聊一聊计算机视觉中常用的注意力机制 附Pytorch代码实现
Posted 肆十二
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了聊一聊计算机视觉中常用的注意力机制 附Pytorch代码实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
聊一聊计算机视觉中常用的注意力机制以及Pytorch代码实现
注意力机制(Attention)是深度学习中常用的tricks,可以在模型原有的基础上直接插入,进一步增强你模型的性能。注意力机制起初是作为自然语言处理中的工作Attention Is All You Need被大家所熟知,从而也引发了一系列的XX is All You Need的论文命题,SENET-Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks是注意力机制在计算机视觉中应用的早期工作之一,并获得了2017年imagenet, 同时也是最后一届Imagenet比赛的冠军,后面就又出现了各种各样的注意力机制,应用在计算机视觉的任务中,今天我们就来一起聊一聊计算机视觉中常用的注意力机制以及他们对应的Pytorch代码实现,另外我还使用这些注意力机制做了一些目标检测的实验,实验效果我也一并放在博客中,大家可以一起对自己感兴趣的部分讨论讨论。
新出的手把手教程,感兴趣的兄弟们快去自己动手试试看!
这里是我数据集的基本情况,这里我使用的是交通标志检测的数据集
CocoDataset Train dataset with number of images 2226, and instance counts:
+------------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------------------------+-------+---------------------+-------+
| category | count | category | count | category | count | category | count | category | count |
+------------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------------------------+-------+---------------------+-------+
| 0 [red_tl] | 1465 | 1 [arr_s] | 1133 | 2 [arr_l] | 638 | 3 [no_driving_mark_allsort] | 622 | 4 [no_parking_mark] | 1142 |
+------------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------+-------+-----------------------------+-------+---------------------+-------+
baseline选择的是fasterrcnn,实验的结果如下:
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.341
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.502
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.400
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.115
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.473
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.655
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.417
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=300 ] = 0.417
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.417
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.156
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.570
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.726
如果大家遇到论文下载比较慢
推荐使用中科院的 arxiv 镜像: http://xxx.itp.ac.cn, 国内网络能流畅访问
简单直接的方法是, 把要访问 arxiv 链接中的域名从 https://arxiv.org 换成 http://xxx.itp.ac.cn , 比如:
从 https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07249 改为 http://xxx.itp.ac.cn/abs/1901.07249
1. SeNet: Squeeze-and-Excitation Attention
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507
-
网络结构
对通道做注意力机制,通过全连接层对每个通道进行加权。
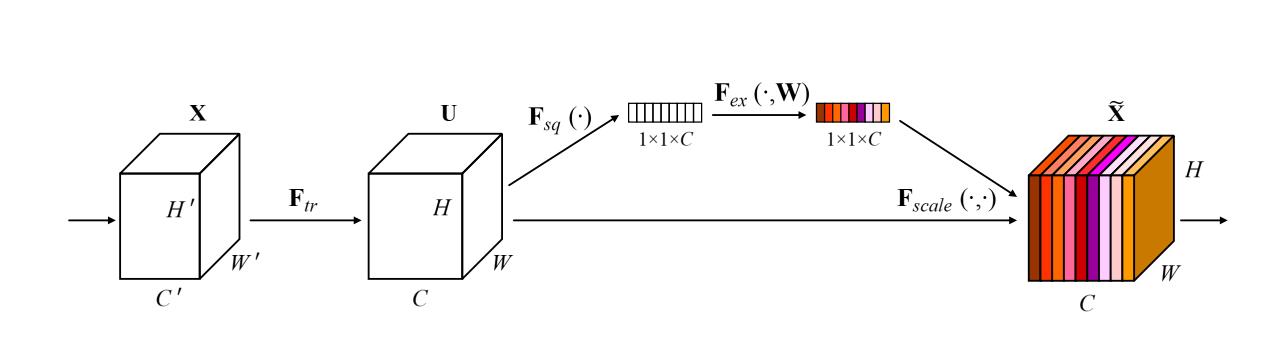
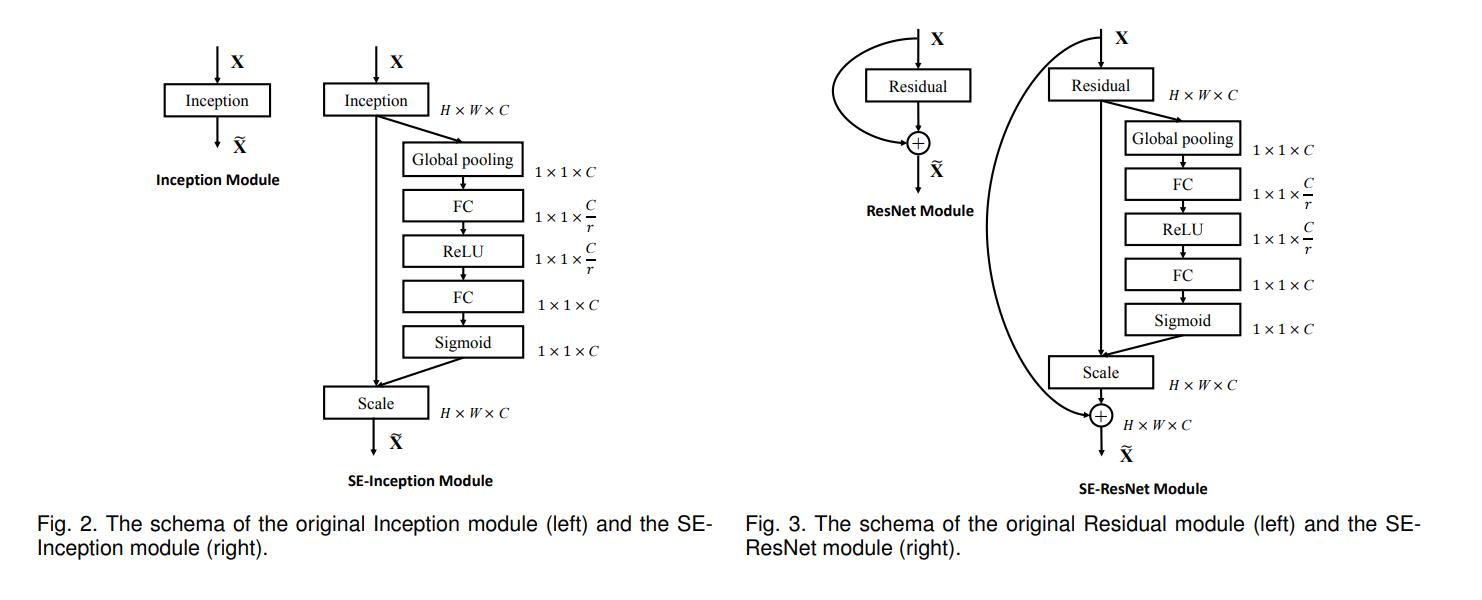
-
Pytorch代码
