java的SimpleDateFormat线程不安全出问题了,虚竹教你多种解决方案
Posted 小虚竹
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java的SimpleDateFormat线程不安全出问题了,虚竹教你多种解决方案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
技术活,该赏
点赞再看,养成习惯

场景
在java8以前,要格式化日期时间,就需要用到SimpleDateFormat。
但我们知道SimpleDateFormat是线程不安全的,处理时要特别小心,要加锁或者不能定义为static,要在方法内new出对象,再进行格式化。很麻烦,而且重复地new出对象,也加大了内存开销。
SimpleDateFormat线程为什么是线程不安全的呢?
来看看SimpleDateFormat的源码,先看format方法:
// Called from Format after creating a FieldDelegate
private StringBuffer format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldDelegate delegate)
// Convert input date to time field list
calendar.setTime(date);
...
问题就出在成员变量calendar,如果在使用SimpleDateFormat时,用static定义,那SimpleDateFormat变成了共享变量。那SimpleDateFormat中的calendar就可以被多个线程访问到。
SimpleDateFormat的parse方法也是线程不安全的:
public Date parse(String text, ParsePosition pos)
...
Date parsedDate;
try
parsedDate = calb.establish(calendar).getTime();
// If the year value is ambiguous,
// then the two-digit year == the default start year
if (ambiguousYear[0])
if (parsedDate.before(defaultCenturyStart))
parsedDate = calb.addYear(100).establish(calendar).getTime();
// An IllegalArgumentException will be thrown by Calendar.getTime()
// if any fields are out of range, e.g., MONTH == 17.
catch (IllegalArgumentException e)
pos.errorIndex = start;
pos.index = oldStart;
return null;
return parsedDate;
由源码可知,最后是调用**parsedDate = calb.establish(calendar).getTime();**获取返回值。方法的参数是calendar,calendar可以被多个线程访问到,存在线程不安全问题。
我们再来看看**calb.establish(calendar)**的源码
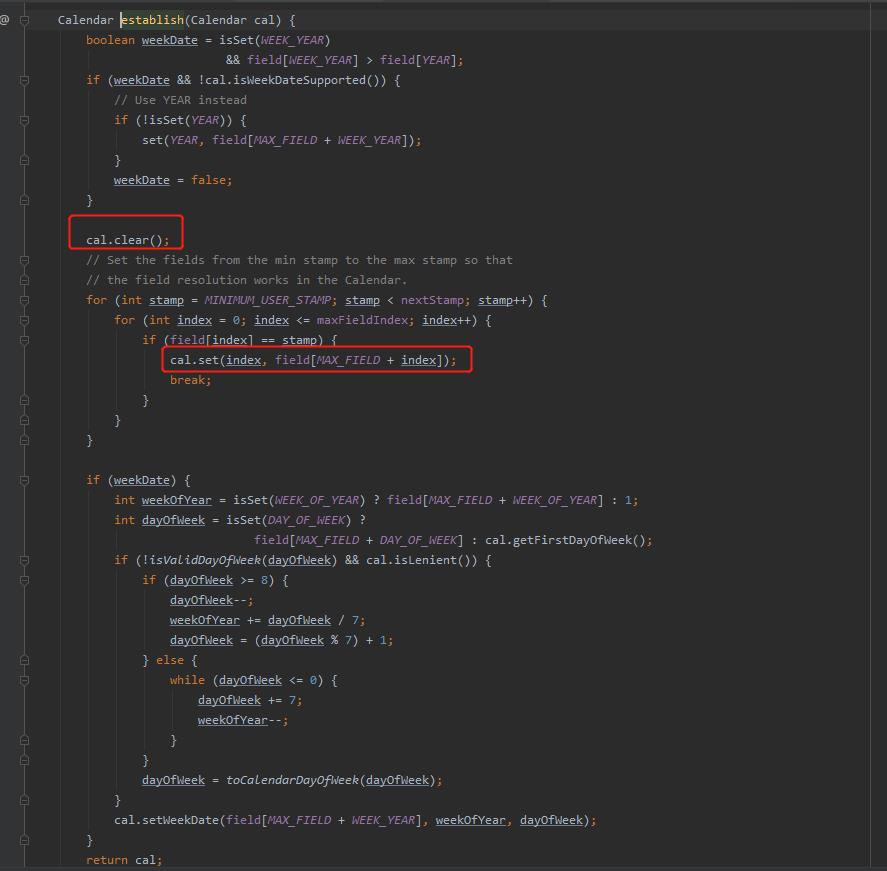
calb.establish(calendar)方法先后调用了cal.clear()和cal.set(),先清理值,再设值。但是这两个操作并不是原子性的,也没有线程安全机制来保证,导致多线程并发时,可能会引起cal的值出现问题了。
验证SimpleDateFormat线程不安全
public class SimpleDateFormatDemoTest
private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
String dateString = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
try
Date parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = simpleDateFormat.format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
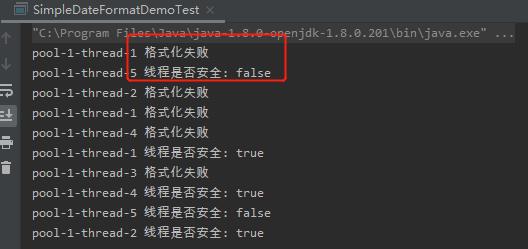
出现了两次false,说明线程是不安全的。而且还抛异常,这个就严重了。
解决方案
解决方案1:不要定义为static变量,使用局部变量
就是要使用SimpleDateFormat对象进行format或parse时,再定义为局部变量。就能保证线程安全。
