Java Review - 并发编程_读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock的原理&源码剖析
Posted 小小工匠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java Review - 并发编程_读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock的原理&源码剖析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录

ReentrantLock VS ReentrantReadWriteLock
解决线程安全问题使用ReentrantLock就可以,但是ReentrantLock是独占锁,某时只有一个线程可以获取该锁,而实际中会有写少读多的场景,显然ReentrantLock满足不了这个需求,所以ReentrantReadWriteLock应运而生。ReentrantReadWriteLock采用读写分离的策略,允许多个线程可以同时获取读锁。

类图结构
为了了解ReentrantReadWriteLock的内部构造,我们先看下它的类图结构
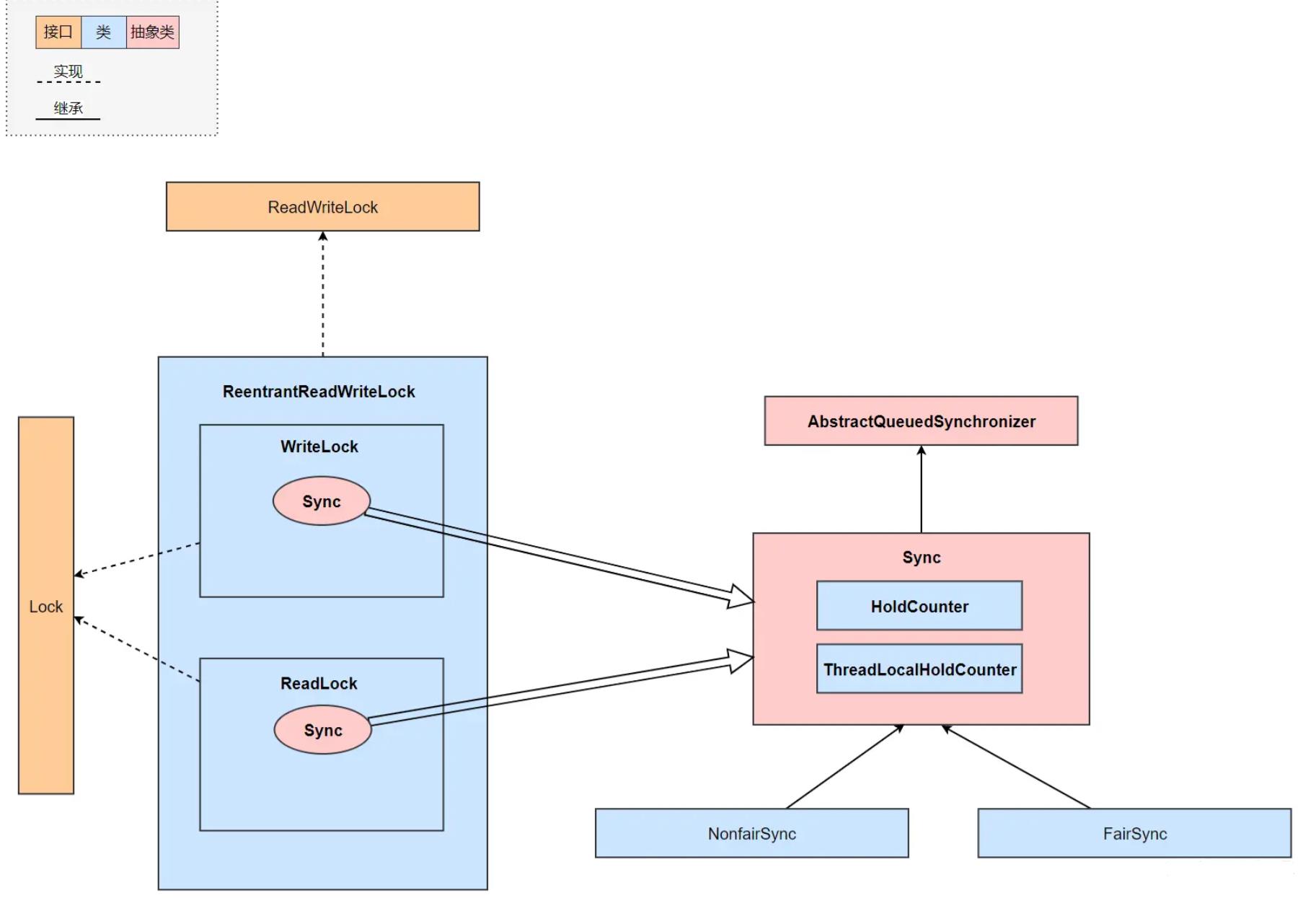
读写锁的内部维护了一个ReadLock和一个WriteLock,它们依赖Sync实现具体功能。
Sync继承自AQS,并且也提供了公平和非公平的实现。

