阿昌教你看懂SpringMVC执行流程
Posted 阿昌喜欢吃黄桃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了阿昌教你看懂SpringMVC执行流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
阿昌教你看懂SpringMVC执行流程
一、前言
Hello呀!!!阿昌又来也 ╰(°▽°)╯!!!
SpringMVC的执行流程大家应该都挺熟悉的,但是真的去debug源码的人应该算少数,这里阿昌一直都想自己记录一下debug-SpringMVC的执行流程源码,做一下总结,今天终于有机会记录一下SpringMVC执行流程
同样我还是建议打开源码一起debug看!!!
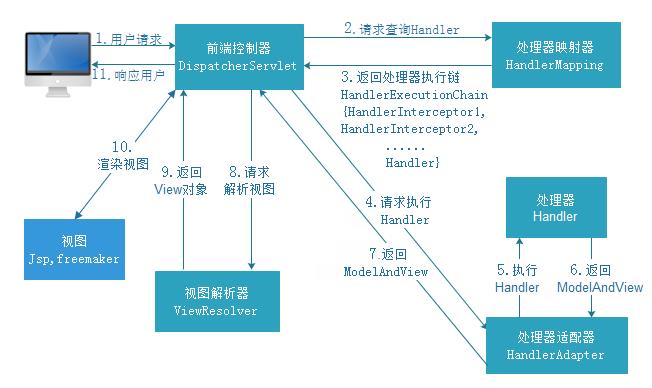
1、流程图
- 执行图
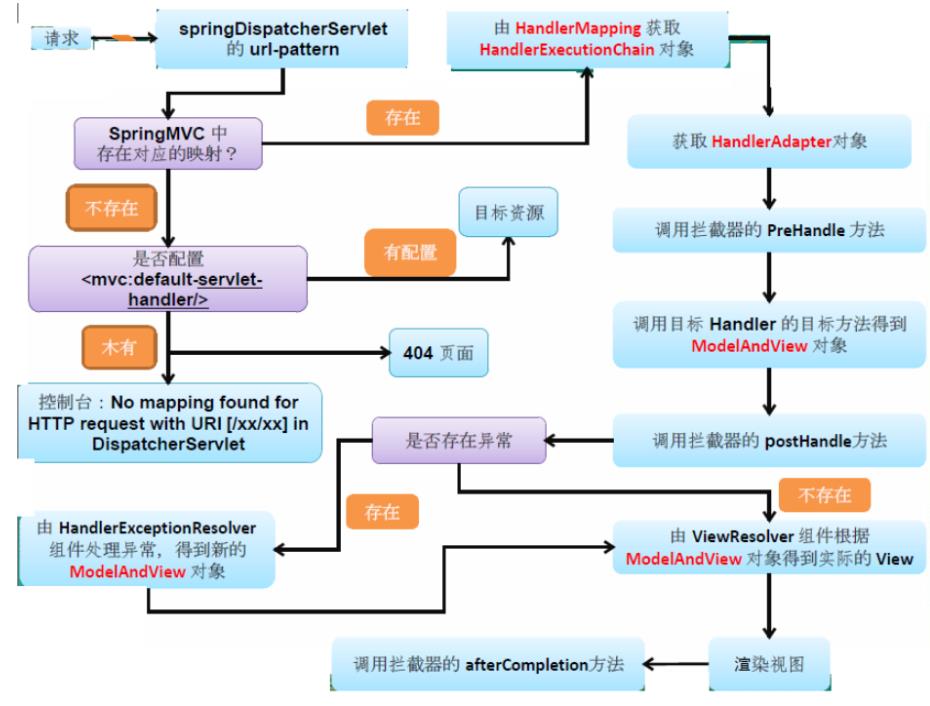
更详细一点:
2、基于版本
SpringBoot:2.4.1
3、前置的测试代码
这里debug只涉及到controller和Interceptor拦截器,且端口在8080 (๑•̀ㅂ•́)و✧
- TestController控制器
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class TestController
@GetMapping("/123")
public String test(@RequestParam String name, ServletResponse response)
System.out.println("name="+name);
System.out.println("response:"+response.isCommitted());
return "我是结果";
