Marlin:Preprocessing zkSNARKs with Universal and Updatable SRS学习笔记
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Marlin:Preprocessing zkSNARKs with Universal and Updatable SRS学习笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
Chiesa等人2019年论文《Marlin:Preprocessing zkSNARKs with Universal and Updatable SRS》。
相关代码实现有:
- https://github.com/arkworks-rs/marlin
- https://github.com/AleoHQ/snarkVM/tree/testnet2/marlin【Aleo 2020/12/30拷贝了arkworks-rs的代码,并在此基础上进行了相应的优化和扩展】
前序博客有:
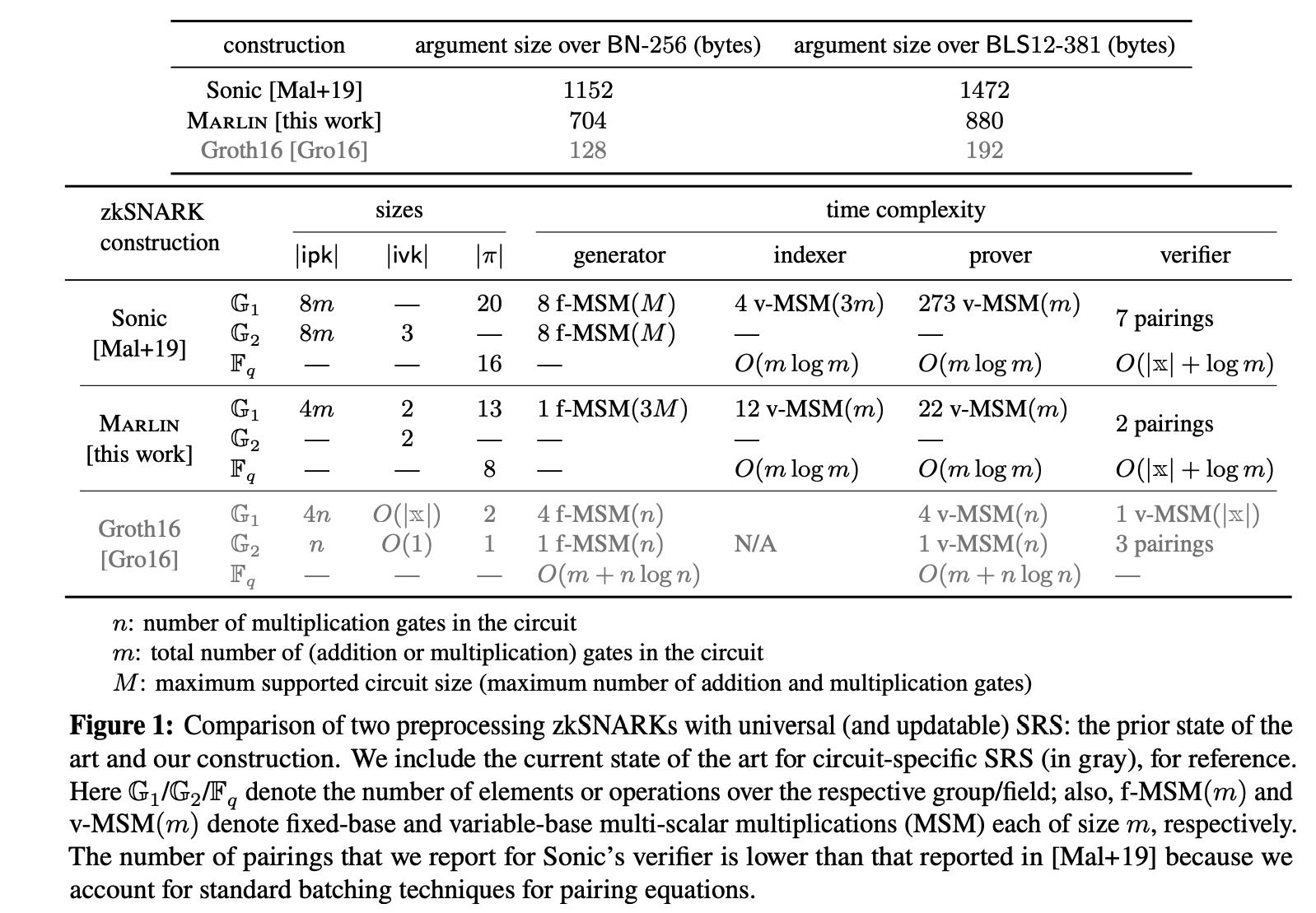
Marlin论文中,构建了预处理zkSNARKs,其structured reference string (SRS)为universal 和 updatable的。SRS具有linear size,生成的argument为constant size。
Marlin比Sonic改进了:
- prove速度快了10倍;
- verify速度快了3倍;
- 具有更小的SRS size和argument size。
Marlin中主要有2大成果:
- 1)AHP(an algebraic holographic proof (AHP) for rank-1 constraint satisfiability (R1CS))——为information-theoretic primitive:具有linear proof length和constant query complexity。待验证的statement以encoded form存在,可实现fast verification。
- 2)a polynomial commitment scheme——为cryptographic primitive:相关实现可参看:https://github.com/arkworks-rs/poly-commit/tree/master/src/marlin。
1.1 fast verification
通常,要求Verifier验证proof的时间 应远小于 自身进行相应计算所需时间。理想情况下,验证时间 应与 read the SNARG 或 read the description of the computation 的时间相当。
为了实现fast verification,可将verification过程分为2个阶段:
- 1)offline phase:生成a short summary for a given circuit。
- 2)online phase:使用offline phase中生成的short summary来verify SNARGs(Succinct non-interactive arguments) that attest to the satisfiability of the circuit with different partial assignments to its input wires。
fast verification可要求online phase与read the SNARG (and the partial assignment)的速度相当,即可认为其是fast的。