非公平的读写锁实现
下面只介绍非公平的读写锁实现。
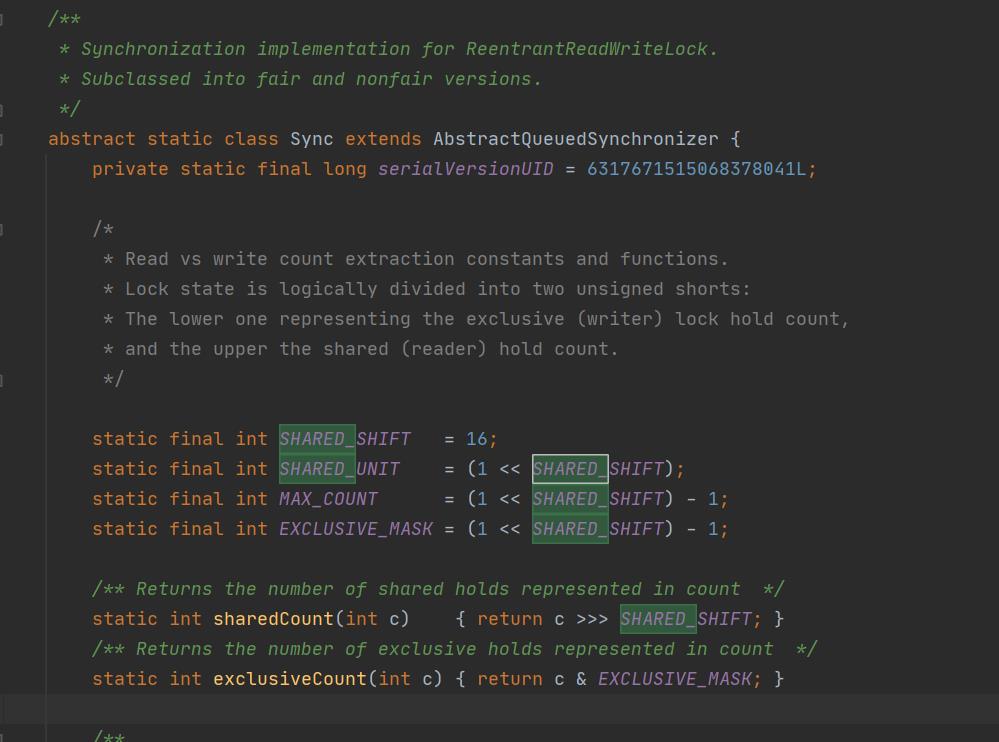
我们知道AQS中只维护了一个state状态,而ReentrantReadWriteLock则需要维护读状态和写状态,一个state怎么表示写和读两种状态呢?
ReentrantReadWriteLock巧妙地使用state的高16位表示读状态,也就是获取到读锁的次数;使用低16位表示获取到写锁的线程的可重入次数。
/*
* Read vs write count extraction constants and functions.
* Lock state is logically divided into two unsigned shorts:
* The lower one representing the exclusive (writer) lock hold count,
* and the upper the shared (reader) hold count.
*/
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
//共享锁(读锁)状态单位值65536
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
//共享锁线程最大个数65535
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
//排它锁(写锁)掩码,二进制,15个1
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
// 返回读锁线程数
/** Returns the number of shared holds represented in count */
static int sharedCount(int c) return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT;
// 返回写锁线程数
/** Returns the number of exclusive holds represented in count */
static int exclusiveCount(int c) return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK;
Sync中的

