二叉树深入剖析
Posted 时空旅客~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树深入剖析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二叉树的基本结构
用指针来指向两个子树节点,依次来把节点来连接起来
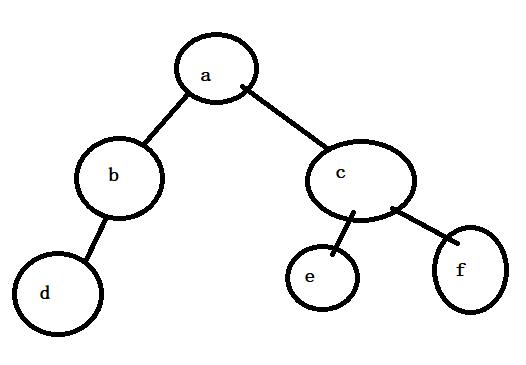
二叉树的遍历(前序,中序,后序)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef char btdata;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
//指针域
struct BinaryTreeNode *left;//链接左孩子
struct BinaryTreeNode *right;//链接右孩子
btdata data;//数据域
btnode;
//开辟节点
btnode* buynode(btdata x)
btnode*node=malloc(sizeof(btnode));
if(node==NULL)//判定是否动态开辟成功
exit(-1);//没开辟成功就退出
node->data=x;//链接数据
node->left=NULL;//还没链接其他指针就置成空
node->right=NULL;
//暴力造一个树
btnode*creatbinarytree()
btnode*nodeA=buynode('A');
btnode*nodeB=buynode('B');
btnode*nodeC=buynode('C');
btnode*nodeD=buynode('D');
btnode*nodeE=buynode('E');
btnode*nodeF=buynode('F');
nodeA->left=nodeB;
nodeB->left=nodeD;
nodeA->right=nodeC;
nodeC->left=nodeE;
nodeC->right=nodeF;
return nodeA;//返回的是根节点
//前序
void preorder(btnode*root)
//如果当前三一个空树
if(root==NULL)
printf("NULL->");
return ;
//不是一个空树
printf("%c->",root->data);//先遍历根,后再遍历左右
preorder(root->left);//左子树
preorder(root->right);//右子树
//中序 左根右
void inorder(btnode*root)
//如果当前三一个空树
if(root==NULL)
printf("NULL->");
return ;
//不是一个空树
inorder(root->left);//左子树
printf("%c->",root->data);//根
inorder(root->right);//右子树
//后序 左右根
void postorder(btnode*root)
//如果当前三一个空树
if(root==NULL)
printf("NULL->");
return ;
//不是一个空树
postorder(root->left);//左子树
postorder(root->right);//右子树
printf("%c->",root->data);//根
计算二叉树的节点的个数
//一.计算节点的个数
//错误方法
int binarytreesize(btnode*root)
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
static int count=0;//用了static的话,每次调用都会在原来的基础上对count进行++,
//如果不加static的话,cout在栈上开辟,调用完就会销毁
count++;
binarytreesize(root->left);
binarytreesize(root->right);
return count;//这样计算出来的结果永远都是1
//正确的做法1.
void binarytreesize2(btnode*root,int*x)//用指针进行操作,这样每次都是对同一个空间进行操作
if(root==NULL)
return;
++(*x);//对地址进行操作就不会出现static和销毁的情况了
binarytreesize2(root->left,x);
binarytreesize2(root->right,x);
//正确的做法2.
