ClickHouse为什么这么快?MergeTree 表存储引擎图文实例详解
Posted 东海陈光剑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ClickHouse为什么这么快?MergeTree 表存储引擎图文实例详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言

ClickHouse 是俄罗斯最大的搜索引擎Yandex在2016年开源的数据库管理系统(DBMS),主要用于联机分析处理(OLAP)。其采用了面向列的存储方式,性能远超传统面向行的DBMS,近几年受到广泛关注。
本文综合介绍(东拼西凑)了 ClickHouse MergeTree系列表引擎的相关知识,并通过示例分析MergeTree存储引擎的数据存储结构。
MergeTree 引擎简介
为什么叫 MergeTree ?
ClickHouse MergeTree 的表存储引擎,在写入一批数据时,数据总会以数据片段的形式写入磁盘,且数据片段不可修改。为了避免片段过多,ClickHouse会通过后台线程定期合并这些数据片段,属于相同分区的数据片段会被合成一个新的片段。这种数据片段往复合并的特点也正是合并树的名称由来。
MergeTree 核心引擎如下:
ReplacingMergeTree:在后台数据合并期间,对具有相同排序键的数据进行去重操作。
SummingMergeTree:当合并数据时,会把具有相同主键的记录合并为一条记录。根据聚合字段设置,该字段的值为聚合后的汇总值,非聚合字段使用第一条记录的值,聚合字段类型必须为数值类型。
AggregatingMergeTree:在同一数据分区下,可以将具有相同主键的数据进行聚合。
CollapsingMergeTree:在同一数据分区下,对具有相同主键的数据进行折叠合并。
VersionedCollapsingMergeTree:基于CollapsingMergeTree引擎,增添了数据版本信息字段配置选项。在数据依据ORDER BY设置对数据进行排序的基础上,如果数据的版本信息列不在排序字段中,那么版本信息会被隐式的作为ORDER BY的最后一列从而影响数据排序。
GraphiteMergeTree:用来存储时序数据库Graphites的数据。
MergeTree是该系列引擎中最核心的引擎,其他引擎均以MergeTree为基础,并在数据合并过程中实现了不同的特性,从而构成了MergeTree表引擎家族。下面我们通过MergeTree来具体了解MergeTree表系列引擎。