-
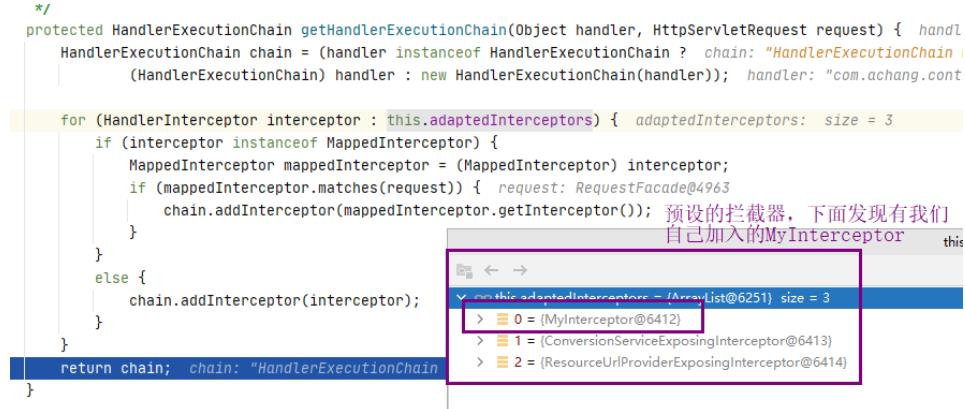
MyInterceptor拦截器
拦截器就涉及到了3个执行方法的
执行顺序- preHandle()
- postHandle()
- afterCompletion()
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception
System.out.println("MyInterceptor.preHandle");
System.out.println("response:"+response.isCommitted());
return true;
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception
System.out.println("MyInterceptor.postHandle");
System.out.println("response:"+response.isCommitted());
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception
System.out.println("MyInterceptor.afterCompletion");
System.out.println("response:"+response.isCommitted());
二、正文
这里我们启动服务,并用浏览器请求:http://localhost:8080/test/123?name=阿昌 (。・∀・)ノ゙
我们都知道对于SpringBoot中是自带Tomcat服务器的组件的,当一个请求发来,会被Tomcat处理,并转交给SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet类来做接下来的处理,他在SpringMVC中非常的重要,起着流程执行骨架的作用。
