:栈 -- 栈的介绍实现方式(链表数组)应用场景快速入门(使用数组模拟栈的使用回文数)栈实现计算器
Posted CodeJiao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了:栈 -- 栈的介绍实现方式(链表数组)应用场景快速入门(使用数组模拟栈的使用回文数)栈实现计算器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 栈
1.1 栈的介绍
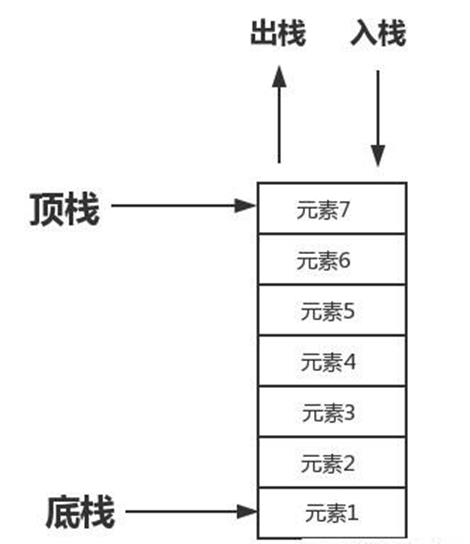
栈是限制插入和删除只能在一个位置上进行的线性表。其中,允许插入和删除的一端位于表的末端,叫做栈顶(top),不允许插入和删除的另一端叫做栈底(bottom)。对栈的基本操作有 PUSH(压栈)和 POP (出栈),前者相当于表的插入操作(向栈顶插入一个元素),后者则是删除操作(删除一个栈顶元素)。栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,最先被删除的是最近压栈的元素,可以理解为弹夹,弹夹最下面有一个弹簧,负责把弹夹最上面的子弹上膛。
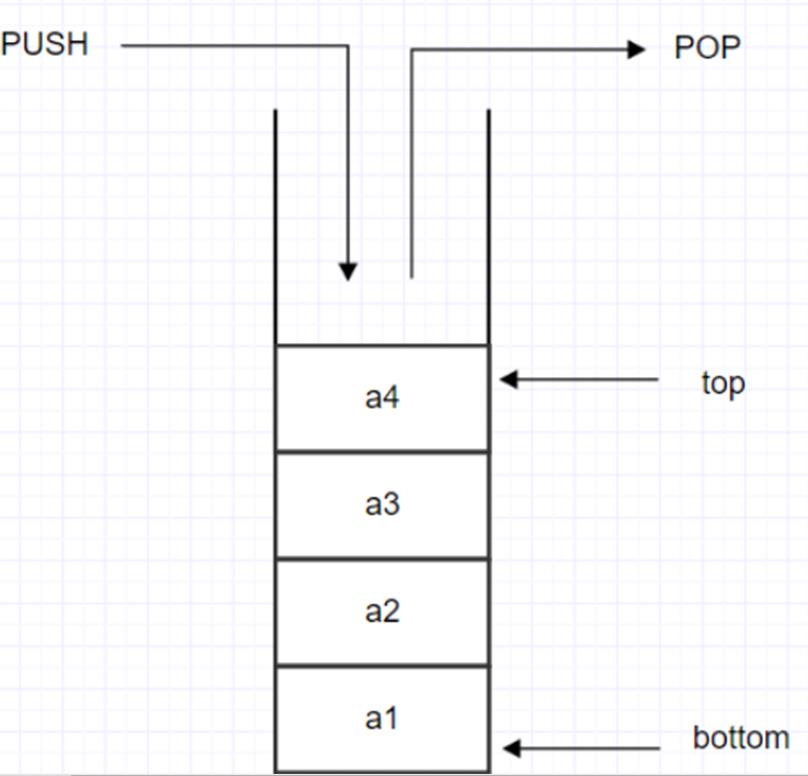
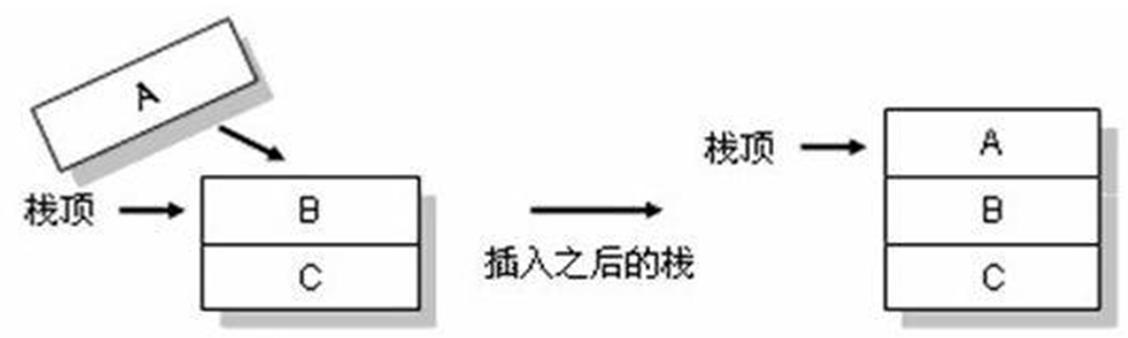
压栈(入栈):
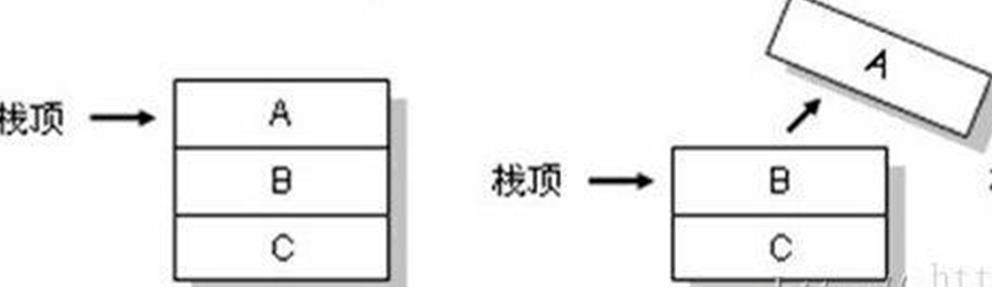
弹栈(出栈):
1.2 栈的实现方式
由于栈是一个表,因此任何实现表的方法都可以用来实现栈。主要有两种方式,链表实现和数组实现。
1.2.1 链表
可以使用单链表来实现栈。通过在表顶端插入一个元素来实现 PUSH,通过删除表顶端元素来实现 POP。使用链表方式实现的栈又叫动态栈。动态栈有链表的部分特性,即元素与元素之间在物理存储上可以不连续,但是功能有些受限制,动态栈只能在栈顶处进行插入和删除操作,不能在栈尾或栈中间进行插入和删除操作。
1.2.2 数组
栈也可以用数组来实现。使用数组方式实现的栈叫静态栈。
1.3 栈的应用场景

1.4 栈的快速入门
1.4.1 使用数组模拟栈的使用
package data_structure;
public class ArrayStack
/**
* 栈的大小
*/
private final int maxStack;
/**
* 数组用来模拟栈
*/
private final int[] stack;
/**
* 表示栈顶所在的位置,默认情况下如果没有数据时,使用-1
*/
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxStack)
this.maxStack = maxStack;
stack = new int[maxStack];
/**
* 判断是否已经满栈
*/
public boolean isFull()
return this.top == this.maxStack - 1;
/**
* 判断栈是否是空栈
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
return this.top == -1;
/**
* 压栈
*/
public void push(int val)
//是否已经栈满
if (isFull())
throw new RuntimeException("此栈已满");
top++;
stack[top] = val;
/*
* 弹栈
*/
public int pop()
//如果栈中是空
if (isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("空栈,未找到数据");
