Processing介绍及几个python模式下的案例
Posted cui_yonghua
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Processing介绍及几个python模式下的案例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一. Processing介绍
Processing 是一门开源编程语言和与之配套的集成开发环境(IDE)的名称。Processing 在电子艺术和视觉设计社区被用来教授编程基础,并运用于大量的新媒体和互动艺术作品中。
Processing 最开始的时候只是一门编程语言,因为发展势头好,在2012年的时候成立了Processing 基金会,开始横向拓展其他项目,比如p5.js, Processing的 R 模式等等。
Processing 可以用三个标签来总结:编程,视觉,易学。
简单来说,就是通过写代码来生成图案,用几行简单的代码就可以写出炫酷的视觉效果。
可以免费下载使用,官网:https://processing.org/。单击 Download Processing 并选择您的操作系统,下载安装即可。
Processing 在 2001 年诞生于麻省理工学院(MIT)的媒体实验室,主创者为 Ben Fry 和 Casey Reas,项目发起的初衷,本是为了满足他们自身的教学和学习需要。后来,当Casey在意大利的伊夫雷亚交互设计学院(Interaction Design Institute Ivrea)进行教学的时候,基于Processing,衍生出了Wiring和Arduino项目。随着时间的推移,又诞生了多个语言的版本,比如基于javascript的Processing.js,还有基于Python、Ruby、ActionScript以及Scala等版本。
Processing项目是Java开发的,所以Processing天生就具有跨平台的特点,同时支持Linux、Windows以及Mac OSX三大平台,并且支持将图像导出成各种格式。
