Notes16proc文件系统,内存分配,数据类型
Posted 码农编程录
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Notes16proc文件系统,内存分配,数据类型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
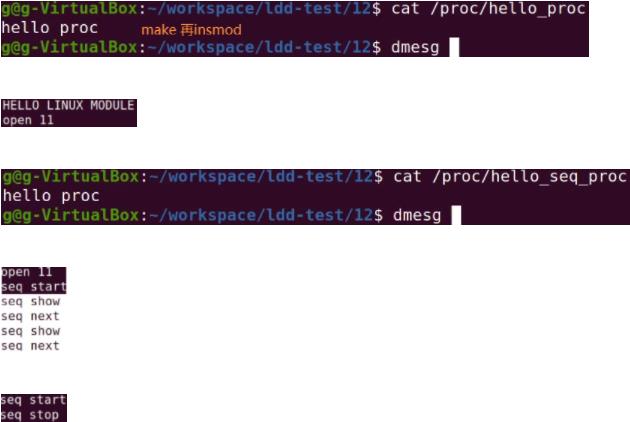
1.创建proc文件系统接口:之前调试内核时都是通过prink打印内核信息,通过dmesg查看输出的信息。新调试方法:利用proc文件系统在pro文件夹下创建接口,读写这个接口就可实现对内核的调试
/*
struct proc_ops //pro文件夹下创建接口第一种方式
proc_create()
struct seq_operations //第二种方式
proc_create_seq()
remove_proc_entry
*/
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/uaccess.h>
#include<linux/string.h>
#define PROC_DEBUG
#ifdef PROC_DEBUG
#include<linux/proc_fs.h>
#include<linux/seq_file.h>
#endif
char * str = "hello proc\\n";
#ifdef PROC_DEBUG //由于proc一般用于调试,通常定义一个宏,将proc对应代码包起来,不需要这调试接口时,就可把这个宏注释掉,这样这个宏包含代码不会编译到内核中了。
//111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
int hp_open(struct inode * inode, struct file * filp)
printk(KERN_INFO"open %ld\\n",strlen(str));
return 0;
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
ssize_t hp_read(struct file * filp, char __user * buff, size_t count, loff_t * f_pos)
ssize_t retval=0;
int n = strlen(str);
if(*f_pos >= n)
goto out;
if(*f_pos + count > n)
count = n - *f_pos;
if(copy_to_user(buff,str,count))
retval = -EFAULT;
goto out;
*f_pos += count;
return count;
out:
return retval;
//111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
struct proc_ops hp_ops =
.proc_open = hp_open,
.proc_read = hp_read,
;
//111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
void * hp_seq_start (struct seq_file *m, loff_t *pos) //pos表示当前读到哪个位置或写到哪个位置了,像索引
printk(KERN_INFO"seq start\\n");
if(*pos >= strlen(str))
return NULL;
return &str[*pos]; //拿出字符串中字符,将地址返回,这返回值作为其他函数的v传入
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
void hp_seq_stop(struct seq_file *m, void *v)
printk(KERN_INFO"seq stop\\n"); //清除start函数一些工作,start里开辟一些空间或申请一些锁,这里清楚
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
void * hp_seq_next (struct seq_file *m, void *v, loff_t *pos)
printk(KERN_INFO"seq next\\n");
(*pos)++;
if(*pos >= strlen(str))
return NULL;
return &str[*pos];
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
int hp_seq_show (struct seq_file *m, void *v)
printk(KERN_INFO"seq show\\n");
seq_putc(m,*(char*)v); //将获得到的字符一个一个打印出
return 0;
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
const struct seq_operations seq_ops=
.start = hp_seq_start,
.stop = hp_seq_stop,
.next = hp_seq_next,
.show = hp_seq_show,
;
#endif
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
static int __init hello_init(void)
printk(KERN_INFO "HELLO LINUX MODULE\\n");
#ifdef PROC_DEBUG
proc_create("hello_proc",0,NULL,&hp_ops); //第一个参数即显示在pro目录下文件名称,第二个参数默认0只读权限。第三个参数父节点,null默认pro目录。最后一个参数是操作的结构体地址。
proc_create_seq("hello_seq_proc",0,NULL,&seq_ops); //就可在pro目录下创建对应节点
#endif
return 0;
//11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
#ifdef PROC_DEBUG
remove_proc_entry("hello_proc",NULL);
remove_proc_entry("hello_seq_proc",NULL);
#endif
printk(KERN_INFO "GOODBYE LINUX\\n");
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");//许可 GPL、GPL v2、Dual MPL/GPL、Proprietary(专有)等,没有内核会提示
MODULE_AUTHOR("KGZ"); //作者
MODULE_VERSION("V1.0"); //版本
2.内核内存分配函数
2.1 hello.c
/*
1.
