数据结构(Java)——No4.常见的排序算法
Posted 风口上的猪A
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构(Java)——No4.常见的排序算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
常见的七种排序算法
引言
何谓排序?就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作,平常的上下文中,如果提到排序,通常指的是排升序,且通常意义上指的都是原地排序.在
《大话数据结构》这本书中将排序算法分为两个类别:内排序和外排序,这里我主要介绍内排序的多种方法。
1.冒泡排序
思路
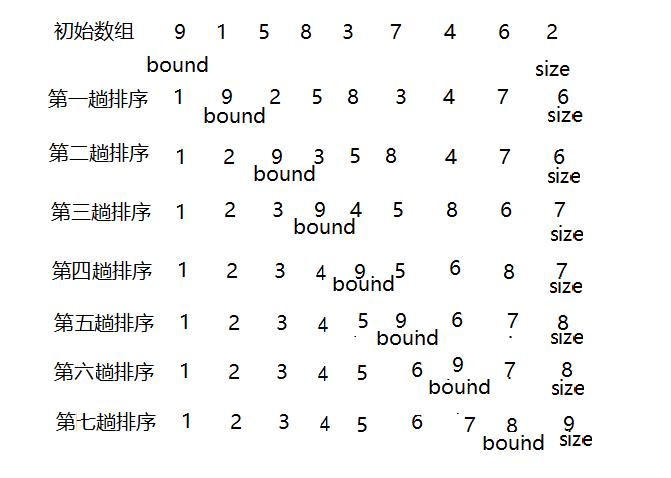
冒泡排序是一种交换排序:在无序区间,两两比较相邻记录的关键字,将最大的数冒泡到无序区间的最后,持续这个过程,直到数组整体有序。

接下来就按照上面的方法将数组进行排序,得到七趟排序结果。
代码
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-10-04 22:56
* @description:冒泡排序
*/
public class TestSort5
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array)
for (int bound = 0; bound < array.length; bound++)
//[0,bound]已排序区间
//[bound,size] 待排序区间
for (int cur = array.length - 1; cur > bound; cur--)
if (array[cur - 1] > array[cur])
swap(array, cur - 1, cur);
public static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j)
int tmp=array[i];
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=tmp;
public static void main (String[]args)
int[] arr = 9, 1, 5, 8, 3, 7, 4, 6, 2;
bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N^2);空间复杂度:O(1);稳定排序
2.插入排序
思路
整个区间被分为有序区间[0,bound],无序区间[bound,size],每次选择无序区间的第一个元素,在有序区间内选择合适位置插入

代码
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-09-30 23:50
* @description:插入排序算法
*/
public class TestSort
//升序排序
public static void insertSort(int[] array)
//通过bound来划分两个区间
//[0,bound]已排序区间
//[bound,size]待排序区间
for (int bound = 1; bound < array.length; bound++)
//bound=1,是因为第一个元素相当于是一个已经排好的数组
int v=array[bound];
int cur=bound-1;
for (; cur >=0 ; cur--)
//从排序好的数组里面最后一个元素往前遍历比较
if (array[cur] > v)
//与排序区间的后一个值进行比较
array[cur+1]=array[cur];
//把区间之间的大小关系按照升序排列
else
//此时说明不用排序了,找到了位置
break;
array[cur+1]=v;
//更新v的值,继续进行比较
public static void main(String[] args)
int[] arr=9,1,5,8,3,7,4,6,2;
insertSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N^2);空间复杂度:O(1);稳定排序
3.希尔排序
思路
其实差不多就是进阶版的插入排序,先分组,针对每个组进行插入排序,逐渐缩小组的个数,最终组的个数就接近有序了.