可借助preprocessing SNARGs来实现online fast verification。
1.2 universal (and updatable) SRS
在preprocessing SNARGs中,其offline phase包含了与待预处理circuit相关的structured reference string (SRS)。这就意味着,生成/验证 不同circuit的proof 需要 不同的SRS。SRS应为无需任何可信一方参与的,可通过如ZCash的trusted setup仪式来构建。但是,对circuit的任何修改,需要再举行一次trusted setup 仪式,当应用很多时这种方式是不可持续的。
因此,要求SRS为universal的,即该SRS可支持 any circuit up to a given size bound by enabling anyone, in an offline phase after the SRS is sampled, to publicly derive a cricuit-specific SRS。
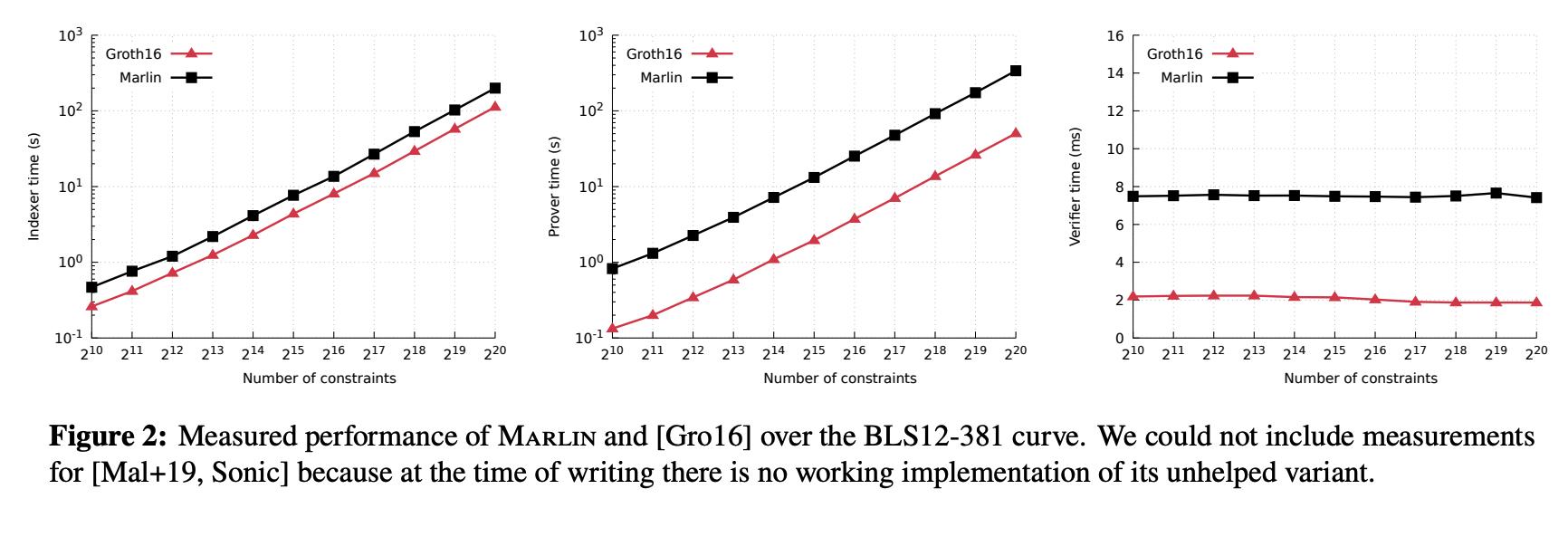
1.3 性能对比
2. 主要成果
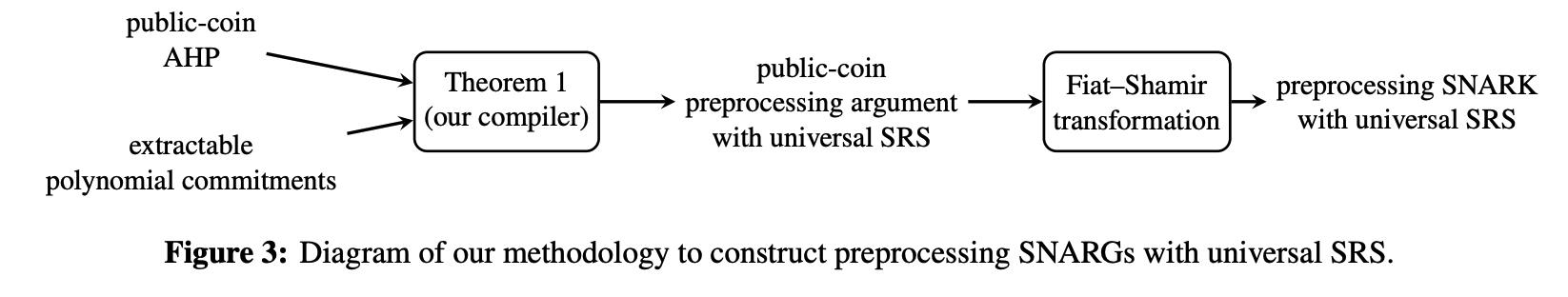
2.1 一种生成Preprocessing SNARK with universal SRS的方法论
在offline phase对circuit进行预处理的方法 类似于构建 “holographic proofs”,即意味着:
- Verifier 无法将circuit description作为input接收,而是,make a small number of queries to an encoding of the circuit description。
- Verifier 会make a small number of queries to the proof sent by the Prover。
在本文中,假设circuit description都是low-degree polynomials,proofs也是low-degree polynomials,同时honest Prover和malicious Prover都是“algebraic”,从而成为algebraic holographic proof (AHP)。
通过合适的extractable polynomial commitment,可将任意public-coin AHP 编译转换为 相应的具有universal (and updatable) SRS的preprocessing argument。

2.2 AHP for R1CS
本文中专门为R1CS设计AHP可实现:
- linear proof length
- constant query complexity
R1CS中的circuit description为coefficient matrices。将Verifier端的输入分为:
- offline phase:称为index,包含了coefficient matrices。offline phase中encode index (coefficient matrices)的算法称为indexer。
- online phase:称为instance:包含了a partial assignment to the variables。

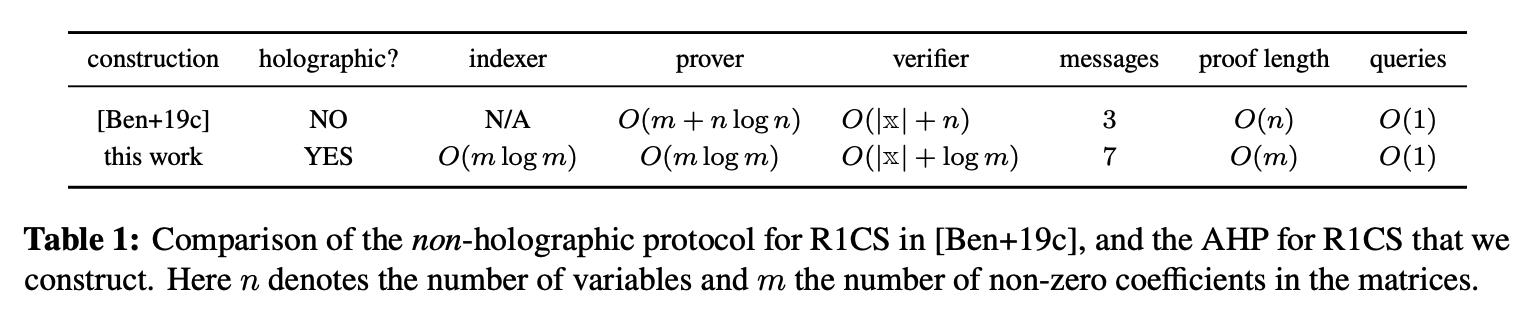
[Bab+91]和[GKR15]等之前的holographic算法无法实现constant query complexity。这些算法依赖multivariate sumcheck protocol applied to certain multivariate polynomials,即因以下原因会引入大量的communication cost:
