Linux下JAVA WEB服务器的搭建二(REDIS)
Posted 孔子-说
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux下JAVA WEB服务器的搭建二(REDIS)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
5.5 复制启动文件到/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin目录中
5.7 安装redis的接口程序(redis 5.0版本之前需要)
5.8 执行redis的创建集群命令创建集群(注意ip地址和端口号)
5.11 redis-cli --cluster help 说明
7.4 错误 fatal error: jemalloc/jemalloc.h: No such file or directory
要部署普通的java web项目,需要在linux上搭建好web服务器运行环境,包括JDK、tomcat、mysql、redis、nginx等,本文主要介绍redis、nginx的下载安装配置,linux系统采用的是ubuntu。
1、redis介绍
Redis是一个字典结构(key-value)的存储服务器,和Memcached类似,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括string(字符串)、list(链表)、set(集合)、zset(sorted set --有序集合)和hash(哈希类型)。这些数据类型都支持push/pop、add/remove及取交集并集和差集及更丰富的操作,而且这些操作都是原子性的。在此基础上,redis支持各种不同方式的排序。与memcached一样,为了保证效率,数据都是缓存在内存中。区别的是redis会周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,并且在此基础上实现了master-slave(主从)同步。Redis属于非关系型数据库(NoSQL)。
NoSQL优点:
- 高可扩展性
- 分布式计算
- 低成本
- 架构的灵活性,半结构化数据
- 没有复杂的关系
NoSQL缺点:
- 没有标准化
- 有限的查询功能(到目前为止)
- 最终一致是不直观的程序
一个Redis实例提供了多个用来存储数据的字典(Redis实例默认建立了16个db,不支持自主进行数据库命名,可以将db理解为“命名空间”),客户端可以指定将数据存储在哪个字典(数据库)中,这与在一个关系数据库实例中可以创建多个数据库类似,所以可以将其中的每个字典都理解成一个独立的数据库。可以通过调整Redis的配置文件redis/redis.conf中的databases来修改这一个值,设置完毕后重启Redis便完成配置。客户端与Redis建立连接后会默认选择0号数据库,不过可以随时使用SELECT命令更换数据库。Redis在集群的情况下不支持使用select命令来切换db,因为Redis集群模式下只有一个db0。
- Redis 官网:https://redis.io/
- Redis菜鸟教程: https://www.runoob.com/redis/redis-tutorial.html
- Windows安装包下载地址:https://github.com/tporadowski/redis/releases