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
/**
* 查看栈中所有元素
*/
public void list()
//是否是空栈
if (isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("空栈,未找到数据");
for (int i = 0; i < stack.length; i++)
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\\n", i, stack[i]);
/**
* 栈中元素存在的个数
*/
public int length()
return this.top + 1;
/**
* 获取栈顶数据(知识获取, 不是弹出)
*/
public int peek()
return this.stack[top];
/**
* 获取栈的容量
*/
public int stackLength()
return this.stack.length;
1.4.2 回文数
回文:回文指的是正读和反读都一样的字符串,如"aba","abba"等。
示例代码:
package data_structure;
public class Palindrome
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println(isPalindrome("aba"));
System.out.println(isPalindrome("hello"));
/**
* 需求:通过上面以数组模拟栈来判断一个字符串是否是一个回文数据
*/
public static boolean isPalindrome(String val)
/*
* 这里的 ArrayStack 是上面我们自己定义的。
* 初始化栈对象
*/
ArrayStack arrayStack = new ArrayStack(10);
/*
* 获取字符串长度
*/
int strLength = val.length();
//把字符串数据逐次获取字符压栈至数组中
for (int i = 0; i < strLength; i++)
arrayStack.push(val.charAt(i));
/*
* 获取
*/
String newVal = "";
int stackLength = arrayStack.length();
for (int i = 0; i < stackLength; i++)
//是否是一个空栈
if (!arrayStack.isEmpty())
char pop = (char) arrayStack.pop();
newVal = newVal + pop;
return val.equals(newVal);
运行结果:

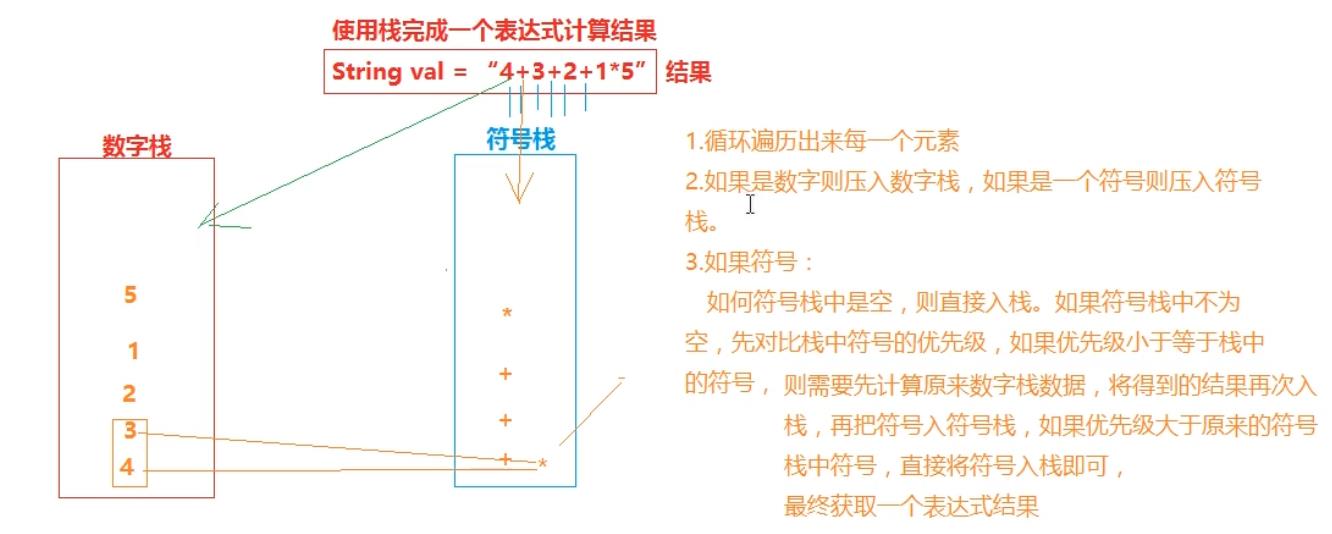
1.5 栈实现计算器

ArrayStack.java
package data_structure;
public class ArrayStack
/**
* 栈的大小
*/
private final int maxStack;
/**
* 数组用来模拟栈
*/
private final int[] stack;
/**
* 表示栈顶所在的位置,默认情况下如果没有数据时,使用-1
*/
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxStack)
this.maxStack = maxStack;
stack = new int[maxStack];
/**
* 判断是否已经满栈
*/
public boolean isFull()
return this.top == this.maxStack - 1;