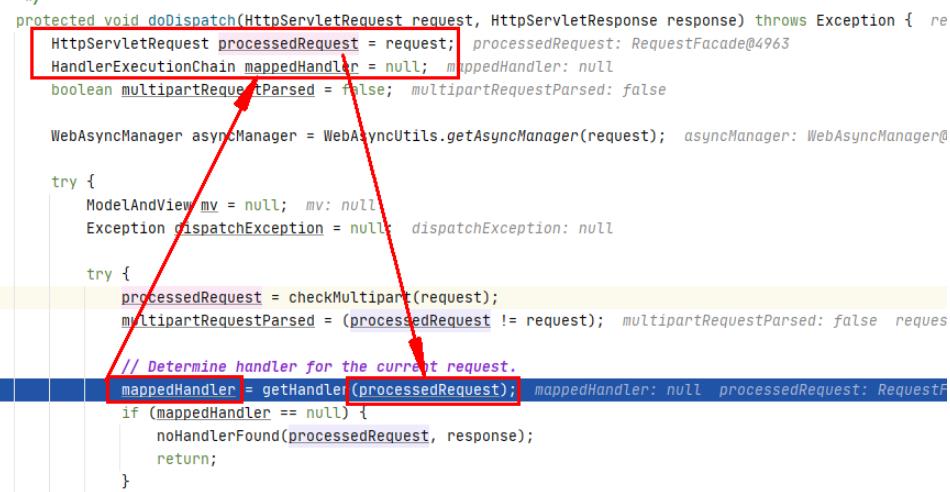
1、doDispatch
那首先Tomcat会经过流转调用去执行DispatcherServlet.doDispatch()方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null)
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
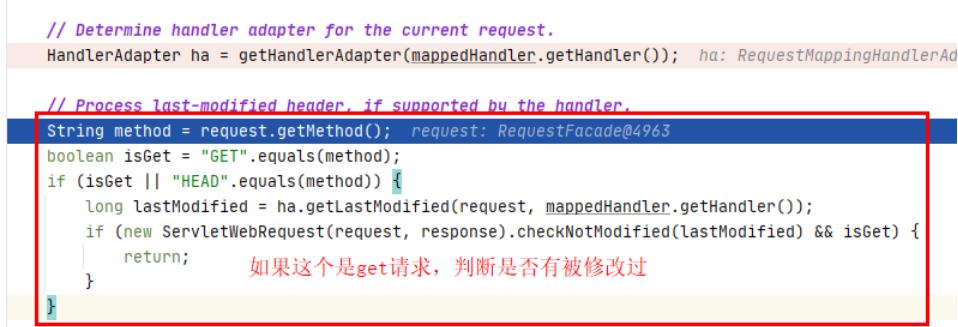
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method))
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet)
return;
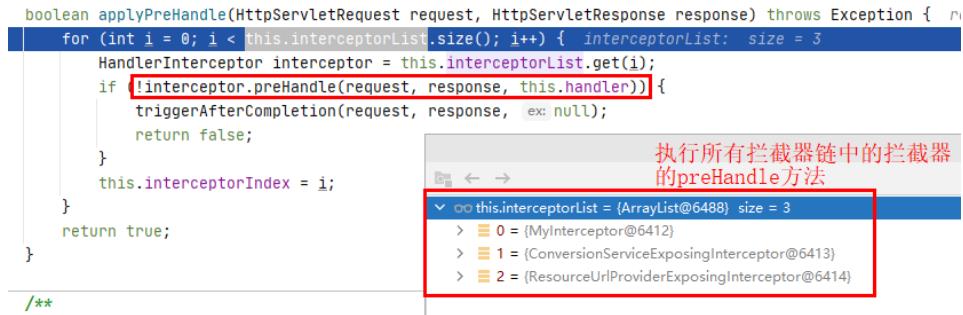
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response))
return;
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
return;
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
catch (Exception ex)
dispatchException = ex;
catch (Throwable err)
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
catch (Exception ex)