1redis> SELECT 1 # 默认0号db,切换为1号db
2OK
3redis [1] > GET username # 从1号库中获取 username
spring项目中可以在配置文件中配置
spring.redis.database=10
管理redis的可视化客户端目前较流行的有三个:Redis Client ; Redis Desktop Manager ; Redis Studio。
2、redis的下载
进入redis官网下载地址:http://redis.io/download,下载最新稳定版本(stable)或者复制下载链接后直接下载到服务器上。
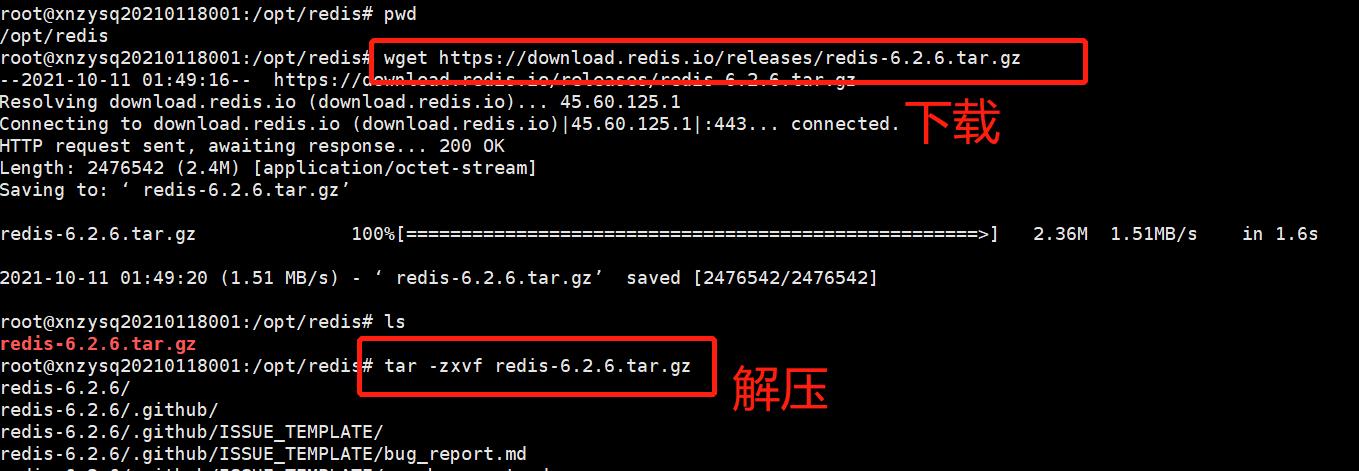
wget https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.6.tar.gz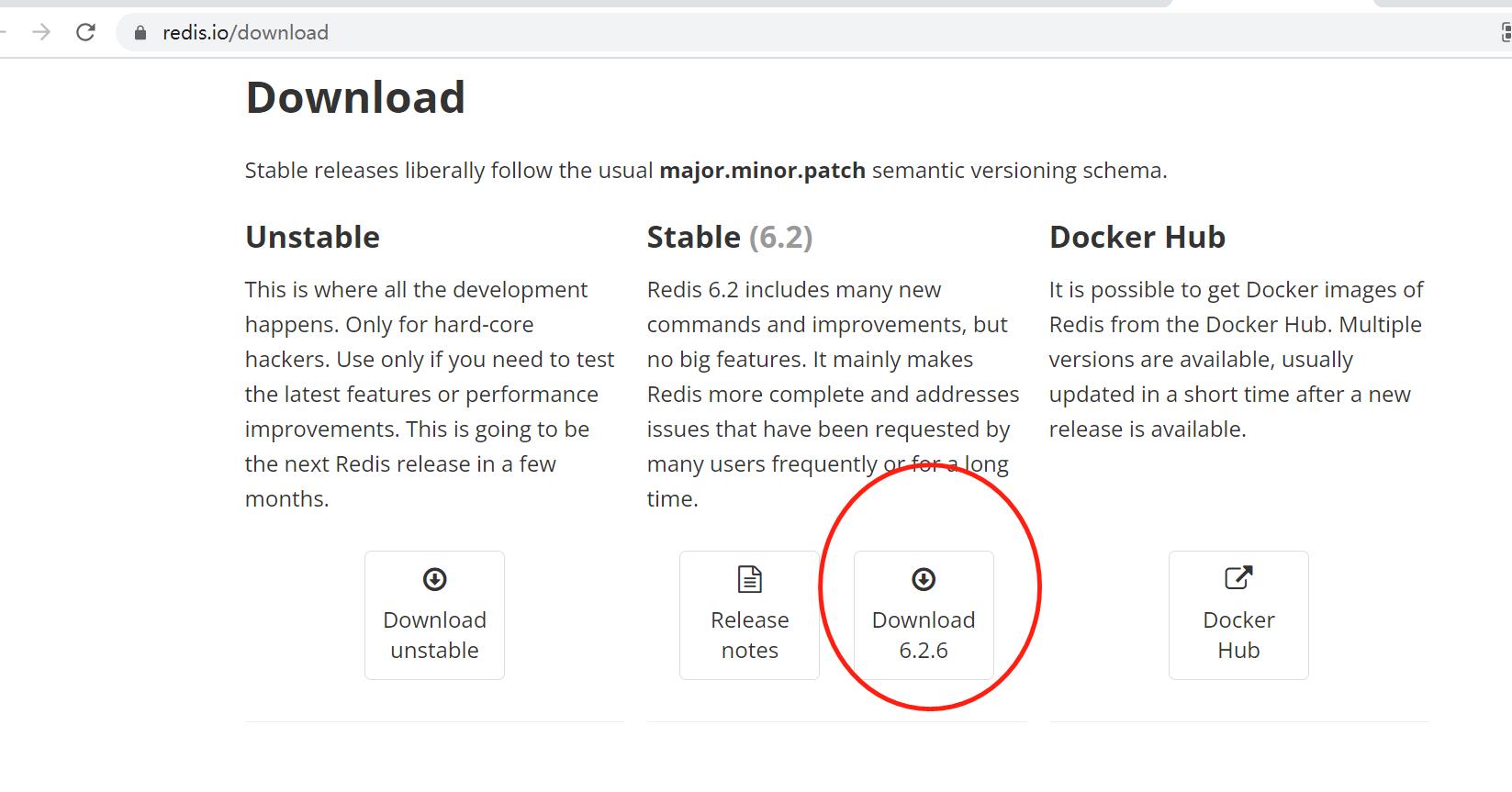
3、redis单机版的安装配置
3.1 redis单机版的安装
1)解压redis tar包
在Ubuntu服务器的/opt目录下新建redis目录,将下载的redis tar安装包复制到该目录下解压。解压命令:tar -zxvf redis-6.2.6.tar.gz 。
- 也可以将redis安装到/usr/local目录下,即 /usr/local/redis 目录。
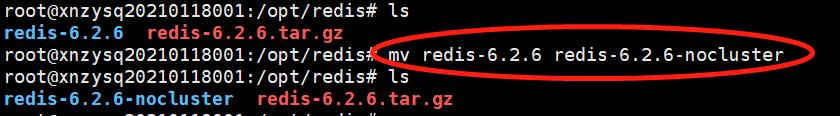
2)解压之后的redis文件夹改名并进入到该目录中 (如果使用的是没有权限的非root账户,则在命令的前面加上 sudo)
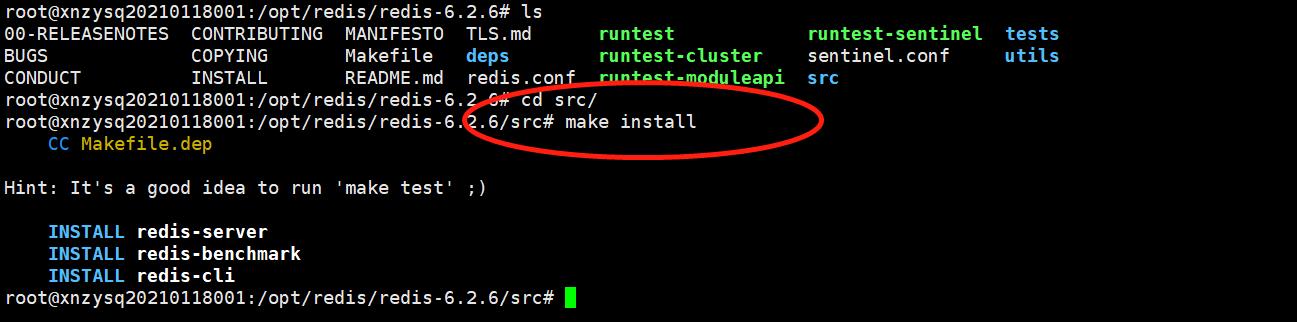
3)使用make命令对源文件进行编译
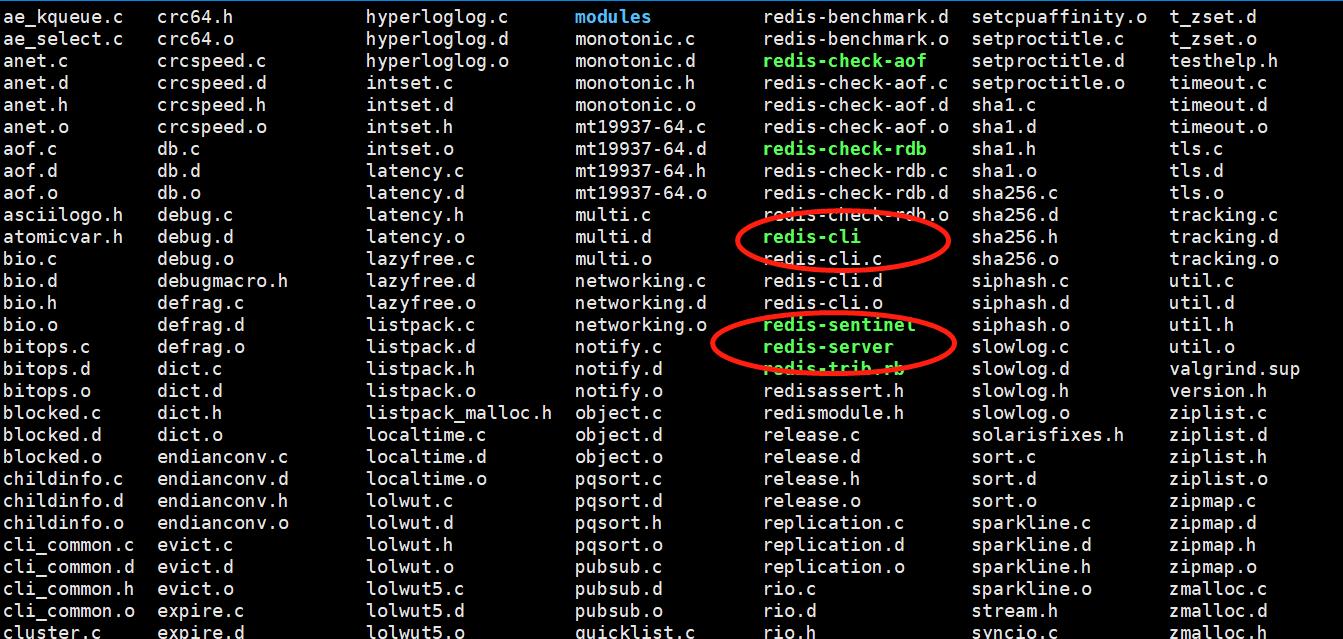
使用make命令对源文件进行编译,若出现安装错误,解决后(可参考本文中的常见错误解决办法),需执行 make distclean 或 make clean 清理后再次执行 make ,检查redis-x.x.x/src 目录下有没有 redis-server、redis-cli 和 /usr/local/bin下有没有。若无,则把redis-x.x.x 文件夹删掉,再解压一次redis的压缩包,cd进入 redis-x.x.x 中, make 一下即可。
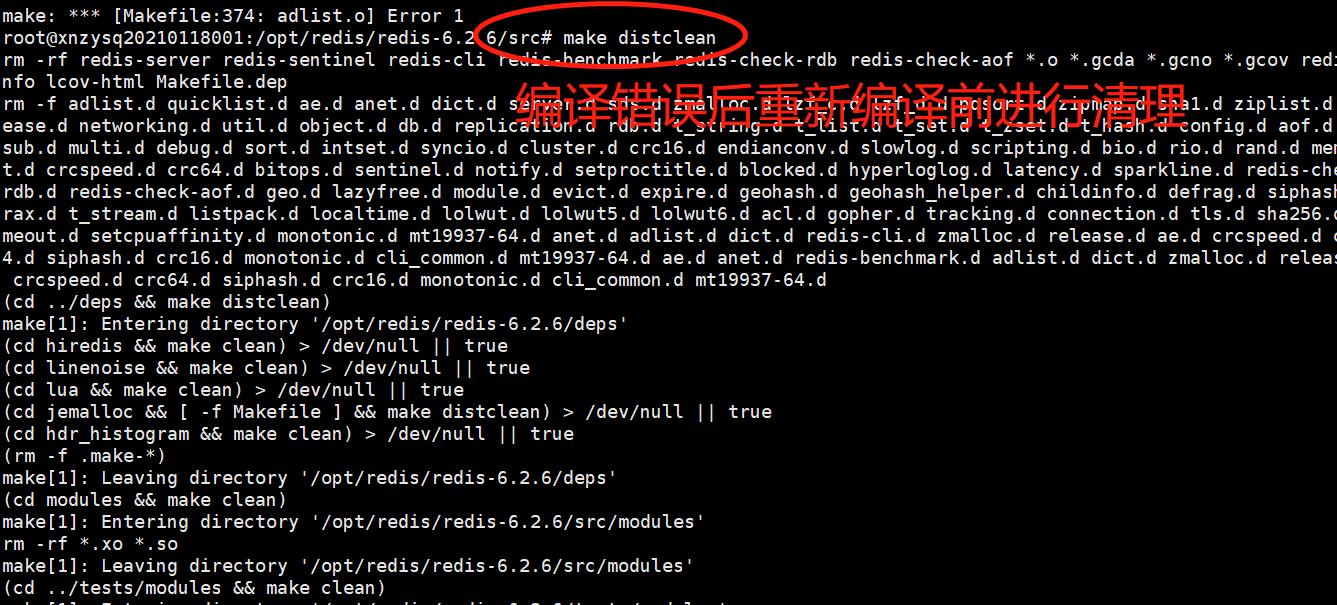
使用make命令编译。
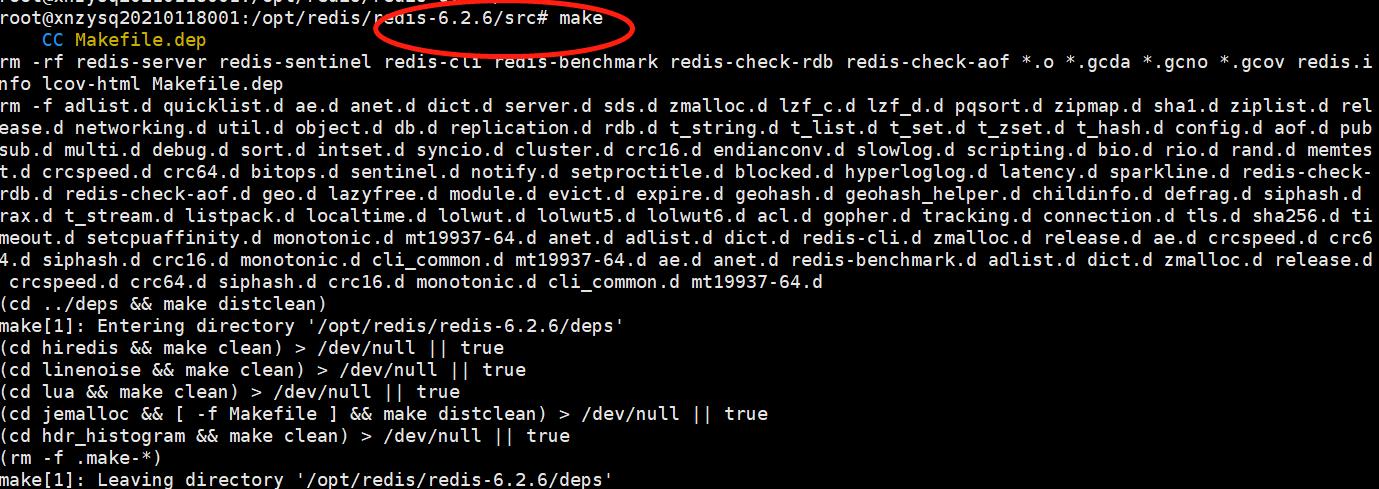
执行完 make 命令后,redis-6.2.6 的 src 目录下会出现编译后的 redis 服务程序 redis-server,还有用于测试的客户端程序 redis-cli,以及redis-benchmark、redis-check-aof、redis-check-dump、redis-sentinel。
4)使用make install 安装redis
执行make install 会将make编译生成的可执行文件拷贝到/usr/local/bin目录下。进入到编译好的src目录,使用make install 命令安装redis,也可以使用PREFIX指定安装目录(make install PREFIX=/usr/local/redis, //redis安装到制定的usr/local/redis的文件夹下面,如果没有redis这个文件夹,会自动创建),一般软件安装到/usr目录下。