Processing 是一种具有革命前瞻性的新兴计算机语言,为图像处理提供开源编程语言和环境,动画和互动。这是使用的学生,艺术家,设计师,研究人员和爱好者学习,原型及生产。这是建立基础教育计算机编程在视觉方面,并作为软件写生簿和专业的生产工具。Processing 开发的艺术家和设计师以替代专有软件工具在同一域中。
二. 基于Python案例
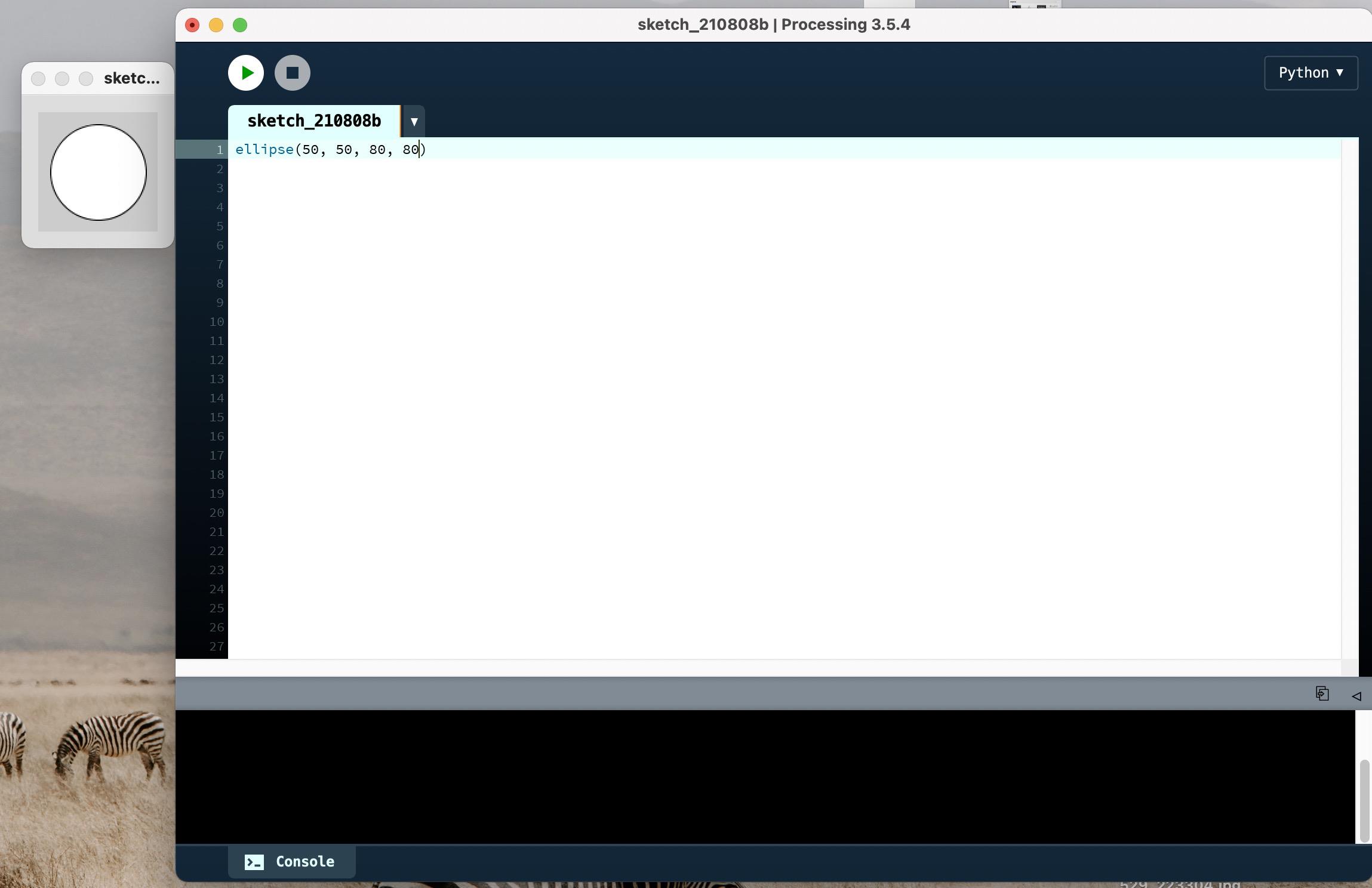
2.1 绘制正方形
ellipse(50, 50, 80, 80)
执行结果如下:
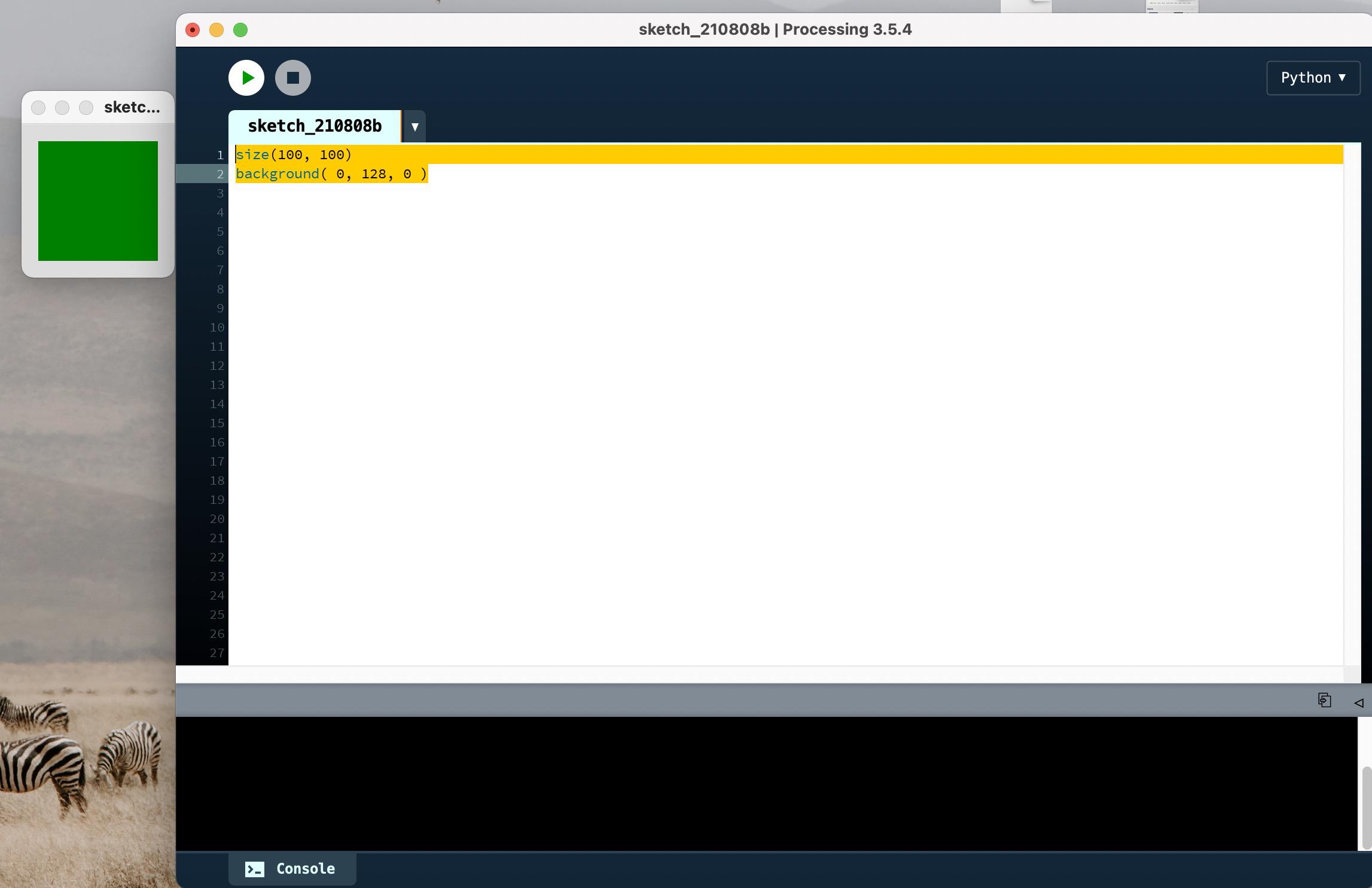
2.2 背景和颜色
background 功能被用来设置显示窗口的颜色。此函数可以使用各种不同的参数(来定义一个灰度值或 Red-Green-Blue [RGB] 颜色)。
size(100, 100)
background( 0, 128, 0 )
执行结果如下图:
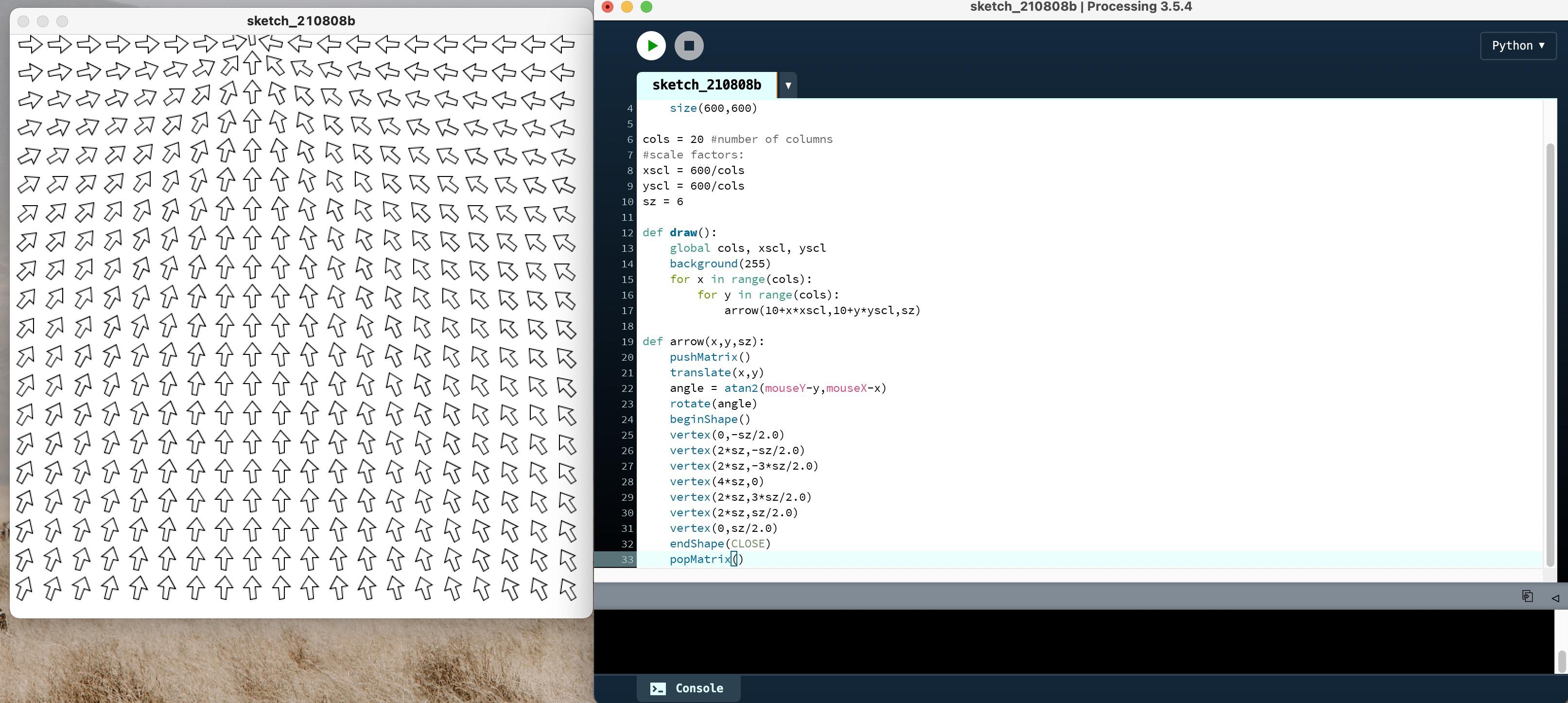
2.3 鼠标控制箭头
#arrow.pyde
def setup():
size(600,600)
cols = 20 #number of columns
#scale factors:
xscl = 600/cols
yscl = 600/cols
sz = 6
def draw():
global cols, xscl, yscl
background(255)
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(cols):
arrow(10+x*xscl,10+y*yscl,sz)
def arrow(x,y,sz):
pushMatrix()
translate(x,y)
angle = atan2(mouseY-y,mouseX-x)
rotate(angle)
beginShape()
vertex(0,-sz/2.0)
vertex(2*sz,-sz/2.0)
vertex(2*sz,-3*sz/2.0)
vertex(4*sz,0)