ClickHouse 建表语句

建表DDL 语法
创建MergeTree的DDL如下所示:
CREATETABLE[IFNOTEXISTS][db.]table_name[ONCLUSTERcluster](name1[type1][DEFAULT|MATERIALIZED|ALIASexpr1][TTLexpr1],name2[type2][DEFAULT|MATERIALIZED|ALIASexpr2][TTLexpr2],...)ENGINE=MergeTree()ORDERBYexpr[PARTITIONBYexpr][PRIMARYKEYexpr][SAMPLEBYexpr][TTLexpr[DELETE|TODISK'xxx'|TOVOLUME'xxx'],...][SETTINGSname=value,...
这里说明一下MergeTree引擎的主要参数:
[必填选项]
ENGINE:引擎名字,MergeTree引擎无参数。
ORDER BY:排序键,可以由一列或多列组成,决定了数据以何种方式进行排序,例如ORDER BY(CounterID, EventDate)。如果没有显示指定PRIMARY KEY,那么将使用ORDER BY作为PRIMARY KEY。通常只指定ORDER BY即可。
[选填选项]
PARTITION BY:分区键,指明表中的数据以何种规则进行分区。分区是在一个表中通过指定的规则划分而成的逻辑数据集。分区可以按任意标准进行,如按月、按日或按事件类型。为了减少需要操作的数据,每个分区都是分开存储的。
PRIMARY KEY:主键,设置后会按照主键生成一级索引(primary.idx),数据会依据索引的设置进行排序,从而加速查询性能。默认情况下,PRIMARY KEY与ORDER BY设置相同,所以通常情况下直接使用ORDER BY设置来替代主键设置。
SAMPLE BY:数据采样设置,如果显示配置了该选项,那么主键配置中也应该包括此配置。例如 ORDER BY CounterID / EventDate / intHash32(UserID)、SAMPLE BY intHash32(UserID)。