3.2 redis单机版的启动/停止
1)Redis命令不区分大小写,常用命令如下:
# 默认配置启动服务
./redis-server
# 指定配置文件启动服务
./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-6.2.6-nocluster/redis.conf
# -h 用于指定 ip -p 用于指定端口 -a 用于指定认证密码
# 打开redis终端,无密码方式
redis-cli
# 打开redis终端,密码方式
redis-cli -a 111111
# 密码方式,可以在redis-cli后单独指定
auth "yourpassword"
ping返回PONG表示畅通
help 命令行的帮助
quit 或 exit 或 Ctrl+d 或 Ctrl+c 退出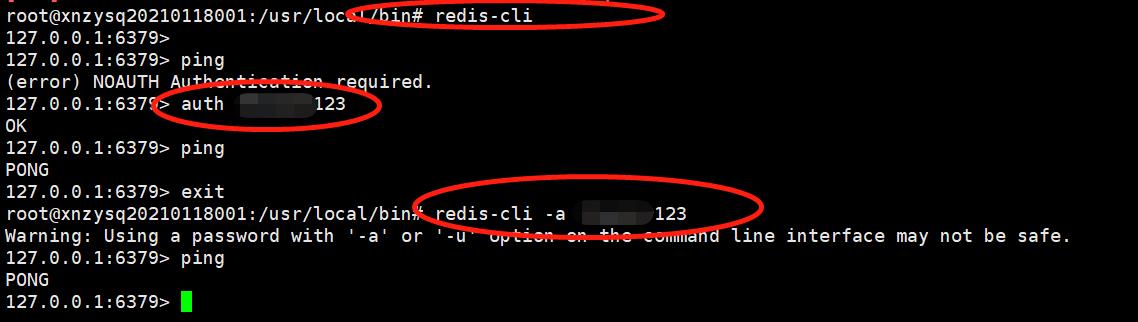
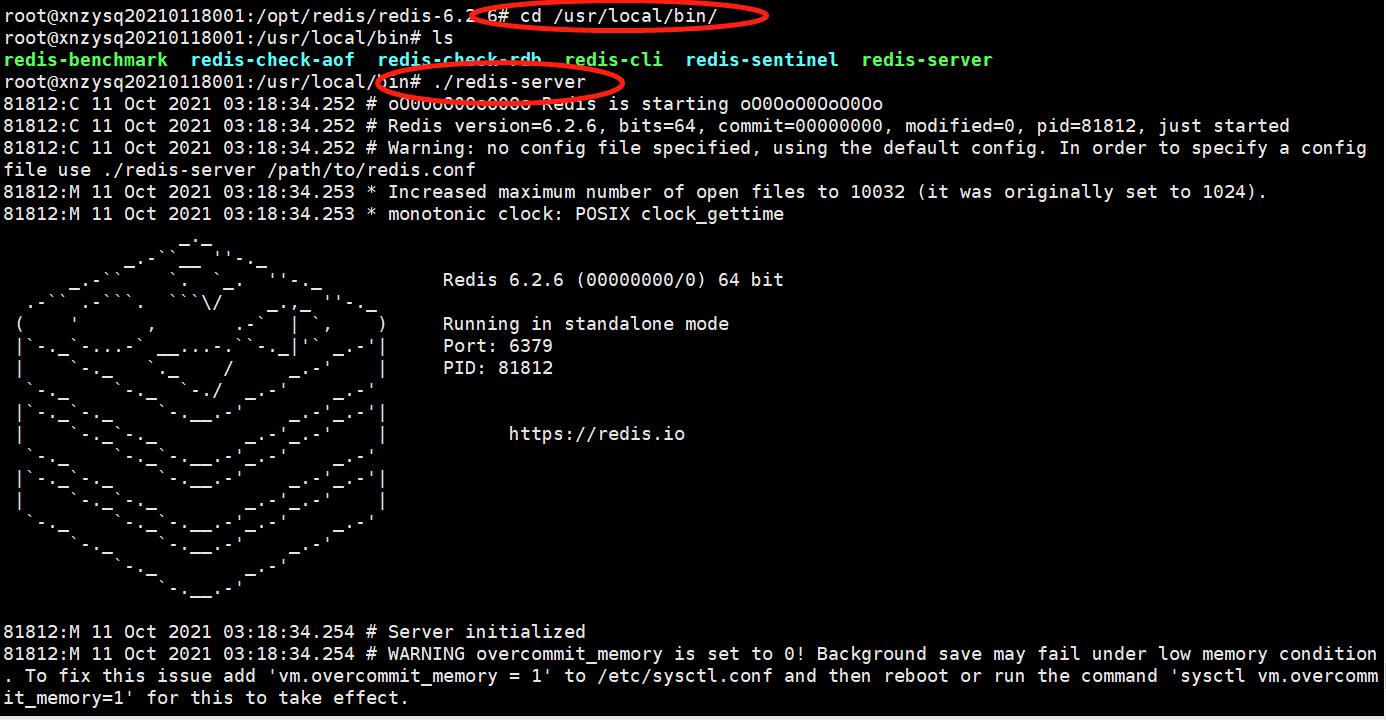
2)启动
进入到redis的安装目录下面的bin文件夹: cd /usr/local/bin/,执行命令启动(使用默认配置): ./redis-server。也可以通过启动参数指定redis的配置: ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-6.2.6-nocluster/redis.conf。

使用redis-cli命令可以打开redis终端(其中127.0.0.1 是本机 IP ,6379 是 redis 服务端口),输入 PING 命令后,如果显示PONG,说明我们已经成功安装了redis。(可据此判断redis服务是否启动)。可以使用ps -ef|grep redis命令查看redis进程。
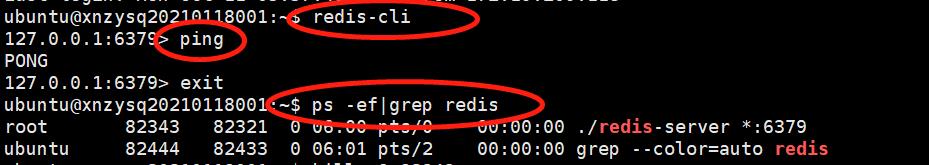
3)停止
以上是通过源码安装的redis,通过redis的客户端程序redis-cli的shutdown命令来停止redis服务。
# redis-cli 客户端控制台,包含参数: -h xxx 指定服务端地址,缺省值是127.0.0.1 -p xxx 指定服务端端口,缺省值是6379
# 停止命令
redis-cli shutdown
# 指定服务器和端口进行停止
redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 shutdown
# 当设置密码后,上面的关闭命令无效,带密码登录:
redis-cli -a [password]
登入后输入 shutdown 即可关闭redis,输入exit 退出。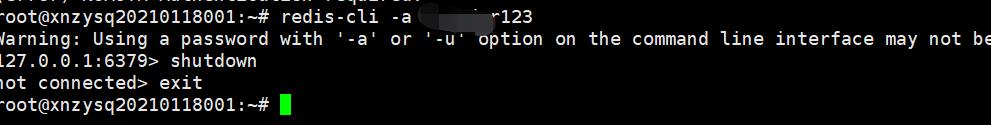
如果是用apt-get或者yum install安装的redis,可以直接通过下面的命令停止/启动/重启redis。
/etc/init.d/redis-server stop
/etc/init.d/redis-server start
/etc/init.d/redis-server restart如果上述方式都没有成功停止redis,则可以使用终极武器 kill -9 。
3.3 redis单机版的配置
进入redis的安装目录/opt/redis/redis-6.2.6-nocluster,编辑redis.conf文件。更改配置完成后保存退出,重新启动redis服务。