int binarytreesize3(btnode*root)
return root==NULL?0:binarytreesize3(root->left)+binarytreesize3(root->right)+1;//把问题分为了左右子树,和自己,不断的细分,左右+1
//二.计算叶子节点的个数,就是没有子树节点的个数,度为0的个数
int binaryleafsize2(btnode*root)//左子树的叶子节点和右子树的叶子节点加起来
if(root==NULL)//并非一定整个树都是空,后面递归可能三左子树或右子树是空
return 0;
return (root->left==NULL)&&(root->right==NULL)?1:binaryleafsize2(root->left)+binaryleafsize2(root->right);//叶子节点左右都没有节点,则+1,为叶子就返回一,不为叶子就继续把左右子树的叶子加起来
在这里插入代码片
计算第k层的节点
//三.计算第k层节点的个数
//如,要求第4层,就求的3层的左子树节点数量加上右子树第3层的节点
//这里我们用了一个相对距离的概念
int binarytreelevelsize(btnode*root,int k)
if(root==NULL)//没有节点,就通通返回0
return 0;
if(k<1)
return 0;
//走到了这里,就不为空
else if(k==1)
return 1;//如果要我们求第一层就返回1,不用求了
//root不为空,k大于1
//说明root第k层的节点在子树里面,
//就转化为了左右子树的第k-1层节点的数量
//如要求我的第4层,相当于求为左子树的第三层和右子树的第3层,
//直到为第一层,本层
return binarytreelevelsize(root->left,k-1)+binarytreelevelsize(root->right,k-1);
```c
二叉树的深度
//计算树的深度(高度)层次
//我们一般规定第一层为1,空树就算0,从1开始
//计算深度就是左子树深度和右子树深度中大的+1
int binarytreedepth(btnode*root)
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
//这样写会重复计算,因为前面比较的时候已经算出结果了,但因为没有保存结果,严重的浪费了,
//return binarytreedepth(root->left)>binarytreedepth(root->right)?binarytreedepth(root->left)+1:binarytreedepth(root->right)+1;//大的那个+1
//用一个变量来记录
int leftdepth=binarytreedepth(root->left);//一层一层留一个大的返回区
int rightdepth=binarytreedepth(root->right);
//相当于后序
return leftdepth>rightdepth?leftdepth+1:rightdepth+1;
```c
查找一个节点
//二叉树中查找值为x的节点
//找到了就返回他的地址
btnode* binarytreefind(btnode*root,btdata x)
//根左右的遍历
//先找根
if(root==NULL)
return NULL;//返回null是为了告诉上一层我没找到
if(root->data==x)//找到了
return root;
btnode*leftret=binarytreefind(root->left,x);
if(leftret)//不为空,也就是左边找到了
return leftret;
btnode*rightret=binarytreefind(root->right,x);
if(rightret)//没走上面的就走下面的,右边找到了
return rightret;
return NULL;//左边没找到,右边也没找到
层序遍历
用队列实现
1.先入根
2.在当前节点出来后,再把他的左右孩子带进去,不为空才带进去,这样上一层节点出的时候,带入下一层
3.直到队列为空,说明最后一层没有节点,遍历结束
void binarytreelevelorder(btnode* root)
if (root == NULL)//必须的操作
return;
queue q;
queueinit(&q);//初始化一个队列
queuepush(&q, root);//入队
while (!queueempty(&q))//队不为空就继续操作
btnode* front = queuefront(&q);//取下队头,避免之后找不到队里面的数据
queuepop(&q);//出队
printf("%c ", front->data);//打印
// 孩子带进队列
if (front->left)
queuepush(&q, front->left);//左右孩子不为空就入
if (front->right)
queuepush(&q, front->right);
printf("\\n");
//queuedestroy(&q);
判断是否为完全二叉树
判断满二叉树,可以计算树的高度,再计算树的节点树,是否等于2^h-1,十分容易
1.判断是否是完全二叉树(非空节点是连续的)
用层序遍历,队列的时候,空也入,null也当作一个元素,遇到空之后,队列里面全是空
非完全二叉树,遇到空后,队列里面并非全空
bool iscompletebinarytree(btnode*root)
queue q;
queueinit(&q);
queuepush(&q, root);
while (!queueempty(&q))//不为空就进入//队头
btnode* front = queuefront(&q);
//空也进
queuepop(&q);
if (front == NULL)//遇到了一个NULL元素就跳出去,ci
//为空的花就跳出去
break;
else
//front不为空就入左右,左右不管是否为空都入,NULL也是元素
queuepush(&q, front->left);
queuepush(&q, front->right);
//跳出去检查剩下的节点是否全是空,剩下的全是空就是完全二叉树,存在非空,则是非完全二叉树,
//出剩下的所有节点
while (queuesize(&q))//null也当作一个元素,直到元素个数完了,就是全是空的
btnode* front = queuefront(&q);
queuepop(&q);
if (front)//遇到了不为空
queuedestroy(&q);
return false;
queuedestroy(&q);
return true;
test.c
int main()
btnode*root=creatbinarytree();//造一个树
// preorder(root);//前序遍历,根,左子树,右子树
//用分治,:分而治之,大事化小,小事化了
//如校长想知道学校有多少人,让10个院报人数,院让专业老师统计人数,老师叫班长,一步一步化小,
//inorder(root);
postorder(root);
int n1=0;
binarytreesize2(root, &n1);//把n1地址传过去,每次都对这个地址进行操作,就没有销毁的问题了
printf("\\n");
printf("n1=%d\\n",n1);
int n2=0;
printf("n2=%d\\n",binarytreesize3(root));
int leafn=0;;
printf("leafn=%d\\n",leafn);
printf("leaf2=%d\\n",binaryleafsize2(root));
int n3=0;
printf("levelk=%d\\n",binarytreelevelsize(root,3));
printf("depth=%d\\n",binarytreedepth(root));
return 0;
以上是关于二叉树深入剖析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章