pytest零基础入门到精通(05)Allure报告的隐藏用法
Posted 七月的小尾巴
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pytest零基础入门到精通(05)Allure报告的隐藏用法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
allure报告功能详解
Environment
Environment 是环境变量,报告默认是没有任何变量参数的,是需要自己配置的。
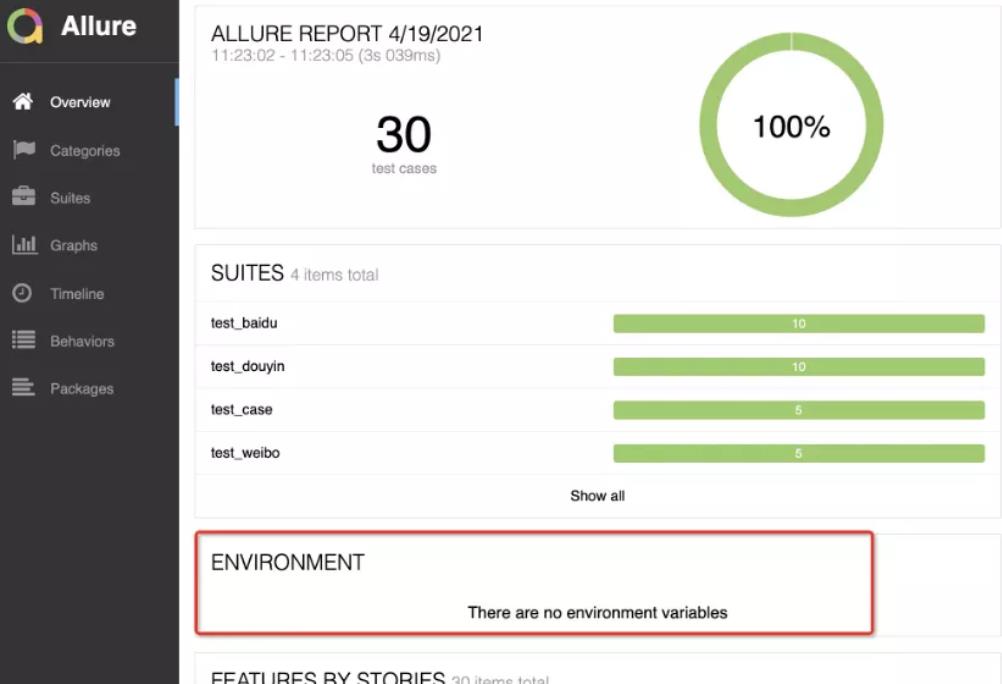
添加Environment
通过创建 environment.properties 或者 environment.xml 文件,并把文件存放到测试结果的文件夹(执行脚本时,–alluredir 选项后指定的目录)。
添加配置文件
- 创建
environment.properties文件,注意名称不需要是这个,不能改!!!
在文件中配置如下信息,但是这种文件格式有个缺点,不能设置中文,中文的话会allure会出现乱码。
Browser=Chrome
Browser.Version=89.0.4389.128
Stand=Test
ApiUrl=127.0.0.1/login
python.Version=3.9.0
xml格式的文件,可以处理中文乱码的问题,下面我们创建 一个 environment.xml 文件
- 创建
environment.xml文件
<environment>
<parameter>
<key>测试平台</key>
<value>婚奢汇</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<key>测试环境</key>
<value>TEST</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<key>测试人员</key>
<value>余少琪</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<key>邮箱</key>
<value>1603453211@qq.com</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<key>python.Version</key>
<value>3.9.0</value>
</parameter>