代码
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-10-03 22:42
* @description:希尔排序算法
*/
public class TestSort2
public static void shellSort(int[] array)
int gap= array.length/2;
while (gap > 1)
//需要循环进行分组插排
insertSortGap(array,gap);
gap=gap / 2;
insertSortGap(array,1);
private static void insertSortGap(int[] array, int gap)
//与插入排序很相似
//通过bound来划分两个区间
//[0,bound]已排序区间
//[bound,size]待排序区间
for (int bound = gap; bound < array.length; bound++)
//bound=gap,此循环要把所有组都处理完毕
//先处理第一组的第一个元素和第二个元素,在处理第二组的第一个元素和第二个元素,以此类推
int v = array[bound];
int cur = bound - gap;//分组排序就与插排的-1不同了
//即找同组中的数字进行比较
for (; cur >= 0; cur -= gap)
//找到同组中的相邻元素,同组元素的下标插值就是gap
if (array[cur] > v)
//与排序区间的后一个值进行比较
array[cur + gap] = array[cur];
//把区间之间的大小关系按照升序排列
else
//此时说明不用排序了,找到了位置
break;
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:理论极限是O(N ^ 1.3)如果按照size/2,size/4,…1这种方式设定gap序列,此时就是O(N^2);空间复杂度:O(1);稳定性:不稳定,分组的时候可能把相同的值分到不同组中,也就无法保证相对顺序
4.选择排序
思路
基于打擂台的思想,每次从数组中找出最小值,然后把最小值放到合适的位置上
代码
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-10-03 23:19
* @description:选择排序算法
*/
public class TestSort3
public static void selectSort(int[] array)
for (int bound=0;bound < array.length;bound++)
//以bound位置的元素作为擂主,循环从待排序区间取出元素与擂主比较
//如果打擂成功,就与擂主交换
for (int cur=bound+1;cur < array.length;cur++)
if (array[cur] < array[bound])
int tmp=array[cur];
array[cur]=array[bound];
array[bound]=tmp;
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N ^ 2);空间复杂度:O(1);稳定性:不稳定排序
5.堆排序
思路
基本原理:选择排序,只是不再使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数.如果将数组按照降序排序:把数组建立大堆,取出最小值放到另外一个数组中,循环取堆顶元素查到新数组即可;如果将数组按照升序排序:建立一个大堆,把堆顶元素和堆的最后一个元素互换,把最后一个元素删除,再从堆顶向下调整

代码
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-10-03 23:27
* @description:堆排序
*/
public class TestSort4
public static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j)
int tmp=array[i];
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=tmp;
public static void heapSort(int[] array)
//先建立堆
createHeap(array);
//循环把堆顶元素交换到最后,并调整堆
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
//交换堆顶元素和对的最后一个元素
//对俄的元素个数相当于array.length
//堆得最后一个元素下标array.length-1-i
swap(array,0, array.length-1-i);
//交换完成之后,还要把最后一个元素从堆中删掉
//【0,array.length-1-i】待排序区间
//[array.length-1-i,array.length]已排序区间
shiftDown(array,array.length-1-i,0);
private static void shiftDown(int[] array, int heapLength, int index)
int parent=index;
int child=2*parent+1;
while (child < parent)
if (child+1 < heapLength && array[child+1] >array[child])
child=child+1;
if (array[child] > array[parent])
swap(array,child,parent);
else
break;
parent=child;
child=2*parent+1;
private static void createHeap(int[] array)
for (int i = (array.length-1-1)/2; i >0 ; i--)
shiftDown(array,array.length,i);
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N * logN);空间复杂度O(1),稳定性:不稳定排序
6.快速插入排序
思路
这里引用递归的思想简化代码:
- 待排序区间中,找到一个基准值(常见的可以取区间的第一个元素或者最后一个元素);
- 以基准值为中心,把整个区间整理成三个部分,左侧部分的元素都小于等于基准值,右侧部分的元素都大于等于基准值;
- 再次针对左侧整理好的区间和右侧整理好的区间,进一步进行递归,重复刚才的整理过程
注意:
1.如果是先从左往右找,再从右往左找,left和right重合位置的元素,一定大于等于基准值,如果是先从右往左找,再从左往右找,left和right重合位置的元素,一定小于等于基准值
2.如果数组正好反序,此时快排就变成慢排,此时的快速排序效率很低,时间复杂度就是O(N^2)
3.快速排序的效率和基准值取的好坏密切相关.基准值是一个接近数组中位数的元素.划分出的左右区间比较均衡.此时效率就比较高.如果当前取到的基准值是最大或者最小值,此时划分的区间不均衡,效率就低