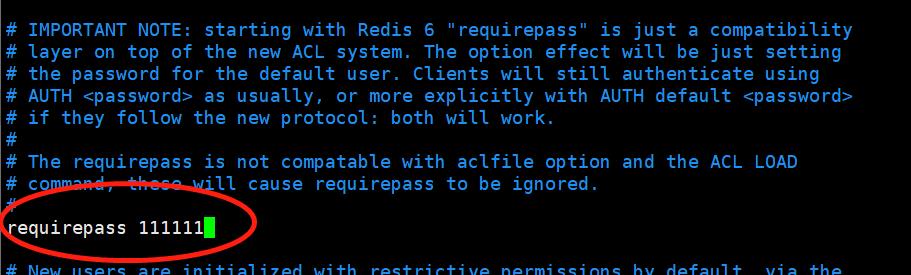
1)设置redis密码
Redis服务器默认是不需要密码的,假设设置密码为111111。去掉requirepass 前面的注释#,在后面添加密码:requirepass 111111
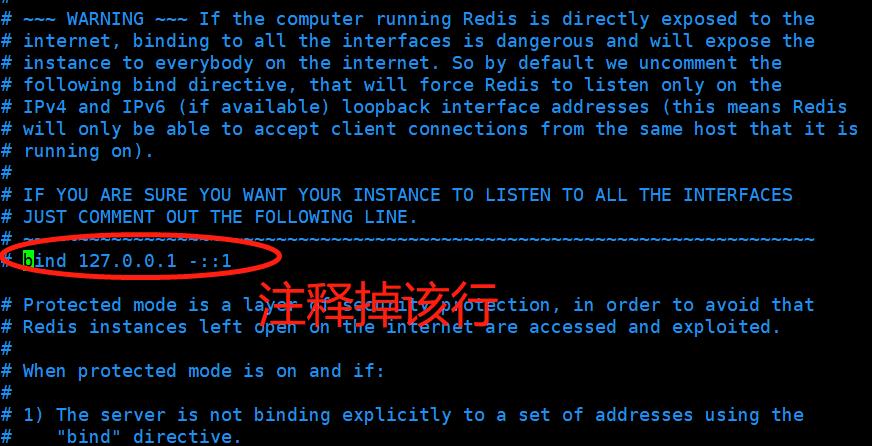
2)开启redis的远程连接
默认情况下只允许本地访问,若需要开启Redis的远程连接,需注释掉绑定地址#bind 127.0.0.1。
3)关闭protected-mode模式
redis3.2版本后新增protected-mode配置,默认是yes,即开启。如果设置外部网络连接redis服务,有以下2种设置方式:
1. 关闭protected-mode模式,此时外部网络可以直接访问。
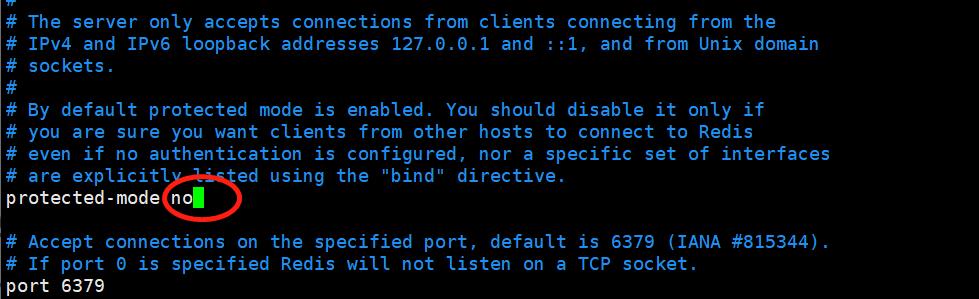
2. 开启protected-mode保护模式,需配置bind ip或者设置访问密码。
bind ip。
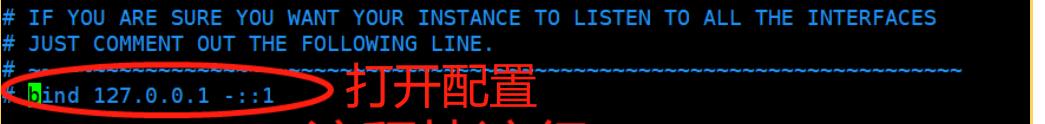
或者设置访问密码。

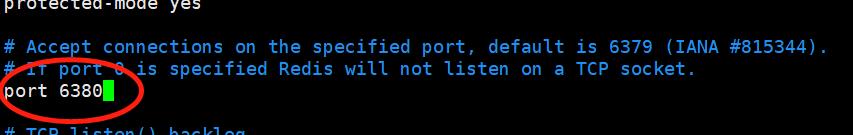
4)修改redis的默认端口
Redis的默认端口为6379,若有需要,更改port后面的值即可。如 port 6380 。
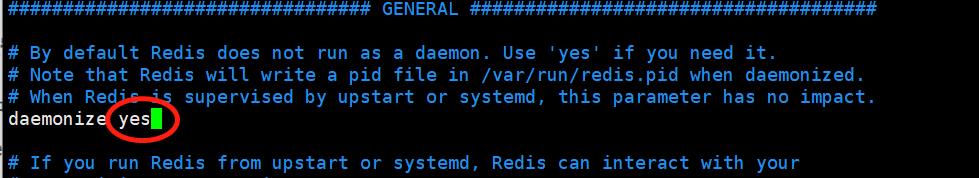
5)修改redis以守护进程运行
如果redis以守护进程运行,则不会在命令行阻塞,类似于服务。如果以非守护进程运行,则当前终端被阻塞,无法使用。推荐改为yes,以守护进程运行。daemonize no 改为 daemonize yes 。
- 当我们采用yes时,redis会在后台运行,此时redis将一直运行,除非手动kill该进程。同时将进程pid号写入至redis.conf选项pidfile设置的文件中,默认会生成在/var/run/redis.pid,也可以通过pidfile来指定pid文件生成的位置。
-
pidfile /path/redis.pid - 而采用no时,当前界面将进入redis的命令行界面,exit强制退出或者关闭连接工具(putty,xshell等)都会导致redis进程退出。
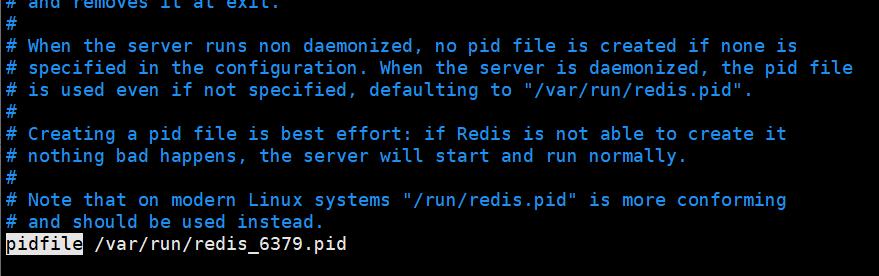
6)更改redis的数据文件名称
有需要的时候可以更改Redis的数据文件名称,dbfilename dump.rdb,一般不需要修改。
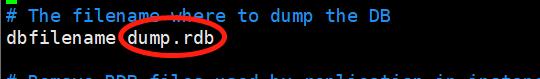
7)更改redis的数据文件存储路径
有需要的时候可以更改Redis的数据文件存储路径,默认值dir ./ 表示在配置文件的同路径下,可以改为如dir /var/lib/redis,一般不需要修改。
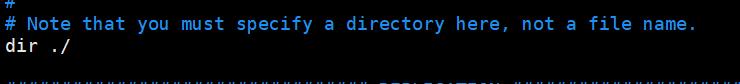
更改配置完成保存退出文件编辑页面,重启redis服务。
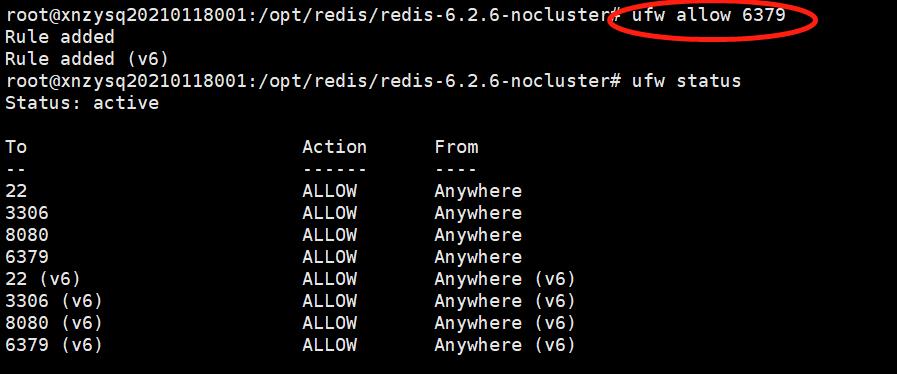
3.4 ubuntu 防火墙开启6379端口
如果redis的端口不在防火墙启用规则中,需添加进去,执行添加6379端口到防火墙规则命令:sudo ufw allow 6379,然后通过sudo ufo status 可以查看到 6379 端口已开放。