/**
* 判断栈是否是空栈
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
return this.top == -1;
/**
* 压栈
*/
public void push(int val)
//是否已经栈满
if (isFull())
throw new RuntimeException("此栈已满");
top++;
stack[top] = val;
/*
* 弹栈
*/
public int pop()
//如果栈中是空
if (isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("空栈,未找到数据");
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
/**
* 查看栈中所有元素
*/
public void list()
//是否是空栈
if (isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("空栈,未找到数据");
for (int i = 0; i < stack.length; i++)
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\\n", i, stack[i]);
/**
* 栈中元素存在的个数
*/
public int length()
return this.top + 1;
/**
* 判断是否是一个运算符 + - * /
*/
public boolean isOperation(char v)
return v == '+' || v == '-' || v == '*' || v == '/';
/**
* 判断运算符优先级 使用数字表示优先级大小,数字越大的优先级越大
*/
public int priority(int operation)
if (operation == '*' || operation == '/')
return 1;
else if (operation == '+' || operation == '-')
return 0;
else
return -1;
/**
* 获取栈顶数据
*/
public int peek()
return this.stack[top];
/**
* 获取栈的容量
*/
public int stackLength()
return this.stack.length;
/**
* 计算两个数进行运算后的结果
* 2-3
* 3:num1(因为3先弹出来),2:num2
*/
public int calculate(int num1, int num2, int operation)
//计算结果
int result = 0;
switch (operation)
case '+':
result = num2 + num1;
break;
case '-':
result = num2 - num1;
break;
case '*':
result = num2 * num1;
break;
case '/':
result = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
return result;
TestCalculator.java
package data_structure;
public class TestCalculator
public static void main(String[] args)
String str = "4+3*2-1";
/*
* 1.需要遍历字符串,获取每一个字符
* 2.判断当前字符是一个运算符还是一个数字