代码
/**
* @author yty
* @date 2021-10-05 22:39
* @version 1.0
* @description:快速排序算法
*/
public class TestSort6
//辅助完成递归过程
//起初为了代码简单,区间设置成前闭后闭
public static void quickSort(int[] array)
quickSortHelper(array,0,array.length-1);
private static void quickSortHelper(int[] array, int left, int right)
if (left >= right)
//区间中有0和元素或者一个元素,此时不需要排序
return;
//针对[left,right]区间进行调整
// index返回值就是整理完毕后,left和right的重合位置,知道了这个位置,才能进一步进行递归
int index=partition(array,left,right);
quickSortHelper(array,left,index-1);
quickSortHelper(array, index+1, right);
private static int partition(int[] array, int left, int right)
int i=left;
int j=right;
int base=array[right];//基准值
while (i < j)
//从左往右找到比基准值大的元素
while (i < j && array[i] <= base)
i++;
//当上面的循环结束是,i要么和j重合,要么i就指向一个大于base的值
//从右往左找比基准值小的元素
while (i < j && array[j] >= base)
j--;
//当上面的循环结束之后,i要么和j重合,要么i就指向一个小于base的值
//交换i 和j 的值
swap(array,i,j);
//当i和j重合的时候,最后一步,要把重合位置的元素和基准值进行交换
swap(array,i,right);
//right是数组中最后一个元素,要求i和j重合的位置必须大于基准值,才能放到最后面
return i;
private static void swap(int[] array,int i, int j)
int tmp=array[i];
array[i]=array[j];
array[j]=tmp;
public static void main(String[] args)
int[] array=8,2,5,4,6,3;
quickSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
复杂度分析
平均时间复杂度:O(N * logN);空间复杂度:O(logN)-O(N):稳定性:不稳定
7.归并排序
思路
有两个重要的特点:1.适用于外部排序(数据存在磁盘上);2.适用于链表排序.基本思路来源于经典问题:把两个链表合并成一个
代码
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author yty
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021-10-09 22:19
* @descripition:归并排序
*/
public class TestSort7
public static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high)
//[low,mid] 有序区间
//[mid,high] 有序区间
//把这两个有序数组合并成一个有序数组
int[] output = new int[high-low];
int outputIndex=0;
int cur1=low;
int cur2=mid;
while(cur1 < mid && cur2 < high)
//这里谁小就把谁返给数组里面
if (array[cur1] <= array[cur2])
//稳定排序,<=才能保证稳定性
output[outputIndex]=array[cur1];
outputIndex++;
cur1++;
else
output[outputIndex]=array[cur2];
outputIndex++;
cur2++;
//循环结束,一个到达结尾,一个还有剩余
//把剩下的拷贝到数组里
while (cur1 < mid)
output[outputIndex]=array[cur1];
outputIndex++;
cur1++;
while (cur2 < high)
output[outputIndex]=array[cur2];
outputIndex++;
cur2++;
//最后一步,output的元素搬运到原来的数组
for (int i = 0; i < high-low; i++)
array[low+i]=output[i];
public static void mergeSort(int[] array)
mergeSortHelper(array,0,array.length);
//(low,high]前闭后开区间
//两者插值小于1,区间中就只有1个或0个元素
public static void mergeSortHelper(int[] array, int low, int high)
if (high-low <= 1)
return;
int mid=(low+high) / 2;
mergeSortHelper(array,low,mid);
//执行完,low,high已经排序完
mergeSortHelper(array,mid,high);
//执行完,mid,high已经排序完
//当左右区间已经排序完了,说明左右区间是有序区间了
//接下来针对两个有序区间进行排序
merge(array,low,mid,high);
public static void main(String[] args)
int[] array=8,2,5,4,6,3;
mergeSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N * logN);空间复杂度:O(logN)+O(N):稳定性:稳定
以上是关于数据结构(Java)——No4.常见的排序算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章