- firstReader用来记录第一个获取到读锁的线程
- firstReaderHoldCount则记录第一个获取到读锁的线程获取读锁的可重入次数。
- cachedHoldCounter用来记录最后一个获取读锁的线程获取读锁的可重入次数
/**
* A counter for per-thread read hold counts.
* Maintained as a ThreadLocal; cached in cachedHoldCounter
*/
static final class HoldCounter
int count = 0;
// Use id, not reference, to avoid garbage retention
final long tid = getThreadId(Thread.currentThread());
readHolds是ThreadLocal变量,用来存放除去第一个获取读锁线程外的其他线程获取读锁的可重入次数。
ThreadLocalHoldCounter继承了ThreadLocal,因而initialValue方法返回一个HoldCounter对象。
/**
* ThreadLocal subclass. Easiest to explicitly define for sake
* of deserialization mechanics.
*/
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter
extends ThreadLocal<HoldCounter>
public HoldCounter initialValue()
return new HoldCounter();

写锁的获取与释放
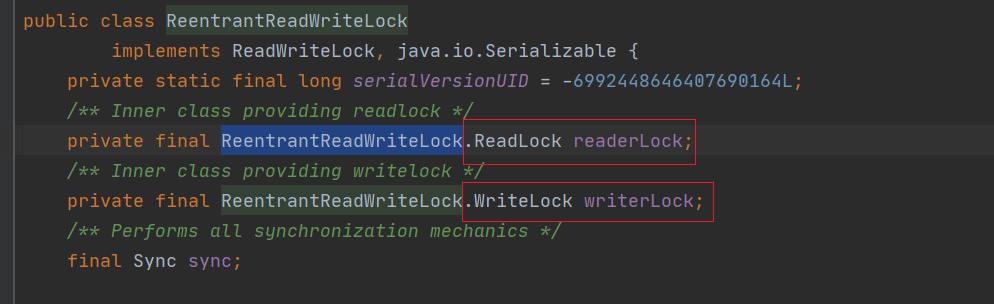
在ReentrantReadWriteLock中写锁使用WriteLock来实现。
void lock()
写锁是个独占锁,某时只有一个线程可以获取该锁。
- 如果当前没有线程获取到读锁和写锁,则当前线程可以获取到写锁然后返回。
- 如果当前已经有线程获取到读锁和写锁,则当前请求写锁的线程会被阻塞挂起。
- 另外,写锁是可重入锁,如果当前线程已经获取了该锁,再次获取只是简单地把可重入次数加1后直接返回。

public void lock()
sync.acquire(1);
public final void acquire(int arg)
// sync重写的tryAcquire方法
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
如以上代码所示,在 lock()内部调用了AQS的acquire方法,其中tryAcquire是ReentrantReadWriteLock内部的sync类重写的,代码如下。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires)
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
// 1 c!=0 说明读锁或者写锁已经被其他线程获取
if (c != 0)
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
// 2 w = 0 说明有线程已经获取了写锁,w!=0 且 当前线程不是写锁的拥有者,返回false
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
// 3 说明当前线程已经获取到了写锁,判断可重入次数
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
// 设置可重入次数(1 )
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
// 5 第一个写线程获取写锁
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
-
代码(1)中,如果当前AQS状态值不为0则说明当前已经有线程获取到了读锁或者写锁。
-
代码(2)中,如果w==0说明状态值的低16位为0,而AQS状态值不为0,则说明高16位不为0,这暗示已经有线程获取了读锁,所以直接返回false 。 如果w!=0则说明当前已经有线程获取了该写锁,再看当前线程是不是该锁的持有者,如果不是则返回false。
-
执行到代码(3)说明当前线程之前已经获取到了该锁,所以判断该线程的可重入次数是不是超过了最大值,是则抛出异常,否则执行代码 (4)增加当前线程的可重入次数,然后返回true.
-
如果AQS的状态值等于0则说明目前没有线程获取到读锁和写锁,所以执行代码(5)。其中,对于writerShouldBlock方法,
非公平锁的实现为
final boolean writerShouldBlock()
return false; // writers can always barge
如果代码对于非公平锁来说总是返回false,则说明代码(5)抢占式执行CAS尝试获取写锁,获取成功则设置当前锁的持有者为当前线程并返回true,否则返回false。
公平锁的实现为
final boolean writerShouldBlock()
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
这里还是使用hasQueuedPredecessors来判断当前线程节点是否有前驱节点,如果有则当前线程放弃获取写锁的权限,直接返回false。

