量子傅里叶变换:Quantum Phase Estimation
Posted 安徽思远
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了量子傅里叶变换:Quantum Phase Estimation相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Overview
如果仅仅想使用QPE,那我们只需要知道QPE干了什么就好。
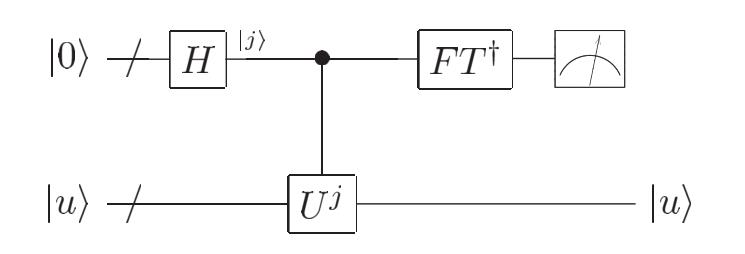
通过Inverse Fourier Transform,我们可以得到:
1
2
t
/
2
∑
j
=
0
2
t
−
1
e
2
π
i
φ
j
∣
j
⟩
∣
u
⟩
→
∣
φ
~
⟩
∣
u
⟩
\\frac12^t / 2 \\sum_j=0^2^t-1 e^2 \\pi i \\varphi j|j\\rangle|u\\rangle \\rightarrow|\\tilde\\varphi\\rangle|u\\rangle
2t/21j=0∑2t−1e2πiφj∣j⟩∣u⟩→∣φ~⟩∣u⟩
Derivation
As mentioned above, this circuit estimates the phase of a unitary operator U. It estimates $\\theta $in U ∣ ψ ⟩ = e 2 π i θ ∣ ψ ⟩ U\\vert\\psi \\rangle =e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta |\\psi \\rangle U∣ψ⟩=e2πiθ∣ψ⟩, where ∣ ψ ⟩ |\\psi\\rangle ∣ψ⟩ is an eigenvector and e 2 π i θ e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i\\theta e2πiθ is the corresponding eigenvalue.
矩阵特征值是对特征向量进行伸缩和旋转程度的度量。
“特征”的含义就是“不变”。
i. Setup: ∣ ψ ⟩ \\vert\\psi\\rangle ∣ψ⟩ is in one set of qubit registers. An additional set of n qubits form the counting register on which we will store the value 2 n θ 2^n\\theta 2nθ:
ψ 0 = ∣ 0 ⟩ ⊗ n ∣ ψ ⟩ \\psi_0 = \\lvert 0 \\rangle^\\otimes n \\lvert \\psi \\rangle ψ0=∣0⟩⊗n∣ψ⟩
ii. Superposition: Apply a n-bit Hadamard gate operation H ⊗ n H^\\otimes n H⊗n on the counting register:
ψ 1 = 1 2 n 2 ( ∣ 0 ⟩ + ∣ 1 ⟩ ) ⊗ n ∣ ψ ⟩ \\psi_1 = \\frac 12^\\frac n2\\left(|0\\rangle +|1\\rangle \\right)^\\otimes n \\lvert \\psi \\rangle ψ1=22n1(∣0⟩+∣1⟩)⊗n∣ψ⟩
iii. Controlled Unitary Operations: We need to introduce the controlled unitary C-U that applies the unitary operator U on the target register only if its corresponding control bit is ∣ 1 ⟩ |1\\rangle ∣1⟩. Since U is a unitary operator with eigenvector |\\psi\\rangle such that U ∣ ψ ⟩ = e 2 π i θ ∣ ψ ⟩ U|\\psi \\rangle =e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta |\\psi \\rangle U∣ψ⟩=e2πiθ∣ψ⟩, this means:
U
2
j
∣
ψ
⟩
=
U
2
j
−
1
U
∣
ψ
⟩
=
U
2
j
−
1
e
2
π
i
θ
∣
ψ
⟩
=
⋯
=
e
2
π
i
2
j
θ
∣
ψ
⟩
U^2^j|\\psi \\rangle =U^2^j-1U|\\psi \\rangle =U^2^j-1e^2\\pi i\\theta |\\psi \\rangle =\\cdots =e^2\\pi i2^j\\theta |\\psi \\rangle
U2j∣ψ⟩=U2j−1U∣ψ⟩=U2j−1e2πiθ∣ψ⟩=⋯=e2πi2jθ∣ψ⟩
Applying all the n controlled operations C −
U
2
j
U^2^j
U2j with
0
≤
j
≤
n
−
1
0\\leq j\\leq n-1
0≤j≤n−1, and using the relation
∣
0
⟩
⊗
∣
ψ
⟩
+
∣
1
⟩
⊗
e
2
π
i
θ
∣
ψ
⟩
=
(
∣
0
⟩
+
e
2
π
i
θ
∣
1
⟩
)
⊗
∣
ψ
⟩
|0\\rangle \\otimes |\\psi \\rangle +|1\\rangle \\otimes e^2\\pi i\\theta |\\psi \\rangle =\\left(|0\\rangle +e^2\\pi i\\theta |1\\rangle \\right)\\otimes |\\psi \\rangle
∣0⟩⊗∣ψ⟩+∣1⟩⊗e2πiθ∣ψ⟩=(∣0⟩+e2πiθ∣1⟩)⊗∣ψ⟩:
ψ 2 = 1 2 n 2 ( ∣ 0 ⟩ + e 2 π i θ 2 n − 1 ∣ 1 ⟩ ) ⊗ ⋯ ⊗ ( ∣ 0 ⟩ + e 2 π i θ 2 1 ∣ 1 ⟩ ) ⊗ ( ∣ 0 ⟩ + e 2 π i θ 2 0 ∣ 1 ⟩ ) ⊗ ∣ ψ ⟩ = 1 2 n 2 ∑ k = 0 2 n − 1 e 2 π i θ k ∣ k ⟩ ⊗ ∣ ψ ⟩ \\beginaligned \\psi_2 & =\\frac 12^\\frac n2 \\left(|0\\rangle+e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta 2^n-1|1\\rangle \\right) \\otimes \\cdots \\otimes \\left(|0\\rangle+e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta 2^1\\vert1\\rangle \\right) \\otimes \\left(|0\\rangle+e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta 2^0\\vert1\\rangle \\right) \\otimes |\\psi\\rangle\\\\\\\\ & = \\frac12^\\frac n2\\sum _k=0^2^n-1e^\\boldsymbol2\\pi i \\theta k|k\\rangle \\otimes \\vert\\psi\\rangle \\endaligned ψ2=22n1(∣0⟩+e2πiθ2n−1∣1⟩)⊗⋯⊗(∣0⟩+e2πiθ21∣1⟩)⊗(∣0⟩+e2πiθ20∣1⟩)⊗∣ψ⟩=22n1k=0∑2n−1e2πiθk∣k⟩⊗∣ψ⟩
where k denotes the integer representation of n-bit binary numbers.
iv. Inverse Fourier Transform: Notice that the above expression is exactly the result of applying a quantum Fourier transform as we derived in the notebook on Quantum Fourier Transform and its Qiskit Implementation. Recall that QFT maps an n-qubit input state ∣ x ⟩ \\vert x\\rangle ∣x⟩ into an output as
Q
F
T
∣
x
⟩
=
1
以上是关于量子傅里叶变换:Quantum Phase Estimation的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章