TTL:数据存活时间,可以为某一字段列或者一整张表设置TTL,设置中必须包含Date或DateTime字段类型。如果设置在列上,那么会删除字段中过期的数据。如果设置的是表级的TTL,那么会删除表中过期的数据。如果设置了两种类型,那么按先到期的为准。例如,TTL createtime + INTERVAL 1 DAY,即一天后过期。使用场景包括定期删除数据,或者定期将数据进行归档。
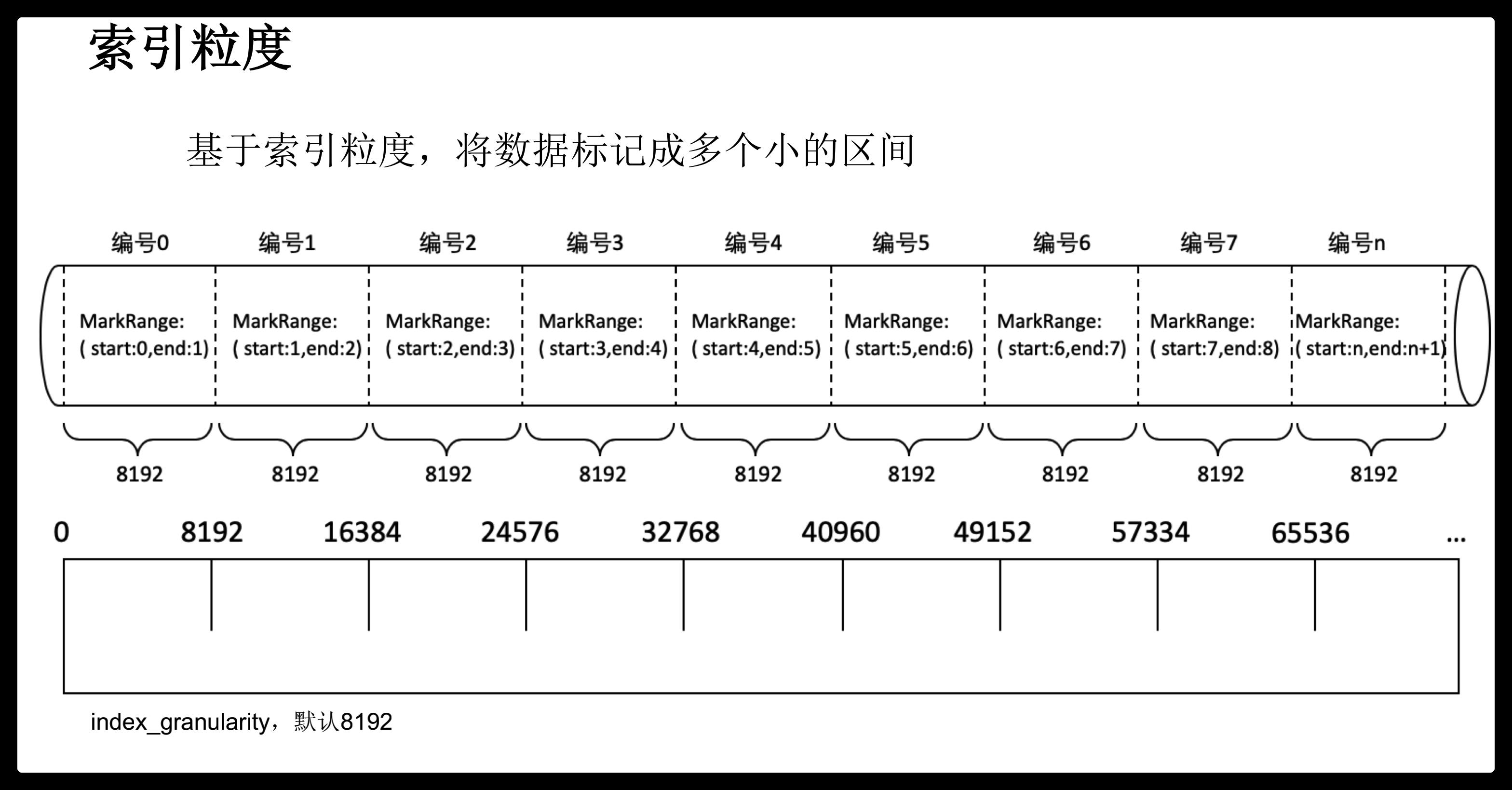
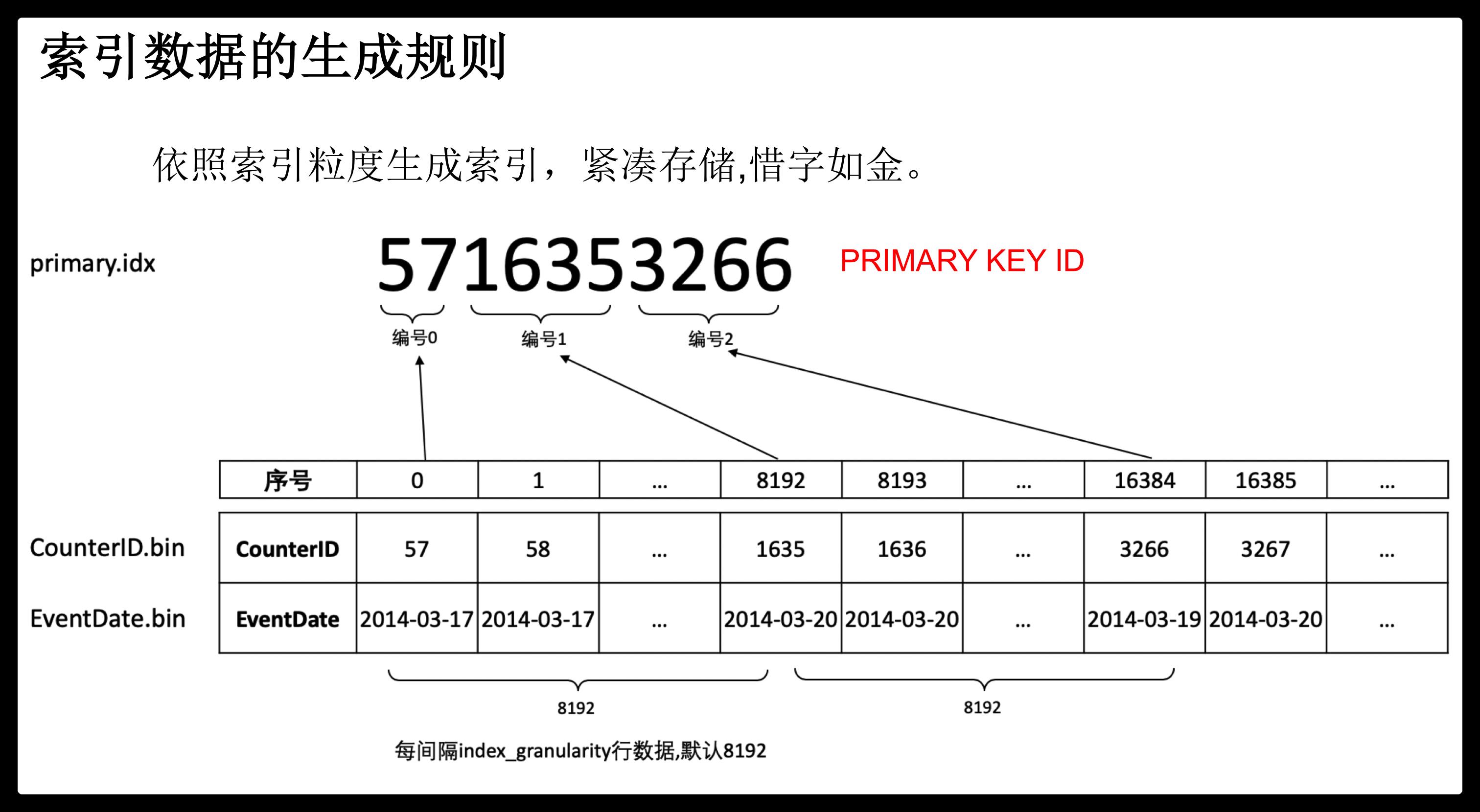
index_granularity:索引间隔粒度。MergeTree索引为稀疏索引,每index_granularity个数据产生一条索引。index_granularity默认设置为8092。
enable_mixed_granularity_parts:是否启动index_granularity_bytes来控制索引粒度大小。
index_granularity_bytes:索引粒度,以字节为单位,默认10Mb。
merge_max_block_size:数据块合并最大记录个数,默认8192。
merge_with_ttl_timeout:合并频率最小时间间隔,默认1天。
建表 SQL 实例
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS mergetree_sample_table
(
name String,
price UInt64,
shop_id UInt64,
quantity UInt64,
p_date DateTime
)
ENGINE =MergeTree()
partition by p_date
order by (name,shop_id,p_date)
SETTINGS index_granularity =2;
插入数据:
INSERT INTO mergetree_sample_table
VALUES ('Apple',2,1,40,now()) ('Apple',2,3,35,now()) ('Apple',3,2,45,now()) ('Apple',3,4,35,now()) ('Orange',1,2,40,now()) ('Orange',3,3,50,now()) ('Banana',2,1,25,now()) ('Banana',2,2,55,now());
查询数据:
SELECT t.*
FROM mydb.mergetree_sample_table t
LIMIT 501
