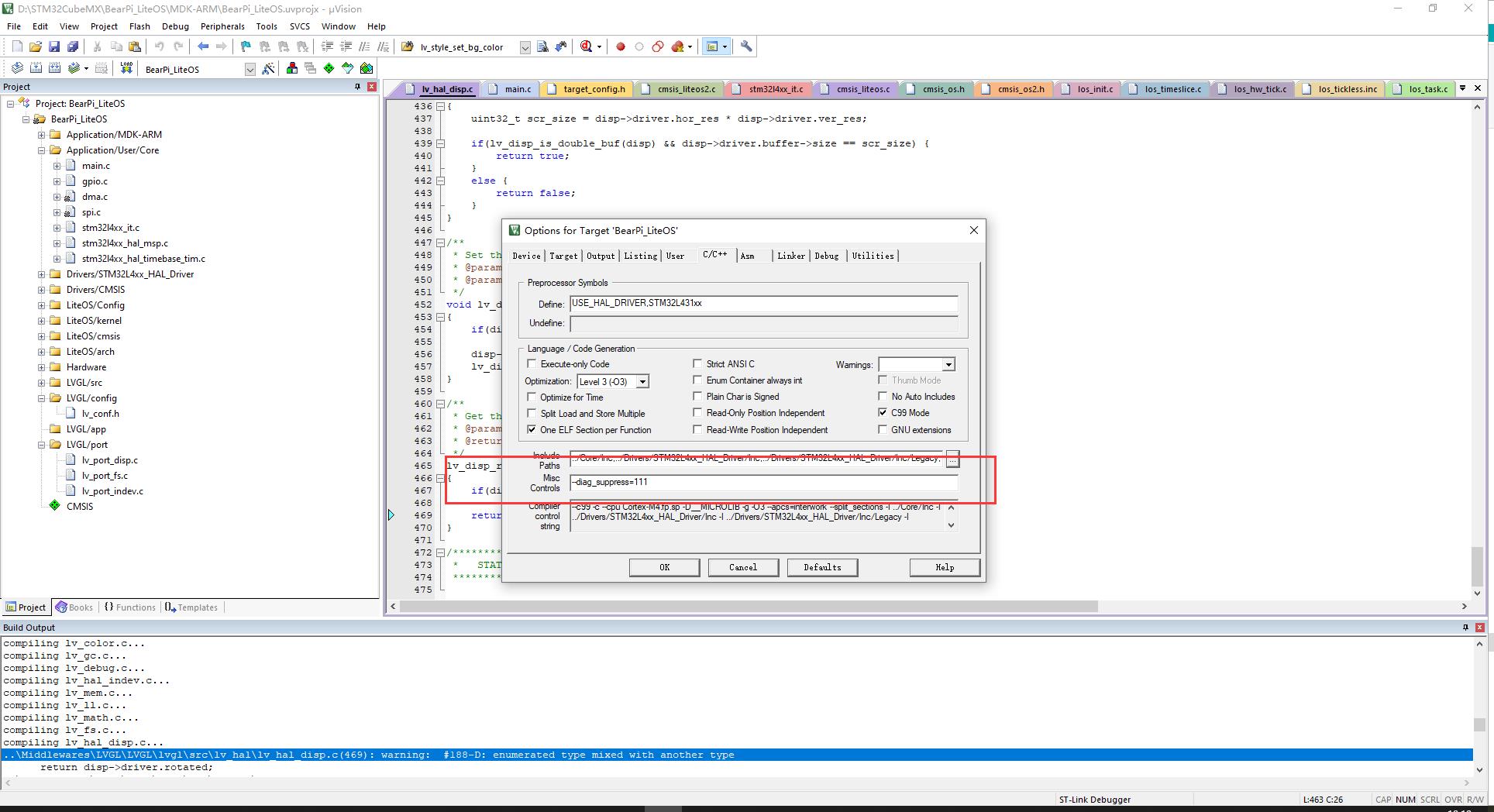
编译后改报错就不显示了
四、显示接口移植
编译通过后,我们下一步就是修改显示接口了,打开 lv_port_disp.c 文件,将开头使能,包括头文件也使能:
/*Copy this file as "lv_port_disp.c" and set this value to "1" to enable content*/
#if 1
修改显示接口,主要关注 void lv_port_disp_init(void) 函数
void lv_port_disp_init(void)
/*-------------------------
* Initialize your display
* -----------------------*/
disp_init();
/*-----------------------------
* Create a buffer for drawing
*----------------------------*/
/* LVGL requires a buffer where it internally draws the widgets.
* Later this buffer will passed your display drivers `flush_cb` to copy its content to your display.
* The buffer has to be greater than 1 display row
*
* There are three buffering configurations:
* 1. Create ONE buffer with some rows:
* LVGL will draw the display's content here and writes it to your display
*
* 2. Create TWO buffer with some rows:
* LVGL will draw the display's content to a buffer and writes it your display.
* You should use DMA to write the buffer's content to the display.
* It will enable LVGL to draw the next part of the screen to the other buffer while
* the data is being sent form the first buffer. It makes rendering and flushing parallel.
*
* 3. Create TWO screen-sized buffer:
* Similar to 2) but the buffer have to be screen sized. When LVGL is ready it will give the
* whole frame to display. This way you only need to change the frame buffer's address instead of
* copying the pixels.
* */
/* Example for 1) */
static lv_disp_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_1;
static lv_color_t draw_buf_1[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/
lv_disp_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_1, draw_buf_1, NULL, LV_HOR_RES_MAX * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/* Example for 2) */
static lv_disp_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;
static lv_color_t draw_buf_2_1[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/
static lv_color_t draw_buf_2_2[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/
lv_disp_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, draw_buf_2_1, draw_buf_2_2, LV_HOR_RES_MAX * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/* Example for 3) */
static lv_disp_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_3;
static lv_color_t draw_buf_3_1[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * LV_VER_RES_MAX]; /*A screen sized buffer*/
static lv_color_t draw_buf_3_2[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * LV_VER_RES_MAX]; /*An other screen sized buffer*/
lv_disp_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_3, draw_buf_3_1, draw_buf_3_2, LV_HOR_RES_MAX * LV_VER_RES_MAX); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/*-----------------------------------
* Register the display in LVGL
*----------------------------------*/
lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*/
/*Set up the functions to access to your display*/
/*Set the resolution of the display*/
disp_drv.hor_res = 480;
disp_drv以上是关于小熊派LiteOS移植LVGL的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章