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
catch (Throwable err)
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
finally
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted())
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null)
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
else
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed)
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
2、getHandler
经过一些的初始化后,首先会去执行getHandler()方法,去寻找对应可以去处理这个请求的mappedHandler
-
mappedHandler对应的类型是HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain就是拦截器链

- getHandler()
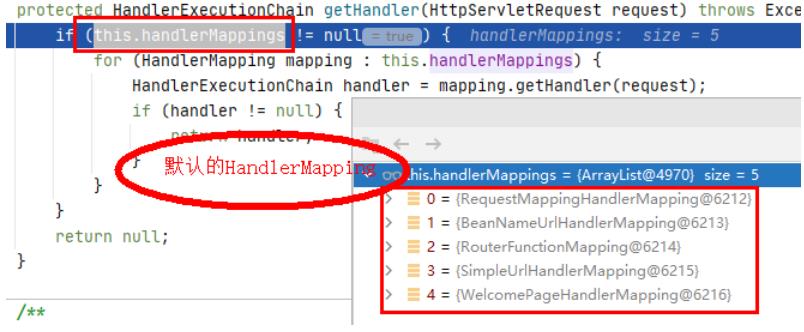
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
if (this.handlerMappings != null) //遍历预设的handlerMappings
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings)
//看看哪个能处理这次的请求
