机器视觉Python+OpenCV+MediaPipe手势识别系统
Posted 学姐带你玩AI
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器视觉Python+OpenCV+MediaPipe手势识别系统相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

安装所需模块:
pip install cv2
pip install midiapipe
MediaPipe
MediaPipe 为直播和流媒体提供跨平台、可定制的机器学习解决方案。
- 端到端加速引擎:内置的快速 ML 推理和处理即使在常见硬件上也能加速
- 一次构建,任意部署:统一解决方案适用于 android、ios、桌面/云、Web 和物联网
- 即用型解决方案:先进的机器学习解决方案展示了框架的全部功能
- 免费开源:Apache 2.0下的框架和解决方案,完全可扩展和可定制
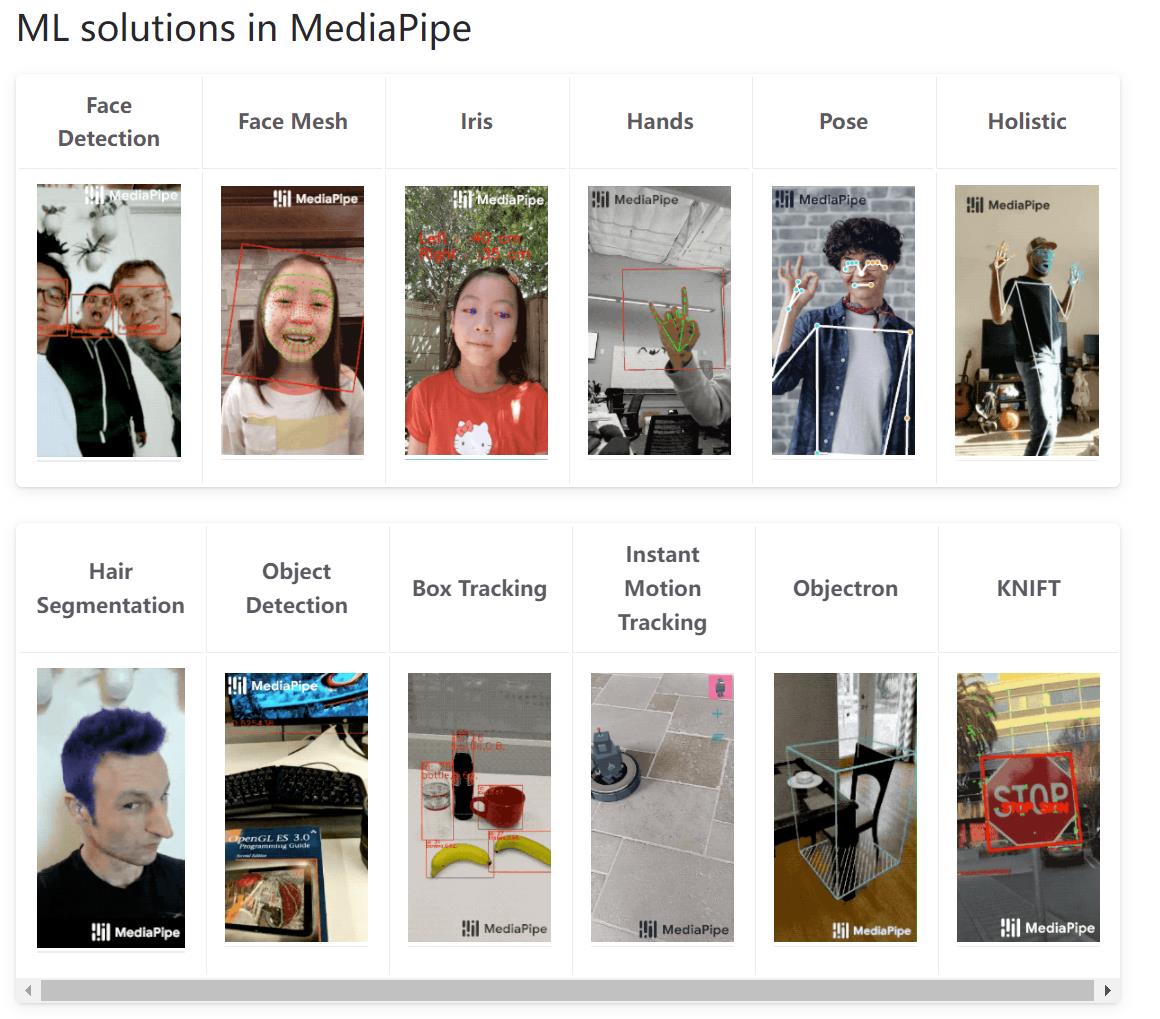
MediaPipe主要应用:
- 人脸检测
- 脸部几何
- 物体检测
- 即时物体追踪
我们首先构建一个Hand对象,然后创建hands和mpDraw两个对象,分别用于检测手和绘制手指关键点。
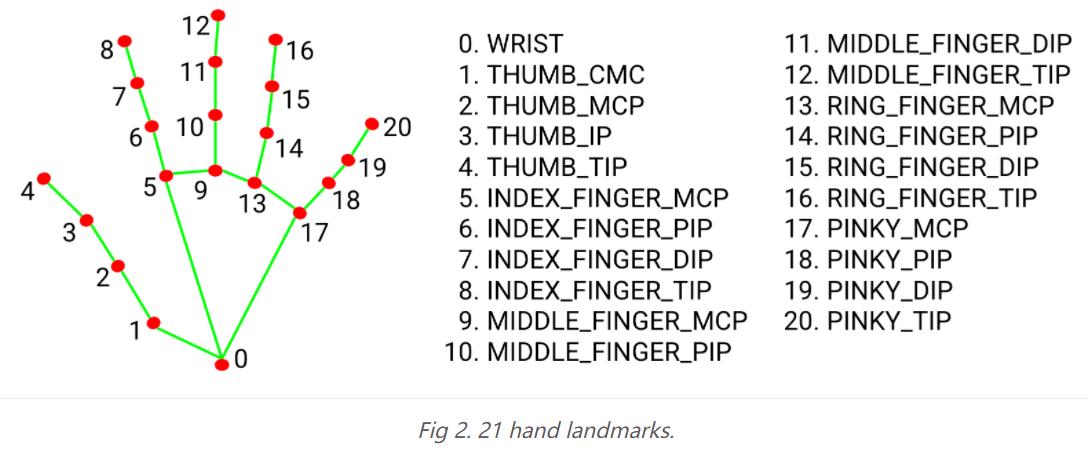
手地标模型:
mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mpHands.Hands(args.mode, args.maxHands, args.model_complexity, args.detectionCon, args.trackCon) # 用于检测手
mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 绘制关键点
results = 0
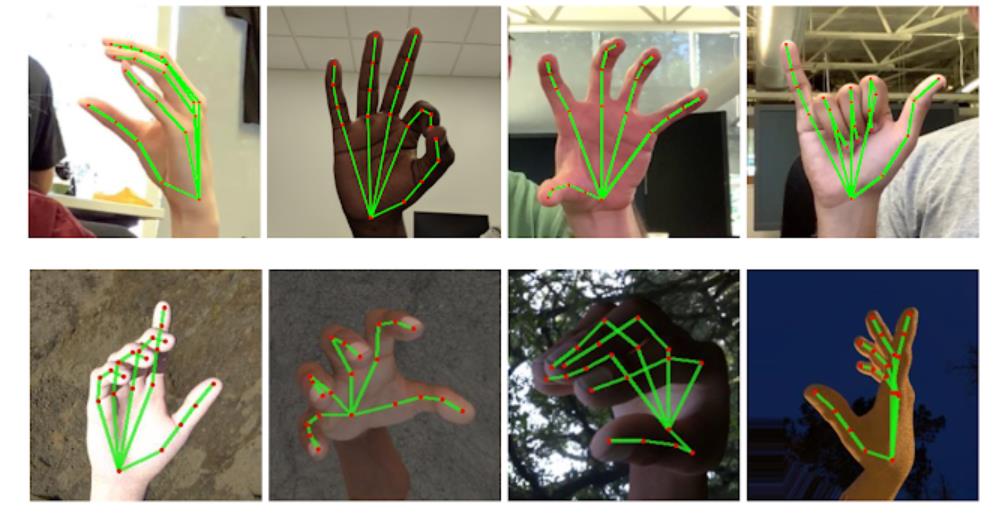
该对象会识别出人手的21个关键点部位,如上图所示,21个关键点分别对应人手的不同关节位置,用于定位手的位置。
def findHands(img, draw=True):
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
global results
results = hands.process(imgRGB)
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
该段代码用于检测图像中的手,首先将图片转成RGB图像,然后利用hands对象进行识别,然后再使用mpDrwa在人手上绘制关键点。
# 获取关节点位置
def findPosition(img, draw=True):
lmLists = []
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for id, lm in enumerate(handLms.landmark):
h, w, c = img.shape
cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