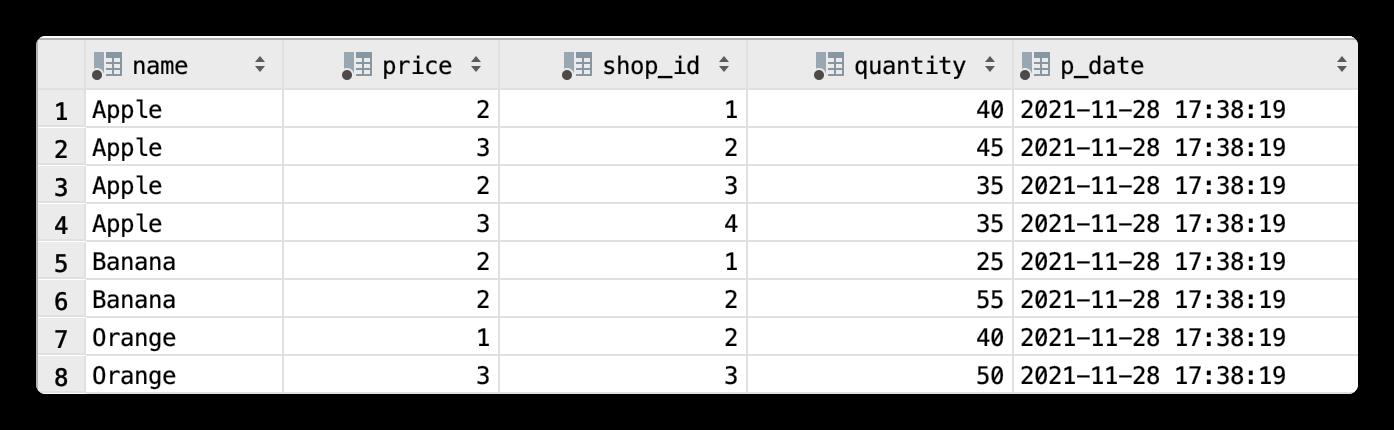
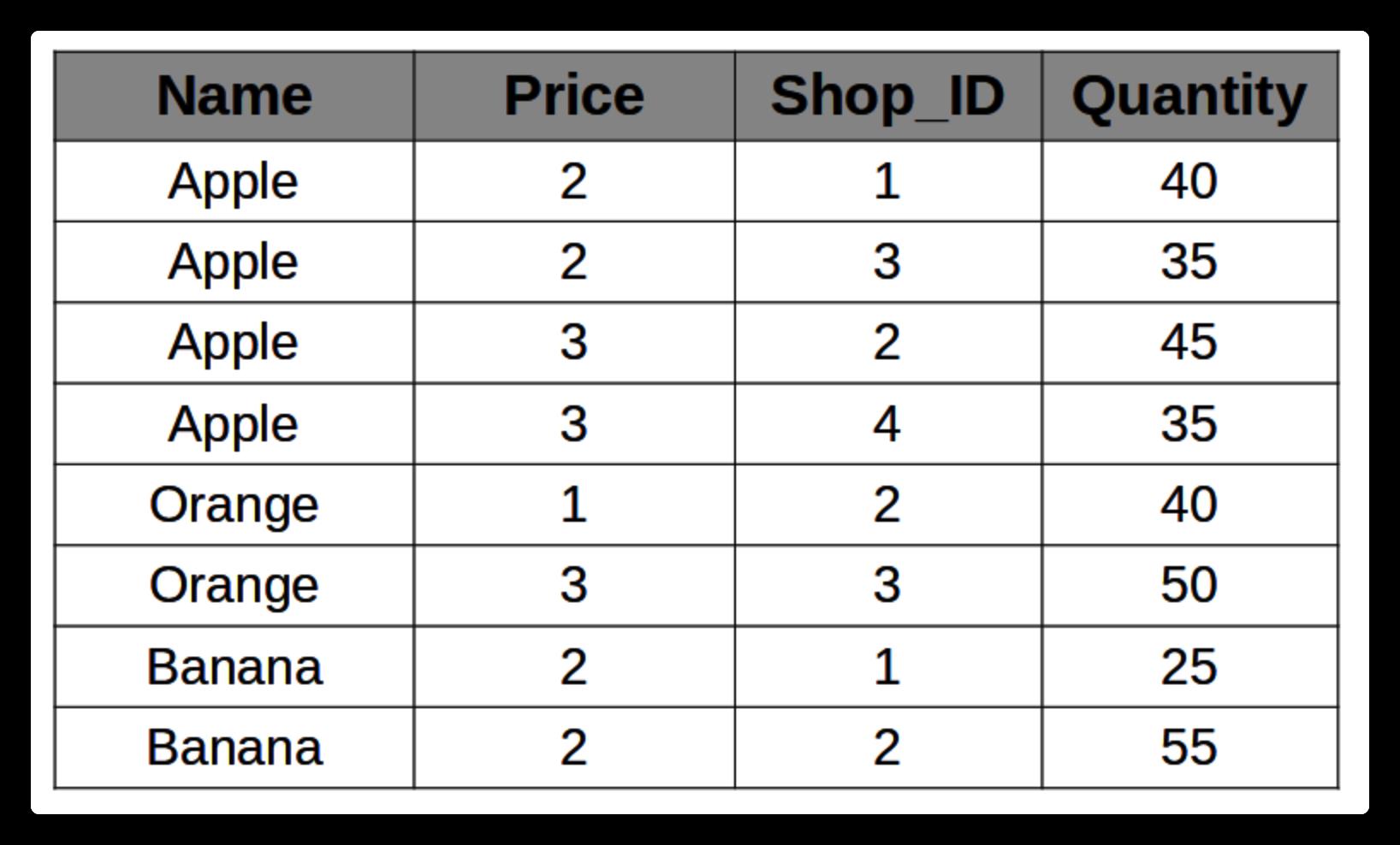
底层文件存储
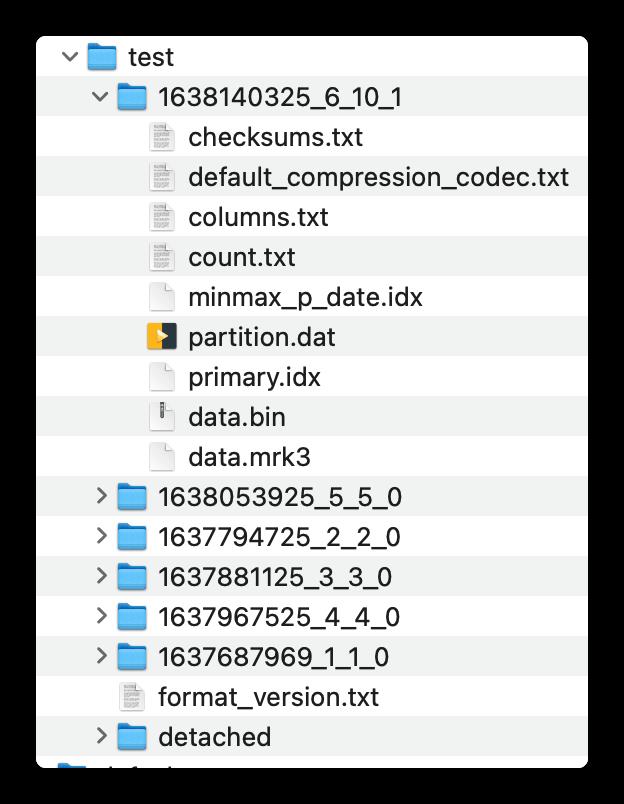
MergeTree 表引擎底层的物理存储文件目录如下:
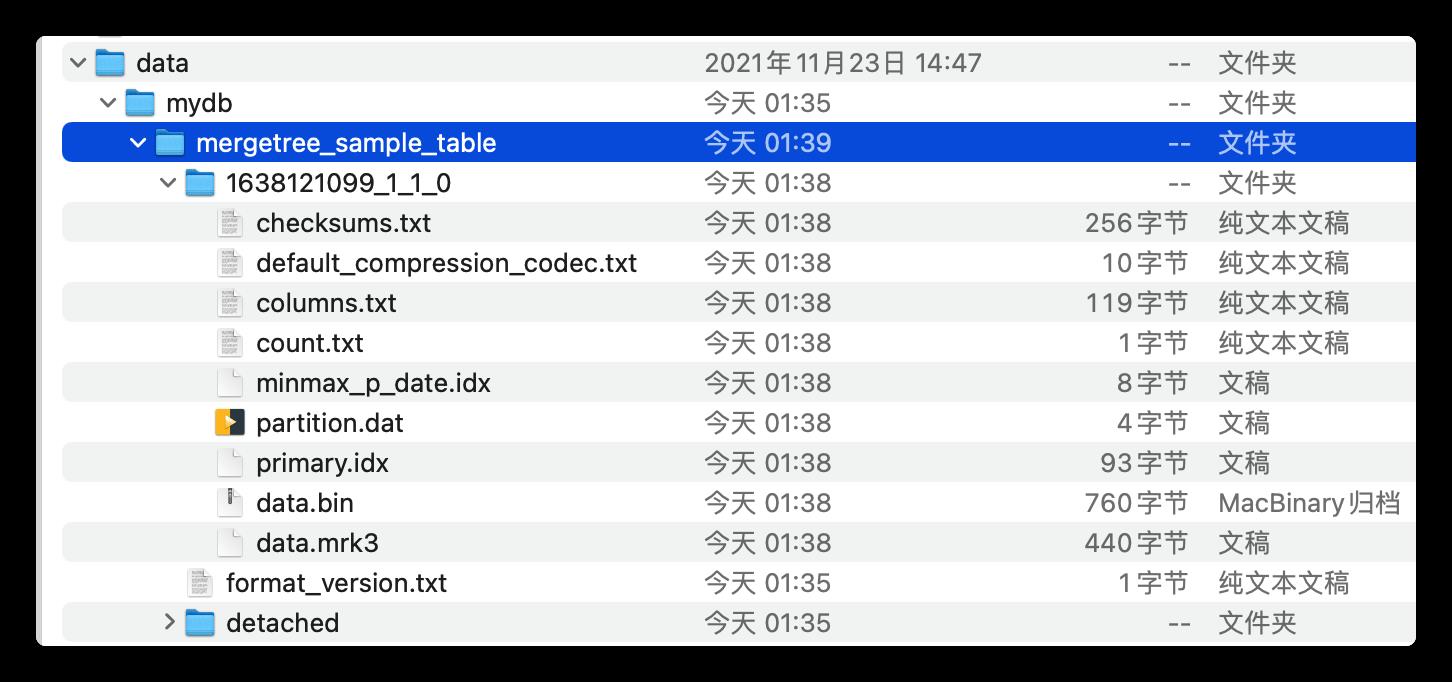
MergeTree 表引擎的物理文件存储目录结构:
├── 1638121099_1_1_0
│ ├── checksums.txt
│ ├── columns.txt
│ ├── count.txt
│ ├── data.bin
│ ├── data.mrk3
│ ├── default_compression_codec.txt
│ ├── minmax_p_date.idx
│ ├── partition.dat
│ └── primary.idx
├── detached
└── format_version.txt
2 directories, 10 files
其中,
$cat default_compression_codec.txt
CODEC(LZ4)%
$cat columns.txt
columns format version: 1
5 columns:
`name` String
`price` UInt64
`shop_id` UInt64
`quantity` UInt64
`p_date` DateTime
$cat count.txt
8%
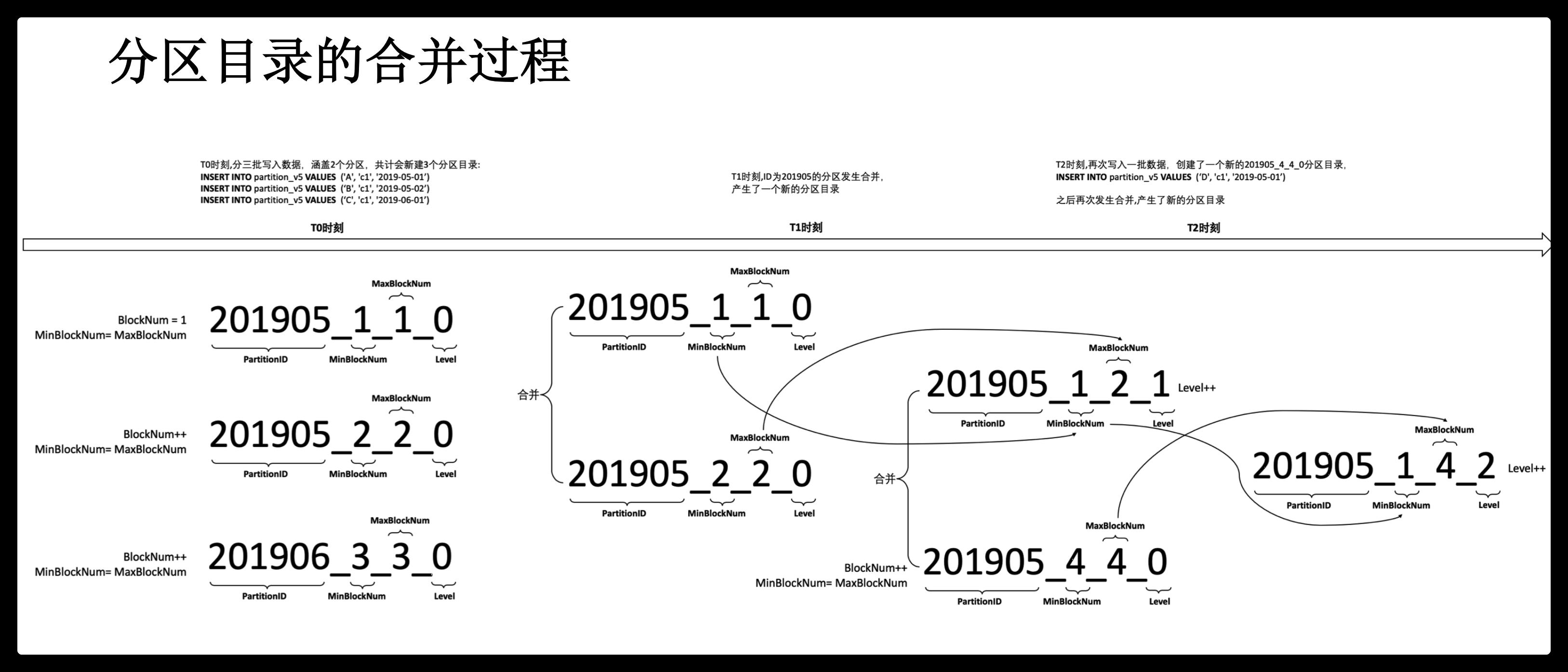
数据分区目录命名规则
目录命名规则如下:
PartitionId_MinBlockNum_MaxBlockNum_Level
PartitionID:分区id,例如20210301。
MinBlockNum:最小分区块编号,自增类型,从1开始向上递增。每产生一个新的目录分区就向上递增一个数字。
MaxBlockNum:最大分区块编号,新创建的分区MinBlockNum等于MaxBlockNum的编号。
Level:合并的层级,被合并的次数。合并次数越多,层级值越大。
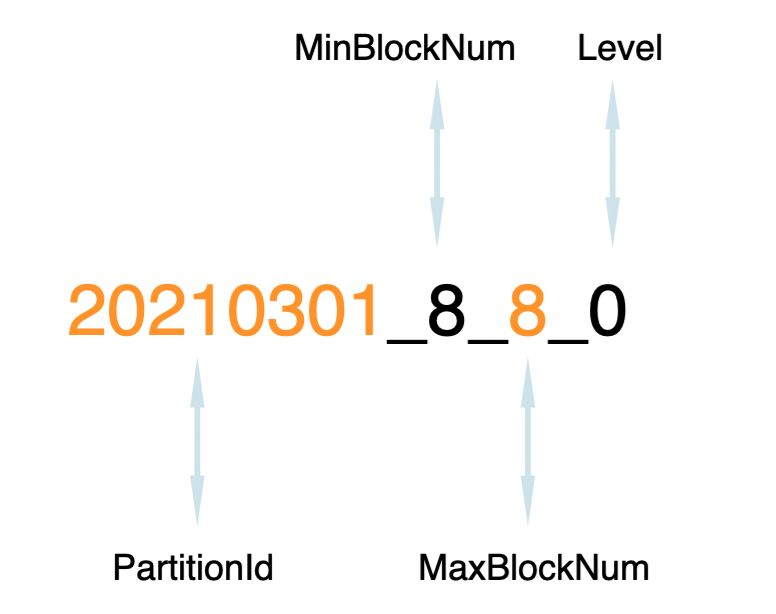
level为0,表示此分区没有合并过。
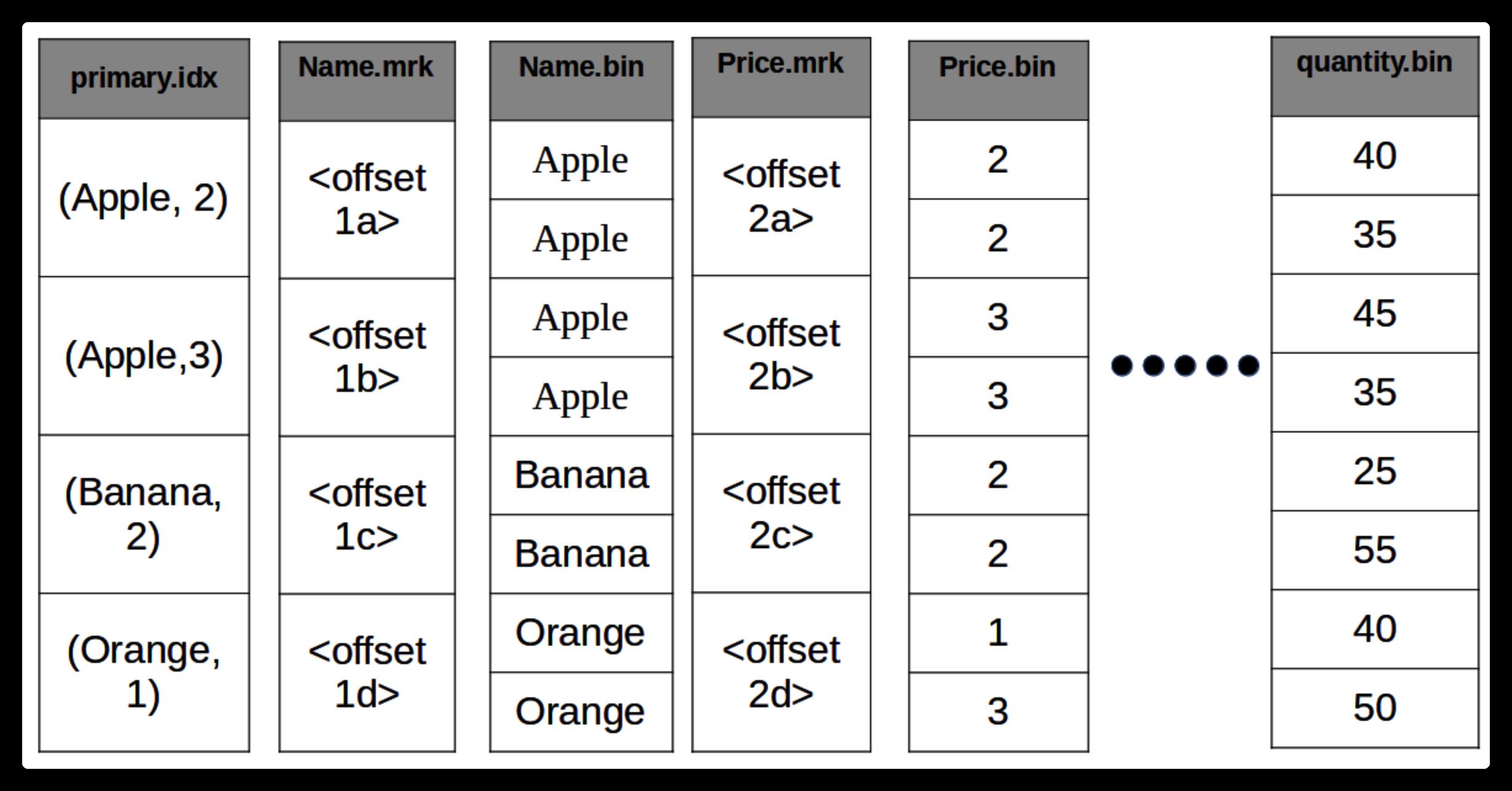