import numpy as np import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import init class SEAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel=512, reduction=16): super().__init__() self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) self.fc = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False), nn.Sigmoid() ) def init_weights(self): for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out') if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): init.constant_(m.weight, 1) init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001) if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, x): b, c, _, _ = x.size() y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c) y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1) return x * y.expand_as(x) if __name__ == '__main__': input = torch.randn(50, 512, 7, 7) se = SEAttention(channel=512, reduction=8) output = se(input) print(output.shape) -
实验结果
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.338 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.511 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.375 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.126 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.458 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.696 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.411 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=300 ] = 0.411 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.411 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.163 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.551 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.758
2. (有用)CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module
-
网络结构
对通道方向上做注意力机制之后再对空间方向上做注意力机制
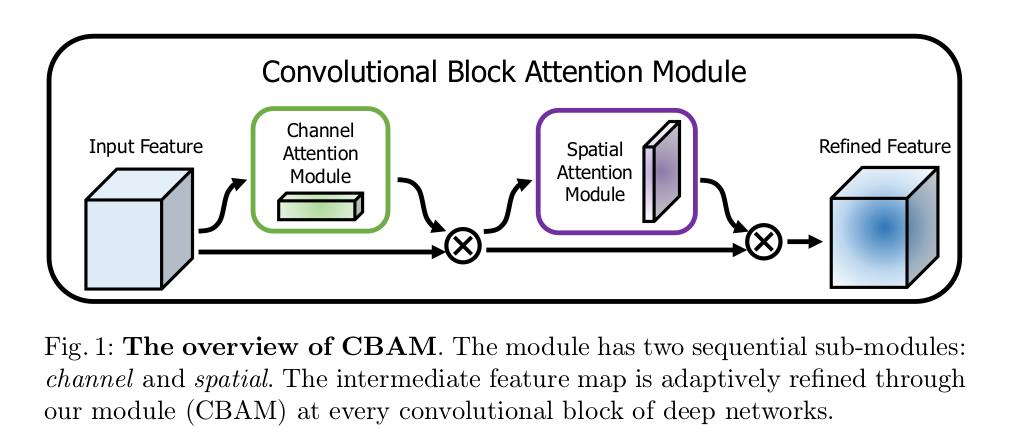
-
Pytorch代码
import numpy as np import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import init class ChannelAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16): super().__init__() self.maxpool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1) self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) self.se = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, bias=False), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, bias=False) ) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x): max_result = self.maxpool(x) avg_result = self.avgpool(x) max_out = self.se(max_result) avg_out = self.se(avg_result) output = self.sigmoid(max_out + avg_out) return output class SpatialAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, kernel_size=7): super().