* 3.把数字存放在数字栈中,把运算符放在运算符栈
* 4.运算符栈: 如果是一个空栈,那么直接运算符入栈,如果运算符栈中已经了其他运算符
* 就需要先对比运算符优先级,新进来的运算符如果小于等于原栈中运算符,那么需要把原运算符弹栈
* ,数字栈中数字进行弹栈,进行运算,运算后的结果重新放入数字栈中,新运算符入栈。
* 如果新运算符优先级大于原符号栈中运算符,那么新的符号直接入栈
*/
ArrayStack numStack = new ArrayStack(10);
ArrayStack symbolStack = new ArrayStack(10);
/*
* 获取字符串长度
*/
int temp1 = 0;
int temp2 = 0;
int symbolChar = 0;
int result = 0;
int length = str.length();
StringBuilder values = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) //33+44
char c = str.charAt(i);
/*
* 是否是一个运算符
*/
if (symbolStack.isOperation(c))
/*
* 如果不是一个空符号栈
*/
if (!symbolStack.isEmpty())
//比较运算符的优先级
if (symbolStack.priority(c) <= symbolStack.priority(symbolStack.peek()))
/*
* 1.去符号栈中获取栈顶的符号
* 2.去数字栈中获取两个数字
*/
temp1 = numStack.pop();
temp2 = numStack.pop();
symbolChar = symbolStack.pop();
result = numStack.calculate(temp1, temp2, symbolChar);
//把运算结果再次放入数字栈中
numStack.push(result);
//把当前符号压入符号栈中
symbolStack.push(c);
else
//如果是空符号栈,讲运算符直接压栈
symbolStack.push(c);
else
//比如 33+44
values.append(c);
if (i == length - 1)
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(values.toString()));
else
char data = str.substring(i + 1, i + 2).charAt(0);
if (symbolStack.isOperation(data))
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(values.toString()));
values = new StringBuilder();
while (!symbolStack.isEmpty())
temp1 = numStack.pop();
temp2 = numStack.pop();
symbolChar = symbolStack.pop();
result = numStack.calculate(temp1, temp2, symbolChar);
numStack.push(result);
int res = numStack.pop();
System.out.println("结果是: " + res);
运行结果:

以上是关于:栈 -- 栈的介绍实现方式(链表数组)应用场景快速入门(使用数组模拟栈的使用回文数)栈实现计算器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章