关于 Linux中缓存清理的一些笔记
Posted 山河已无恙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于 Linux中缓存清理的一些笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面
- 一个群里看到有小伙伴问,之前也有遇到过。
- 给了参考意见之后感觉好像不是特别对,有点误人子弟:(。
- 所以总结下,博文内容涉及
- Linux内存
查看监控 缓存清理及参数介绍- 一个
定时清理的脚本
- Linux内存
归根结底,长得好,无论男女,怎么都是对的,长得不好看,大概就是万般皆罪。 ——烽火戏诸侯《剑来》
嗯,关于缓存清理,小伙伴一定不陌生,个人觉得通过修改drop_caches内核参数的形式来清理缓存,只能是在生产环境用于临时解决问题,本质还是要对应用进行分析,看看是什么原因导致的内存溢出等OOM问题,一般情况下,内存溢出可以通过交换分区来确定
当然,如果是因为业务量的原因,业务高峰,或者需要算力等正常原因,可以定期通过sync将缓存区没有写入数据写入磁盘,然后修改内核参数 drop_caches的值来清理缓存,或者通过新建交换分区调整swappiness交换分区频率来解决问题,如果虚机的话可以申请扩内存
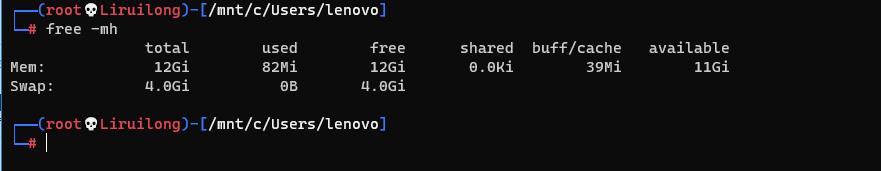
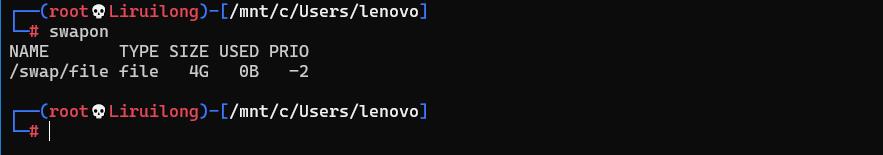
系统内存查看
| 系统内存查看 |
|---|
 |
 |
其中:
Mem:实际的内存 |Swap: 交换分区 |
total内存总数used已经使用的内存数free空闲的内存数shared多个进程共享的内存总额buff/Cache缓存的内存大小available可用内存
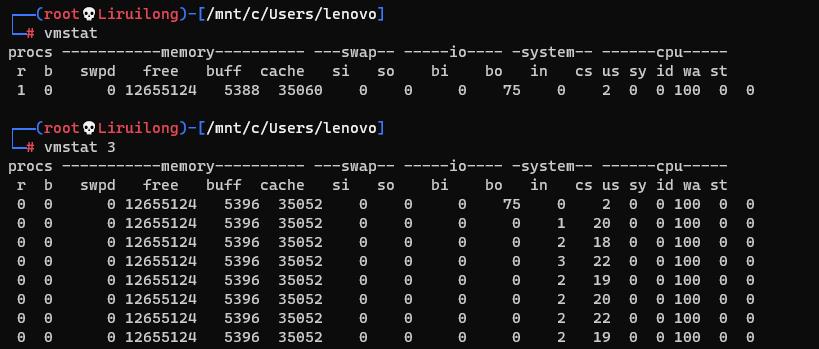
系统内存监控
| 系统内存监控 |
|---|
 |
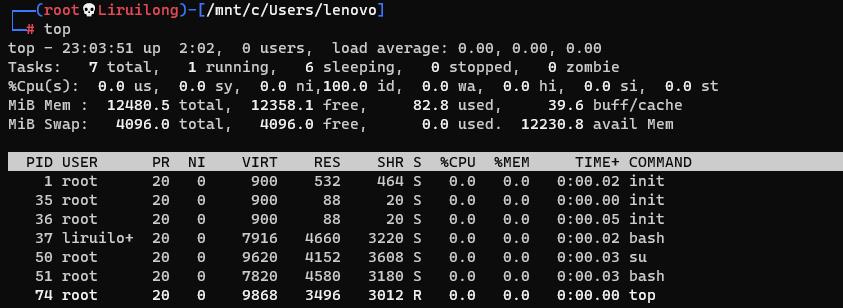 |
vmstat: 是一个内存监控工具,后面的数字为刷新频率 |top不多说
| vmstat | 列描述 |
|---|---|
free | 空闲的物理内存的大小。 |
buff | Linux/Unix系统是用来存储,目录里面有什么内容,权限等的缓存. |
cache | cache直接用来记忆我们打开的文件,给文件做缓冲,我本机大概占用300多M(这里是Linux/Unix的聪明之处,把空闲的物理内存的一部分拿来做文件和目录的缓存,是为了提高 程序执行的性能,当程序使用内存时,buffer/cached会很快地被使用。) |
修改drop_caches内核参数清理缓存
我们先看看帮助文档:内核参数的帮助文档查看方式
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ man -K drop_caches
--Man-- next: proc(5) [ view (return) | skip (Ctrl-D) | quit (Ctrl-C) ]
嗯,英文好的小伙伴可以看看
drop_caches
Writing to this will cause the kernel to drop clean caches, as well as
reclaimable slab objects like dentries and inodes. Once dropped, their
memory becomes free.
To free pagecache:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free reclaimable slab objects (includes dentries and inodes):
echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free slab objects and pagecache:
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
This is a non-destructive operation and will not free any dirty objects.
To increase the number of objects freed by this operation, the user may run
`sync' prior to writing to /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches. This will minimize the
number of dirty objects on the system and create more candidates to be
dropped.
This file is not a means to control the growth of the various kernel caches
(inodes, dentries, pagecache, etc...) These objects are automatically
reclaimed by the kernel when memory is needed elsewhere on the system.
Use of this file can cause performance problems. Since it discards cached
objects, it may cost a significant amount of I/O and CPU to recreate the
dropped objects, especially if they were under heavy use. Because of this,
use outside of a testing or debugging environment is not recommended.
You may see informational messages in your kernel log when this file is
used:
cat (1234): drop_caches: 3
These are informational only. They do not mean that anything is wrong
with your system. To disable them, echo 4 (bit 2) into drop_caches.
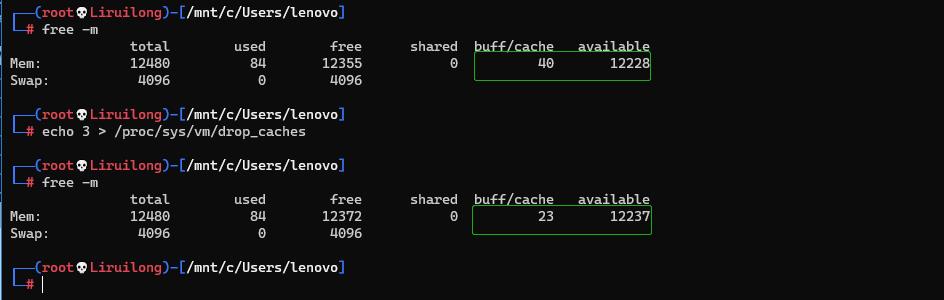
手动执行sync命令(描述:sync 命令运行 sync 子例程。如果必须停止系统,则运行sync 命令以确保文件系统的完整性。sync 命令将所有未写的系统缓冲区写到磁盘中,包含已修改的 i-node、已延迟的块 I/O 和读写映射文件)
┌──(root💀Liruilong)-[/mnt/c/Users/lenovo]
└─# sync
对缓存进行清理
┌──(root💀Liruilong)-[/mnt/c/Users/lenovo]
└─# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 12480 84 12355 0 40 12228
Swap: 4096 0 4096