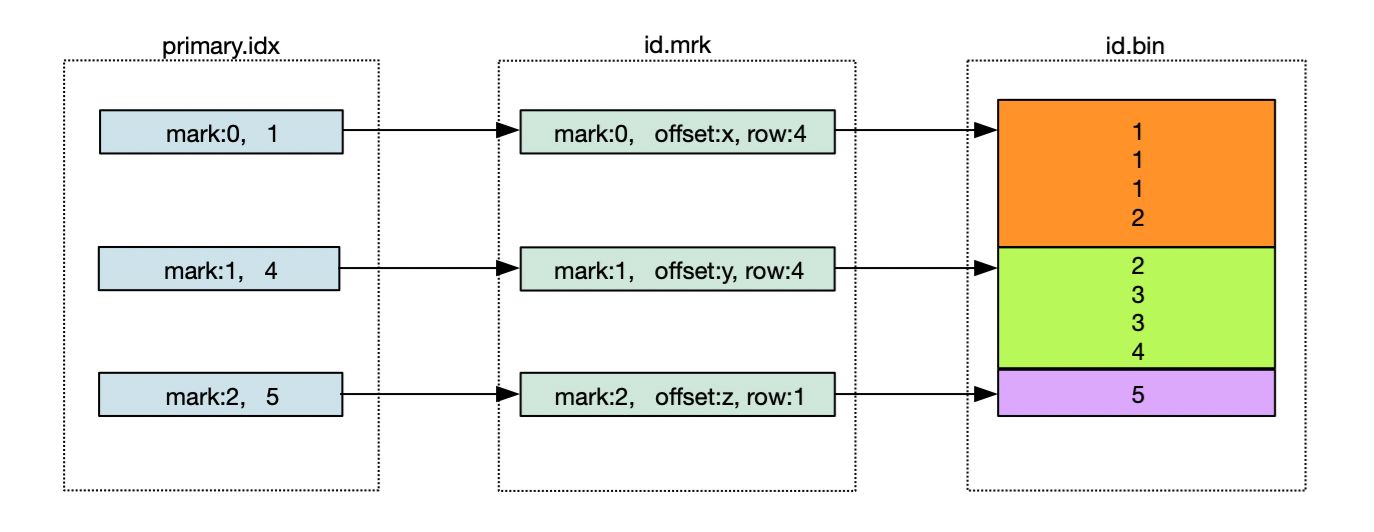
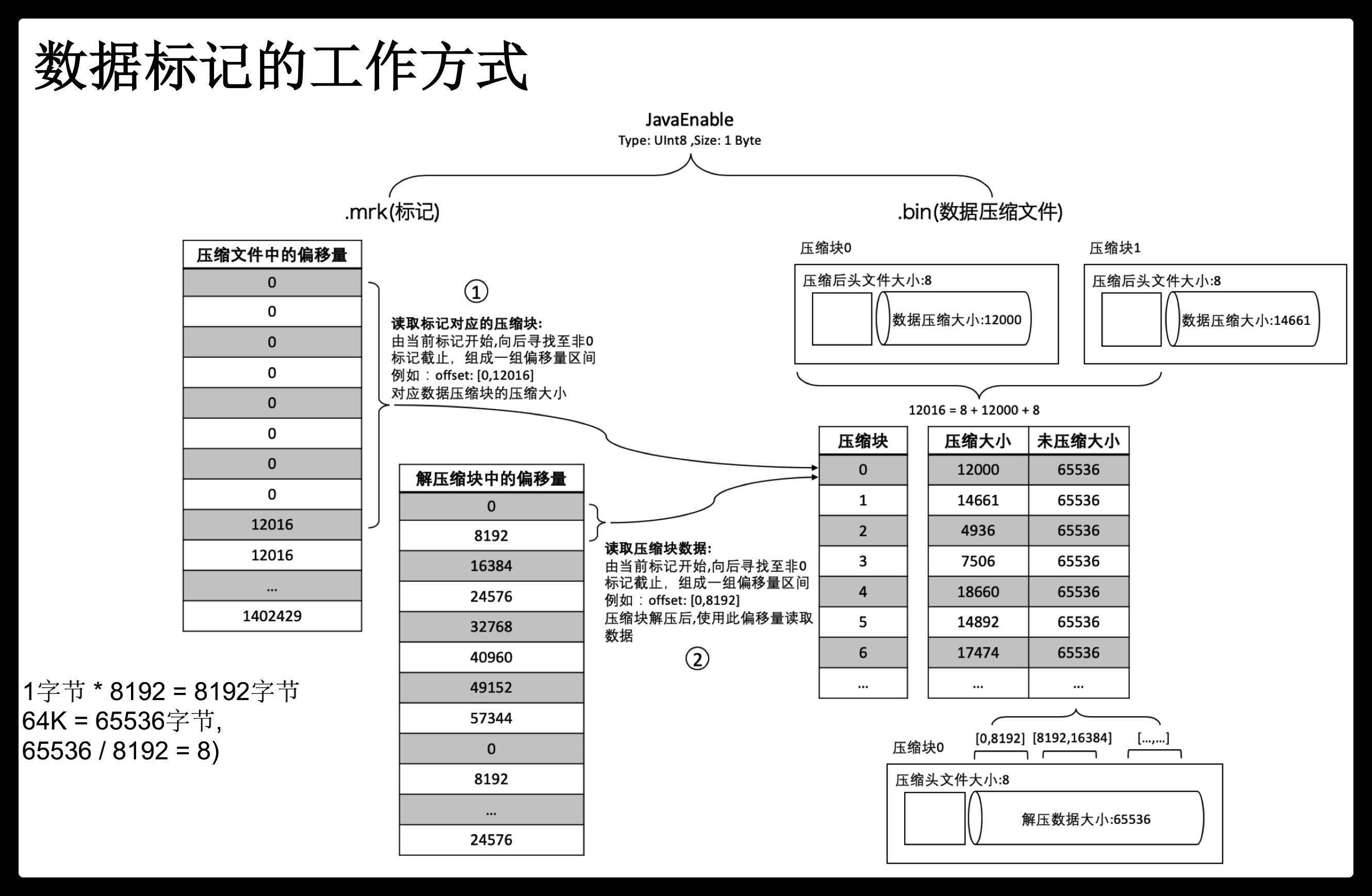
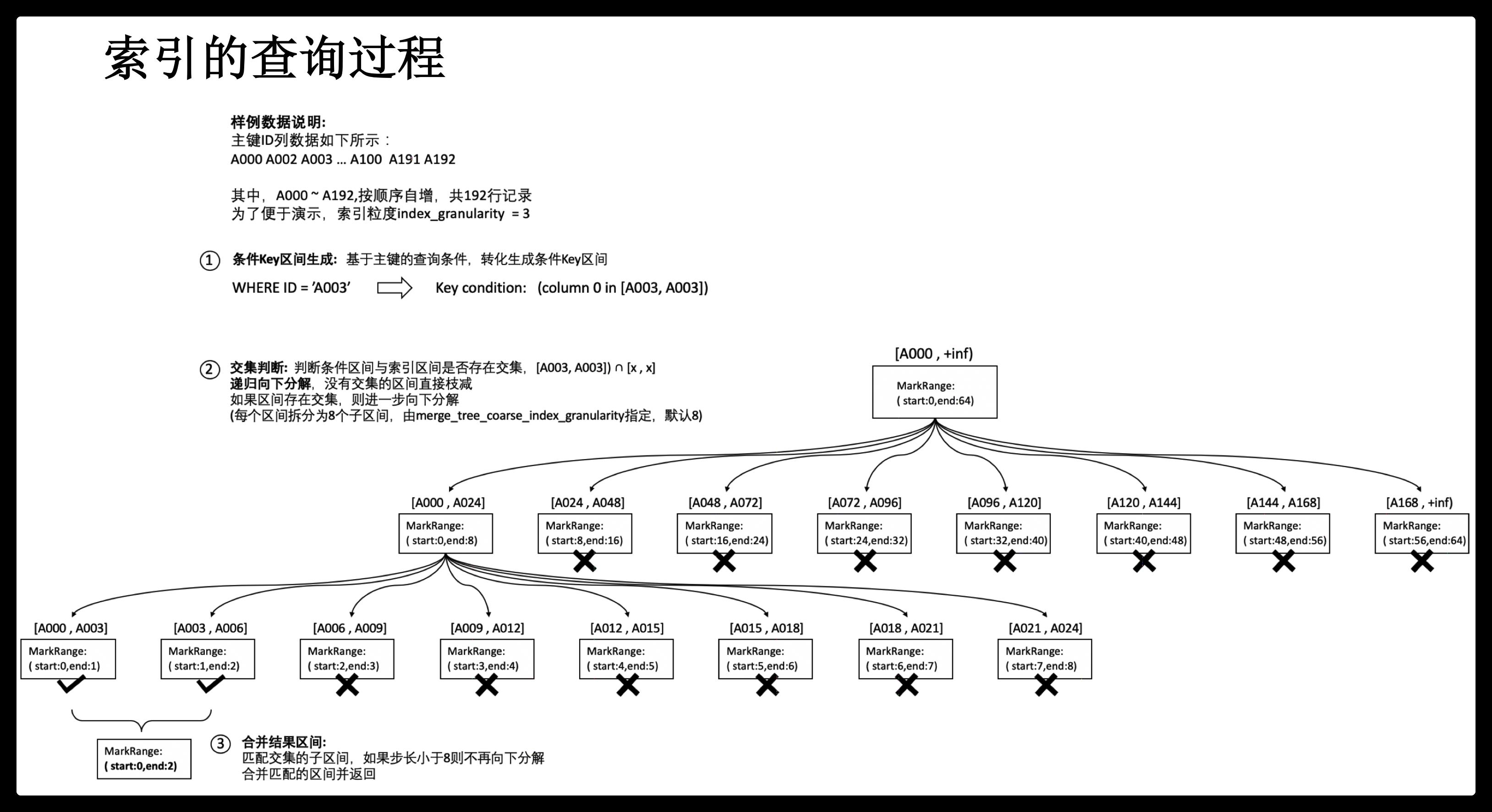
索引文件:稀疏索引
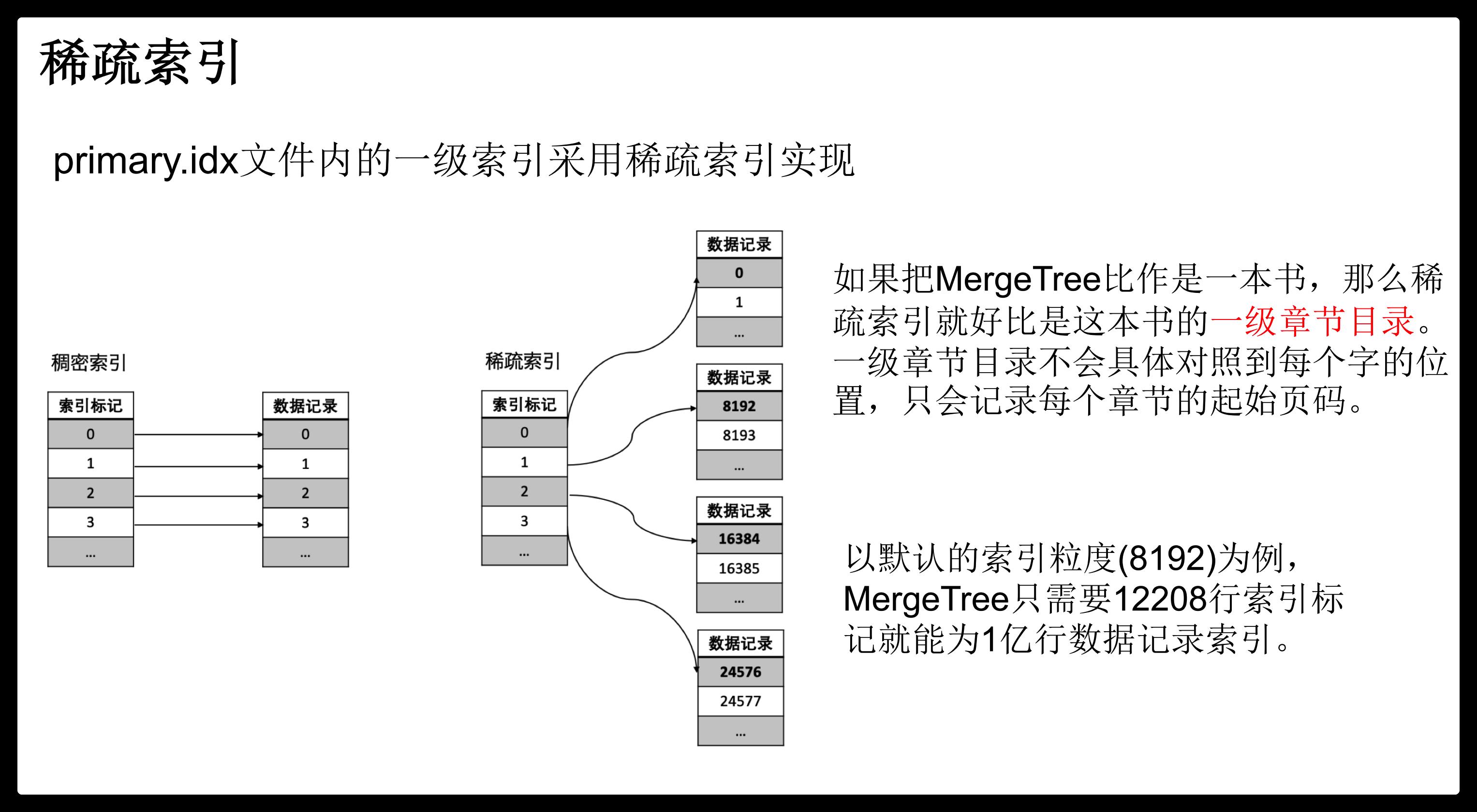
MergeTree索引为稀疏索引,它并不索引单条数据,而是索引一定范围的数据。也就是从已排序的全量数据中,间隔性的选取一些数据记录主键字段的值来生成primary.idx索引文件,从而加快表查询效率。间隔设置参数为index_granularity。
标记文件
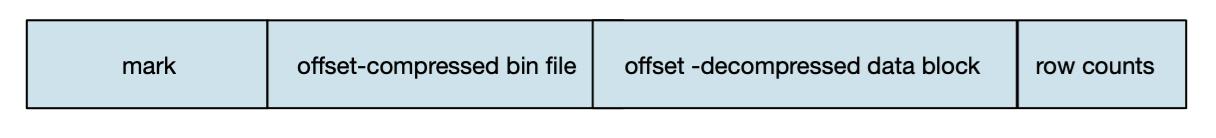
mrk标记文件在primary.idx索引文件和bin数据文件之间起到了桥梁作用。primary.idx文件中的每条索引在mrk文件中都有对应的一条记录。
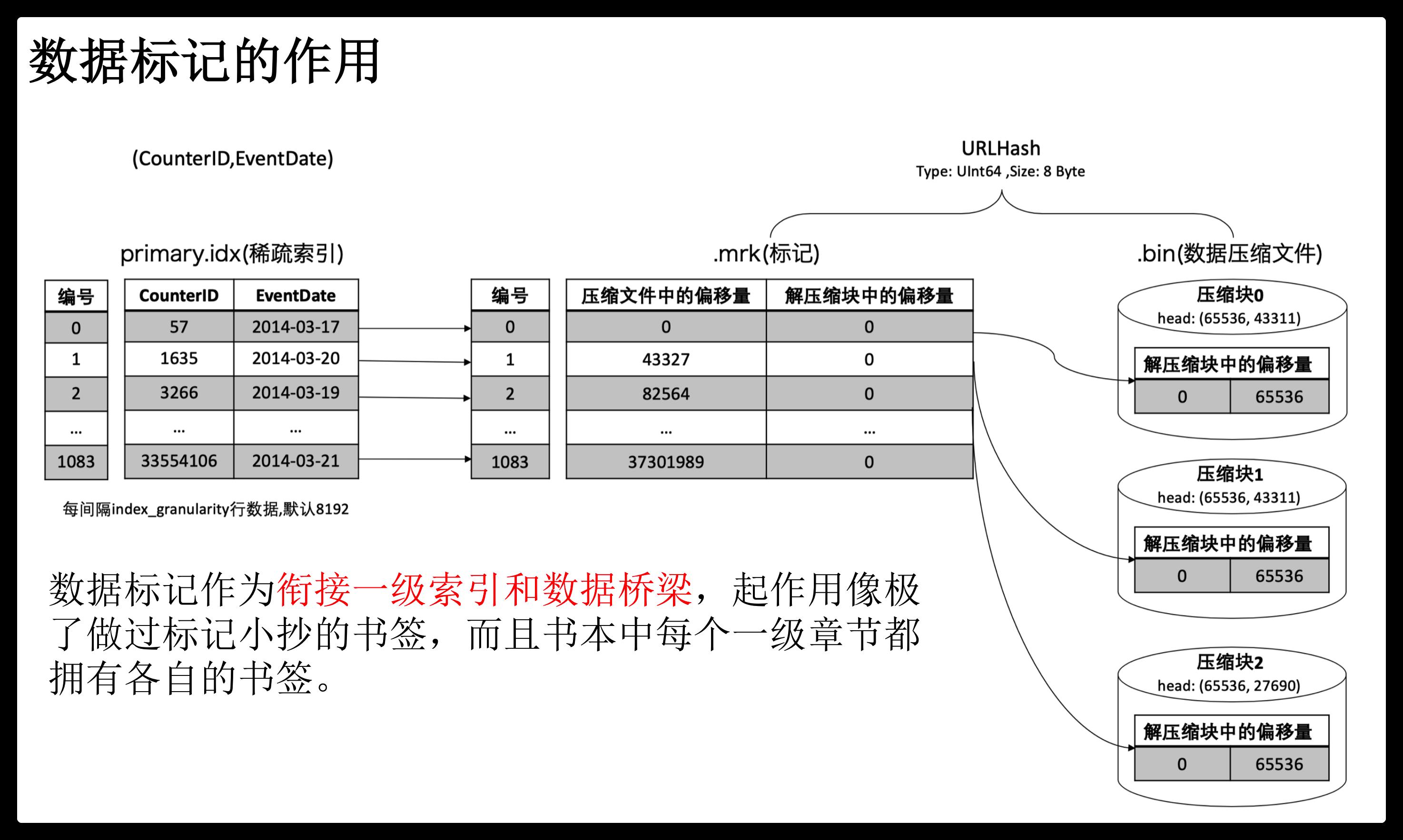
一条记录的组成包括:
offset-compressed bin file:表示指向的压缩数据块在bin文件中的偏移量。
offset-decompressed data block:表示指向的数据在解压数据块中的偏移量。
row counts:代表数据记录行数,小于等于index_granularity所设置的值。
索引、标记和数据文件下图所示:
MergeTree表引擎家族详解
在ClickHouse的整个体系里面,MergeTree表引擎绝对是一等公民,使用ClickHouse就是在使用MergeTree,这种说法一点也不为过。MergeTree表引擎是一个家族系列,目前整个系列一共包含了14种不同类型的MergeTree。
MergeTree(合并树)系列表引擎是ClickHouse提供的最具特色的存储引擎。MergeTree引擎支持数据按主键、数据分区、数据副本以及数据采样等特性。官方提供了包括MergeTree、ReplacingMergeTree、SummingMergeTree、AggregatingMergeTree、CollapsingMergeTree、VersionedCollapsingMergeTree、GraphiteMergeTree等7种不同类型的MergeTree引擎的实现,以及与其相对应的支持数据副本的MergeTree引擎(Replicated*)。
这么多表引擎,它们之间是什么关系?