vertex(2*sz,3*sz/2.0)
vertex(2*sz,sz/2.0)
vertex(0,sz/2.0)
endShape(CLOSE)
popMatrix()
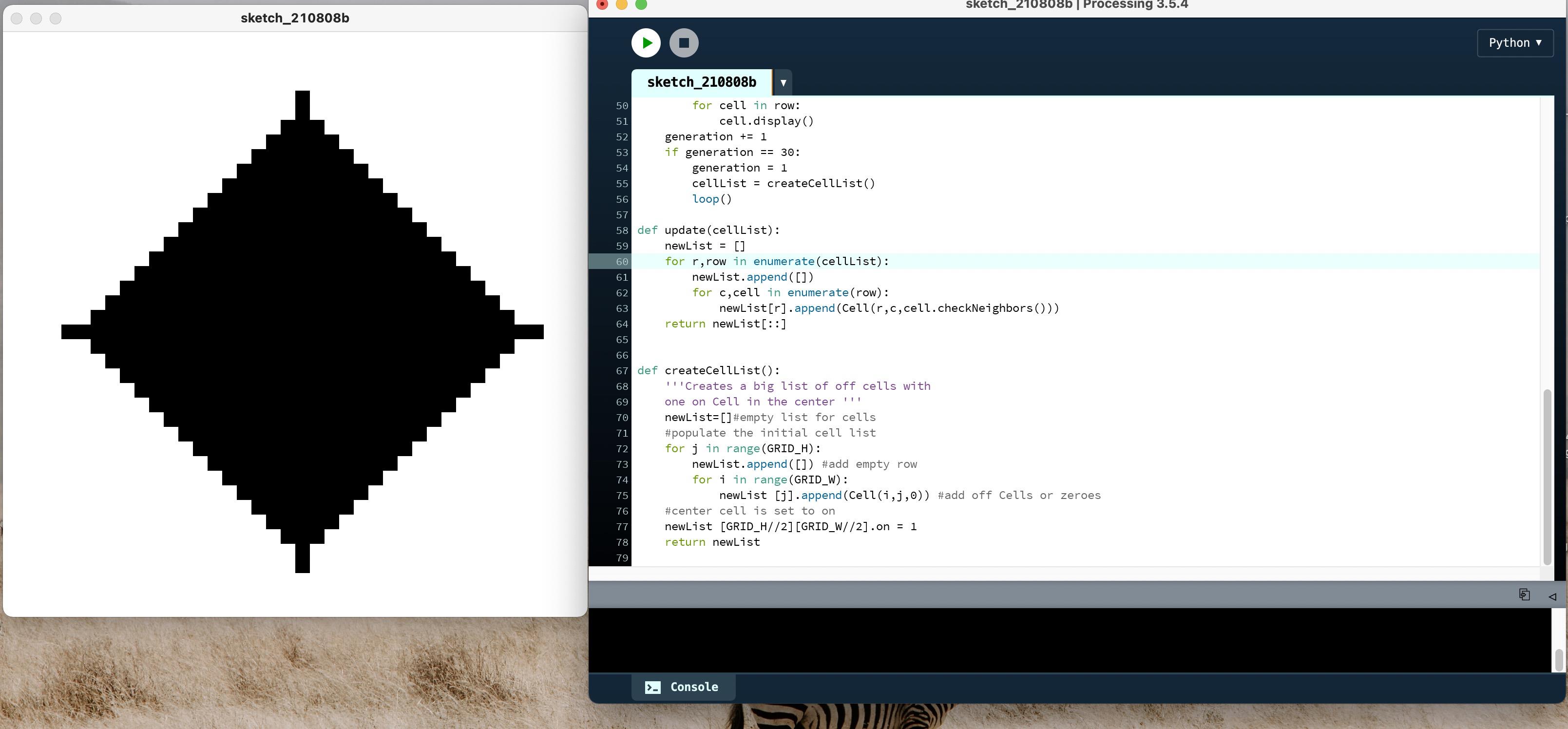
2.4 正方向四周扩散
GRID_W = 41
GRID_H = 41
generation = 0
class Cell:
def __init__(self,r,c,on=0):
self.c = c
self.r = r
self.on = on
def display(self):
if self.on == 1:
fill(0) #black
else:
fill(255) #white
rect(SZ*self.r, SZ*self.c, SZ, SZ)
def checkNeighbors(self):
neighbs = 0 #check the neighbors
if self.on == 1: return 1
for dr,dc in [[-1,0], [1,0], [0,-1],[0,1]]:
try:
if cellList[self.r + dr][self.c + dc].on == 1:
neighbs += 1
except IndexError:
continue
if neighbs in [1,4]:
return 1
else:
return 0
def setup():
global SZ, cellList
noStroke()
size(600,600)
SZ = width // GRID_W + 1
cellList = createCellList()
def draw():
global generation,cellList
frameRate(10)
cellList = update(cellList)
for row in cellList:
for cell in row:
cell.display()
generation += 1
if generation == 30:
generation = 1
