JUC学习之无锁---乐观锁(非阻塞)
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC学习之无锁---乐观锁(非阻塞)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JUC学习之无锁---乐观锁(非阻塞
CAS 与 volatile
问题提出
有如下需求,保证 account.withdraw 取款方法的线程安全
package cas;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface Account
// 获取余额
Integer getBalance();
// 取款
void withdraw(Integer amount);
/**
* 方法内会启动 1000 个线程,每个线程做 -10 元 的操作
* 如果初始余额为 10000 那么正确的结果应当是 0
*/
static void demo(Account account)
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
//加入1000个线程,每个线程启动都执行取款10元的方法
ts.add(new Thread(() ->
account.withdraw(10);
));
//启动1000个线程
ts.forEach(Thread::start);
ts.forEach(t ->
try
//等待每一个线程执行结束
t.join();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(account.getBalance()
+ " cost: " + (end - start) / 1000_000 + " ms");
执行测试代码
public static void main(String[] args)
Account.demo(new AccountUnsafe(10000));
某次的执行结果
400 cost: 217 ms
为什么不安全
withdraw 方法
public void withdraw(Integer amount)
balance -= amount;
对应的字节码
ALOAD 0 // <- this
ALOAD 0
GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance : Ljava/lang/Integer; // <- this.balance
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I // 拆箱
ALOAD 1 // <- amount
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I // 拆箱
ISUB // 减法
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf (I)Ljava/lang/Integer; // 结果装箱
PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance : Ljava/lang/Integer; // -> this.balance
多线程执行流程
ALOAD 0 // thread-0 <- this
ALOAD 0
GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-0 <- this.balance
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-0 拆箱
ALOAD 1 // thread-0 <- amount
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-0 拆箱
ISUB // thread-0 减法
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf // thread-0 结果装箱
PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-0 -> this.balance
ALOAD 0 // thread-1 <- this
ALOAD 0
GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-1 <- this.balance
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-1 拆箱
ALOAD 1 // thread-1 <- amount
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-1 拆箱
ISUB // thread-1 减法
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf // thread-1 结果装箱
PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-1 -> this.balance
- 单核的指令交错
- 多核的指令交错
解决思路-锁
首先想到的是给 Account 对象加锁
class AccountUnsafe implements Account
private Integer balance;
public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance)
this.balance = balance;
@Override
public Integer getBalance()
return balance;
@Override
public synchronized void withdraw(Integer amount)
balance -= amount;
结果为
0 cost: 399 ms
解决思路-无锁
class AccountUnsafe implements Account
private AtomicInteger balance;
public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance)
this.balance = new AtomicInteger(balance);
@Override
public Integer getBalance()
return balance.get();
@Override
public synchronized void withdraw(Integer amount)
while (true)
int prev = balance.get();
int next = prev - amount;
if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next))
break;
// 可以简化为下面的方法
// balance.addAndGet(-1 * amount);
测试结果
0 cost: 106 ms
CAS 与 volatile
前面看到的 AtomicInteger 的解决方法,内部并没有用锁来保护共享变量的线程安全。那么它是如何实现的呢?