</environment>
解决配置文件被删的问题
运行 pytest 生成 allure 报告时,有时候需要加参数 --clean-alluredir(清除之前的报告记录),而配置文件(environment.properties 或 environment.xml)也会被删除。
解决方法
不单独使用 pytest 的 clean 方法,自己封装一个方法,放在conftest文件中。allure 报告生成的数据,主要是依赖于我们报告文件的 tmp 文件中,那么我们每次程序执行之前,将tmp文件中包含 .json 和 txt 文件全部删除。
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def clear_report():
try:
# ConfigHandler.report_path 测试报告的目录文件
for one in os.listdir(ConfigHandler.report_path + f'/tmp'):
if 'json' in one:
os.remove(ConfigHandler.report_path + f'/tmp/one')
if 'txt' in one:
os.remove(ConfigHandler.report_path + f'/tmp/one')
except Exception as e:
print("allure数据清除失败", e)
yield
print("自动化测试执行完成")
解决方法二
将 environment.properties 或 environment.xml 文件放在根目录下,每次运行报告之前,拷贝到报告目录里即可。
Categories
Categories 是分类(测试用例结果的分类)
默认情况下,有两类缺陷:
- Product defects 产品缺陷(测试结果:failed)
- Test defects 测试缺陷(测试结果:error/broken)
可以创建自定义缺陷分类,将 categories.json 文件添加到测试结果的目录即可(和 environment.properties 放同一个目录)。
categories.json 参数:
- name:分类名称。
- matchedStatuses:测试用例的运行状态,默认[“failed”, “broken”, “passed”, “skipped”, “unknown”]。
- messageRegex:测试用例运行的错误信息,默认是 .* ,是通过正则去匹配的。