- 1)the many rounds of the sumcheck protocol。
- 2)需要多变量polynomial commitment scheme,使得相应的communication cost与变量数呈线性关系。
而Marlin中的AHP:
- 1)依赖的是单变量多项式
- 2)并实现了constant query complexity
- 3)具有small communication costs
Marlin中的AHP可看成是Aurora [Ben+19c] 中R1CS algebraic protocol的“holographic 变种”。相比于Aurora,其verification time 实现了指数级改进:
2.3 Extractable polynomial commitment
[KZG10]为单变量polynomial commitment scheme。本文在此基础上进行了扩展,使其具有足够的安全性。
Papamanthou等人2013年论文 PST13——Signatures of Correct Computation 中包含多变量polynomial commitment scheme。本文算法也可扩展为基于多变量polynomial commitment scheme实现,详细可参见:
3. AHP
Interactive oracle proofs (IOPs)为multi-round protocol,在每一轮中,Verifier发送a challenge,Prover会发送an oracle (which the verifier can query)。
IOP结合了 interactive proof 和 probabilistically checkable proof 的特征。
AHP在以下两方面对IOP进行了修改:
- 1)Holographic:Verifier does not receive its input explicitly,但是,具有oracle access to a prescribed encoding of it。使得Verifier可run in time that is much faster than the time to read its input in full。(基于此,可实现fast verification。)
- 2)Algebraic:honest Prover必须produce oracles that are low-degree polynomials(可保证完备性)。malicious Prover必须produce oracles that are low-degree polynomials(可保证soundness)。同时the encoded input to the verifier也必须为a low-degree polynomial。
relation表示以triple ( I , X , W ) (\\mathbbI,\\mathbbX,\\mathbbW) (I,X,W),其中 I \\mathbbI I为index, X \\mathbbX X为instance, w \\mathbbw w为witness。 I \\mathbbI I代表Verifier offline phase进行预处理的输入(如circuit description)。 X \\mathbbX X代表Verifier offline phase的输入(如a partial assignment to the circuit’s input wires)。