kmalloc() 一般千字节以下
kzalloc() 分配空间并清0
kfree()
2.
struct kmem_cache //slab分配器/专用高速缓存 速度快 利用率高
kmem_cache_create() //创建高速缓冲区,返回地址保存在上面一行的结构指针中,然后可调用kmem_cache_alloc函数分配空间,使用完后,free释放
kmem_cache_alloc()
kmem_cache_free()
kmem_cache_destroy() //清除高速缓冲区
3.
__get_free_page() //大块内存,按页分配
__get_free_pages()
get_zeroed_page()
free_page()
free_pages()
4.
vmalloc() 虚拟地址连续,物理地址不连续,效率不高,
vfree() 用在分配大的连续的、只在软件中使用的,用于缓存的内存区域
5.
others
*/
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/slab.h>
#include<linux/gfp.h>
#include<linux/vmalloc.h>
char * kmlcp;
struct kmem_cache *h_cache;
char * kmemcp;
char * frpgp;
char * vmlcp;
static int hello_init(void)
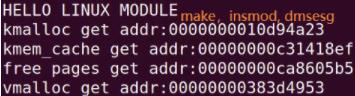
printk(KERN_INFO "HELLO LINUX MODULE\\n");
//1
kmlcp = kmalloc(1024,GFP_KERNEL); //常用flag有GFP_KERNEL和GFP_ATOMIC
if(!kmlcp)
return -ENOMEM;
printk(KERN_INFO"kmalloc get addr:%p\\n",kmlcp);
//2
h_cache = kmem_cache_create("h_cache",512,0,SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN|SLAB_POISON,NULL);
if(!h_cache)
kfree(kmlcp);
return -ENOMEM;
kmemcp = kmem_cache_alloc(h_cache,GFP_KERNEL);
if(!kmemcp)
//do something
return -ENOMEM;
printk(KERN_INFO"kmem_cache get addr:%p\\n",kmemcp);
//3
frpgp =(void *) __get_free_pages(GFP_KERNEL,0); //第二个参数是页面数的对数值,0:1 1:2 2:4 3:8
if(!frpgp)
//do something
return -ENOMEM;
printk(KERN_INFO"free pages get addr:%p\\n",frpgp);
//4
vmlcp = vmalloc(PAGE_SIZE<<4); //大空间
if(!vmlcp)
//do something
return -ENOMEM;
printk(KERN_INFO"vmalloc get addr:%p\\n",vmlcp);
return 0;
//111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
printk(KERN_INFO "GOODBYE LINUX\\n");
//1
kfree(kmlcp);
//2
kmem_cache_free(h_cache,kmemcp);
kmem_cache_destroy(h_cache);
//3
free_pages((unsigned long)frpgp,0);
//4
vfree(vmlcp);
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");//许可 GPL、GPL v2、Dual MPL/GPL、Proprietary(专有)等,没有内核会提示
MODULE_AUTHOR("KGZ"); //作者
MODULE_VERSION("V1.0"); //版本
top,free,cat /pro/meminfo查看内存使用情况。cat /pro/slabinfo。cat /pro/buddyinfo。虚拟内存更详细信息:proc/sys/vm/下文件。如下有地址,说明分配成功。
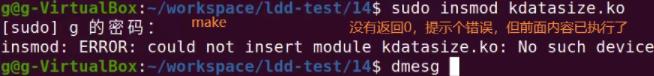
3.内核基础数据类型,移植性和数据对齐
3.1 kdatasize.c
/*
三大类:C标准(int),大小确定(u32),特定内核对象(pid_t)
不同的架构,基础类型大小可能不同,主要区别在long和指针上
可移植性:-Wall,消除所有警告;使用uint32_t等标准类型;页大小为PAGE_SIZE,不要假设4K
大小端:cpu_to_le32() le32_to_cpu()
cpu_to_be32() be32_to_cpu()
......