lmLists.append([id, cx, cy])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 12, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
return lmLists
如果已经检测到手部,之后会进行检测关键点位置,将其进行返回,返回的是一个包含21个元素的列表,每个元素由为一个列表,内置有不同关键点的相对坐标。
if len(lmList) != 0:
max_list = [lmList[4][2], lmList[8][2], lmList[12][2], lmList[16][2], lmList[20][2]] # 每个手指的尖端部位
count = 0 # 手势数字结果
# 手势为4
if max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[3] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[
4] < \\
lmList[9][2] and max_list[0] > lmList[9][2] and max_list[0] > lmList[17][2]:
count = 4
# 手势为3
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[3] < lmList[9][2] and \\
lmList[20][
2] > lmList[9][2]:
count = 3
# 手势为2
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[16][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[20][2]:
count = 2
# 手势为1
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[16][2] and lmList[20][2] > lmList[9][2] and lmList[12][2] > \\
lmList[9][
2]:
count = 1
# 手势为5
else:
count = 5
该段代码用于进行手势识别,按照21个关键点的相对位置,判断此时图像的手势情况。

完整代码
本项目可以使用文件输入和摄像头进行输入,下面代码采用的是文件输入,如果需要使用摄像头作为输入源,只需要将 cap = cv2.VideoCapture("video/finger3.MP4") 内部参数置为0即可,不过还需要调整一下其它位置,这里不做过多叙述。
import argparse
import time
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--mode", default=False,
help="Whether to treat the input images as a batch of static and possibly unrelated images, or a video stream.")