我们可以使用两种关系,来理解整个MergeTree系列:
继承关系
首先,为了便于理解,可以使用继承关系来看待MergeTree。通过最基础的MergeTree表引擎,向下派生出6个变种表引擎,如下图所示
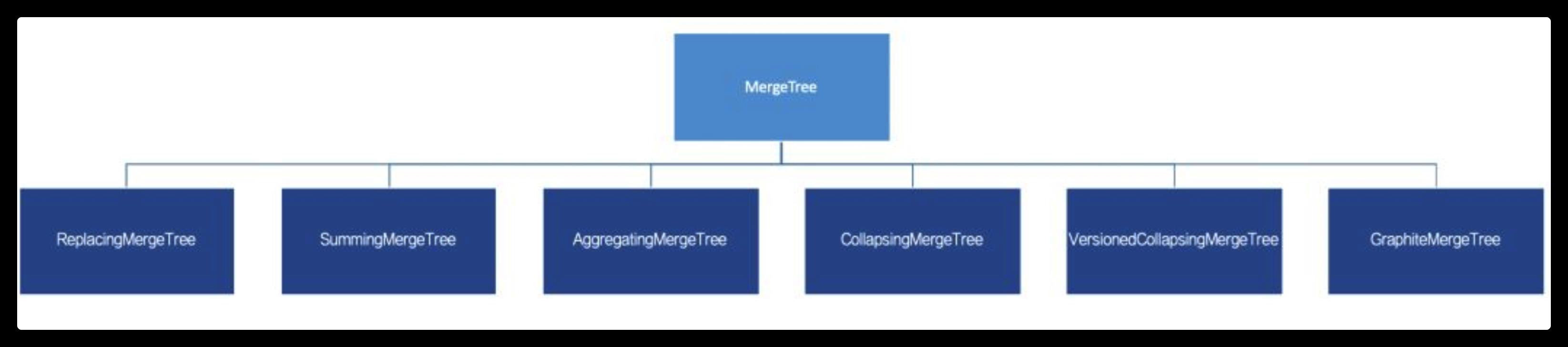
在ClickHouse底层具体的实现方法中,上述7种表引擎的区别主要体现在Merge合并的逻辑部分。如下图所示:
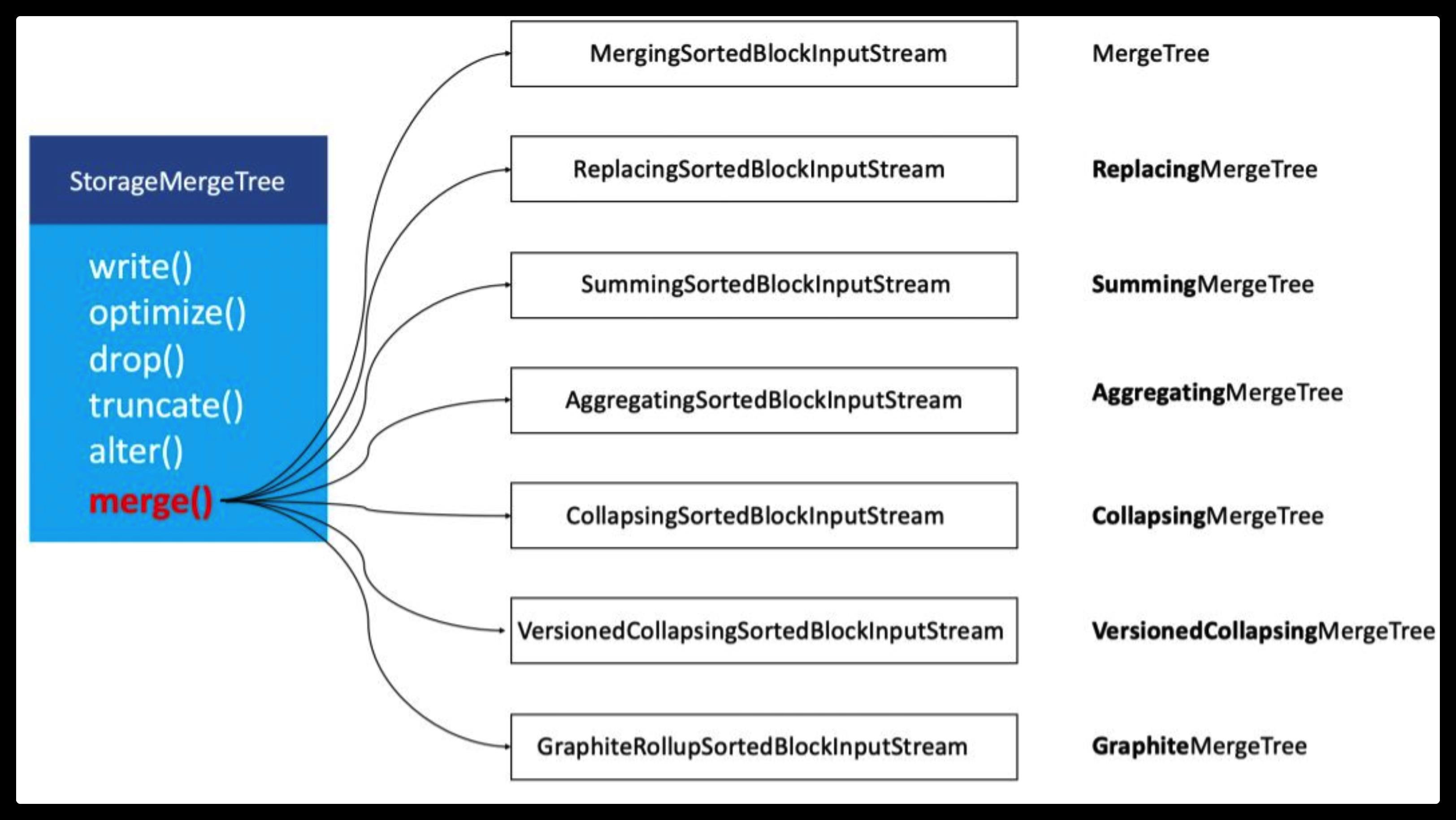
在具体的实现逻辑部分,7种MergeTree共用一个主体,在触发Merge动作时,调用了各自独有的合并逻辑。特殊功能只会在Merge合并时才会触发。
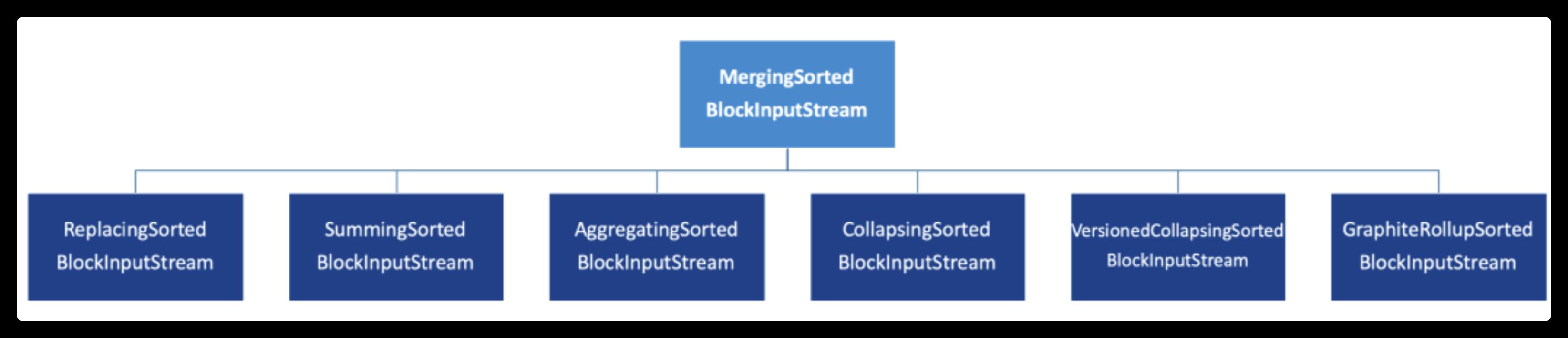
组合关系
刚才已经介绍了7种MergeTree的关系,余下的7种是ReplicatedMergeTree系列。

ReplicatedMergeTree与普通的MergeTree又有什么区别呢? 我们接着看下面这张图:
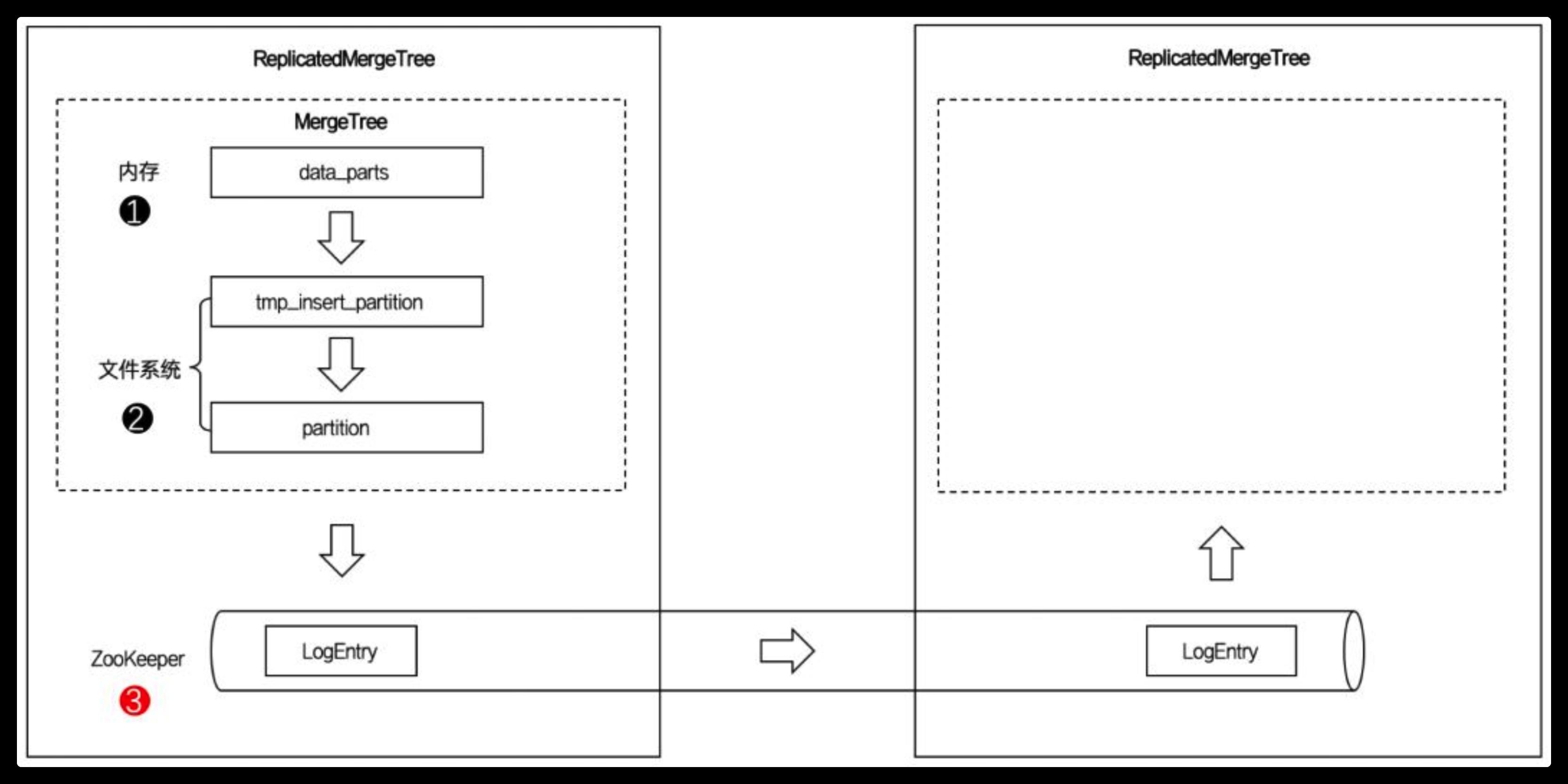
图中的虚线框部分是MergeTree的能力边界,而ReplicatedMergeTree在它的基础之上增加了分布式协同的能力(HA)。ClickHouse 集群借助ZooKeeper的消息日志广播,实现了副本实例之间的数据同步功能。
ReplicatedMergeTree系列可以用组合关系来理解,如下图所示:
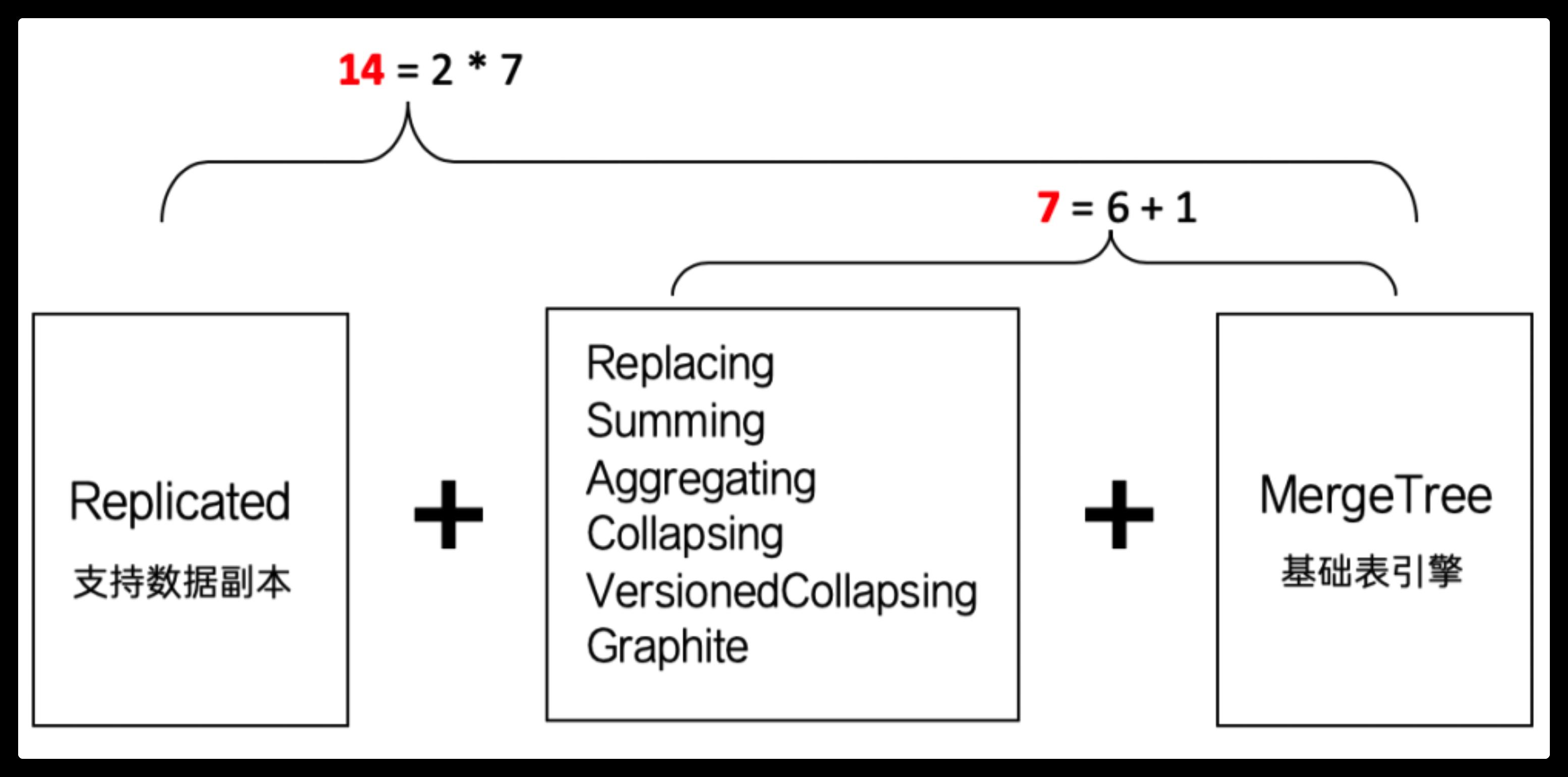
当我们为7种MergeTree加上Replicated前缀后,又能组合出7种新的表引擎,这些ReplicatedMergeTree 拥有副本协同的能力。
我们到底应该使用哪一种表引擎?
现在回答第二个问题,按照使用的场景划分,可以将上述14种表引擎大致分成以下6类应用场景:
默认情况
在没有特殊要求的场合,使用基础的MergeTree表引擎即可,它不仅拥有高效的性能,也提供了所有MergeTree共有的基础功能,包括列存、数据分区、分区索引、一级索引、二级索引、TTL、多路径存储等等。
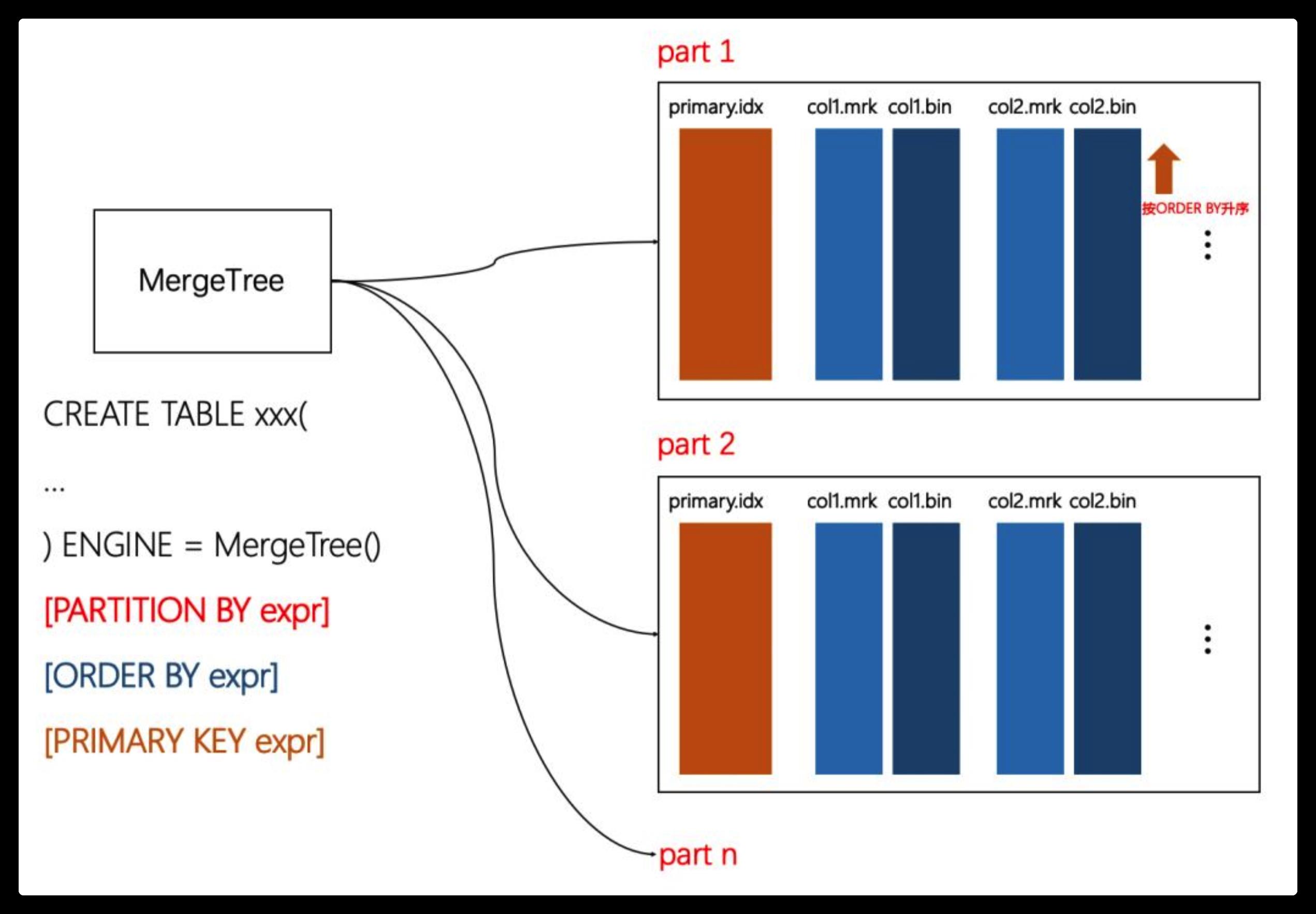
与此同时,它也定义了整个MergeTree家族的基调,例如:
ORDER BY 决定了每个分区中数据的排序规则;
PRIMARY KEY 决定了一级索引(primary.idx);
ORDER BY 可以指代PRIMARY KEY, 通常只用声明ORDER BY 即可。
接下来将要介绍的其他表引擎,除开ReplicatedMergeTree系列外,都是在Merge合并动作时添加了各自独有的逻辑。
数据去重
ReplacingMergeTree 使用示例
