学习数据结构笔记(21) --- [克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal Algorithm) 由公交车站连接问题引入]
Posted 小智RE0
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了学习数据结构笔记(21) --- [克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal Algorithm) 由公交车站连接问题引入]相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
B站学习传送门–>尚硅谷Java数据结构与java算法(Java数据结构与算法)
情景引入
某个城市需要连接7个公交站;需要设计出最短路径的路线进行建设;
克鲁斯卡尔算法
与普里姆算法不同,它的时间复杂度为O(eloge)(e为网中的边数);
适合于求边稀疏的网的最小生成树
分析
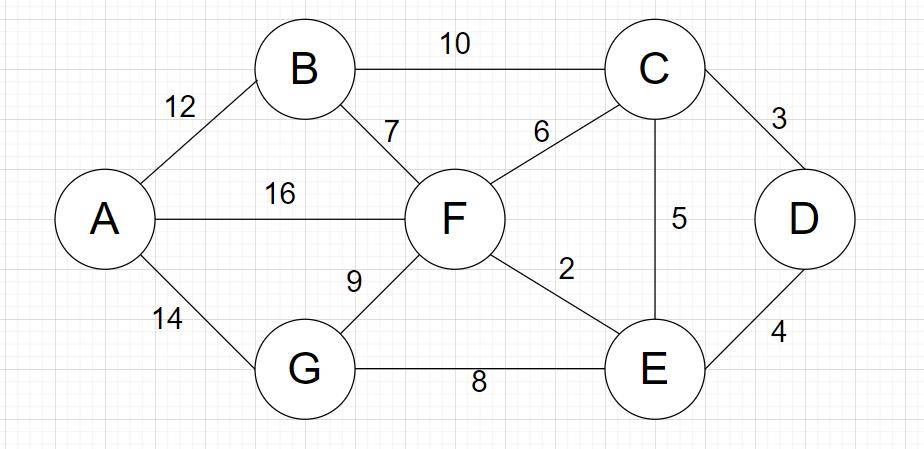
先找到权值最小的边
FE;进行连接
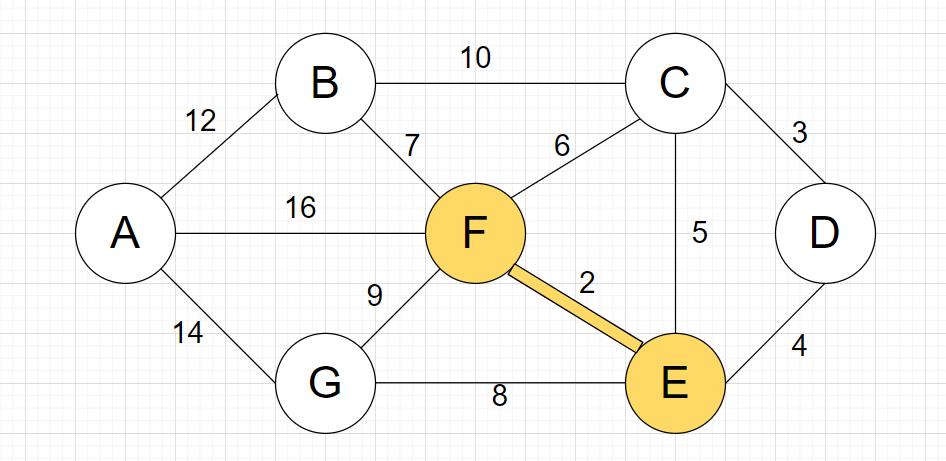
排除已使用的边,找到权值最小的边
CD;连接
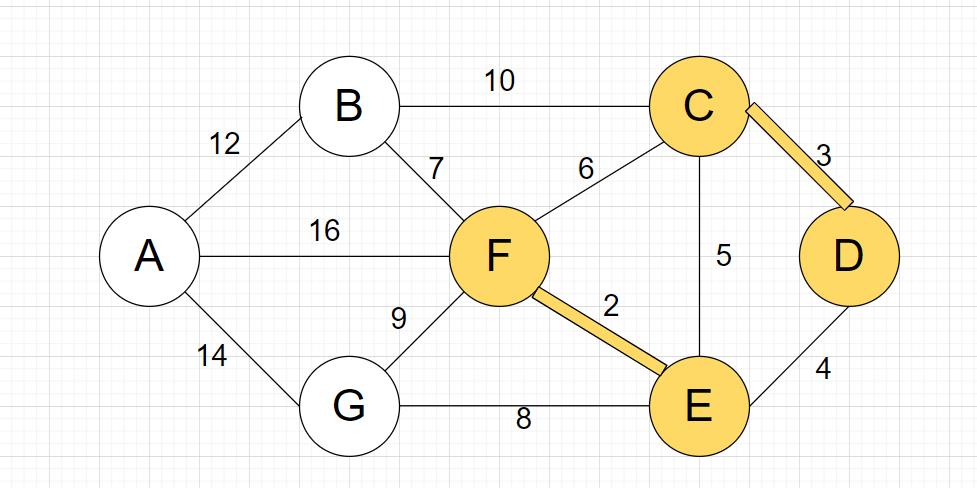
找到权值最小的边
DE;连接
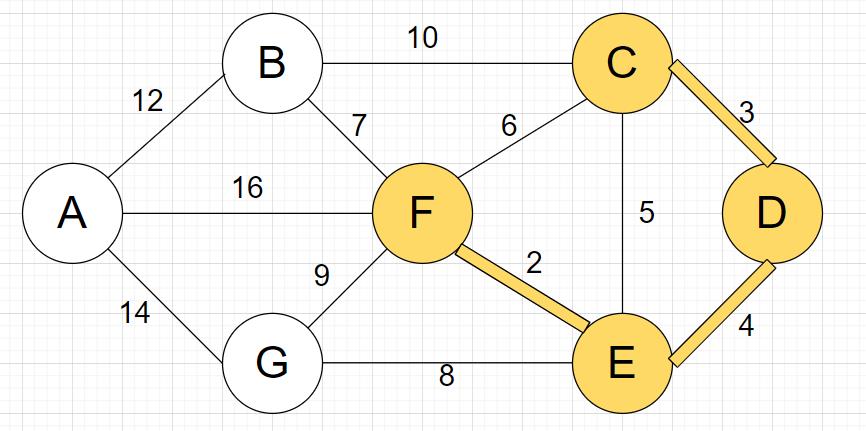
在不构成回路的情况下,找到权值小的边
BF;连接
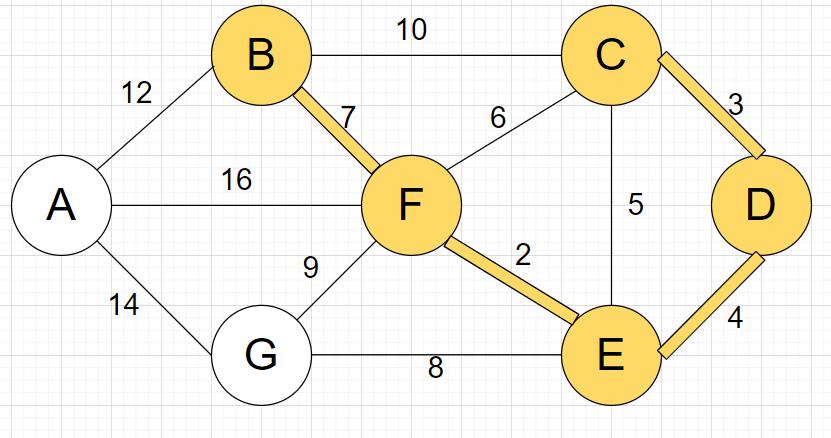
不构成回路的情况下,找到权值小的边
GE;
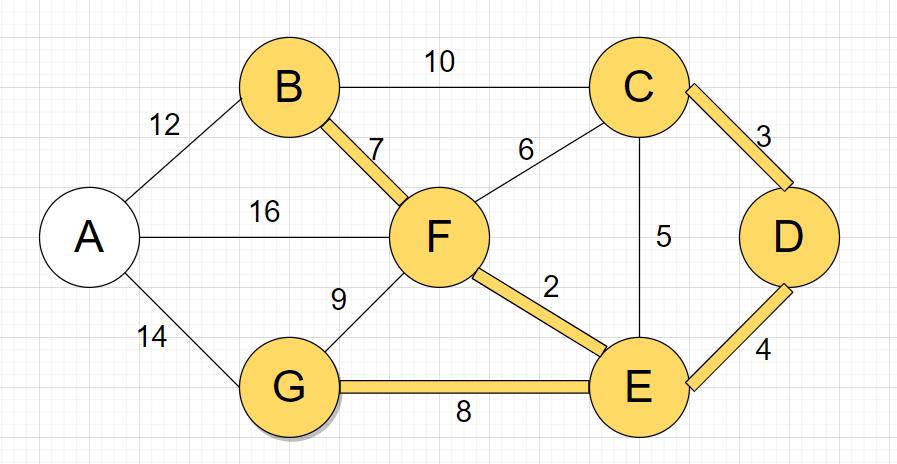
在不构成回路的情况下,找到权值小的边
AB
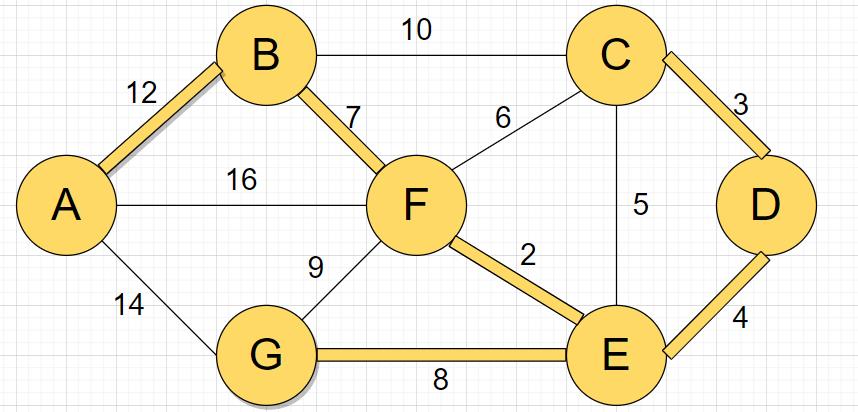
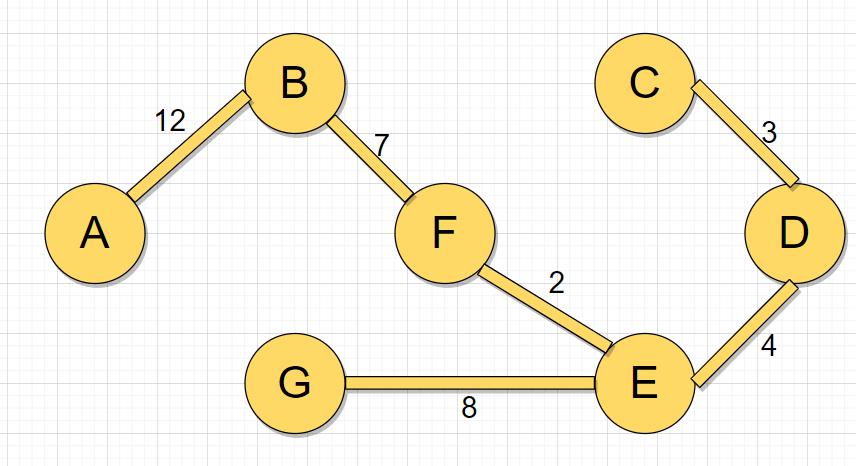
解决
具体的实现解决过程
package day22kruskalalgorithm;
/**
* @author by CSDN@小智RE0
* @date 2021-12-07
* 克鲁斯卡尔算法
*/
public class KruskalAlgorithm
//测试使用;
public static void main(String[] args)
char[] busStop = 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G';
//邻接矩阵描绘;
int[][] adjacencyMatrix =
0, 12, BAN, BAN, BAN, 16, 14,
12, 0, 10, BAN, BAN, 7, BAN,
BAN, 10, 0, 3, 5, 6, BAN,
BAN, BAN, 3, 0, 4, BAN, BAN,
BAN, BAN, 5, 4, 0, 2, 8,
16, 7, 6, BAN, 2, 0, 9,
14, BAN, BAN, BAN, 8, 9, 0