对应an indexed relation R \\mathcalR R的indexed language 表示为 L ( R ) \\mathcalL(\\mathcalR) L(R),为对于set of pairs ( I , X ) (\\mathbbI,\\mathbbX) (I,X),存在witness W \\mathbbW W使得 ( I , X , W ) ∈ R (\\mathbbI,\\mathbbX,\\mathbbW)\\in\\mathcalR (I,X,W)∈R。
AHP中包含3种角色:
- 1)Indexer I \\mathbfI I
- 2)Prover P \\mathbfP P
- 3)Verifier V \\mathbfV V
a (public-coin) AHP over a field F \\mathbbF F for an indexed relation R \\mathcalR R 中相应的流程为:
- 1)offline phase:Indexer I \\mathbfI I 收到待预处理的输入 index I \\mathbbI I,输出为一个或多个单变量多项式over F \\mathbbF F encoding I \\mathbbI I。
- 2)online phase:Prover的输入为 ( I , X , W ) (\\mathbbI,\\mathbbX,\\mathbbW) (I,X,W),Verifier的输入为 X \\mathbbX X。Prover和Verifier进行constant round交互。在每一轮中,Verifier发送a challenge,Prover发送一个或多个多项式。交互完成后, V ( X ) \\mathbfV(\\mathbbX) V(X) probabilistically queries the polynomials output by the indexer and the polynomials output by the prover,然后accept或reject。最重要的是,线上阶段,Verifier V \\mathbfV V的输入不包含 I \\mathbbI I,而是query the polynomials output by Indexer I \\mathbfI I that encode I \\mathbbI I。从而使所构建的Verifier V \\mathbfV V 可run in time that is sublinear in ∣ I ∣ |\\mathbbI| ∣I∣。
4. (Extractable) polynomial commitment
[KZG10] polynomial commitment scheme中的流程为:
- 1)Prover:为单变量多项式 p ∈ F [ X ] p\\in\\mathbbF[X] p∈F[X]生成commitment c c c
- 2)Prover:open p ( X ) p(X) p(X) at any point z ∈ F z\\in\\mathbbF z∈F,open的值为 p ( z ) p(z) p(z)
- 3)Prover:生成evaluation proof π \\pi π 来证明the opened value p ( z ) p(z) p(z) is consistent with the polynomial “inside” c c c at z z z。
polynomial commitment scheme应满足如下要求:
- 1)commitment c c c 要远小于 多项式 p p p(如 c c c中包含a constant number of group elements)。【efficiency属性】
- 2)proof π \\pi π必须可快速验证(如in a constant number of cryptographic operations)。【efficiency属性】
