LinkedList底层源码入门分析以及list集合选择
Posted 爱上口袋的天空
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LinkedList底层源码入门分析以及list集合选择相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、LinkedList底层双向连接简介
- LinkedList底层实现了双向链表和双端队列特点
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括null
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步
LinkedList的底层操作机制:
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表.
- LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了prev、next、item三个属性,其中通过prev指向前一个,通过next指向后一个节点。最终实现双向链表.
- 所以LinkedList的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高。
二、根据上面的简介模拟一个简单的双向链表案例
package com.kgf.kgfjavalearning2021.collection; public class LinkedListSource01 public static void main(String[] args) //模拟一个简单的双向列表 Node jack = new Node("jack"); Node tom = new Node("tom"); Node roser = new Node("roser"); //下面我们使用上面的3个节点形成双向链表 //1、jack->tom->roser jack.next = tom; tom.next = roser; //2、roser->tom->jack roser.pre = tom; tom.pre = jack; //下面指定头结点和尾节点 Node first = jack;//让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的头节点 Node last = roser;//让last引用指向roser,就是双向链表的尾节点 //演示从头到尾遍历 System.out.println("================从头到尾遍历=================="); while (true) if (first==null) break; System.out.println(first); first = first.next; //演示从尾到头遍历 System.out.println("================从尾到头遍历=================="); while (true) if (last==null) break; System.out.println(last); last = last.pre; //下面我们在tom和roser直接插入一个smith Node smith = new Node("smith"); smith.next = roser; smith.pre = tom; roser.pre = smith; tom.next = smith; //其实上面主要就是修改指向 //下面我们重置一下first和last指向 first = jack;//让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的头节点 //演示从头到尾遍历 System.out.println("================在tom和roser直接插入一个smith遍历=================="); while (true) if (first==null) break; System.out.println(first); first = first.next; /*** * 定义一个Node类,Node对象表示双向链表的一个节点 */ class Node public Object item;//真正存放数据的地方 public Node next;//指向后一个节点 public Node pre;//指向前一个节点 public Node(Object item) this.item = item; @Override public String toString() return "Node name=" +item;效果:
================从头到尾遍历==================
Node name=jack
Node name=tom
Node name=roser
================从尾到头遍历==================
Node name=roser
Node name=tom
Node name=jack
================在tom和roser直接插入一个smith遍历==================
Node name=jack
Node name=tom
Node name=smith
Node name=roserProcess finished with exit code 0
三、LinkedList源码分析
1、查询LinkedList添加元素的源码
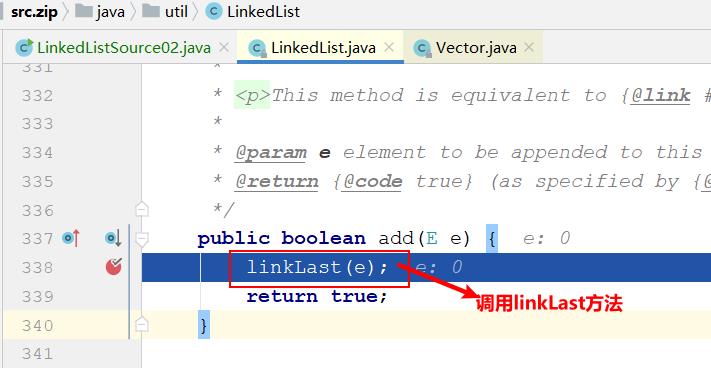
进入linkLast方法:
/** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;我们可以看一下上面的代码:
1)、首先我们将last这个指向LinkedList尾结点的引用对象复制给一个新的l对象
2)、然后我们将l对象以及e要添加的元素作为参数传递进入Node有参构造方法,
最后得到一个新的Node节点对象newNode,这个对象将l节点作为上一个节点
3)、将newNodex赋值给last作为尾节点
4)、最后就是判断l节点是否为null,通过判断这个尾结点的值来处理我们新增的元素,
最终做到如下:
综上、其实LinkedList这个集合是一个双向链表的结构,当我们新增元素的时候其实就是改变节点之间的指向,所以再新增元素的性能方面,LinkedList表现的比较好
三、list集合选择
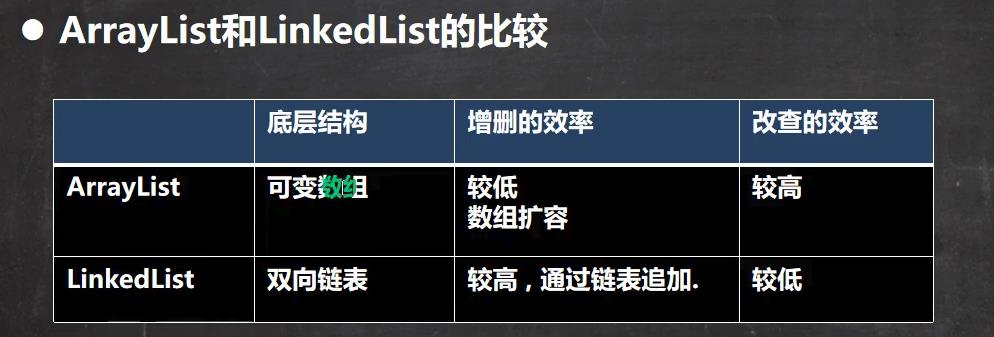
ArrayList插入数据涉及扩容操作,效率低,改和查的效率比较高,因为可以通过索引定位

以上是关于LinkedList底层源码入门分析以及list集合选择的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章