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null)
//找到了就返回这个handler(其实这个handler被包装了一层,HandlerExecutionChain)
return handler;
return null;
- mapping.getHandler(request)
mapping.getHandler(request)拿到的是被包装后的handlerMapping,也就是HandlerExecutionChain
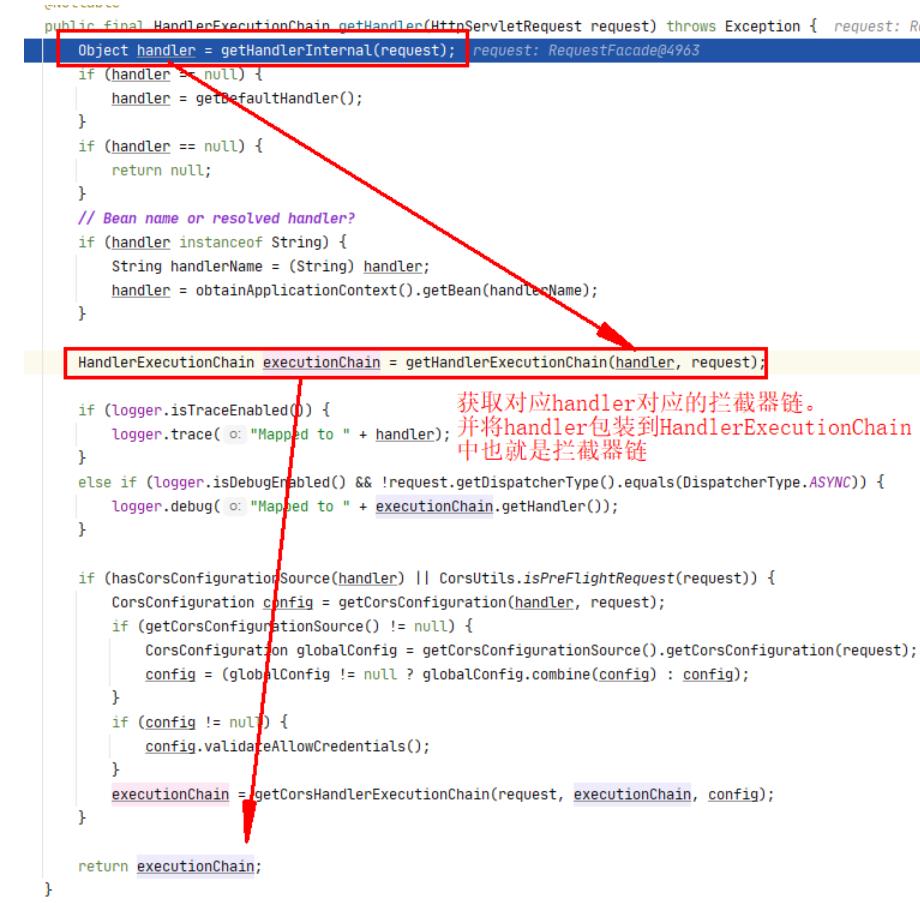
- getHandlerExecutionChain
- handlerMapping处理器
- 对应的拦截器
- 这次的请求request
封装成
HandlerExecutionChain
- getHandlerInternal
获取handlerMapping
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception
///这次请求的uri为:test/123
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);//获取这次请求的uri
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try
//根据这次请求和这个uri,判断获取对应能处理的HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
finally
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
4、小总结
执行这里就会遍历所有this.handlerMappings,获取请求的uri和请求,拿到对应能够处理这次请求的handlerMapping,并将拿到:↓
