SPI原理剖析
Posted huaweitman
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SPI原理剖析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SPI ,全称为 Service Provider Interface,是一种服务发现机制。它通过在ClassPath路径下的META-INF/services文件夹查找文件,自动加载文件里所定义的类。
这一机制为很多框架扩展提供了可能,比如在Dubbo、JDBC中都使用到了SPI机制。
先举个例子
新建一个maven工程
定义接口 MyApi
package api;
public interface MyApi
void sayHello(String inputStr);
实现类 MyApiJerryImpl
package impl;
import api.MyApi;
public class MyApiJerryImpl implements MyApi
@Override
public void sayHello(String inputStr)
System.out.println("this is jerry" + " " + inputStr);
实现类 MyApiTomImpl
package impl;
import api.MyApi;
public class MyApiTomImpl implements MyApi
@Override
public void sayHello(String inputStr)
System.out.println("this is tom" + " " + inputStr);
主类 Test
import api.MyApi;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
public class Test
public static void main(String[] args)
ServiceLoader<MyApi> printers = ServiceLoader.load(MyApi.class);
for (MyApi printer : printers)
printer.sayHello("SPI");
在 resources 新建META-INF/services 目录
新建文件api.MyApi
impl.MyApiJerryImpl
impl.MyApiTomImpl整体文件目录
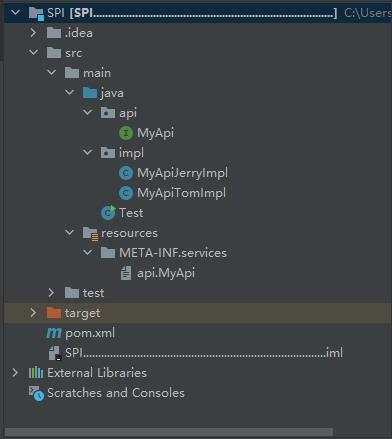
运行结果
this is jerry SPI
this is tom SPI分析主类代码 1.ServiceLoader<MyApi> printers = ServiceLoader.load(MyApi.class);
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service)
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl);
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service,
ClassLoader loader)
return new ServiceLoader<>(service, loader);
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl)
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
生成一个ServiceLoader对象
2.for (MyApi printer : printers)
public final class ServiceLoader<S>
implements Iterable<S>
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
// The class or interface representing the service being loaded
private final Class<S> service;
// The class loader used to locate, load, and instantiate providers
private final ClassLoader loader;
// The access control context taken when the ServiceLoader is created
private final AccessControlContext acc;
// Cached providers, in instantiation order
private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// The current lazy-lookup iterator
private LazyIterator lookupIterator;由于实现了Iterable接口
public Iterator<S> iterator()
return new Iterator<S>()
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,S>> knownProviders
= providers.entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext()
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return true;
return lookupIterator.hasNext();
public S next()
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return knownProviders.next().getValue();
return lookupIterator.next();
public void remove()
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
;
所以会调用上面的hasNext()方法,调用 return lookupIterator.hasNext();
public boolean hasNext()
if (acc == null)
return hasNextService();
else
PrivilegedAction<Boolean> action = new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>()
public Boolean run() return hasNextService();
;
return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc);
调用这行代码 return hasNextService();
private boolean hasNextService()
if (nextName != null)
return true;
if (configs == null)
try
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
catch (IOException x)
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext())
if (!configs.hasMoreElements())
return false;
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
调用到这行代码 String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
在ServiceLoader类的第一个成员变量 private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
到了这里就解释了为什么配置文件必须放到META-INF/services 目录下面了
找到配置文件以后,要解析文件里面的内容
调用到这行代码 pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
private Iterator<String> parse(Class<?> service, URL u)
throws ServiceConfigurationError
InputStream in = null;
BufferedReader r = null;
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
try
in = u.openStream();
r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, "utf-8"));
int lc = 1;
while ((lc = parseLine(service, u, r, lc, names)) >= 0);
catch (IOException x)
fail(service, "Error reading configuration file", x);
finally
try
if (r != null) r.close();
if (in != null) in.close();
catch (IOException y)
fail(service, "Error closing configuration file", y);
return names.iterator();
names的值是
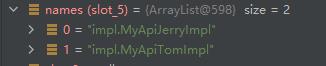
然后调用nextService()方法
private S nextService()
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
catch (ClassNotFoundException x)
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c))
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
try
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
catch (Throwable x)
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
代码 c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
使用java反射
获取类
代码 S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
生成对象
over
以上是关于SPI原理剖析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章