public class SimpleDateFormatDemoTest1
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String dateString = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
try
Date parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = simpleDateFormat.format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
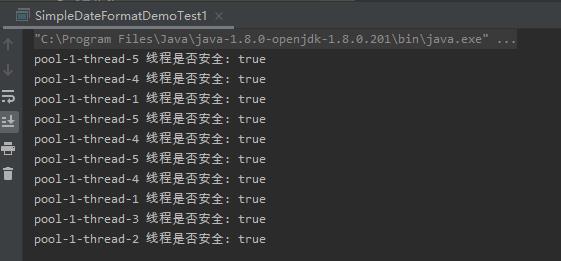
由图可知,已经保证了线程安全,但这种方案不建议在高并发场景下使用,因为会创建大量的SimpleDateFormat对象,影响性能。
解决方案2:加锁:synchronized锁和Lock锁
加synchronized锁
SimpleDateFormat对象还是定义为全局变量,然后需要调用SimpleDateFormat进行格式化时间时,再用synchronized保证线程安全。
public class SimpleDateFormatDemoTest2
private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
try
synchronized (simpleDateFormat)
String dateString = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
Date parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = simpleDateFormat.format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
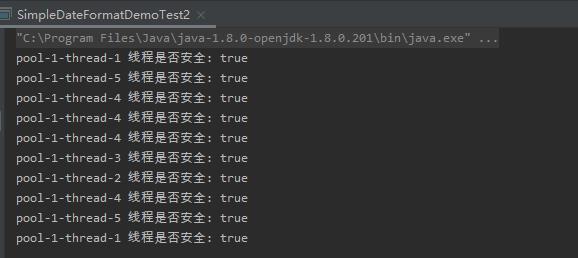
如图所示,线程是安全的。定义了全局变量SimpleDateFormat,减少了创建大量SimpleDateFormat对象的损耗。但是使用synchronized锁,
同一时刻只有一个线程能执行锁住的代码块,在高并发的情况下会影响性能。但这种方案不建议在高并发场景下使用
加Lock锁
加Lock锁和synchronized锁原理是一样的,都是使用锁机制保证线程的安全。
public class SimpleDateFormatDemoTest3
private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
try
lock.lock();
String dateString = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
Date parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = simpleDateFormat.format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
finally
lock.unlock();
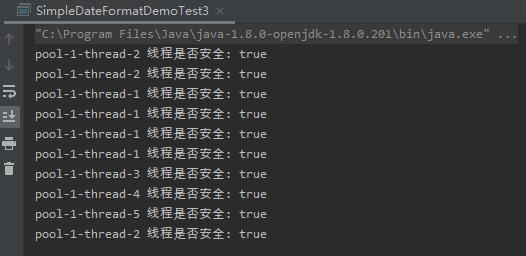
由结果可知,加Lock锁也能保证线程安全。要注意的是,最后一定要释放锁,代码里在finally里增加了lock.unlock();,保证释放锁。
在高并发的情况下会影响性能。这种方案不建议在高并发场景下使用
解决方案3:使用ThreadLocal方式
使用ThreadLocal保证每一个线程有SimpleDateFormat对象副本。这样就能保证线程的安全。
public class SimpleDateFormatDemoTest4
private static ThreadLocal<DateFormat> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<DateFormat>()
@Override
protected DateFormat initialValue()
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
;
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
try
String dateString = threadLocal.get().format(new Date());
Date parseDate = threadLocal.get().parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = threadLocal.get().format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