void lockInterruptibly()
类似于lock()方法,它的不同之处在于,它会对中断进行响应,也就是当其他线程调用了该线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程时,当前线程会抛出异常InterruptedException异常。
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
boolean tryLock()
尝试获取写锁,如果当前没有其他线程持有写锁或者读锁,则当前线程获取写锁会成功,然后返回true。 如果当前已经有其他线程持有写锁或者读锁则该方法直接返回false,且当前线程并不会被阻塞。 如果当前线程已经持有了该写锁则简单增加AQS的状态值后直接返回true。
public boolean tryLock( )
return sync.tryWriteLock();
/**
* Performs tryLock for write, enabling barging in both modes.
* This is identical in effect to tryAcquire except for lack
* of calls to writerShouldBlock.
*/
final boolean tryWriteLock()
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c != 0)
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
if (w == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (!compareAndSetState(c, c + 1))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
如上代码与tryAcquire方法类似,不同在于这里使用的是非公平策略。
boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
与tryAcquire()的不同之处在于,多了超时时间参数,如果尝试获取写锁失败则会把当前线程挂起指定时间,待超时时间到后当前线程被激活,如果还是没有获取到写锁则返回false。另外,该方法会对中断进行响应,也就是当其他线程调用了该线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程时,当前线程会抛出InterruptedException异常。
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
void unlock()
尝试释放锁,如果当前线程持有该锁,调用该方法会让该线程对该线程持有的AQS状态值减1,如果减去1后当前状态值为0则当前线程会释放该锁,否则仅仅减1而已。如果当前线程没有持有该锁而调用了该方法则会抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常
public void unlock()
sync.release(1);
public final boolean release(int arg)
// 调用ReentrantReadWriteLock#Sync重写的tryRelease
if (tryRelease(arg))
// 激活阻塞队列里面的一个线程
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
return false;
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases)
// 6 看是否是拥有写锁的线程调用的unLock
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// 7 获取可重入值,没有考虑高16位,因为获取写锁时读锁的值肯定为0
int nextc = getState() - releases;
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
// 如果可重入锁值为0则释放锁,否则只是简单的更新状态值
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(nextc);
return free;
-
tryRelease首先通过isHeldExclusively判断是否当前线程是该写锁的持有者,如果不是则抛出异常
-
否则执行代码(7),这说明当前线程持有写锁,持有写锁说明状态值的高16位为0,所以这里nextc值就是当前线程写锁的剩余可重入次数。
-
代码(8)判断当前可重入次数是否为0,如果free为true则说明可重入次数为0,所以当前线程会释放写锁,将当前锁的持有者设置为null。如果free为false则简单地更新可重入次数。