;
//初始化类;
KruskalAlgorithm ka = new KruskalAlgorithm(busStop, adjacencyMatrix);
//初始化打印;
ka.toStrings();
//进行排序;
ka.getSide();
//System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(kaSide));
//最终路径;
ka.finallyMethod();
//边的个数;
private int sideNum;
//图中顶点的;
private final char[] peak;
//邻接矩阵存储顶点之间的边连接关系;
private final int[][] adjacencyMatrix;
//禁止连通的边的标志;
private static final int BAN = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//初始化构造;
public KruskalAlgorithm(char[] peak, int[][] adjacencyMatrix)
this.peak = new char[peak.length];
//将顶点初始化;
System.arraycopy(peak, 0, this.peak, 0, peak.length);
this.adjacencyMatrix = new int[peak.length][peak.length];
//二维数组初始化;
System.arraycopy(adjacencyMatrix, 0, this.adjacencyMatrix, 0, adjacencyMatrix.length);
//边的数量数组初始化;
for (int i = 0; i < this.adjacencyMatrix.length; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < this.adjacencyMatrix.length; j++)
if (this.adjacencyMatrix[i][j] != BAN)
sideNum++;
//根据输入的顶点字符寻找该字符的索引;输入错误则返回-1;
public int findIndexByPeak(char p)
for (int i = 0; i < this.peak.length; i++)
if (peak[i] == p)
return i;
return -1;
//获取图里的边; 实际就是从邻接矩阵中进行过滤;
public Side[] getSide()
int k = 0;
Side[] res = new Side[this.sideNum];
for (int i = 0; i < this.adjacencyMatrix.length; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < this.adjacencyMatrix.length; j++)
if (this.adjacencyMatrix[i][j] != BAN)