- traceRegex:测试用例运行的错误堆栈信息,默认是 .* ,是通过正则去匹配的
- 创建
categories.json:
[
"name": "Ignored tests",
"matchedStatuses": ["skipped"]
,
"name": "Infrastructure problems",
"matchedStatuses": ["broken", "failed"],
"messageRegex": ".*signOut.*"
,
"name": "Outdated tests",
"matchedStatuses": ["broken"],
"traceRegex": ".*FileNotFoundException.*"
,
"name": "Product defects",
"matchedStatuses": ["failed"]
,
"name": "Test defects",
"matchedStatuses": ["broken"]
]
测试用例报错时显示
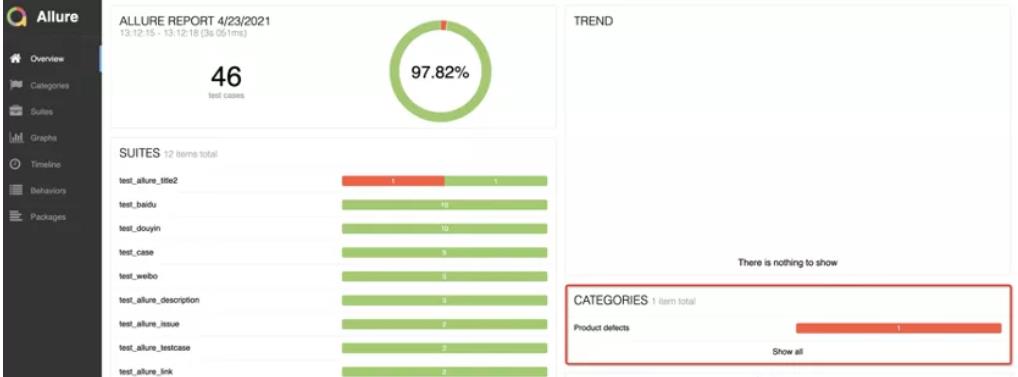
allure.step()
在 allure 报告中添加测试用例步骤有两种方式:
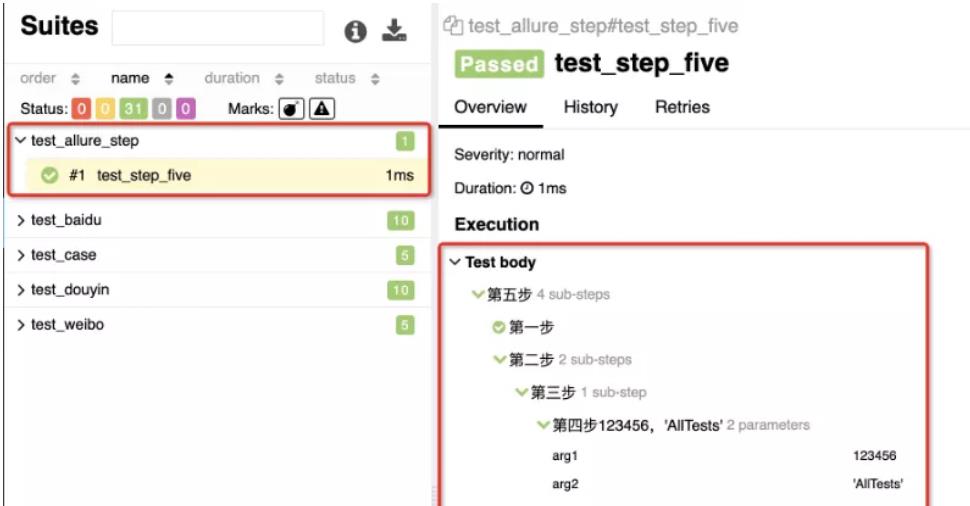
1、@allure.step() 这种方式会带上函数的传参和对应的值。
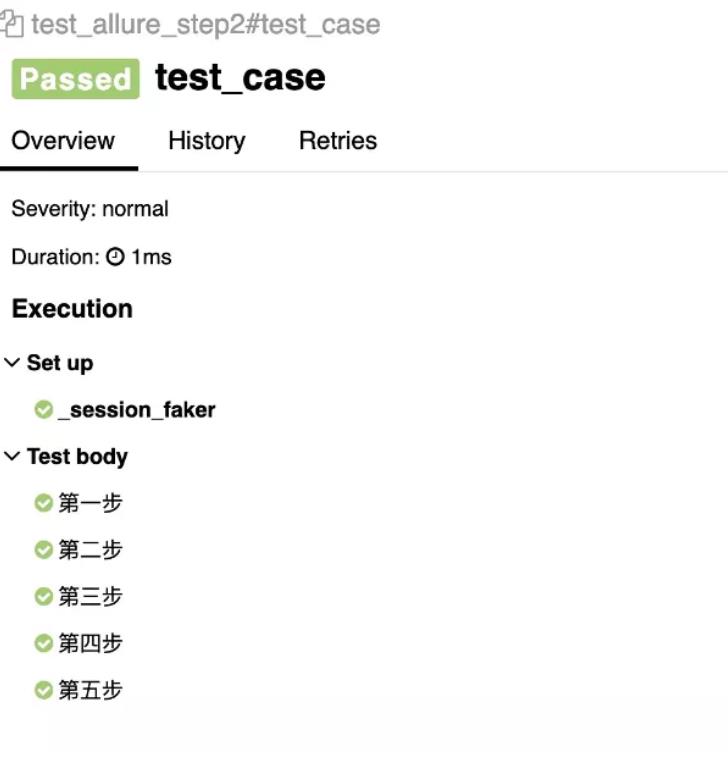
2、with allure.step() 这种方式代码可读性更好一点,但不会带上函数里面的传参和对应的值。
@allure.step()方式
allure 报告允许对每个测试用例进行非常详细的步骤说明,通过 @allure.step() 装饰器,可以让测试用例在 allure 报告中显示更详细的测试过程。
@allure.step() 只有一个参数,就是 title,输入标题内容,allure 报告上就会显示出来。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import allure
@allure.step("第一步")
def step_one():
pass
@allure.step("第二步")
def step_two_with_nested():
step_three()
@allure.step("第三步")
def step_three():