读锁的获取与释放
ReentrantReadWriteLock中的读锁是使用ReadLock来实现的。
void lock()
获取读锁,如果当前没有其他线程持有写锁,则当前线程可以获取读锁,AQS的状态值state的高16位的值会增加1,然后方法返回。否则如果其他一个线程持有写锁,则当前线程会被阻塞。
/**
* Acquires the read lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then
* the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the read lock has been acquired.
*/
public void lock()
sync.acquireShared(1);
public final void acquireShared(int arg)
// 调用ReentrantReadWriteLock中syn的tryAcquireShared
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
// 调用AQS的doAcquireShared
doAcquireShared(arg);
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused)
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 1 获取当前状态值
int c = getState();
// 2 判断是否写锁被占用
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// 3 获取读锁计数
int r = sharedCount(c);
// 4 尝试获取锁,多个读线程只有一个会成功,不成功的进入fullTryAcquireShared进行重试
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT))
// 5 第一个线程获取到锁
if (r == 0)
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
// 6 如果当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程
else if (firstReader == current)
firstReaderHoldCount++;
else
// 7 记录最后一个获取读锁的线程或记录其他线程读锁的可重入次数
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
return 1;
// 8 类似tryAcquireShared,但是自旋获取
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
- 首先获取了当前AQS的状态值
- 然后代码(2)查看是否有其他线程获取到了写锁,如果是则直接返回-1,而后调用AQS的doAcquireShared方法把当前线程放入AQS阻塞队列。
如果当前要获取读锁的线程已经持有了写锁,则也可以获取读锁。但是需要注意,当一个线程先获取了写锁,然后获取了读锁处理事情完毕后,要记得把读锁和写锁都释放掉,不能只释放写锁。
- 否则执行代码(3),得到获取到的读锁的个数,到这里说明目前没有线程获取到写锁,但是可能有线程持有读锁,然后执行代码(4)
其中非公平锁的readerShouldBlock实现代码如下
final boolean readerShouldBlock()
/* As a heuristic to avoid indefinite writer starvation,
* block if the thread that momentarily appears to be head
* of queue, if one exists, is a waiting writer. This is
* only a probabilistic effect since a new reader will not
* block if there is a waiting writer behind other enabled
* readers that have not yet drained from the queue.
*/
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive()
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null &&
(s = h.next) != null &&
!s.isShared() &&
s.thread != null;
如上代码的作用是,如果队列里面存在一个元素,则判断第一个元素是不是正在尝试获取写锁,如果不是,则当前线程判断当前获取读锁的线程是否达到了最大值。最后执行CAS操作将AQS状态值的高16位值增加1。
-
代码(5)(6)记录第一个获取读锁的线程并统计该线程获取读锁的可重入数。
-
代码(7)使用cachedHoldCounter记录最后一个获取到读锁的线程和该线程获取读锁的可重入数,readHolds记录了当前线程获取读锁的可重入数。
-
如果readerShouldBlock返回true则说明有线程正在获取写锁,所以执行代码(8)。
-
fullTryAcquireShared的代码与tryAcquireShared类似,它们的不同之处在于,前者通过循环自旋获取。
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current)
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;)
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0)
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
else if (readerShouldBlock())
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current)
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
else
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT))
if (sharedCount(c) == 0)
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
else if (firstReader == current)
firstReaderHoldCount++;
else
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
return 1;

void lockInterruptibly()
类似于lock()方法,不同之处在于,该方法会对中断进行响应,也就是当其他线程调用了该线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程时,当前线程会抛出InterruptedException异常。
boolean tryLock()
-
尝试获取读锁,如果当前没有其他线程持有写锁,则当前线程获取读锁会成功,然后返回true 。
-
如果当前已经有其他线程持有写锁则该方法直接返回false,但当前线程并不会被阻塞。
-
如果当前线程已经持有了该读锁则简单增加AQS的状态值高16位后直接返回true。
其代码类似tryLock的代码,这里不再讲述。
boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
与tryLock()的不同之处在于,多了超时时间参数,如果尝试获取读锁失败则会把当前线程挂起指定时间,待超时时间到后当前线程被激活,如果此时还没有获取到读锁则返回false。
另外,该方法对中断响应,也就是当其他线程调用了该线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程时,当前线程会抛出InterruptedException异常。
void unlock()
public void unlock()
sync.releaseShared(1