C++中的STL(超详细的操作)
Posted 嫚嫚_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++中的STL(超详细的操作)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
vector
vector构造函数

vector赋值操作

vector容器和大小

vector插入和删除

vector数据存取

vector互换容器

vector预留空间

string
string构造函数

string赋值操作

string字符串的拼接

string查找和替换

rfind从右向左查,find从左向右查
string字符串比较

主要是判断字符串是否相等
string字符串存取

字符串插入与删除

string字符串获取
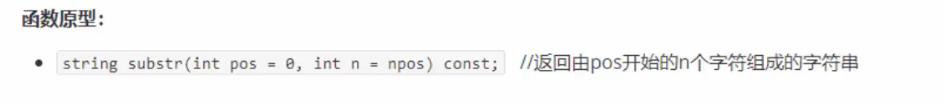
deque双端数组
deque构造函数
deque赋值操作

deque大小操作

deque插入和删除

deque容器的数据存取

deque容器排序

stack
stack的接口

queue容器(先进先出)

list容器链表
list构造函数

list赋值和交换
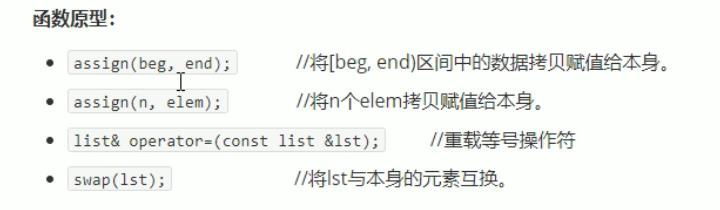
list大小操作

list插入与删除

list数据存取

list容器反转与排序

set容器()插入时自动排序
set构造和赋值

set大小和交换

set插入和删除

set查找和统计

常用算法
遍历算法
for_each
void print(int val)
cout << val << endl;
class Print
public:
void operator()(int val)
cout << val << endl;
;
int main()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print());
transform
class trans
public:
int operator()(int val)
return val;
;
class Myprint
public:
void operator()(int val)
cout << val << " ";
;
int mian()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
vector<int>tag;
tag.resize(v.size());
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), tag.begin(), trans());
for_each(tag.begin(), tag.end(), Myprint());
return 0;
常用查找算法
find
//查找内置数据类型
void test01()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
//查找容器中的5
vector<int>::iterator it= find(v.begin(), v.end(), 50);
if (it == v.end())
cout << "没有" << endl;
else
cout << "有" << endl;
//查找自定义数据
class Person
public:
Person(string name,int age)
this->age = age;
this->name = name;
//重载==号
bool operator==(const Person&p1)
if (this->age == p1.age && this->name == p1.name)
return true;
else
return false;
string name;
int age;
;
void test02()
vector<Person>v1;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
v1.push_back(p1);
v1.push_back(p2);
v1.push_back(p3);
vector<Person>::iterator it= find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), p1);
if (it == v1.end())
cout << "没找到" << endl;
else
cout << it->age << " " << it->name << endl;
int main()
test01();
test02();
find_if
//内置数据类型
class Five
public:
bool operator()(int val)
return val > 5;
;
void test01()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
vector<int>::iterator it= find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Five());
if (it == v.end())
cout<<"没有"<<endl;
else
cout << *it << endl;
//自定义数据类型
class Person
public:
Person(string name,int age)
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
string name;
int age;
;
class Great
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p)
return p.age > 20;
;
void test02()
vector<Person>v1;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
v1.push_back(p1);
v1.push_back(p2);
v1.push_back(p3);
vector<Person>::iterator it= find_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Great());
if (it == v1.end())
cout << "没找到" << endl;
else
cout << it->name << " " << it->age << endl;
int main()
test01();
test02();
adjacent_find(查找相邻重复的元素)
int main()
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it == v.end())
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
else
cout << *it << endl;
binary_search(有序的)
int main()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
bool ret=binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);
if (ret)
cout << "找到了" << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
count
//内置数据类型
void test01()
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(10);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);
cout << num << endl;
class Person
public:
Person(string name,int age)
this->age = age;
this->name = name;
bool operator==(const Person &p)
if (p.age == this->age )
return true;
else
return false;
string name;
int age;
;
void test02()
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 20);
Person p5("eee", 10);
Person p6("bbb", 20);
vector<Person>v1;
v1.push_back(p1);
v1.push_back(p2);
v1.push_back(p3);
v1.push_back(p4);
v1.push_back(p5);
v1.push_back(p6);
Person p("aaa", 10);
int num = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(), p);
cout << num << endl;
//自定义数据类型
int main()
test01();
test02();
count_if
常用排序算法
sort
void Myprint(int val)
cout << val << " ";
int main()
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),Myprint);
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint);
random_shuffle 随机调整位置
void print(int val)
cout << val << " ";
int main()
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
//利用洗牌算法,打乱顺序
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
merge 两个有序的容器合并成一个有序容器
void Myprint(int val)
cout << val << " ";
int main()
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 1);
vector<int>v3;
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Myprint);
** reverse 数据反转**
void Myprint(int val)
cout << val << " ";
int main()
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v1.push_back(i);
reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Myprint);
常用拷贝和替代算法
copy 容器中元素拷贝到另一个容器
void print(int val)
cout << val << " ";
int main()
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v1.push_back(i);
vector<int>v2;
v2.resize(v1.size());
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
replace 替换 区间旧元素替换成新元素
class Myprint
public:
void operator()(int val)
cout << val << " ";
;
int main()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 4, 100);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint());
replace_if 条件替换
class Myprint
public:
void operator()(int val)
cout << val << " ";
;
class Great
public:
bool operator()(int val)
return val > 5;
;
int main()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint());
cout << endl;
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Great(), 2000);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint());
swap 互换两个容器的元素
常用算数生成算法
accumulate 计算区间内容器的总和
int main()
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
v.push_back(i);
int sum=accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
cout << sum << endl;
以上是关于C++中的STL(超详细的操作)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章