- handlerMapping处理器
- 对应的拦截器
- 这次的请求request
包装成一个HandlerExecutionChain。
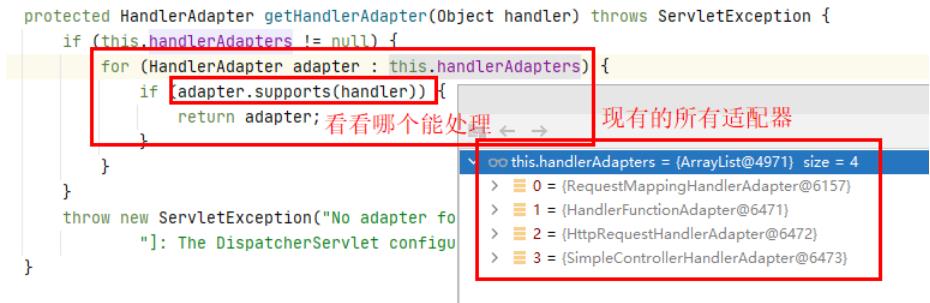
5、getHandlerAdapter()
上面我们获取到的对应的HandlerExecutionChain拦截器链(处理器handlermapping+拦截器链+这次请求)。
接下来就要获取对应这个handlermapping对应的的适配器HandlerAdapter
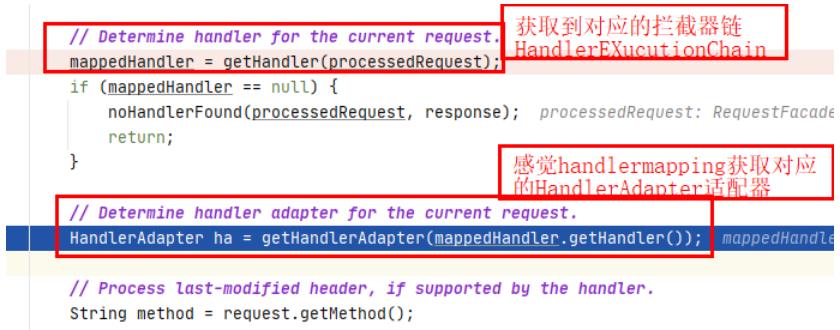
- getHandlerAdapter
里面的逻辑也很简单,遍历所有的handlerAdapter,看看哪个可以处理个handlerMapping,找到后返回
6、判断如果是get请求,是否被修改
7、applyPreHandle()
这里就是上面流程图的执行器链中的一个执行时机之一applyPreHandle,他会去执行所有拦截器链中的每个拦截的applyPreHandle()方法
- 我们自定义的拦截器
MyInterceptor.preHandle
- 执行所有拦截器链中的每个拦截的
applyPreHandle()方法 - 每执行成功一个
this.interceptorIndex就会给赋上i的值(拦截器变量的索引)
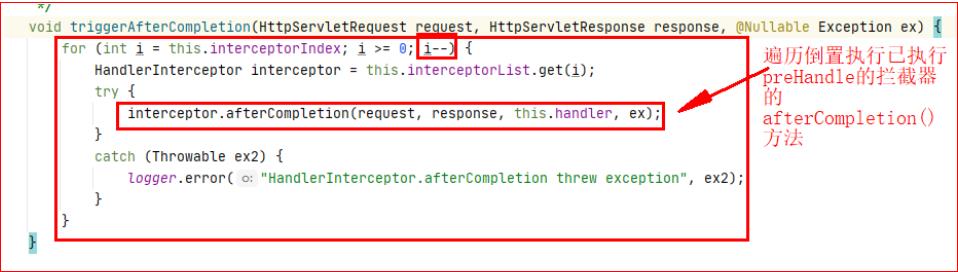
-
当某个拦截器中的
preHandle()返回了false,就会触发执行triggerAfterCompletion -
triggerAfterCompletion
这里因为上面每次执行preHandle都会记录一下拦截器变量的索引