cellList = createCellList()
loop()
def update(cellList):
newList = []
for r,row in enumerate(cellList):
newList.append([])
for c,cell in enumerate(row):
newList[r].append(Cell(r,c,cell.checkNeighbors()))
return newList[::]
def createCellList():
'''Creates a big list of off cells with
one on Cell in the center '''
newList=[]#empty list for cells
#populate the initial cell list
for j in range(GRID_H):
newList.append([]) #add empty row
for i in range(GRID_W):
newList [j].append(Cell(i,j,0)) #add off Cells or zeroes
#center cell is set to on
newList [GRID_H//2][GRID_W//2].on = 1
return newList
执行结果如下:
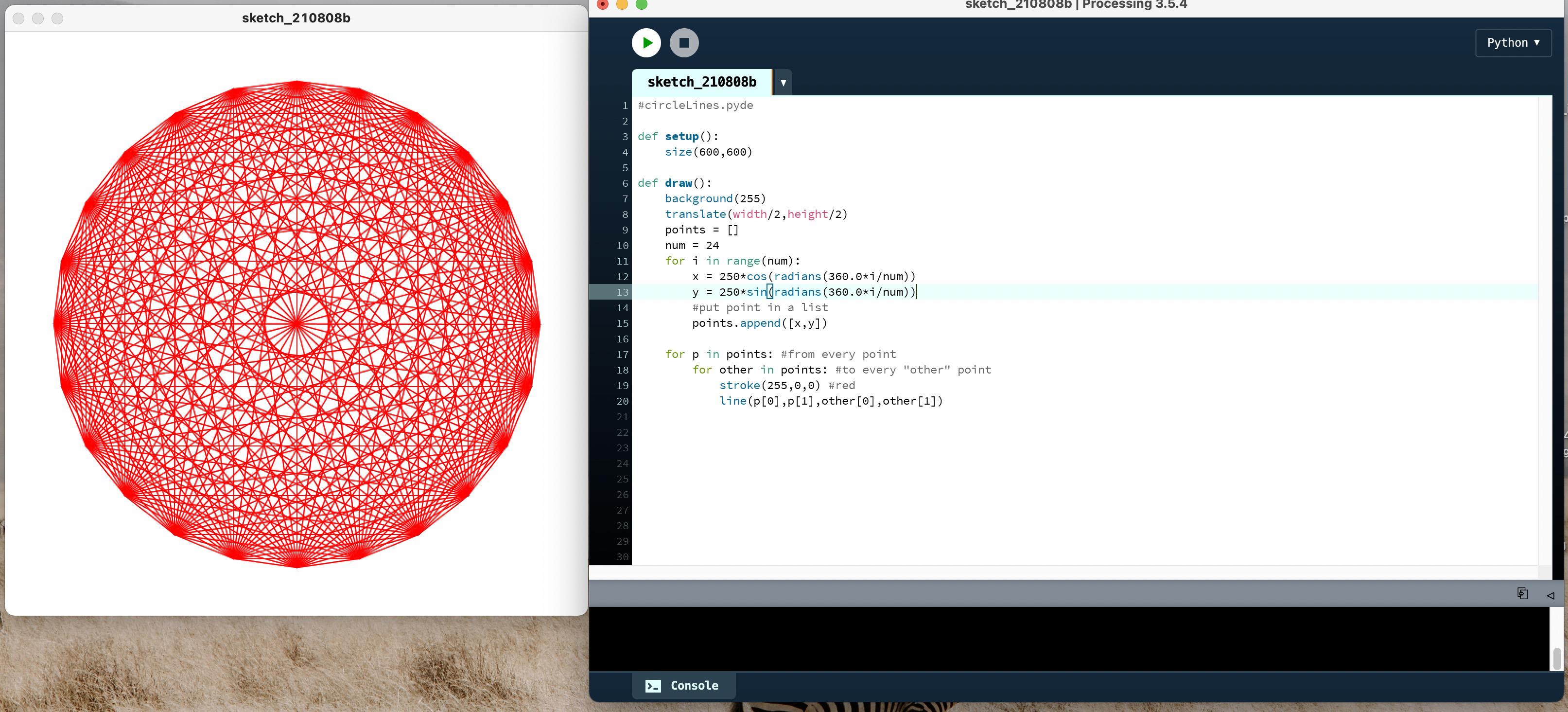
2.5 红色圆圈
def setup():
size(600,600)
def draw():
background(255)
translate(width/2,height/2)
points = []
num = 24
for i in range(num):
x = 250*cos(radians(360.0*i/num))
y = 250*sin(radians(360.0*i/num))
#put point in a list
points.append([x,y])
for p in points: #from every point