res[k++] = new Side(this.peak[i], this.peak[j], this.adjacencyMatrix[i][j]);
return res;
//获取指定索引的顶点的这条边的结束点;
public int getEndIndex(int[] endCollect, int index)
//终点集合数组:在连接时逐渐形成;
while (endCollect[index] != 0)
index = endCollect[index];
return index;
//对于图的边进行冒泡排序;
private void sortEng(Side[] sides)
for (int i = 0; i < sides.length - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < sides.length - i - 1; j++)
if (sides[j].weight > sides[j + 1].weight)
//用临时数作为中介;
Side temp = sides[j];
sides[j] = sides[j + 1];
sides[j + 1] = temp;
//输出邻接矩阵关系;
public void toStrings()
System.out.println("--该图的邻接矩阵--");
for (int[] matrix : this.adjacencyMatrix)
for (int j = 0; j < this.adjacencyMatrix.length; j++)
System.out.printf("%15d", matrix[j]);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------------");
//最终方法;---------------------------------
public void finallyMethod()
//结果集数组的索引;
int resIndex = 0;
//最终的最小生成树的顶点连接的边的终点数组;
int[] endCollect = new int[sideNum];
//结果数组;
Side[] resArr = new Side[sideNum];
//图中所有边的集合;
Side[] sideArr = getSide();
//当前这个图,边的集合输出打印;
//Arrays.stream(sideArr).forEach(a -> System.out.print(a + " "));
//System.out.println("共有" + sideArr.length + "条边");
//按照边的权值大小;排序操作;
sortEng(sideArr);
//遍历数组;添加时判断是否构成回路;
for (Side side : sideArr)
//当前边的起点;
int s1 = findIndexByPeak(side.startPeak);
//当前边的终点;
int s2 = findIndexByPeak(side.endPeak);
//判断是否已经有回路了;