所以如果有一个preHandle执行返回了false,那么这里就会倒置的去执行已经执行的拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
8、handle
ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
这里是真正执行我们这次请求处理的controller对应的方法
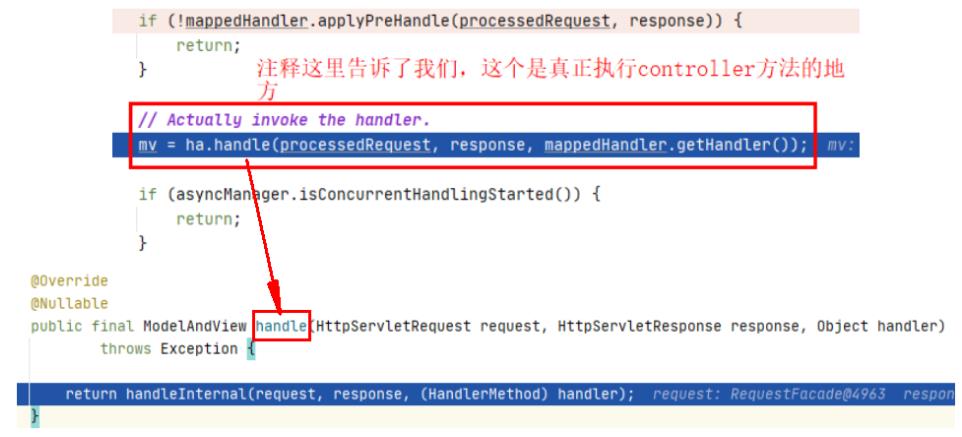
那阿昌这里就好奇了,他是如何执行,并拿到对应的结果的,这个结果封装在哪里???
- handleInternal()
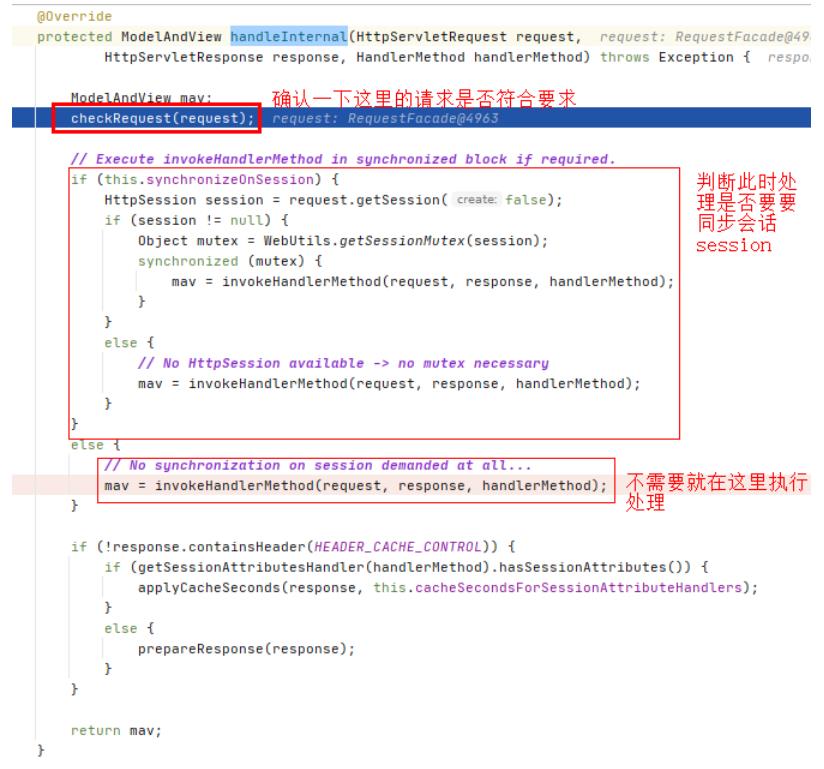
- invokeHandlerMethod()
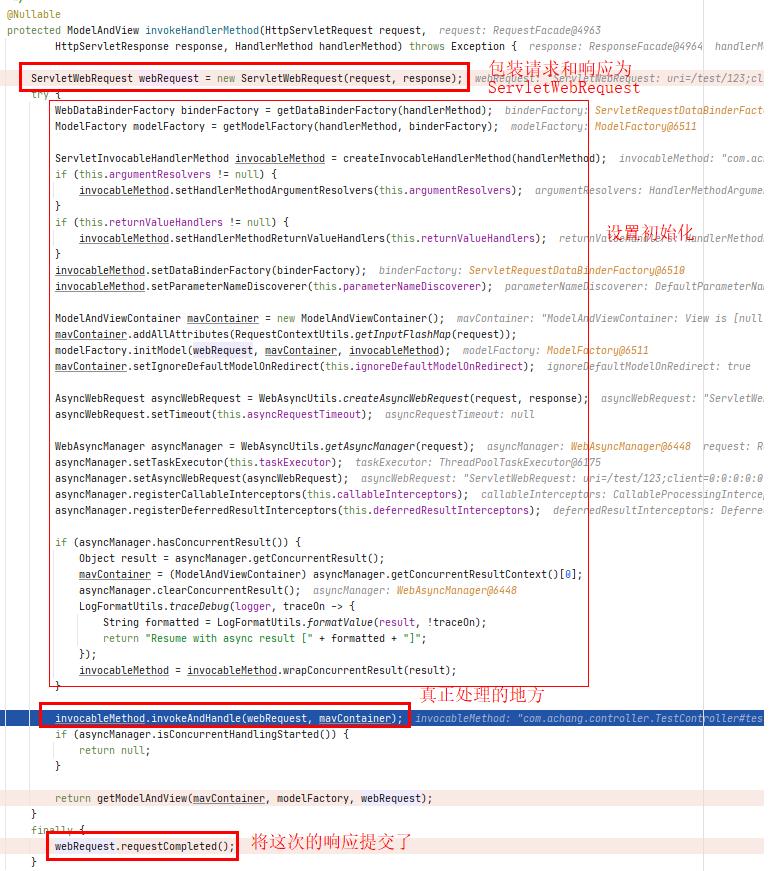
- invokeAndHandle()
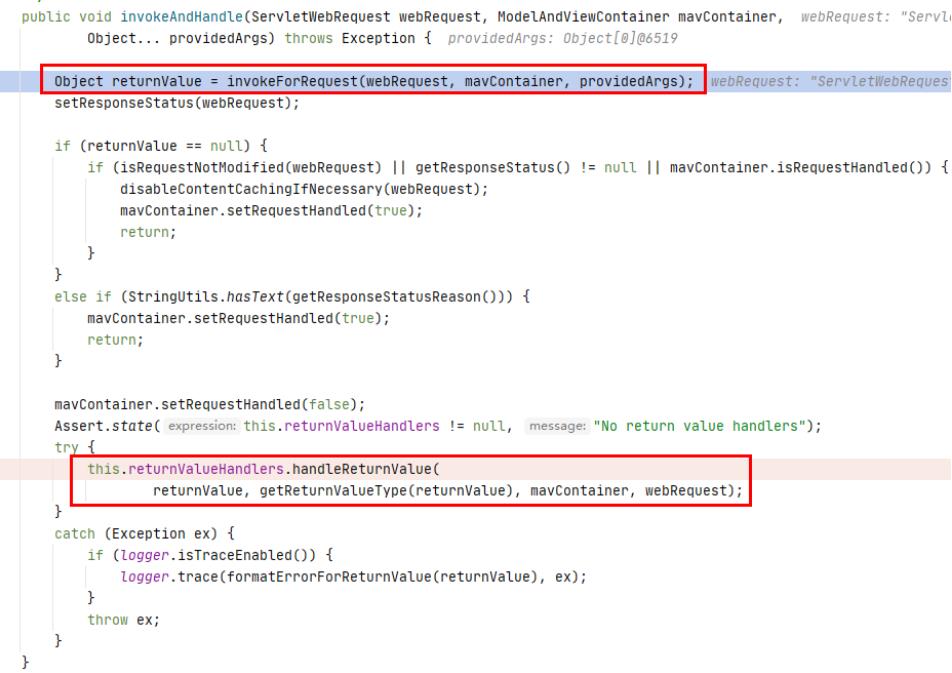
- invokeForRequest
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception
//获取这次请求的参数
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
//执行对应的controller方法
return doInvoke(args);
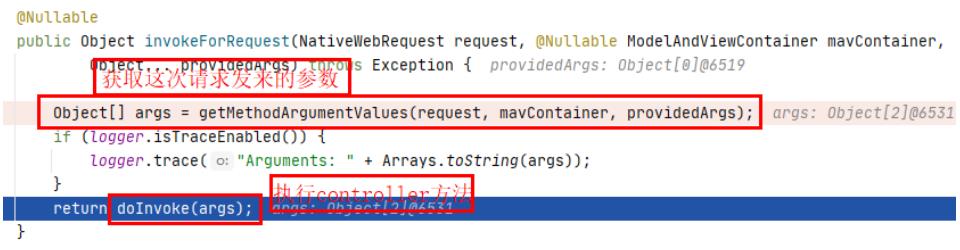
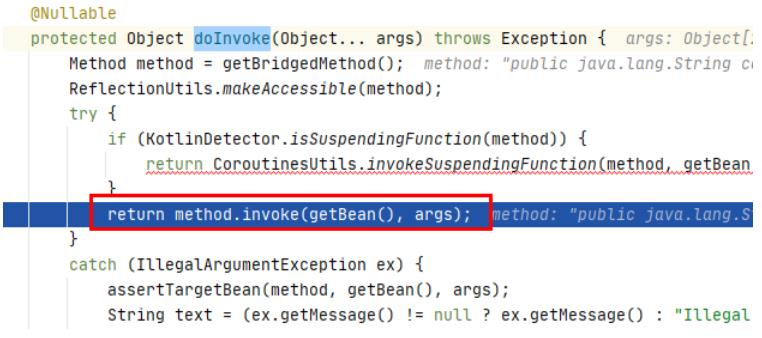
- doInvoke
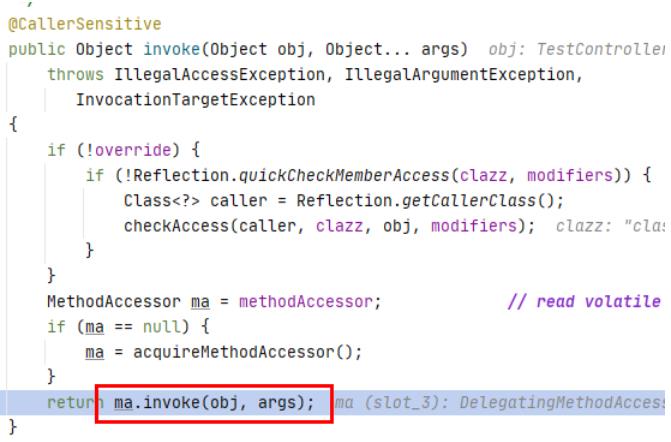
这里就是controller的代理了,对应的代理设计模式
- invoke
那上面拿到执行了controller的方法后,拿到的结果是如何处理的呢?