for other in points: #to every "other" point
stroke(255,0,0) #red
line(p[0],p[1],other[0],other[1])
执行结果如下图:
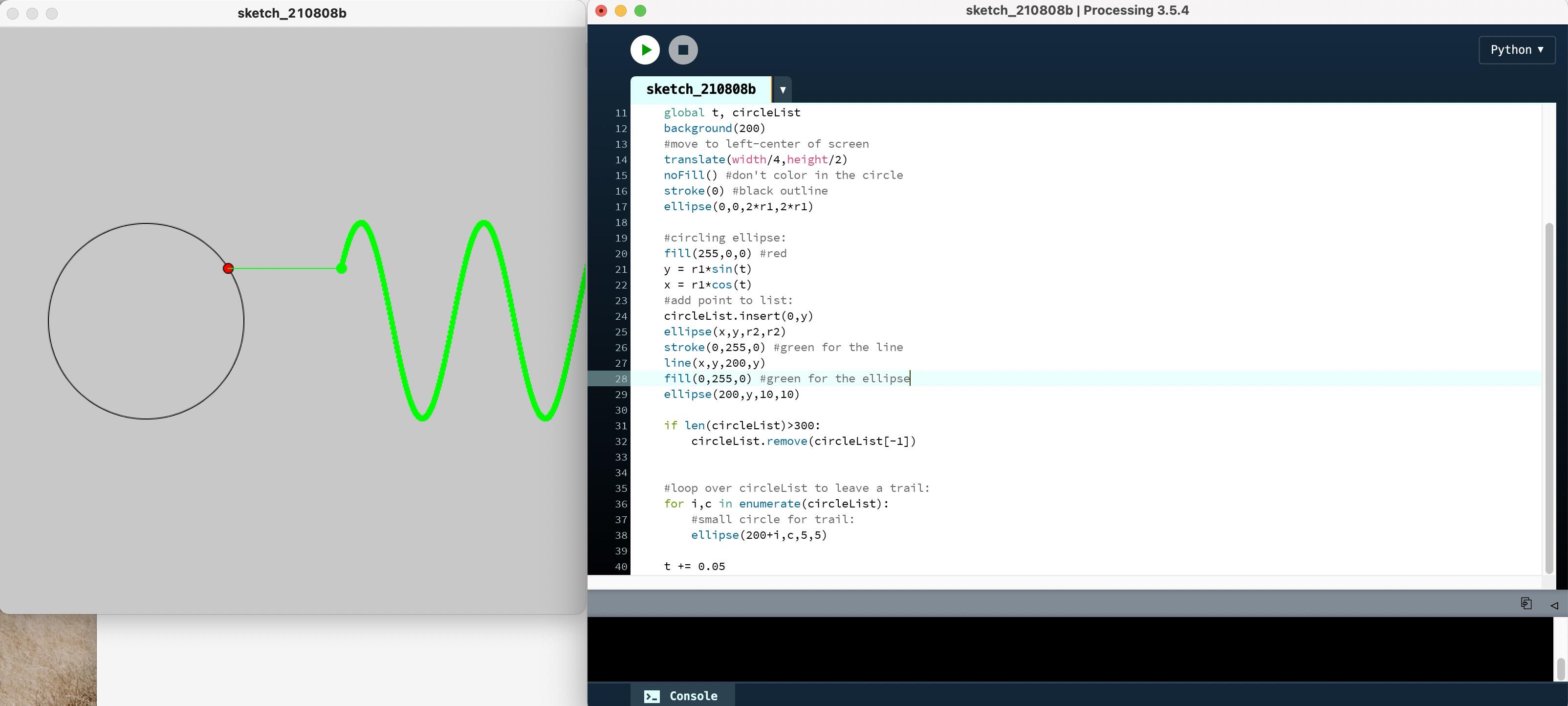
2.6 绘制正弦曲线
#CircleSineWave.pyde
r1 = 100 #radius of big circle
r2 = 10 #radius of small circle
t = 0 #time variable
circleList = []
def setup():
size(600,600)
def draw():
global t, circleList
background(200)
#move to left-center of screen
translate(width/4,height/2)
noFill() #don't color in the circle
stroke(0) #black outline
ellipse(0,0,2*r1,2*r1)
#circling ellipse:
fill(255,0,0) #red
y = r1*sin(t)
x = r1*cos(t)
#add point to list:
circleList.insert(0,y)
ellipse(x,y,r2,r2)
stroke(0,255,0) #green for the line
line(x,y,200,y)
fill(0,255,0) #green for the ellipse
ellipse(200,y,10,10)
if len(circleList)>300:
circleList.remove(circleList[-1])
#loop over circleList to leave a trail:
for i,c in enumerate(circleList):
#small circle for trail:
ellipse(200+i,c,5,5)
t += 0.05
执行结果如下图:
2.7 生成各种颜色