int end1 = getEndIndex(endCollect, s1);
int end2 = getEndIndex(endCollect, s2);
//没有回路;
if (end1 != end2)
endCollect[end1] = end2;
resArr[resIndex++] = side;
System.out.println("---------结果集---------");
// Arrays.stream(resArr).forEach(System.out::println);
for (int i = 0; i < resIndex; i++)
System.out.println(resArr[i]);
//该类来表示连接的边;
class Side
char startPeak;
char endPeak;
//边的权值;
int weight;
//初始化边类;
public Side(char startPeak, char endPeak, int weight)
this.startPeak = startPeak;
this.endPeak = endPeak;
this.weight = weight;
//打印边;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Side" +
"startPeak=" + startPeak +
", endPeak=" + endPeak +
", weight=" + weight +
'';
测试结果
--该图的邻接矩阵--
0 12 2147483647 2147483647 2147483647 16 14
12 0 10 2147483647 2147483647 7 2147483647
2147483647 10 0 3 5 6 2147483647
2147483647 2147483647 3 0 4 2147483647 2147483647
2147483647 2147483647 5 4 0 2 8
16 7 6 2147483647 2 0 9
14 2147483647 2147483647 2147483647 8 9 0
---------------
---------结果集---------
SidestartPeak=E, endPeak=F, weight=2
SidestartPeak=C, endPeak=D, weight=3
SidestartPeak=D, endPeak=E, weight=4
SidestartPeak=B, endPeak=F, weight=7
SidestartPeak=E, endPeak=G, weight=8
SidestartPeak=A, endPeak=B, weight=12
以上是关于学习数据结构笔记(21) --- [克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal Algorithm) 由公交车站连接问题引入]的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章