1.建表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS replacingmergetree_test
(
ID String,
Name String,
DateOfBirth Date
)
ENGINE =ReplacingMergeTree()
PARTITION BY ID
ORDER BY (ID,DateOfBirth)
SETTINGS
index_granularity =1024;
2.插入数据
INSERT INTO replacingmergetree_test
VALUES ('a1','Jim','1995-05-01'),
('a1','Jim','1995-05-01'),
('a1','Jim','1995-05-02'),
('a2','Jil','1995-06-01'),
('a2','Jil','1995-06-01'),
('a2','Jil','1995-06-02');
查询数据,看看效果:
desc replacingmergetree_test
DESCRIBE TABLE replacingmergetree_test
Query id: 59ab6932-9912-4d86-b97d-7782a8e11f65
┌─name────────┬─type───┬─default_type─┬─default_expression─┬─comment─┬─codec_expression─┬─ttl_expression─┐
│ ID │ String │ │ │ │ │ │
│ Name │ String │ │ │ │ │ │
│ DateOfBirth │ Date │ │ │ │ │ │
└─────────────┴────────┴──────────────┴────────────────────┴─────────┴──────────────────┴────────────────┘
3 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.001 sec.
SELECT *
FROM replacingmergetree_test
Query id: 082de655-db24-4679-ab10-8d431320fae2
┌─ID─┬─Name─┬─DateOfBirth─┐
│ a2 │ Jil │ 1995-06-01 │
│ a2 │ Jil │ 1995-06-02 │
└────┴──────┴─────────────┘
┌─ID─┬─Name─┬─DateOfBirth─┐
│ a1 │ Jim │ 1995-05-01 │
│ a1 │ Jim │ 1995-05-02 │
└────┴──────┴─────────────┘
4 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.003 sec.