def setup():
size(600,600)
#rectMode(CENTER)
colorMode(HSB)
def draw():
#set background black
background(0)
#translate(5,5)
for x in range(20):
for y in range(20):
d = dist(30*x,30*y,mouseX,mouseY)
fill(0.5*d,360,360)
rect(30*x,30*y,25,25)
'''def draw():
#set background white
background(255)
translate(20,20)
textSize(12)
for i in range(10):
fill(20*i,255,255)
rect(31*i,0,25,25)
fill(0)
text(str(20*i),31*i+5,50)'''
执行结果如下:

2.8 绘制滚动的圆
t = 0.0 #time
dt = 0.01 #change in time
r = 50 #radius of circle
ground = 250 # y-val of line circle rolls on
x,Y = 0,ground-r #initial location of circle
v = 2.0 #horizontal velocity factor of circle
points = [] #list to store points
def setup():
size(942,300)
def draw():
global t,dt,r,ground,x,y,points
background(255) #white
strokeWeight(2)
stroke(150)
line(0,ground,width,ground) #line for the "ground"
noFill()
ellipse(x,Y,2*r,2*r)
#calculate position of drawing "dot"
dot = PVector(x+r*cos(v*TWO_PI*t+PI/2),Y+r*sin(TWO_PI*v*t+PI/2))
#save that position to the points list, to be drawn later
points.append(dot)
line(dot.x,dot.y,x,Y) #radial segment
fill(255,0,0) #red dot
ellipse(dot.x,dot.y,10,10)
#loop through the points list to draw the curve
for i,pt in enumerate(points):
if i < len(points) - 2:
stroke(255,0,0)
line(pt.x,pt.y,points[i+1].x,points[i+1].y)
x += TWO_PI*r*dt*v #update x-value by velocity
if x > width: #when the wheel gets all the way to the right
#noLoop() # uncomment this out to only run it once
x = 0.0 # reset position all the way to the left
points = [] # erase the trail
#println(x) #just for testing
#println(dot.x)
t += dt #increment the time variable
执行结果如下

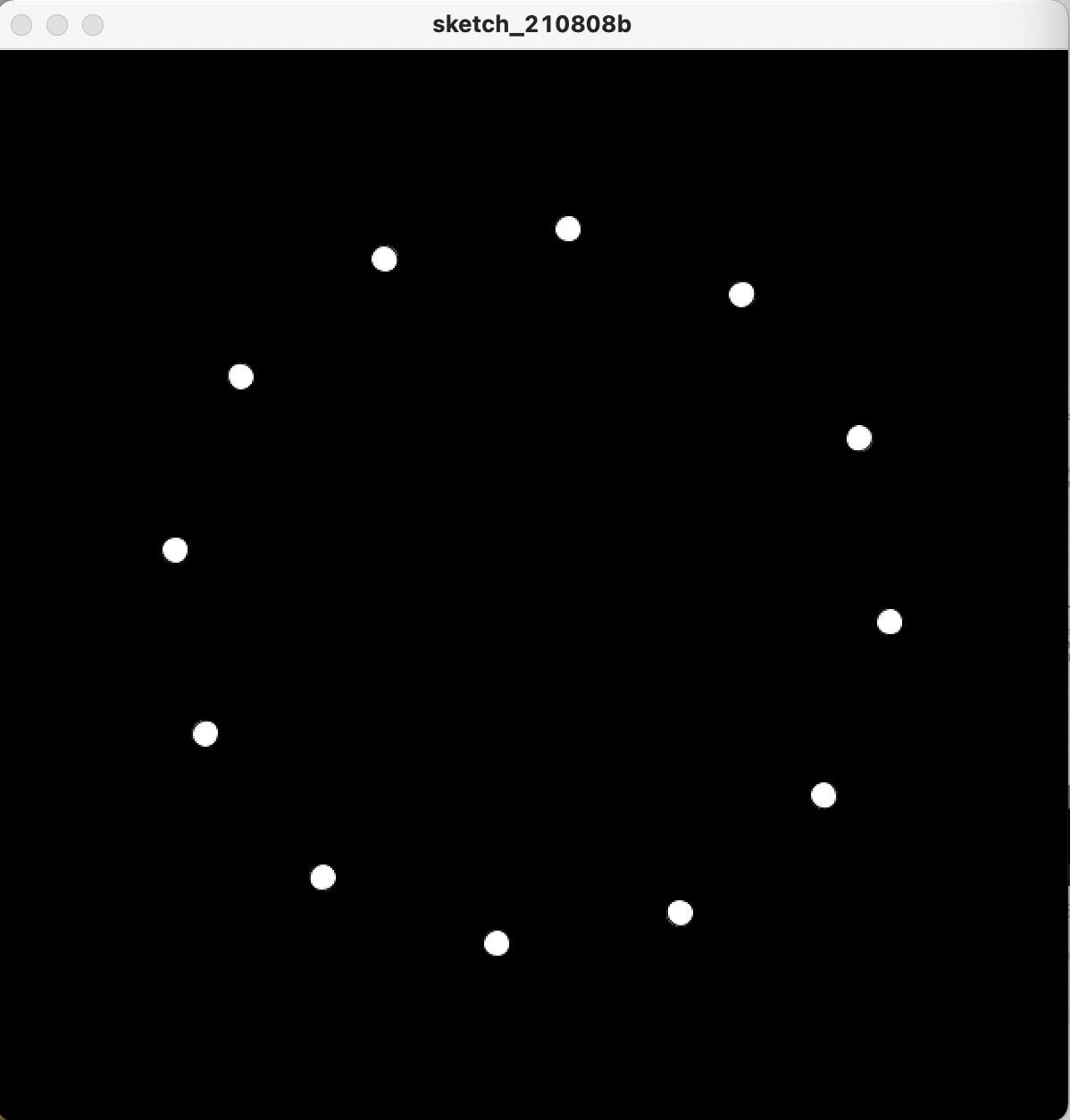
2.9 黑色背景白点圆
def setup():
size(600,600)
def draw():
background(0)
translate(width/2, height/2)
for i in range(12):
ellipse(200,20,15,15)
rotate(radians(360/12))
执行结果如下:
2. 10 无限圆圈放大
'''Web/Vortex of Circles
June 14, 2018'''
factor = 1.3
def setup():
size(600,600)
noFill()
stroke(255) #white lines
def draw():
global factor
background(0)
#Uncomment to display the value of factor
'''fill(255,0,0)
textSize(18)
text(factor,20,20)'''
factor -= 0.005
#move the mouse to vary the factor
#factor = map(mouseX,0,255,1,1.5)
translate(width/2,height/2)
vortex(500,100)
#uncomment these lines to save screenshots:
'''saveFrame('####.png')'''
if factor <= 1.07:
factor = 1.3 #noLoop() #will stop the loop
def vortex(r,level):
num = 30 #number of circles in one ring
if level > 0:
r2 = r/4.0
for i in range(num):
pushMatrix()
rotate(radians(360*i/float(num)))
translate(r,0)
st = map(r2,0,100,0,3) #make strokeWeight vary
strokeWeight(st)
noFill()
ellipse(0,0,r2,r2)
popMatrix()
rotate(TWO_PI/(2*num))
vortex(r/factor,level-1)#1.065,level-1)

以上是关于Processing介绍及几个python模式下的案例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章