3.5 默认配置文件redis.conf详解
# Redis配置文件样例
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specifiy
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
#
# 1k => 1000 bytes
# 1kb => 1024 bytes
# 1m => 1000000 bytes
# 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes
# 1g => 1000000000 bytes
# 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes
#
# units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
# Redis默认不是以守护进程的方式运行,可以通过该配置项修改,使用yes启用守护进程
# 启用守护进程后,Redis会把pid写到一个pidfile中,在/var/run/redis.pid
daemonize no
# 当Redis以守护进程方式运行时,Redis默认会把pid写入/var/run/redis.pid文件,可以通过pidfile指定
pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
# 指定Redis监听端口,默认端口为6379
# 如果指定0端口,表示Redis不监听TCP连接
port 6379
# 绑定的主机地址
# 你可以绑定单一接口,如果没有绑定,所有接口都会监听到来的连接
# bind 127.0.0.1
# Specify the path for the unix socket that will be used to listen for
# incoming connections. There is no default, so Redis will not listen
# on a unix socket when not specified.
#
# unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock
# unixsocketperm 755
# 当客户端闲置多长时间后关闭连接,如果指定为0,表示关闭该功能
timeout 0
# 指定日志记录级别,Redis总共支持四个级别:debug、verbose、notice、warning,默认为verbose
# debug (很多信息, 对开发/测试比较有用)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
loglevel verbose
# 日志记录方式,默认为标准输出,如果配置为redis为守护进程方式运行,而这里又配置为标准输出,则日志将会发送给/dev/null
logfile stdout
# To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes,
# and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs.
# syslog-enabled no
# Specify the syslog identity.
# syslog-ident redis
# Specify the syslog facility. Must be USER or between LOCAL0-LOCAL7.
# syslog-facility local0
# 设置数据库的数量,默认数据库为0,可以使用select <dbid>命令在连接上指定数据库id
# dbid是从0到‘databases’-1的数目
databases 16
################################ SNAPSHOTTING #################################
# 指定在多长时间内,有多少次更新操作,就将数据同步到数据文件,可以多个条件配合
# Save the DB on disk:
#
# save <seconds> <changes>
#
# Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given
# number of write operations against the DB occurred.
#
# 满足以下条件将会同步数据:
# 900秒(15分钟)内有1个更改
# 300秒(5分钟)内有10个更改
# 60秒内有10000个更改
# Note: 可以把所有“save”行注释掉,这样就取消同步操作了
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
# 指定存储至本地数据库时是否压缩数据,默认为yes,Redis采用LZF压缩,如果为了节省CPU时间,可以关闭该选项,但会导致数据库文件变的巨大
rdbcompression yes
# 指定本地数据库文件名,默认值为dump.rdb
dbfilename dump.rdb
# 工作目录.
# 指定本地数据库存放目录,文件名由上一个dbfilename配置项指定
#
# Also the Append Only File will be created inside this directory.
#
# 注意,这里只能指定一个目录,不能指定文件名
dir ./
################################# REPLICATION #################################
# 主从复制。使用slaveof从 Redis服务器复制一个Redis实例。注意,该配置仅限于当前slave有效
# so for example it is possible to configure the slave to save the DB with a
# different interval, or to listen to another port, and so on.
# 设置当本机为slav服务时,设置master服务的ip地址及端口,在Redis启动时,它会自动从master进行数据同步
# slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
# 当master服务设置了密码保护时,slav服务连接master的密码
# 下文的“requirepass”配置项可以指定密码
# masterauth <master-password>
# When a slave lost the connection with the master, or when the replication
# is still in progress, the slave can act in two different ways:
#
# 1) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'yes' (the default) the slave will
# still reply to client requests, possibly with out of data data, or the
# data set may just be empty if this is the first synchronization.
#
# 2) if slave-serve-stale data is set to 'no' the slave will reply with
# an error "SYNC with master in progress" to all the kind of commands
# but to INFO and SLAVEOF.
#
slave-serve-stale-data yes
# Slaves send PINGs to server in a predefined interval. It's possible to change
# this interval with the repl_ping_slave_period option. The default value is 10
# seconds.
#
# repl-ping-slave-period 10
# The following option sets a timeout for both Bulk transfer I/O timeout and
# master data or ping response timeout. The default value is 60 seconds.
#
# It is important to make sure that this value is greater than the value
# specified for repl-ping-slave-period otherwise a timeout will be detected
# every time there is low traffic between the master and the slave.
#
# repl-timeout 60
################################## SECURITY ###################################
# Warning: since Redis is pretty fast an outside user can try up to
# 150k passwords per second against a good box. This means that you should
# use a very strong password otherwise it will be very easy to break.
# 设置Redis连接密码,如果配置了连接密码,客户端在连接Redis时需要通过auth <password>命令提供密码,默认关闭
# requirepass foobared
# Command renaming.
#
# It is possilbe to change the name of dangerous commands in a shared
# environment. For instance the CONFIG command may be renamed into something
# of hard to guess so that it will be still available for internal-use
# tools but not available for general clients.
#
# Example:
#
# rename-command CONFIG b840fc02d524045429941cc15f59e41cb7be6c52
#
# It is also possilbe to completely kill a command renaming it into
# an empty string:
#
# rename-command CONFIG ""
################################### LIMITS ####################################
# 设置同一时间最大客户端连接数,默认无限制,Redis可以同时打开的客户端连接数为Redis进程可以打开的最大文件描述符数,
# 如果设置maxclients 0,表示不作限制。当客户端连接数到达限制时,Redis会关闭新的连接并向客户端返回max Number of clients reached错误信息
# maxclients 128
# Don't use more memory than the specified amount of bytes.
# When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys with an
# EXPIRE set. It will try to start freeing keys that are going to expire
# in little time and preserve keys with a longer time to live.
# Redis will also try to remove objects from free lists if possible.
#
# If all this fails, Redis will start to reply with errors to commands
# that will use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue
# to reply to most read-only commands like GET.
#
# WARNING: maxmemory can be a good idea mainly if you want to use Redis as a
# 'state' server or cache, not as a real DB. When Redis is used as a real
# database the memory usage will grow over the weeks, it will be obvious if
# it is going to use too much memory in the long run, and you'll have the time
# to upgrade. With maxmemory after the limit is reached you'll start to get
# errors for write operations, and this may even lead to DB inconsistency.
# 指定Redis最大内存限制,Redis在启动时会把数据加载到内存中,达到最大内存后,Redis会先尝试清除已到期或即将到期的Key,
# 当此方法处理后,仍然到达最大内存设置,将无法再进行写入操作,但仍然可以进行读取操作。
# Redis新的vm机制,会把Key存放内存,Value会存放在swap区
# maxmemory <bytes>
# MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory
# is reached? You can select among five behavior:
#
# volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm
# allkeys-lru -> remove any key accordingly to the LRU algorithm
# volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set
# allkeys->random -> remove a random key, any key
# volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)
# noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations
#
# Note: with all the kind of policies, Redis will return an error on write
# operations, when there are not suitable keys for eviction.
#
# At the date of writing this commands are: set setnx setex append
# incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd
# sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby
# zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby
# getset mset msetnx exec sort
#
# The default is:
#
# maxmemory-policy volatile-lru
# LRU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated
# algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can select as well the sample
# size to check. For instance for default Redis will check three keys and
# pick the one that was used less recently, you can change the sample size
# using the following configuration directive.
#
# maxmemory-samples 3
############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ###############################