step_four_with_arguments(123456, 'AllTests')
@allure.step("第四步0,arg2")
def step_four_with_arguments(arg1, arg2):
pass
@allure.step("第五步")
def test_step_five():
step_one()
step_two_with_nested()
with allure.step()方式
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import allure
def one():
pass
def two_with_nested():
three()
def three():
pass
def four(arg1, arg2):
pass
def five():
one()
two_with_nested()
def test_case():
with allure.step("第一步"):
one()
with allure.step("第二步"):
two_with_nested()
with allure.step("第三步"):
three()
with allure.step("第四步"):
four(arg1=123456, arg2='AllTests')
with allure.step("第五步"):
five()
allure.attach
allure 报告可以显示许多不同类型的附件,这些附件可以补充测试、步骤或装置结果。
可以通过调用:
方式一:
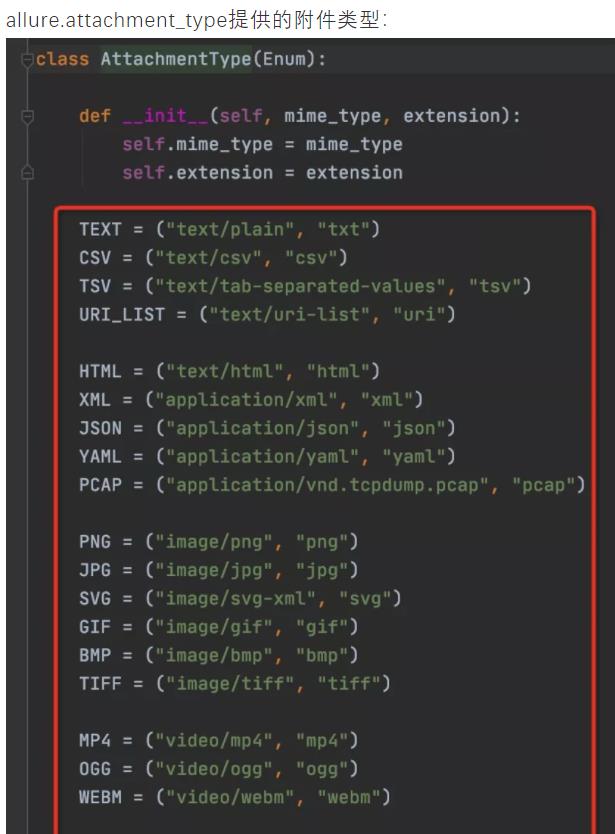
allure.attach(body, name, attachment_type, extension)
参数:
- body:要写入文件的原始内容。
- name:附件名。
- attachment_type:附件类型(是 allure.attachment_type 里面的其中一种)。
- extension:所创建文件的扩展名。
方式二:
allure.attach.file(source, name, attachment_type, extension)
参数:
- source:包含文件路径的字符串。(其他参数相同)
1、创建test_allure_attach.py文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import pytest