┌──(root💀Liruilong)-[/mnt/c/Users/lenovo]
└─# echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
┌──(root💀Liruilong)-[/mnt/c/Users/lenovo]
└─# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 12480 84 12372 0 23 12237
Swap: 4096 0 4096
| 清理缓存 |
|---|
 |
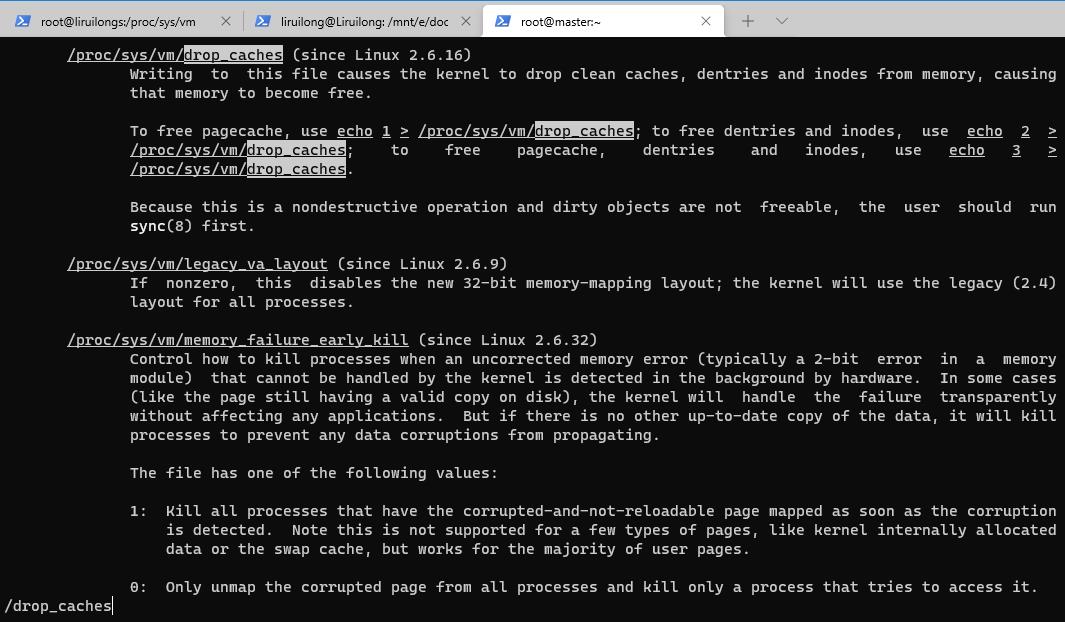 |
我们来看看文档
写入
drop_caches将导致内核丢弃干净的缓存,以及可回收的slab对象,如dentry和inode。一旦下降,他们内存得到释放。
具体的参数描述
To free pagecache:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free reclaimable slab objects (includes dentries and inodes):
echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free slab objects and pagecache:
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
使用此文件可能会导致性能问题。因为它丢弃了缓存对象,它可能会花费大量的I/O和CPU来重新创建掉落的物体,特别是大量使用时。由于这个原因,不建议在测试或调试环境之外使用。
在内核的文档里也说不建议在测试或调试环境之外使用,重建一些需要的缓存还是会消耗大量的I/O和CPU,同时这也不是一个必要操作,一些不用的缓存系统会自动的清理掉
一个SHELL
最后在和小伙伴分享一个清理缓存的shell
#!/bin/bash
#@File : clear.sh
#@Time : 2021/12/27 23:52:20
#@Author : Li Ruilong
#@Version : 1.0
#@Desc : 清除缓存的shell
#@Contact : 1224965096@qq.com
max=10000 # 缓存的最大值
clearLog=/var/log/clearfreelog
if [ ! -f $clearLog ];then
touch $clearLog
fi
filesize=$(du -m $clearLog | awk ' print $1 ')
echo "filesize=$filesize"
if [ $filesize -gt 300 ]; then
echo $clearLog
> $clearLog
fi
cache=$( free -m | grep Mem | awk 'print $(NF-1)')
time=$(date)
if [ $cache -gt $max ]
then
echo "$time cache=$cache flush cache start!" >> $clearLog
sync
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
echo "$time FreeMemory Success!" >> $clearLog
else
echo "$time cache=$cache Memory is normal" >> $clearLog
fi
以上是关于关于 Linux中缓存清理的一些笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章