package cas;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class AccountUnsafe implements Account
private AtomicInteger balance;
public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance)
this.balance = new AtomicInteger(balance);
@Override
public Integer getBalance()
return balance.get();
public void withdraw(Integer amount)
// 需要不断尝试,直到成功为止
while (true)
// 比如拿到了旧值 1000
int prev = balance.get();
// 在这个基础上 1000-10 = 990
int next = prev - amount;
/*
compareAndSet 正是做这个检查,在 set 前,先比较 prev 与当前值
- 不一致了,next 作废,返回 false 表示失败
比如,别的线程已经做了减法,当前值已经被减成了 990
那么本线程的这次 990 就作废了,进入 while 下次循环重试
- 一致,以 next 设置为新值,返回 true 表示成功
*/
if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next))
break;
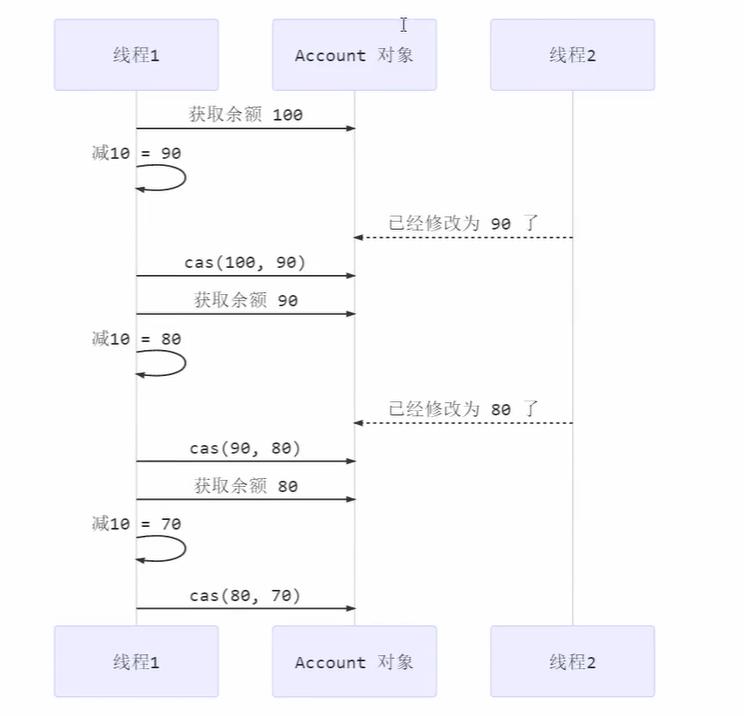
其中的关键是 compareAndSet,它的简称就是 CAS (也有 Compare And Swap 的说法),它必须是原子操作。
注意
- 其实 CAS 的底层是 lock cmpxchg 指令(X86 架构),在单核 CPU 和多核 CPU 下都能够保证【比较-交换】的原子性。
- 在多核状态下,某个核执行到带 lock 的指令时,CPU 会让总线锁住,当这个核把此指令执行完毕,再开启总线。这个过程中不会被线程的调度机制所打断,保证了多个线程对内存操作的准确性,是原子的。
慢动作分析
package cas;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j
public class SlowMotion
public static void main(String[] args)
AtomicInteger balance = new AtomicInteger(10000);
int mainPrev = balance.get();
log.debug("try get ", mainPrev);
new Thread(() ->
sleep(1000);
int prev = balance.get();
balance.compareAndSet(prev, 9000);
log.debug(balance.toString());
, "t1").start();
sleep(2000);
log.debug("try set 8000...");
boolean isSuccess = balance.compareAndSet(mainPrev, 8000);
log.debug("is success ? ", isSuccess);
if (!isSuccess)
mainPrev = balance.get();
log.debug("try set 8000...");
isSuccess = balance.compareAndSet(mainPrev, 8000);
log.debug("is success ? ", isSuccess);
private static void sleep(int millis)
try
Thread.sleep(millis);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
输出结果
2019-10-13 11:28:37.134 [main] try get 10000
2019-10-13 11:28:38.154 [t1] 9000
2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] try set 8000...
2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] is success ? false
2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] try set 8000...