import allure
@pytest.fixture
def attach_fixture_one(request):
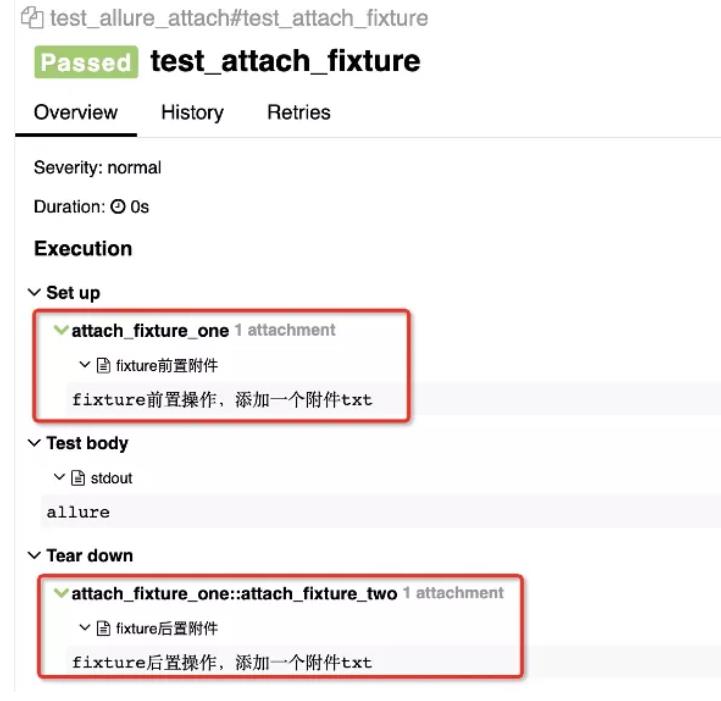
allure.attach('fixture前置操作,添加一个附件txt', 'fixture前置附件', allure.attachment_type.TEXT)
def attach_fixture_two():
allure.attach('fixture后置操作,添加一个附件txt', 'fixture后置附件', allure.attachment_type.TEXT)
request.addfinalizer(attach_fixture_two)
def test_attach_fixture(attach_fixture_one):
print("allure")
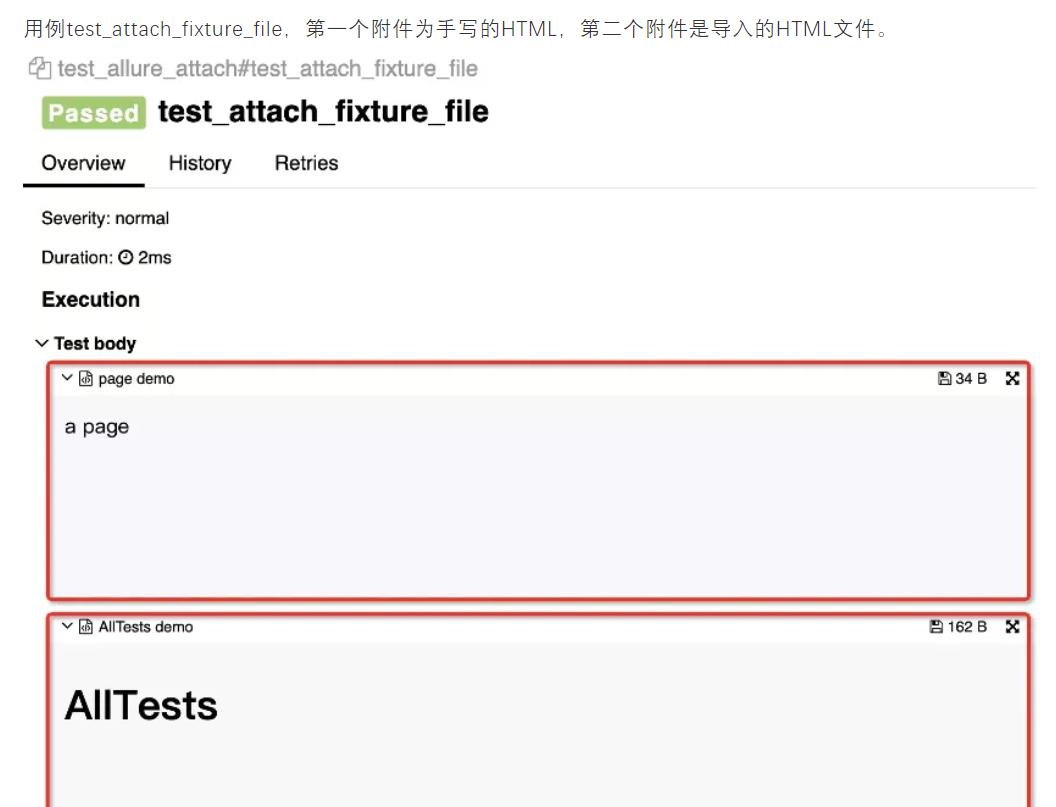
def test_attach_fixture_file():
allure.attach('<head></head><body> a page </body>', 'page demo', allure.attachment_type.html)
allure.attach.file('./demo.html', 'AllTests demo', attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.HTML)
创建demo.html文件(存放到项目的根目录上)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>软件测试</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>AllTests</h1>
</body>
</html>
@allure.description()
添加足够详细的测试用例描述,更加方便查看测试步骤。
方式一:
@allure.description_html(str):传一个HTML代码组成的字符串
方式二:
@allure.description(str)
方式三:
在测试用例函数下方添加 """ """
@allure.title()
测试用例的标题可以通过特殊的方式变得更易读,标题支持参数占位符并支持动态替换。
import pytest
import allure
