优化算法多目标花朵授粉算法(MOFPA)含Matlab源码 1594期
Posted 紫极神光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了优化算法多目标花朵授粉算法(MOFPA)含Matlab源码 1594期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【优化算法】多目标花朵授粉算法(MOFPA)【含Matlab源码 1594期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、花朵授粉算法简介
介绍了一种新的元启发式群智能算法——花朵授粉算法(flower pollinate algorithm,FPA)和一种新型的差分进化变异策略——定向变异(targeted mutation,TM)策略。针对FPA存在的收敛速度慢、寻优精度低、易陷入局部最优等问题,提出了一种基于变异策略的改进型花朵授粉算法——MFPA。该算法通过改进TM策略,并应用到FPA的局部搜索过程中,以增强算法的局部开发能力。



三、部分源代码
% -------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% Multiobjective flower pollenation algorithm (MOFPA) %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Notes: This demo program contains the very basic components of %
% the multiobjective flower pollination algorithm (MOFPA) %
% for bi-objective optimization. It usually works well for %
% unconstrained functions only. For functions/problems with %
% limits/bounds and constraints, constraint-handling techniques %
% should be implemented to deal with constrained problems properly. %
% %
%% Notes: --------------------------------------------------------------- %
% n=# of the solutions in the population
% m=# of objectives, d=# of dimensions
% S or Sol has a size of n by d
% f = objective values of [n by m]
% RnD = Rank of solutions and crowding Distances, so size of [n by 2] %
function [best,fmin,N_iter]=mofpa(para)
% Default parameters
if nargin<1,
para=[100 1000 0.8];
end
n=para(1); % Population size, typically 10 to 25
Iter_max=para(2); % Max number of iterations
p=para(3); % probabibility switch
% Number of objectives
m=2;
% Rank and distance matrix
RnD=zeros(n,2);
% Dimension of the search variables
d=30;
% Simple lower and upper bounds
Lb=0*ones(1,d); Ub=1*ones(1,d);
%% Initialize the population
for i=1:n,
Sol(i,:)=Lb+(Ub-Lb).*rand(1,d);
f(i,1:m) = obj_funs(Sol(i,:), m);
end
% Store the fitness or objective values
f_new=f;
%% Sort the initialized population
x=[Sol f]; % combined into a single input
% Non-dominated sorting for the initila population
Sorted=solutions_sorting(x, m,d);
% Decompose into solutions, fitness, rank and distances
Sol=Sorted(:,1:d);
f=Sorted(:,(d+1):(d+m));
RnD=Sorted(:,(d+m+1):end);
% Start the iterations -- Flower Algorithm
for t=1:Iter_max,
% Loop over all flowers/solutions
for i=1:n,
% Pollens are carried by insects and thus can move in
% large scale, large distance.
% This L should replace by Levy flights
% Formula: x_i^t+1=x_i^t+ L (x_i^t-gbest)
if rand>p,
%% L=rand;
L=Levy(d);
% The best is stored as the first row Sol(1,:) of the sorted solutions
dS=L.*(Sol(i,:)-Sol(1,:));
S(i,:)=Sol(i,:)+dS;
% Check if the simple limits/bounds are OK
S(i,:)=simplebounds(S(i,:),Lb,Ub);
% If not, then local pollenation of neighbor flowers
else
epsilon=rand;
% Find random flowers in the neighbourhood
JK=randperm(n);
% As they are random, the first two entries also random
% If the flower are the same or similar species, then
% they can be pollenated, otherwise, no action.
% Formula: x_i^t+1+epsilon*(x_j^t-x_k^t)
S(i,:)=Sol(1,:)+epsilon*(Sol(JK(1),:)-Sol(JK(2),:));
% Check if the simple limits/bounds are OK
S(i,:)=simplebounds(S(i,:),Lb,Ub);
end
end % end of for loop
%% Evalute the fitness/function values of the new population
for i=1:n,
f_new(i, 1:m) = obj_funs(S(i,1:d),m);
if (f_new(i,1:m) <= f(i,1:m)),
f(i,1:m)=f_new(i,1:m);
end
% Update the current best (stored in the first row)
if (f_new(i,1:m) <= f(1,1:m)),
Sol(1,1:d) = S(i,1:d);
f(1,:)=f_new(i,:);
end
end % end of for loop
%% ! It's very important to combine both populations, otherwise,
%% the results may look odd and will be very inefficient. !
%% The combined population consits of both the old and new solutions
%% So the total size of the combined population for sorting is 2*n
X(1:n,:)=[S f_new]; % Combine new solutions
X((n+1):(2*n),:)=[Sol f]; % Combine old solutions
Sorted=solutions_sorting(X, m, d);
%% Select n solutions among a combined population of 2*n solutions
new_Sol=Select_pop(Sorted, m, d, n);
% Decompose into solutions, fitness and ranking
Sol=new_Sol(:,1:d); % Sorted solutions
f=new_Sol(:,(d+1):(d+m)); % Sorted objective values
RnD=new_Sol(:,(d+m+1):end); % Sorted ranks and distances
%% Running display at each 100 iterations
if ~mod(t,100),
disp(strcat('Iterations t=',num2str(t)));
plot(f(:, 1), f(:, 2),'ro','MarkerSize',3);
% axis([0 1 -0.8 1]);
xlabel('f_1'); ylabel('f_2');
drawnow;
end
end % end of iterations
%% End of the main program %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Application of simple constraints or bounds
function s=simplebounds(s,Lb,Ub)
% Apply the lower bound
ns_tmp=s;
I=ns_tmp<Lb;
ns_tmp(I)=Lb(I);
% Apply the upper bounds
J=ns_tmp>Ub;
ns_tmp(J)=Ub(J);
% Update this new move
s=ns_tmp;
% Draw n Levy flight sample
function L=Levy(d)
% Levy exponent and coefficient
% For details, see Chapter 11 of the following book:
% Xin-She Yang, Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms, Elsevier, (2014).
beta=3/2;
sigma=(gamma(1+beta)*sin(pi*beta/2)/(gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*2^((beta-1)/2)))^(1/beta);
u=randn(1,d)*sigma;
v=randn(1,d);
step=u./abs(v).^(1/beta);
L=0.1*step;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Make sure all the new solutions are within the limits
function [ns]=findlimits(ns,Lb,Ub)
% Apply the lower bound
ns_tmp=ns;
I=ns_tmp < Lb;
ns_tmp(I)=Lb(I);
% Apply the upper bounds
J=ns_tmp>Ub;
ns_tmp(J)=Ub(J);
% Update this new move
ns=ns_tmp;
四、运行结果
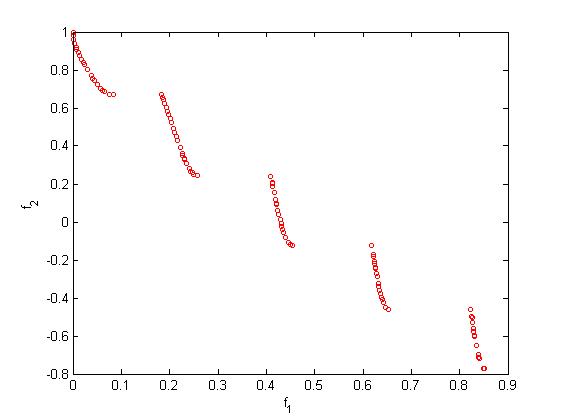
五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
以上是关于优化算法多目标花朵授粉算法(MOFPA)含Matlab源码 1594期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章