2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] is success ? true
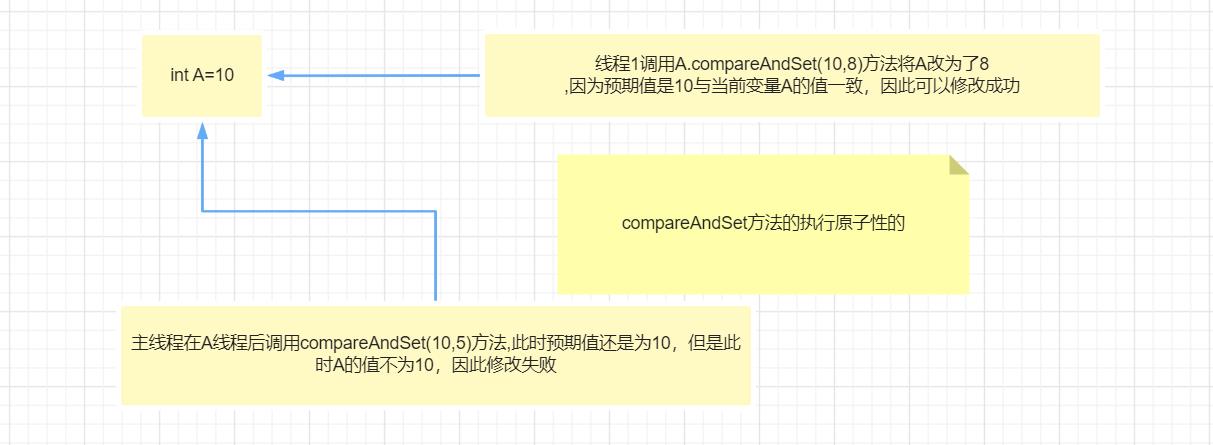
volatile
获取共享变量时,为了保证该变量的可见性,需要使用 volatile 修饰。
它可以用来修饰成员变量和静态成员变量,他可以避免线程从自己的工作缓存中查找变量的值,必须到主存中获取
它的值,线程操作 volatile 变量都是直接操作主存。即一个线程对 volatile 变量的修改,对另一个线程可见。
注意
volatile 仅仅保证了共享变量的可见性,让其它线程能够看到最新值,但不能解决指令交错问题(不能保证原 子性)
CAS 必须借助 volatile 才能读取到共享变量的最新值来实现【比较并交换】的效果
为什么无锁效率高
- 无锁情况下,即使重试失败,线程始终在高速运行,没有停歇,而 synchronized 会让线程在没有获得锁的时候,发生上下文切换,进入阻塞。打个比喻
- 线程就好像高速跑道上的赛车,高速运行时,速度超快,一旦发生上下文切换,就好比赛车要减速、熄火,等被唤醒又得重新打火、启动、加速… 恢复到高速运行,代价比较大
- 但无锁情况下,因为线程要保持运行,需要额外 CPU 的支持,CPU 在这里就好比高速跑道,没有额外的跑道,线程想高速运行也无从谈起(线程数多于cpu核心数),虽然不会进入阻塞,但由于没有分到时间片,仍然会进入可运行状态,还 是会导致上下文切换。
CAS 的特点
结合 CAS 和 volatile 可以实现无锁并发,适用于线程数少、多核 CPU 的场景下。
- CAS 是基于乐观锁的思想:最乐观的估计,不怕别的线程来修改共享变量,就算改了也没关系,我吃亏点再
重试呗。 - synchronized 是基于悲观锁的思想:最悲观的估计,得防着其它线程来修改共享变量,我上了锁你们都别想
改,我改完了解开锁,你们才有机会。 - CAS 体现的是无锁并发、无阻塞并发,请仔细体会这两句话的意思
因为没有使用 synchronized,所以线程不会陷入阻塞,这是效率提升的因素之一
但如果竞争激烈,可以想到重试必然频繁发生,反而效率会受影响
原子类
原子整数–AtomicInteger
J.U.C 并发包提供了:
- AtomicBoolean
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicLong
以 AtomicInteger 为例
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 获取并自增(i = 0, 结果 i = 1, 返回 0),类似于 i++
System.out.println(i.getAndIncrement());
// 自增并获取(i = 1, 结果 i = 2, 返回 2),类似于 ++i
System.out.println(i.incrementAndGet());
// 自减并获取(i = 2, 结果 i = 1, 返回 1),类似于 --i
System.out.println(i.decrementAndGet());
// 获取并自减(i = 1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 1),类似于 i--
System.out.println(i.getAndDecrement());
// 获取并加值(i = 0, 结果 i = 5, 返回 0)
System.out.println(i.getAndAdd(5));
// 加值并获取(i = 5, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)
System.out.println(i.addAndGet(-5));
// 获取并更新(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = -2, 返回 0)
// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用