finally
//避免内存泄漏,使用完threadLocal后要调用remove方法清除数据
threadLocal.remove();
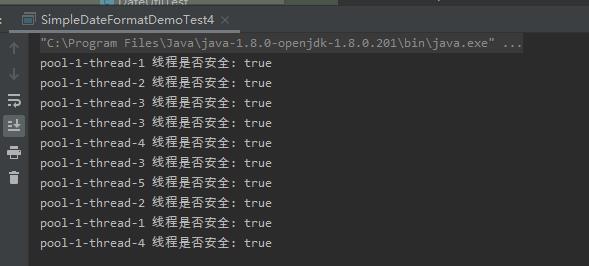
使用ThreadLocal能保证线程安全,且效率也是挺高的。适合高并发场景使用。
解决方案4:使用DateTimeFormatter代替SimpleDateFormat
使用DateTimeFormatter代替SimpleDateFormat(DateTimeFormatter是线程安全的,java 8+支持)
DateTimeFormatter介绍 传送门:万字博文教你搞懂java源码的日期和时间相关用法
public class DateTimeFormatterDemoTest5
private static DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
try
String dateString = dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalDateTime.now());
TemporalAccessor temporalAccessor = dateTimeFormatter.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = dateTimeFormatter.format(temporalAccessor);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
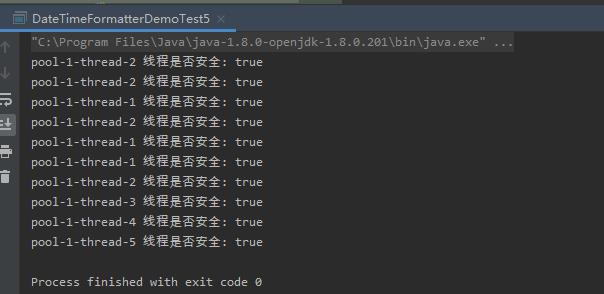
使用DateTimeFormatter能保证线程安全,且效率也是挺高的。适合高并发场景使用。
解决方案5:使用FastDateFormat 替换SimpleDateFormat
使用FastDateFormat 替换SimpleDateFormat(FastDateFormat 是线程安全的,Apache Commons Lang包支持,不受限于java版本)
public class FastDateFormatDemo6
private static FastDateFormat fastDateFormat = FastDateFormat.getInstance("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args)
//1、创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//2、为线程池分配任务
ThreadPoolTest threadPoolTest = new ThreadPoolTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
pool.submit(threadPoolTest);
//3、关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
static class ThreadPoolTest implements Runnable
@Override
public void run()
try
String dateString = fastDateFormat.format(new Date());
Date parseDate = fastDateFormat.parse(dateString);
String dateString2 = fastDateFormat.format(parseDate);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程是否安全: "+dateString.equals(dateString2));
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 格式化失败 ");
使用FastDateFormat能保证线程安全,且效率也是挺高的。适合高并发场景使用。
FastDateFormat源码分析
Apache Commons Lang 3.5
//FastDateFormat@Overridepublic String format(final Date date) return printer.format(date); @Override public String format(final Date date) final Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(timeZone, locale); c.setTime(date以上是关于java的SimpleDateFormat线程不安全出问题了,虚竹教你多种解决方案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章