#
# Note that you can have both the async dumps and the append only file if you
# like (you have to comment the "save" statements above to disable the dumps).
# Still if append only mode is enabled Redis will load the data from the
# log file at startup ignoring the dump.rdb file.
# 指定是否在每次更新操作后进行日志记录,Redis在默认情况下是异步的把数据写入磁盘,如果不开启,可能会在断电时导致一段时间内的数据丢失。
# 因为redis本身同步数据文件是按上面save条件来同步的,所以有的数据会在一段时间内只存在于内存中。默认为no
# IMPORTANT: Check the BGREWRITEAOF to check how to rewrite the append
# log file in background when it gets too big.
appendonly no
# 指定更新日志文件名,默认为appendonly.aof
# appendfilename appendonly.aof
# The fsync() call tells the Operating System to actually write data on disk
# instead to wait for more data in the output buffer. Some OS will really flush
# data on disk, some other OS will just try to do it ASAP.
# 指定更新日志条件,共有3个可选值:
# no:表示等操作系统进行数据缓存同步到磁盘(快)
# always:表示每次更新操作后手动调用fsync()将数据写到磁盘(慢,安全)
# everysec:表示每秒同步一次(折衷,默认值)
appendfsync everysec
# appendfsync no
# When the AOF fsync policy is set to always or everysec, and a background
# saving process (a background save or AOF log background rewriting) is
# performing a lot of I/O against the disk, in some Linux configurations
# Redis may block too long on the fsync() call. Note that there is no fix for
# this currently, as even performing fsync in a different thread will block
# our synchronous write(2) call.
#
# In order to mitigate this problem it's possible to use the following option
# that will prevent fsync() from being called in the main process while a
# BGSAVE or BGREWRITEAOF is in progress.
#
# This means that while another child is saving the durability of Redis is
# the same as "appendfsync none", that in pratical terms means that it is
# possible to lost up to 30 seconds of log in the worst scenario (with the
# default Linux settings).
#
# If you have latency problems turn this to "yes". Otherwise leave it as
# "no" that is the safest pick from the point of view of durability.
no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no
# Automatic rewrite of the append only file.
# Redis is able to automatically rewrite the log file implicitly calling
# BGREWRITEAOF when the AOF log size will growth by the specified percentage.
#
# This is how it works: Redis remembers the size of the AOF file after the
# latest rewrite (or if no rewrite happened since the restart, the size of
# the AOF at startup is used).
#
# This base size is compared to the current size. If the current size is
# bigger than the specified percentage, the rewrite is triggered. Also
# you need to specify a minimal size for the AOF file to be rewritten, this
# is useful to avoid rewriting the AOF file even if the percentage increase
# is reached but it is still pretty small.
#
# Specify a precentage of zero in order to disable the automatic AOF
# rewrite feature.
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
################################## SLOW LOG ###################################
# The Redis Slow Log is a system to log queries that exceeded a specified
# execution time. The execution time does not include the I/O operations
# like talking with the client, sending the reply and so forth,
# but just the time needed to actually execute the command (this is the only
# stage of command execution where the thread is blocked and can not serve
# other requests in the meantime).
#
# You can configure the slow log with two parameters: one tells Redis
# what is the execution time, in microseconds, to exceed in order for the
# command to get logged, and the other parameter is the length of the
# slow log. When a new command is logged the oldest one is removed from the
# queue of logged commands.
# The following time is expressed in microseconds, so 1000000 is equivalent
# to one second. Note that a negative number disables the slow log, while
# a value of zero forces the logging of every command.
slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
# There is no limit to this length. Just be aware that it will consume memory.
# You can reclaim memory used by the slow log with SLOWLOG RESET.
slowlog-max-len 1024
################################ VIRTUAL MEMORY ###############################
### WARNING! Virtual Memory is deprecated in Redis 2.4
### The use of Virtual Memory is strongly discouraged.
### WARNING! Virtual Memory is deprecated in Redis 2.4
### The use of Virtual Memory is strongly discouraged.
# Virtual Memory allows Redis to work with datasets bigger than the actual
# amount of RAM needed to hold the whole dataset in memory.
# In order to do so very used keys are taken in memory while the other keys
# are swapped into a swap file, similarly to what operating systems do
# with memory pages.
# 指定是否启用虚拟内存机制,默认值为no,
# VM机制将数据分页存放,由Redis将访问量较少的页即冷数据swap到磁盘上,访问多的页面由磁盘自动换出到内存中
# 把vm-enabled设置为yes,根据需要设置好接下来的三个VM参数,就可以启动VM了
vm-enabled no