- 3)应满足binding属性,即an efficient adversary无法open the same commitment to two different values。【binding属性】
- 4)可保证the degree of the committed function。即若某adversary可open values of some function f : F → F f:\\mathbbF\\rightarrow \\mathbbF f:F→F,则该函数 f f f的degree 应高于 所声明的多项式的degree。【extractability属性】
此外,很多polynomial commitment应用场景中,包含了多个多项式的多个commitment,也可能包含open多个point values。此时,需要考虑:
- 1)仅基于一组public parameter来commit to 多项式,这些多项式可具有不同的degree。可将[KZG10]修改为commit both to the polynomial and its shift to the maximum degree,类似于Aurora中bundle multiple low-degree tests into a single one的技术。【Enforcing multiple degree bounds:即若不同多项式
p
i
p_i
pi的degree
d
i
d_i
di小于setup时的degree bound
D
D
D,则由对
p
i
p_i
pi的commit 改为 对“shifted polynomials”
p
i
′
=
X
D
−
d
i
p
i
(
X
)
p_i'=X^D-d_ip_i(X)
pi′=XD−dipi(X) 进行commit。proof evaluation时,若
p
i
p_i
pi evaluate to
v
i
v_i
vi at
z
z
z,则
p
i
′
p_i'
pi′ evaluate to
z
D
−
d
i
v
i
z^D-d_iv_i
zD−divi。Aurora中基于此派生了low-degree tests for specific degree bounds。
为了进一步减少scalar multiplications(由 Ω ( D ) \\Omega(D) Ω(D) reduce为 O ( d i ) O(d_i) O(di)),Marlin中构建的多项式为 p i ⋆ ( X ) = p i ′ ( x ) − p i ( z ) X D − d i p_i^\\star(X)=p_i'(x)-p_i(z)X^D-d_i pi⋆(X)=pi′(x)−pi(z)XD−di,该多项式evaluate to 0 0 0 at z z z。 】 - 2)需要可batch evaluation proofs across different polynomials for the same location。【Committing to multiple polynomials at once:针对的场景为open multiple polynomials [ p i ] i = 1 n [p_i]_i=1^n [pi]i=1n at the same point z z z。由Verifier提供challenge ξ \\xi ξ,Prover构建多项式 p = ∑ i = 1 n ξ i p i p=\\sum_i=1^n\\xi^ip_i p=∑i=1nξipi,然后改为对 p p p进行commit和open。利用了commitment的加法同态属性。有 c = ∑ i = 1 n ξ i c i c=\\sum_i=1^n\\xi^ic_i c=∑