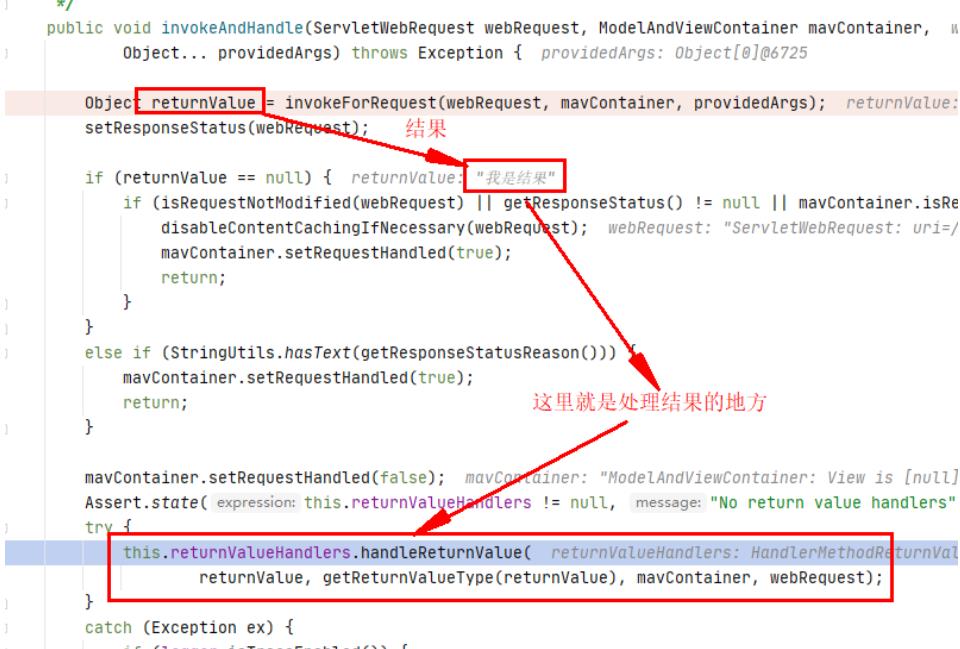
- handleReturnValue
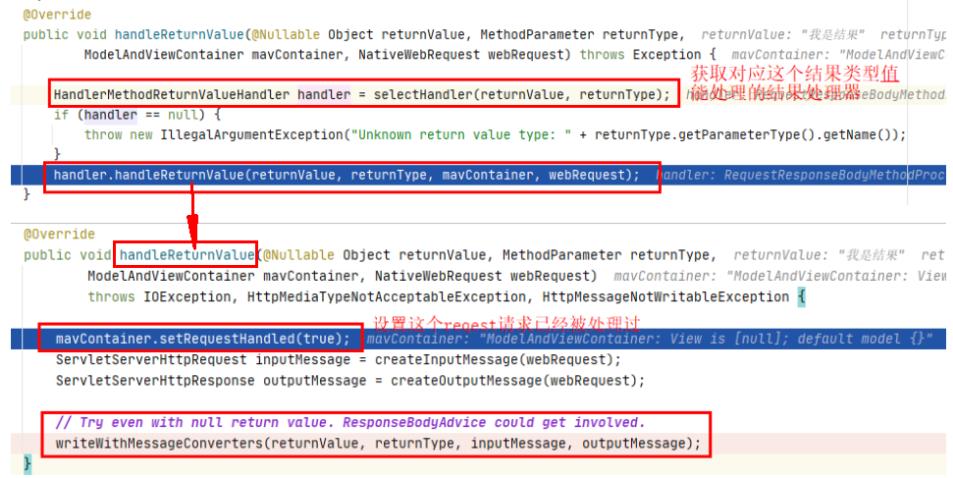
- writeWithMessageConverters
将处理响应的结果,写入响应中,这个方法很长,对应与servletHttp响应的介绍
protected <T> void writeWithMessageConverters(@Nullable T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException
Object body;
Class<?> valueType;
Type targetType;
if (value instanceof CharSequence)
body = value.toString();
valueType = String.class;
targetType = String.class;
else
body = value;
valueType = getReturnValueType(body, returnType);
targetType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveType(getGenericType(returnType), returnType.getContainingClass());
if (isResourceType(value, returnType))
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes");
if (value != null && inputMessage.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.RANGE) != null &&
outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() == 200)
Resource resource = (Resource) value;
try
List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange();
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value());
body = HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource);
valueType = body.getClass();
targetType = RESOURCE_REGION_LIST_TYPE;
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex)
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE, "bytes */" + resource.contentLength());
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE.value());
MediaType selectedMediaType = null;
MediaType contentType = outputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType();
boolean isContentTypePreset = contentType != null && contentType.isConcrete();
if (isContentTypePreset)
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Found 'Content-Type:" + contentType + "' in response");
selectedMediaType = contentType;
else
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
List<MediaType> acceptableTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
List<MediaType> producibleTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, targetType);
if (body != null && producibleTypes.isEmpty())
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
List<MediaType> mediaTypesToUse = new ArrayList<>();
for (MediaType requestedType : acceptableTypes)
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleTypes)
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType))
mediaTypesToUse.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
if (mediaTypesToUse.isEmpty())
if (body != null)
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleTypes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("No match for " + acceptableTypes + ", supported: " + producibleTypes);
return;
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypesToUse);
for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypesToUse)
if (mediaType.isConcrete())
selectedMediaType = mediaType;
break;
else if (mediaType.isPresentIn(ALL_APPLICATION_MEDIA_TYPES)