@allure.title("前置操作:登录")
@pytest.fixture
def test_login(request):
params = request.param
name = params["username"]
pwd = params["pwd"]
allure.attach(f"测试用例传的参数params")
print(name, pwd, params)
yield name, pwd
@allure.title("登录成功,测试数据:test_login")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_login", ["username": "admin", "pwd": "123456", "username": "root", "pwd": "root"], indirect=True)
def test_login_success(test_login):
name, pwd = test_login
allure.attach(f"账号:name,密码:pwd")
@allure.link()
import allure
@allure.link('https://www.baidu.com/')
def test_with_link():
pass
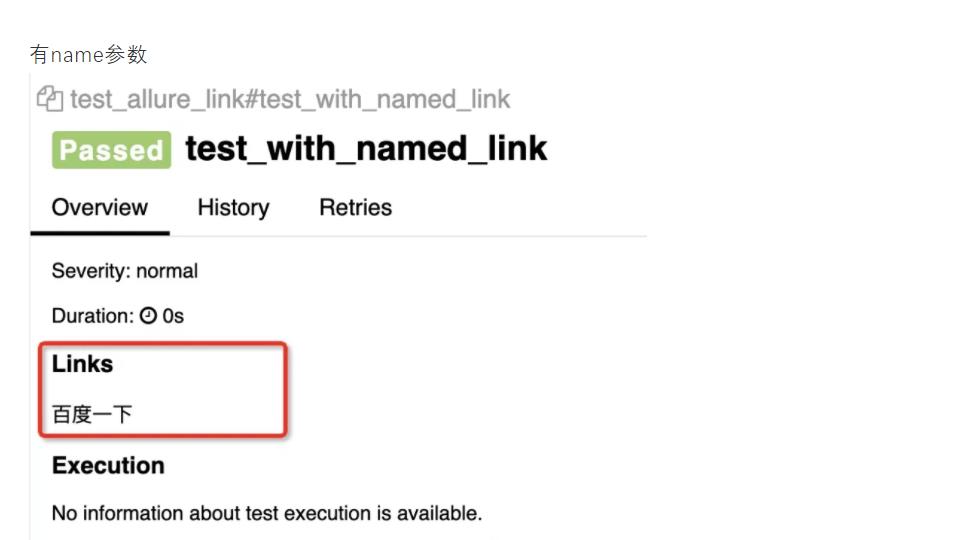
@allure.link('https://www.baidu.com/', name='百度一下')
def test_with_named_link():
pass
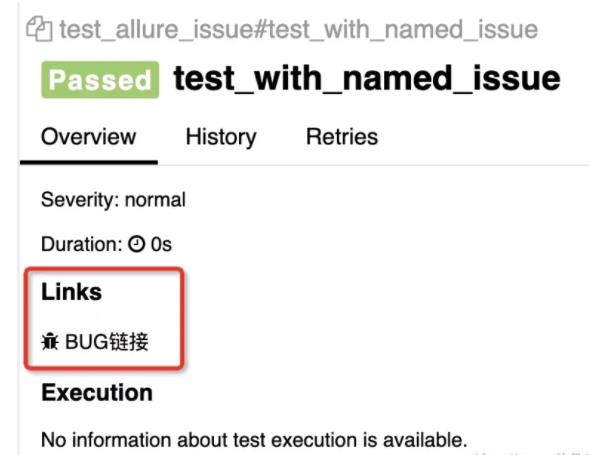
@allure.issue()
链接(Bug链接)
请求参数:
- url:跳转的链接。
- name:显示在 allure 报告的名字,如果不传就是显示完整的链接。
import allure
@allure.issue('https://www.baidu.com/')
def test_with_issue():
pass
@allure.issue('https://www.baidu.com/', 'BUG链接')
def test_with_named_issue():
pass
@allure.testcase()
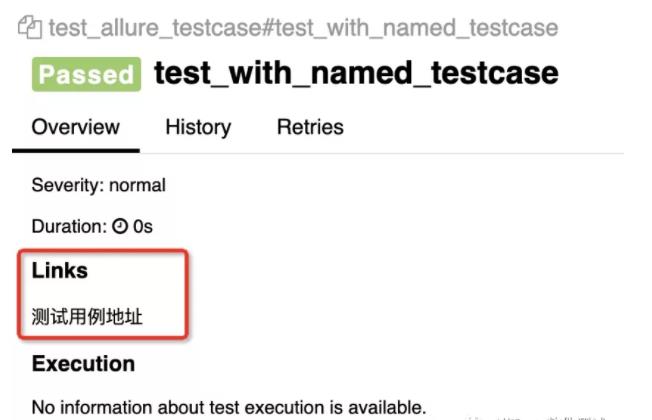
@allure.testcase() 是 测试用例链接,用法和上方一致,不做赘述