__init__() self.conv = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=kernel_size // 2) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x): max_result, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True) avg_result = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True) result = torch.cat([max_result, avg_result], 1) output = self.conv(result) output = self.sigmoid(output) return output class CBAMBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel=512, reduction=16, kernel_size=49): super().__init__() self.ca = ChannelAttention(channel=channel, reduction=reduction) self.sa = SpatialAttention(kernel_size=kernel_size) def init_weights(self): for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out') if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): init.constant_(m.weight, 1) init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001) if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, x): b, c, _, _ = x.size() residual = x out = x * self.ca(x) out = out * self.sa(out) return out + residual if __name__ == '__main__': input = torch.randn(50, 512, 7, 7) kernel_size = input.shape[2] cbam = CBAMBlock(channel=512, reduction=16, kernel_size=kernel_size) output = cbam(input) print(output.shape) -
实验结果
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.364 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.544 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.425 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.137 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.499 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.674 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.439 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=300 ] = 0.439 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.439 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.185 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.590 Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=1000 ] = 0.755
3. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.06514.pdf
-
网络结构
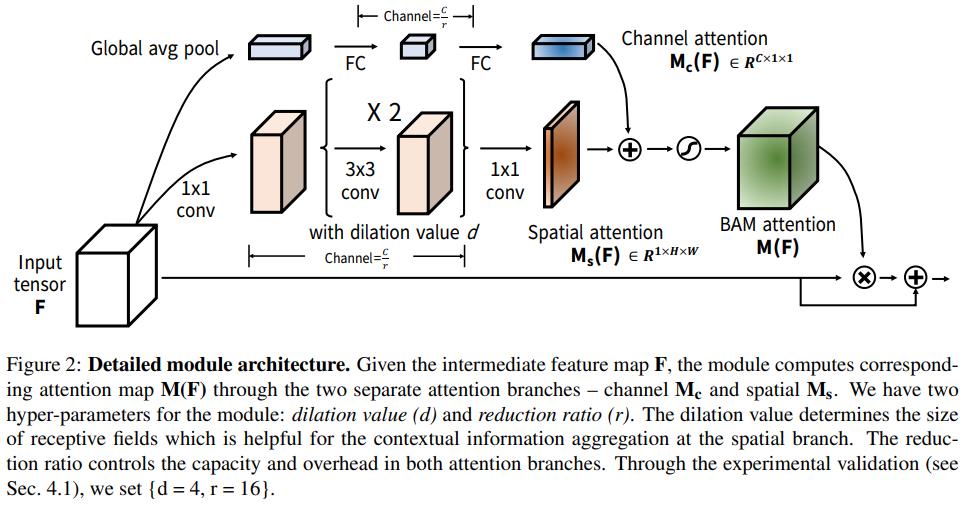
-
Pytorch代码
import numpy as np import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import init class Flatten(nn.Module): def forward(self, x): return x.view(x.shape[0], -1) class ChannelAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16, num_layers=3): super().__init__() self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) gate_channels = [channel] gate_channels += [channel // reduction] * num_layers gate_channels += [channel] self.ca = nn.Sequential() self.ca.add_module('flatten', Flatten()) for i in range(len(gate_channels) - 2): self.ca.add_module('fc%d' % i, nn.Linear(gate_channels[i], gate_channels[i + 1])) self.ca.add_module('bn%d' % i, nn.BatchNorm1d(gate_channels[i + 1])) self.ca.add_module('relu%d' % i, nn.ReLU()) self.ca.add_module(以上是关于聊一聊计算机视觉中常用的注意力机制 附Pytorch代码实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章