htonl() ntohl()
htons() ntohs()
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/utsname.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
static void data_cleanup(void)
/* never called */
int data_init(void)
ssize_t n=90888;
/* print information and return an error */
printk("arch Size: char short int long ptr long-long "
" u8 u16 u32 u64\\n");
printk("%-12s %3i %3i %3i %3i %3i %3i "
"%3i %3i %3i %3i\\n",
init_uts_ns.name.machine,
(int)sizeof(char), (int)sizeof(short), (int)sizeof(int),
(int)sizeof(long),
(int)sizeof(void *), (int)sizeof(long long), (int)sizeof(__u8),
(int)sizeof(__u16), (int)sizeof(__u32), (int)sizeof(__u64));
printk("%i, %li, %i, %li\\n",(int)sizeof(pid_t),(long)current->pid,(int)sizeof(ssize_t),(long)n);
printk("le32:%x be32:%x htonl:%x ntohl:%x\\n", cpu_to_le32(0x1234abcd),
cpu_to_be32(0x1234abcd),
htonl(0x1234abcd),
ntohl(0x1234abcd));
return -ENODEV;
module_init(data_init);
module_exit(data_cleanup);
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
3.2 kdataalign.c
/*
自然对齐:在数据项大小的整数倍的地址处存储数据项
字节对齐可以提高CPU的访问效率
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/utsname.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
struct c char c; char t; c;
struct s char c; short t; s;
struct i char c; int t; i;
struct l char c; long t; l;
struct ll char c; long long t; ll;
struct p char c; void * t; p;
struct u1b char c; __u8 t; u1b;
struct u2b char c; __u16 t; u2b;
struct u4b char c; __u32 t; u4b;
struct u8b char c; __u64 t; u8b;
struct
u16 id;
u8 a;
u64 lun;
u16 reserved1;
u32 reserved2;
__attribute__((packed)) scsi;
struct
u16 id;
u8 a;
u64 lun;
u16 reserved1;
u32 reserved2;
scsi1;
static void data_cleanup(void)
/* never called */
static int data_init(void)
/* print information and return an error */
printk("arch Align: char short int long ptr long-long "
" u8 u16 u32 u64\\n");
printk("%-12s %3i %3i %3i %3i %3i %3i "
"%3i %3i %3i %3i\\n",
init_uts_ns.name.machine,
/* note that gcc can subtract void * values, but it's not ansi */
(int)((void *)(&c.t) - (void *)&c),
(int)((void *)(&s.t) - (void *)&s),
(int)((void *)(&i.t) - (void *)&i),
(int)((void *)(&l.t) - (void *)&l),
(int)((void *)(&p.t) - (void *)&p),
(int)((void *)(&ll.t) - (void *)&ll),
(int)((void *)(&u1b.t) - (void *)&u1b),
(int)((void *)(&u2b.t) - (void *)&u2b),
(int)((void *)(&u4b.t) - (void *)&u4b),
(int)((void *)(&u8b.t) - (void *)&u8b));
//printk("%lx %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx \\n",(unsigned long)&c,(unsigned long)&s,(unsigned long)&i,(unsigned long)&l,(unsigned long)&p,(unsigned long)&ll,(unsigned long)&u1b,(unsigned long)&u2b,(unsigned long)&u4b,(unsigned long)&u8b);
printk("packed %i unpacked %i\\n",(int)sizeof(scsi),(int)sizeof(scsi1));
printk(" id a lun reserved1 reserved2\\n");
printk("scsi %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx",(unsigned long)&scsi.id,(unsigned long)&scsi.a,(unsigned long)&scsi.lun,(unsigned long)&scsi.reserved1,(unsigned long)&scsi.reserved2);
printk("scsi1 %lx %lx %lx %lx %lx\\n",(unsigned long)&scsi1.id,(unsigned long)&scsi1.a,(unsigned long)&scsi1.lun,(unsigned long)&scsi1.reserved1,(unsigned long)&scsi1.reserved2);
return -ENODEV;
module_init(data_init);
module_exit(data_cleanup);
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");

以上是关于Notes16proc文件系统,内存分配,数据类型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章