@allure.testcase('https://www.baidu.com/')
def test_with_testcase():
pass
@allure.testcase('https://www.baidu.com/', '测试用例地址')
def test_with_named_testcase():
pass
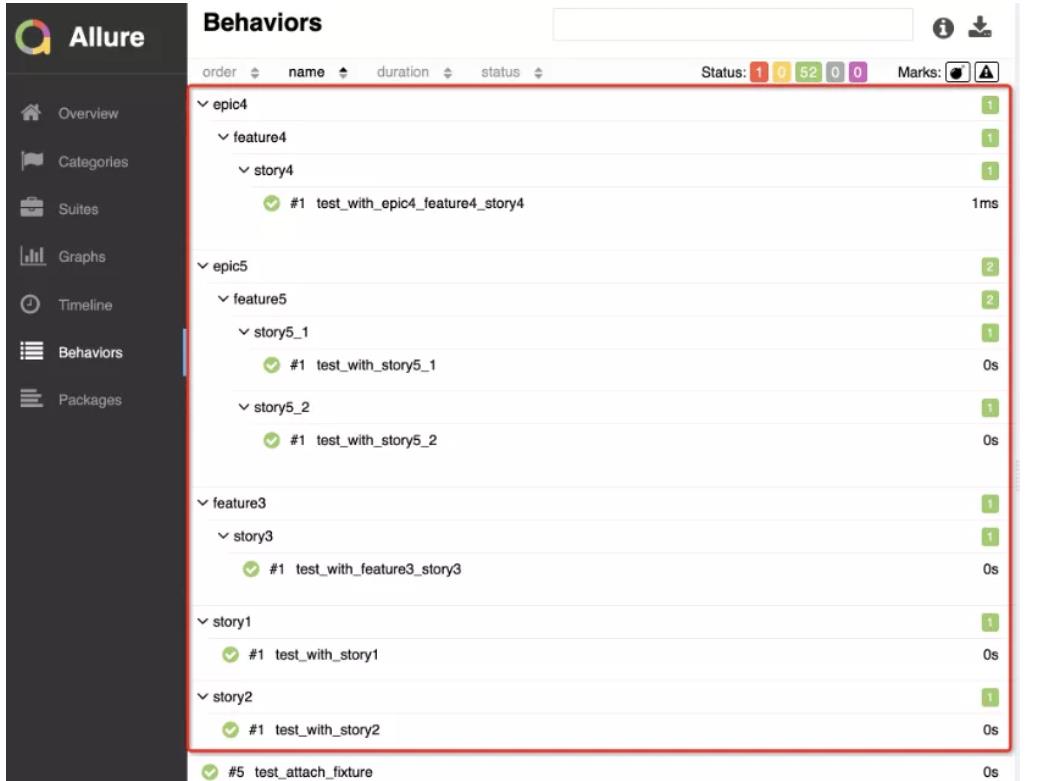
@allure.epic()/feature()/story()
allure 标记装饰器(可显示在测试报告上):
@allure.epic:敏捷里面的概念,定义史诗,往下是 feature。
@allure.feature:功能点的描述,理解成模块,往下是 story。
@allure.story:故事,往下是 title。
import allure
def test_without_any_annotations_that_wont_be_executed():
pass
@allure.story('story1')
def test_with_story1():
pass
@allure.story('story2')
def test_with_story2():
pass
@allure.feature('feature3')
@allure.story('story3')
def test_with_feature3_story3():
pass
@allure.epic('epic4')
@allure.feature('feature4')
@allure.story('story4')
def test_with_epic4_feature4_story4():
pass
@allure.epic('epic5')
@allure.feature('feature5')
class TestCase:
@allure.story('story5_1')
def test_with_story5_1(self):
print("执行 test_with_story5_1")
@allure.story('story5_2')
def test_with_story5_2(self):
print("执行 test_with_story5_2")
以上是关于pytest零基础入门到精通(05)Allure报告的隐藏用法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章