System.out.println(i.getAndUpdate(p -> p - 2));
// 更新并获取(i = -2, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)
// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用
System.out.println(i.updateAndGet(p -> p + 2));
// 获取并计算(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 10, 返回 0)
// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用
// getAndUpdate 如果在 lambda 中引用了外部的局部变量,要保证该局部变量是 final 的
// getAndAccumulate 可以通过 参数1 来引用外部的局部变量,但因为其不在 lambda 中因此不必是 final
System.out.println(i.getAndAccumulate(10, (p, x) -> p + x));
// 计算并获取(i = 10, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)
// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用
System.out.println(i.accumulateAndGet(-10, (p, x) -> p + x));
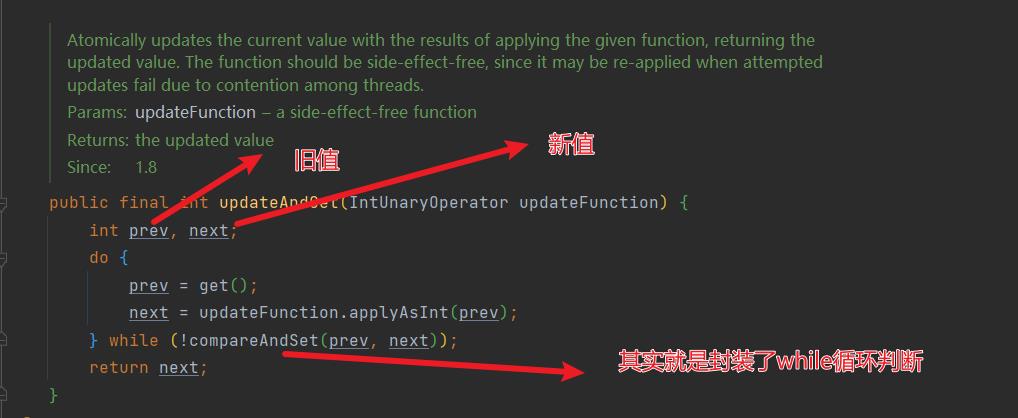
updateAndGet方法剖析
模拟实现一下:
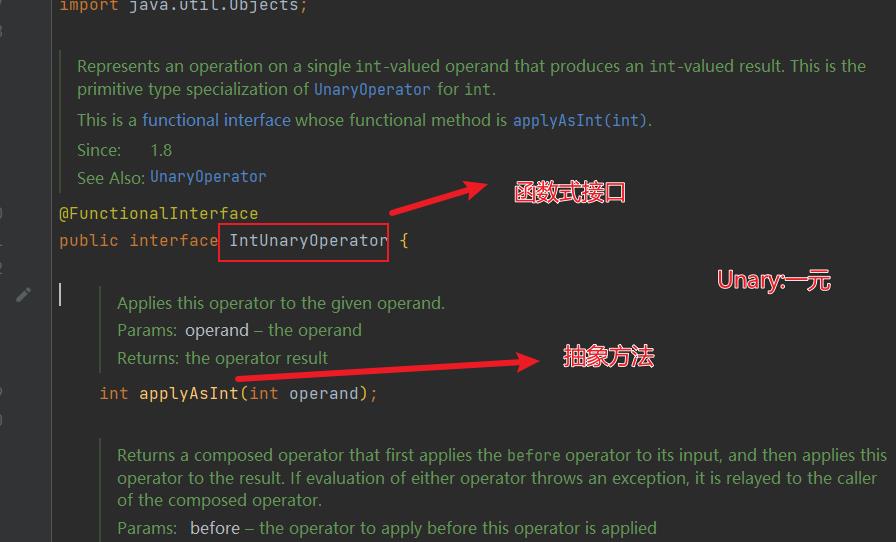
//Unary是一元的意思,表示只有一个参数
private int updateAndGet(AtomicInteger i,IntUnaryOperator intUnaryOperator)
while(true)
//修改之前的旧值
int prev=i.get();
//修改后的新值
int next=intUnaryOperator.applyAsInt(prev);
//比较当前值和是否被其他线程修改
if(i.compareAndSet(prev,next))
return next;
源码:
原子引用–AtomicReference
为什么需要原子引用类型?
- AtomicReference
- AtomicMarkableReference
- AtomicStampedReference
有如下方法
package aotic;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public interface DecimalAccount
// 获取余额
BigDecimal getBalance();
// 取款
void withdraw(BigDecimal amount);
/**
* 方法内会启动 1000 个线程,每个线程做 -10 元 的操作
* 如果初始余额为 10000 那么正确的结果应当是 0
*/
static void demo(DecimalAccount account)
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
ts.add(new Thread(() ->
account.withdraw(BigDecimal.TEN);
));
ts.forEach(Thread::start);
ts.forEach(t ->
try
t.join();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
System.out.println(account.getBalance());
非阻塞同步算法与CAS(Compare and Swap)无锁算法