ap.add_argument("--maxHands", default=2, help="Maximum number of hands to detect")
ap.add_argument("--model_complexity", default=1, help="Complexity of the hand landmark model: 0 or 1. ")
ap.add_argument("--detectionCon", default=0.8, help="Minimum confidence value for hand detection")
ap.add_argument("--trackCon", default=0.8, help="Minimum confidence value for the hand landmarks")
ap.add_argument("--wCam", default=360, help="width of window")
ap.add_argument("--hCam", default=640, help="height of window")
args = ap.parse_args()
# cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 若使用笔记本自带摄像头则编号为0 若使用外接摄像头 则更改为1或其他编号
# cap.set(3, args.wCam) # 设置窗口的宽高
# cap.set(4, args.hCam)
mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mpHands.Hands(args.mode, args.maxHands, args.model_complexity, args.detectionCon, args.trackCon) # 用于检测手
mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 绘制关键点
results = 0
# 检测图像帧中的手
def findHands(img, draw=True):
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
global results
results = hands.process(imgRGB)
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
# 获取关节点位置
def findPosition(img, draw=True):
lmLists = []
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for id, lm in enumerate(handLms.landmark):
h, w, c = img.shape
cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
lmLists.append([id, cx, cy])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), 12, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
return lmLists
def main():
pTime = 0
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("video/finger3.MP4")
cap.set(3, args.wCam) # 设置窗口的宽高
cap.set(4, args.hCam)
# 检查是否正确打开视频
if cap.isOpened():
open, frame = cap.read()
else:
open = False
while open:
success, img = cap.read() # 读取数据帧
img = cv2.transpose(img)
img = findHands(img) # 检测手
lmList = findPosition(img, draw=False) # 获取手部20个关键点坐标
if len(lmList) != 0:
max_list = [lmList[4][2], lmList[8][2], lmList[12][2], lmList[16][2], lmList[20][2]] # 每个手指的尖端部位
count = 0 # 手势数字结果
# 手势为4
if max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[3] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[
4] < \\
lmList[9][2] and max_list[0] > lmList[9][2] and max_list[0] > lmList[17][2]:
count = 4
# 手势为3
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] and max_list[3] < lmList[9][2] and \\
lmList[20][
2] > lmList[9][2]:
count = 3
# 手势为2
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[16][2] and max_list[2] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[20][2]:
count = 2
# 手势为1
elif max_list[1] < lmList[9][2] < lmList[16][2] and lmList[20][2] > lmList[9][2] and lmList[12][2] > \\
lmList[9][
2]:
count = 1
# 手势为5
else:
count = 5
HandImage = cv2.imread(f'FingerImg/count.jpg')
HandImage = cv2.resize(HandImage, (300, 390))
h, w, c = HandImage.shape
img[0:h, 0:w] = HandImage # 将视频左上角覆盖手势图片
cv2.putText(img, f'int(count)', (400, 280), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 20, (255, 0, 255), 10) # 显示手势图片
cTime = time.time()
fps = 1 / (cTime - pTime) # 每秒传输帧数
pTime = cTime
# cv2.putText(img, f'fps: int(fps)', (500, 180), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 15, (255, 0, 0), 2) # 将帧数显示在窗口
cv2.imshow("Image", cv2.resize(img, (args.wCam, args.hCam)))
cv2.waitKey(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
以上是关于机器视觉Python+OpenCV+MediaPipe手势识别系统的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章