# vm-enabled yes
# This is the path of the Redis swap file. As you can guess, swap files
# can't be shared by different Redis instances, so make sure to use a swap
# file for every redis process you are running. Redis will complain if the
# swap file is already in use.
#
# Redis交换文件最好的存储是SSD(固态硬盘)
# 虚拟内存文件路径,默认值为/tmp/redis.swap,不可多个Redis实例共享
# *** WARNING *** if you are using a shared hosting the default of putting
# the swap file under /tmp is not secure. Create a dir with access granted
# only to Redis user and configure Redis to create the swap file there.
vm-swap-file /tmp/redis.swap
# With vm-max-memory 0 the system will swap everything it can. Not a good
# default, just specify the max amount of RAM you can in bytes, but it's
# better to leave some margin. For instance specify an amount of RAM
# that's more or less between 60 and 80% of your free RAM.
# 将所有大于vm-max-memory的数据存入虚拟内存,无论vm-max-memory设置多少,所有索引数据都是内存存储的(Redis的索引数据就是keys)
# 也就是说当vm-max-memory设置为0的时候,其实是所有value都存在于磁盘。默认值为0
vm-max-memory 0
# Redis swap文件分成了很多的page,一个对象可以保存在多个page上面,但一个page上不能被多个对象共享,vm-page-size是要根据存储的数据大小来设定的。
# 建议如果存储很多小对象,page大小最后设置为32或64bytes;如果存储很大的对象,则可以使用更大的page,如果不确定,就使用默认值
vm-page-size 32
# 设置swap文件中的page数量由于页表(一种表示页面空闲或使用的bitmap)是存放在内存中的,在磁盘上每8个pages将消耗1byte的内存
# swap空间总容量为 vm-page-size * vm-pages
#
# With the default of 32-bytes memory pages and 134217728 pages Redis will
# use a 4 GB swap file, that will use 16 MB of RAM for the page table.
#
# It's better to use the smallest acceptable value for your application,
# but the default is large in order to work in most conditions.
vm-pages 134217728
# Max number of VM I/O threads running at the same time.
# This threads are used to read/write data from/to swap file, since they
# also encode and decode objects from disk to memory or the reverse, a bigger
# number of threads can help with big objects even if they can't help with
# I/O itself as the physical device may not be able to couple with many
# reads/writes operations at the same time.
# 设置访问swap文件的I/O线程数,最后不要超过机器的核数,如果设置为0,那么所有对swap文件的操作都是串行的,可能会造成比较长时间的延迟,默认值为4
vm-max-threads 4
############################### ADVANCED CONFIG ###############################
# Hashes are encoded in a special way (much more memory efficient) when they
# have at max a given numer of elements, and the biggest element does not
# exceed a given threshold. You can configure this limits with the following
# configuration directives.
# 指定在超过一定的数量或者最大的元素超过某一临界值时,采用一种特殊的哈希算法
hash-max-zipmap-entries 512
hash-max-zipmap-value 64
# Similarly to hashes, small lists are also encoded in a special way in order
# to save a lot of space. The special representation is only used when
# you are under the following limits:
list-max-ziplist-entries 512
list-max-ziplist-value 64
# Sets have a special encoding in just one case: when a set is composed
# of just strings that happens to be integers in radix 10 in the range
# of 64 bit signed integers.
# The following configuration setting sets the limit in the size of the
# set in order to use this special memory saving encoding.
set-max-intset-entries 512
# Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded in
# order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the length and
# elements of a sorted set are below the following limits:
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128
zset-max-ziplist-value 64
# Active rehashing uses 1 millisecond every 100 milliseconds of CPU time in
# order to help rehashing the main Redis hash table (the one mapping top-level
# keys to values). The hash table implementation redis uses (see dict.c)
# performs a lazy rehashing: the more operation you run into an hash table
# that is rhashing, the more rehashing "steps" are performed, so if the
# server is idle the rehashing is never complete and some more memory is used
# by the hash table.
#
# The default is to use this millisecond 10 times every second in order to
# active rehashing the main dictionaries, freeing memory when possible.
#
# If unsure:
# use "activerehashing no" if you have hard latency requirements and it is
# not a good thing in your environment that Redis can reply form time to time
# to queries with 2 milliseconds delay.
# 指定是否激活重置哈希,默认为开启
activerehashing yes
################################## INCLUDES ###################################
# 指定包含其他的配置文件,可以在同一主机上多个Redis实例之间使用同一份配置文件,而同时各实例又拥有自己的特定配置文件
# include /path/to/local.conf
# include /path/to/other.conf
4、Java 使用 Redis
1)首先下载驱动包,下载 jedis.jar,或通过maven工程引入。
<!--redis的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</dependency>2)redis的连接和操作
package com.kz.example.common.redis;
/**
* redis的连接和操作测试
*
* @Author kongzi
* @Date 2021/10/11 15:36
* @Version 1.0
*/
import org.junit.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class RedisTest
private Jedis jedis = new Jedis("172.19.82.206", 6379);
@Test
public void RedisFun1()
// 若没有密码注释掉下面这行
jedis.auth("founder123");
String string = jedis.set("zzz", "11");
String value = jedis.get("zzz");
System.out.println(value);
jedis.incr("zzz");
System.out.println("自增之后的zzz的值为" + jedis.get("zzz"));
System.out.println("decr之后的值" + jedis.decr("zzz"));
jedis.append("zzz", "append");
System.out.println(jedis.get("zzz"));
jedis.del("zzz");
System.out.println("is exist?" + jedis.exists("zzz"));
jedis.close();
@Test
public void RedisList()
// 若没有密码注释掉下面这行
jedis.auth("founder123");
//将数据存储到list数据中的时候,先存储在list中的数据,是在最左面,删除的话,删除的是最左面的。
jedis.lpush("list5", "1", "2", "3");
List<String> lrange = jedis.lrange("list5", 0, -1);
for (String string2 : lrange)
System.out.println(string2);
String lpop = jedis.lpop("list5");
String rpop = jedis.rpop("list5");
System.out.println("删除的左边的元素是" + lpop + "删除的右边的元素是" + rpop);
jedis.del("list5");
System.out.println("is list5 exist?" + jedis.exists("list5"));
@Test
public void RedisSet()
// 若没有密码注释掉下面这行
jedis.auth("founder123");
jedis.sadd("set1", "e", "a", "b", "c", "d");
Set<String> smembers = jedis.smembers("set1");
System.out.println(smembers);
//弹出右边的一个
String lpop = jedis.spop("set1");
System.out.println(lpop);
@Test
public void hash()
// 若没有密码注释掉下面这行
jedis.auth("founder123");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("k1", "v1");
map.put("k2", "v2");
map.put("k3", "v3");
jedis.hmset("map1", map);
Map<String, String> map2 = jedis.hgetAll("map1");
System.out.println(map2.toString());
5、redis集群版的安装配置
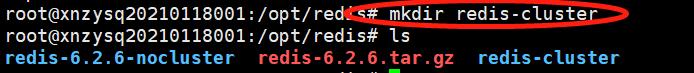
5.1 创建redis集群目录
在/opt/redis目录下创建redis集群目录(目录一般也可以设置到/usr/local/下面),命令:mkdir redis-cluster 。
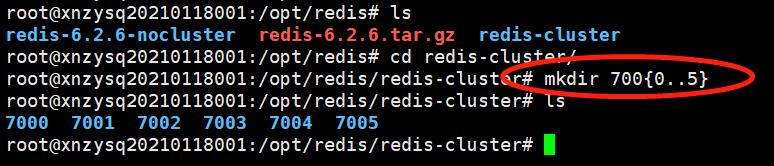
5.2 创建redis集群节点
进入redis-cluster目录,创建6个文件夹,作为redis的6个节点,对应3个服务和3个备份机。文件夹以端口命名,文件夹名分别为7000 7001 7002 7003 7004 7005。命令:mkdir 7000..5 。
搭建的redis的集群,因为选举投票的机制,所以必须为奇数,并且为了保证高可用,所以搭建了3个机器的redis集群,并且为每个节点,搭建了一个备份机。
5.3 复制配置文件到6个节点目录
从已经安装的redis中,复制redis.conf文件到上面的6个文件目录。
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7000/7000.conf
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7001/7001.conf
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7002/7002.conf
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7003/7003.conf
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7004/7004.conf
cp redis.conf /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7005/7005.conf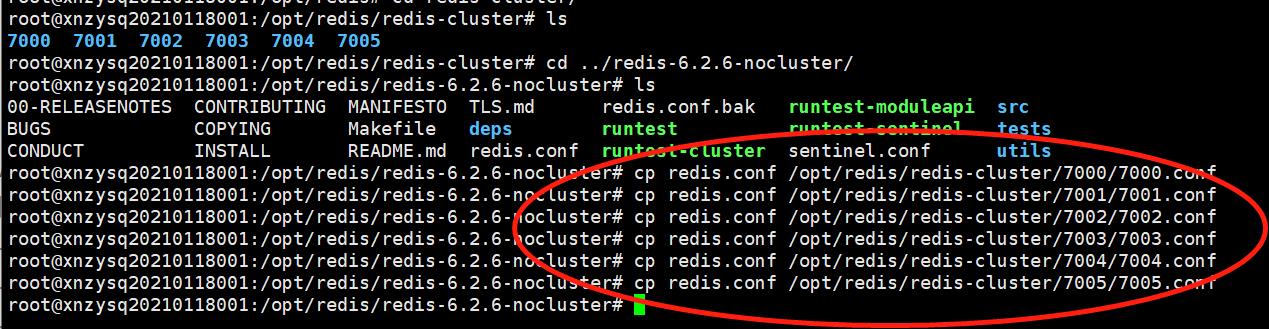
5.4 修改6个节点的redis配置文件
修改每个节点的port、daemonize、pidfile、cluster-enabled、cluster-config-file、cluster-node-timeout、appendonly、appendfilename、loglevel等配置。参考下图:
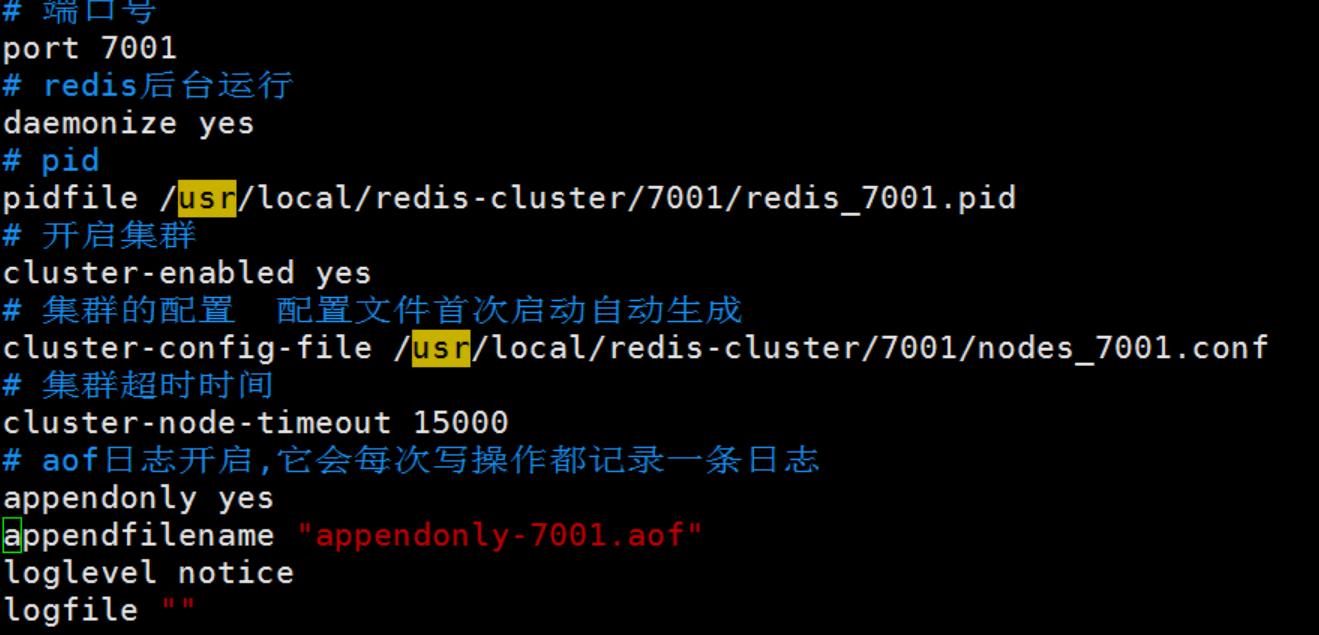
pidfile和配置文件路径可以只写文件名,表示路径和配置文件路径一致。
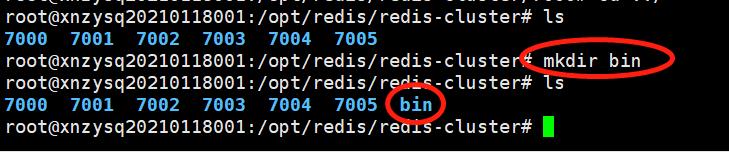
5.5 复制启动文件到/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin目录中
1)在redis-cluster节点下创建bin目录,命令:mkdir bin。
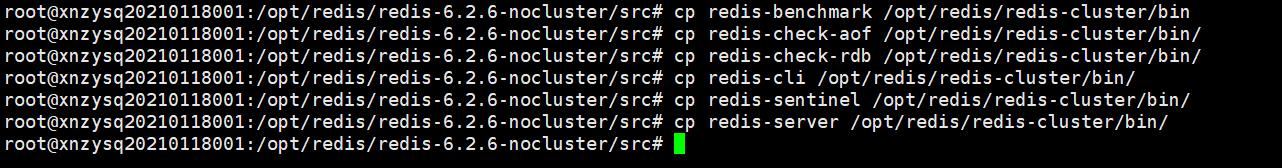
2)复制解压缩文件中的src下面的7个启动文件到/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin目录中, 以后可以在bin目录中启动。
- 7个启动文件分别为:redis-benchmark、redis-check-aof、redis-check-rdb、redis-cli、redis-sentinel、redis-server、mkreleasehdr.sh。
- 该步骤若省略,则在src目录使用集群各个节点的配置启动命令如下: ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7000.conf)。

5.6 启动各个节点服务
进入/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin目录,指定配置文件分别启动6个节点的服务。
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7000/7000.conf
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7001/7001.conf
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7002/7002.conf
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7003/7003.conf
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7004/7004.conf
root@xnzysq20210118001:/opt/redis/redis-cluster/bin# ./redis-server /opt/redis/redis-cluster/7005/7005.conf 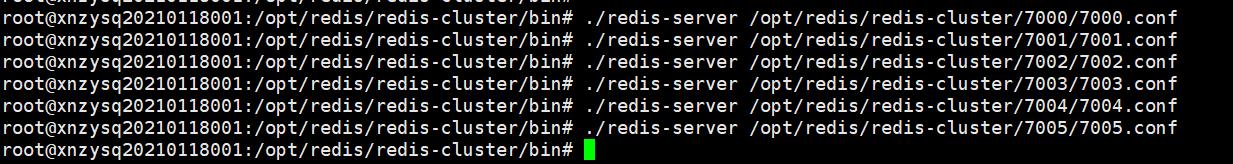
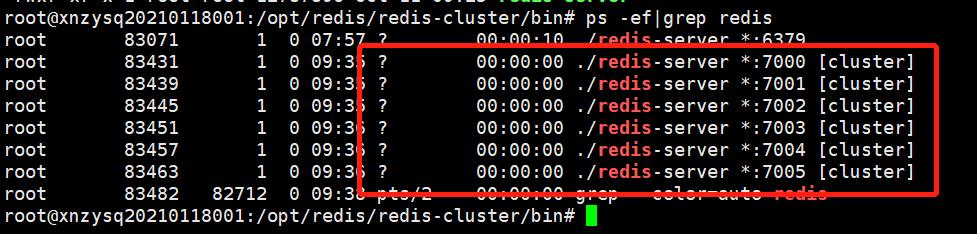
使用ps查看进程,可以看到集群的6个节点均已启动。
5.7 安装ruby(redis 5.0版本之前需要)
由于Redis 集群客户端实现很少,redis集群的启动需要用到ruby实现的redis-trib.rb,所以我们需要先安装ruby。从Ubuntu存储库安装Ruby,以超级用户或具有sudo特权的用户身份运行以下命令,以更新软件包索引并安装Ruby:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ruby-fullLinux环境下搭建Java Web 环境