3.执行merge
可以手动执行:
OPTIMIZE TABLE replacingmergetree_test FINAL;
一般ClickHouse会由后台程序自动执行 merge 操作。
4.查询数据
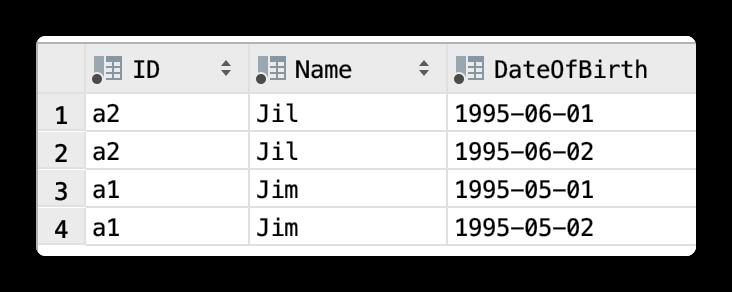
通过刚才的说明,大家应该明白,MergeTree的主键(PRIMARY KEY)只是用来生成一级索引(primary.idx)的,并没有唯一性约束这样的语义。
一些朋友在使用MergeTree的时候,用传统数据库的思维来理解MergeTree就会出现问题。
如果业务上不允许数据重复,遇到这类场景就可以使用ReplacingMergeTree,如下图所示:
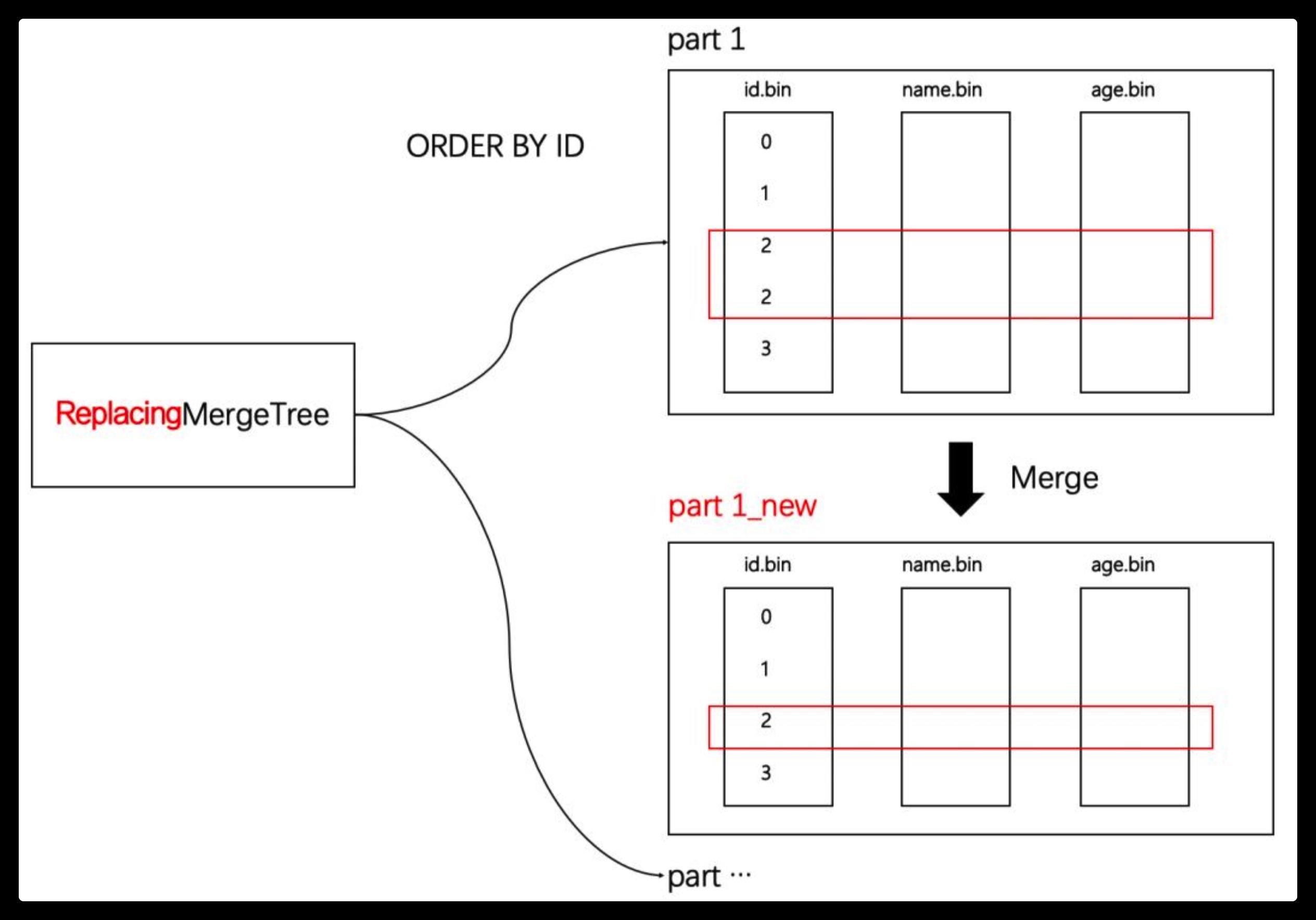
ReplacingMergeTree通过ORDER BY,表示判断唯一约束的条件。当分区合并之时,根据ORDER BY排序后,相邻重复的数据会被排除。
由此,可以得出几点结论:
第一,使用ORDER BY作为特殊判断标识,而不是PRIMARY KEY。关于这一点网上有一些误传,但是如果理解了ORDER BY与PRIMARY KEY的作用,以及合并逻辑之后,都能够推理出应该是由ORDER BY决定。
ORDER BY的作用, 负责分区内数据排序;
PRIMARY KEY的作用, 负责一级索引生成;
Merge的逻辑, 分区内数据排序后,找到相邻的数据,做特殊处理。
第二,只有在触发合并之后,才能触发特殊逻辑。以去重为例,在没有合并的时候,还是会出现重复数据。
第三,只对同一分区内的数据有效。以去重为例,只有属于相同分区的数据才能去重,跨越不同分区的重复数据不能去重。
上述几点结论,适用于包含ReplacingMergeTree在内的6种MergeTree,所以后面不在赘述。
小结:ReplacingMergeTree 引擎会把相同索引的数据进行替换,但仅限本地单台机器。如果使用分布式表,就要确保相同索引的数据入到同一台机器,否则每台机器可能会有一条相同索引的数据。
该索引只有在 merge 的时候才会执行替换,因为 merge 是不定时的,如果没有 merge 的情况下,会出现多条数据的情况。因此必要的话,可以进行手动进行 merge。手动 merge 命令:optimize table db.table;
该索引的建表语句如果没有用某个字段标定版本,该字段可以是 int、double、date 类型,数据库就一定会把后入库的覆盖新入库 (如果有区分版本的字段,则会留下数值大的那条记录)。
预聚合(数据立方体)
有这么一类场景,它的查询主题是非常明确的,也就是说聚合查询的维度字段是固定,并且没有明细数据的查询需求,这类场合就可以使用SummingMergeTree或是AggregatingMergeTree,如下图所示:
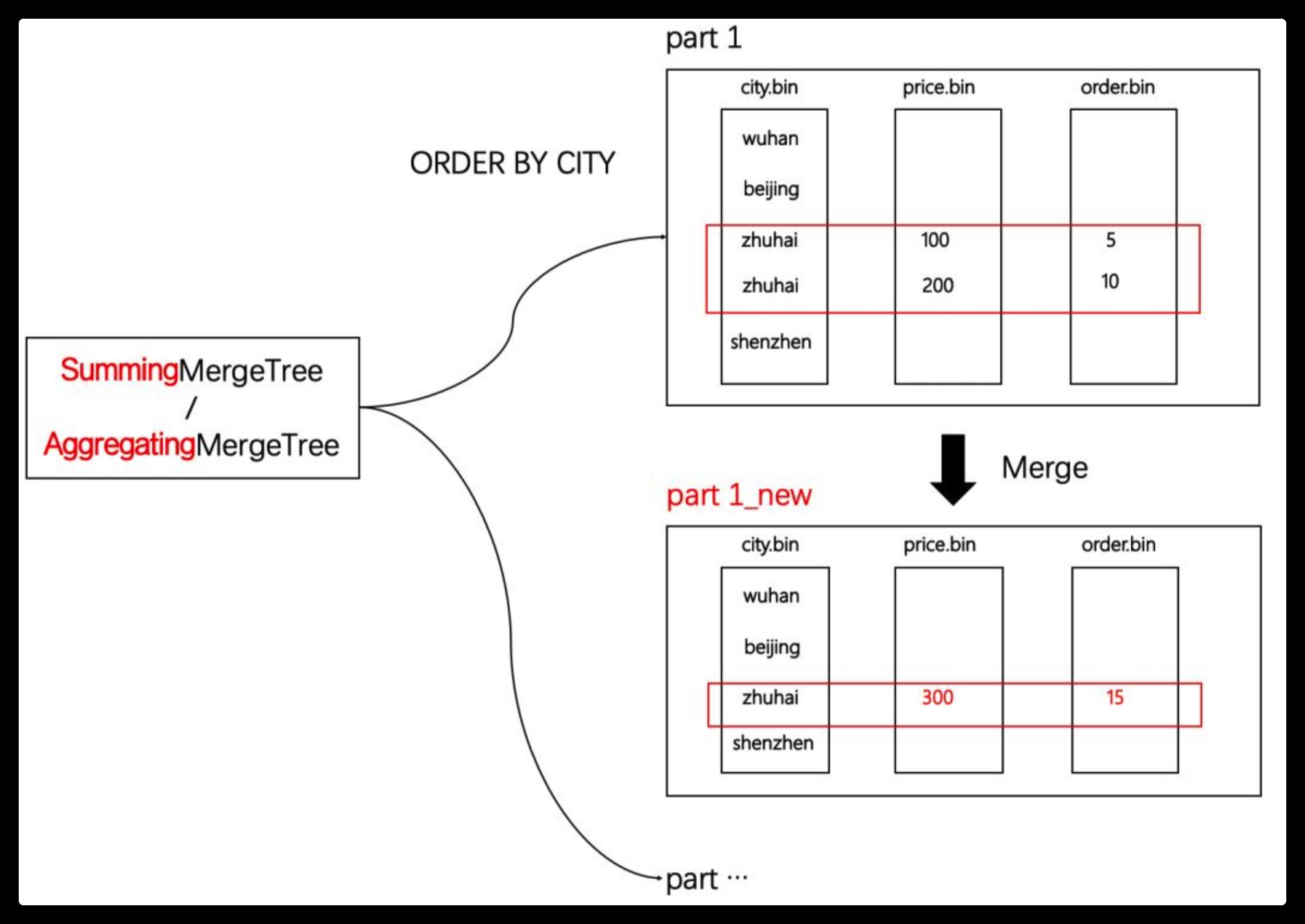
可以看到,在新分区合并后,在同一分区内,ORDER BY条件相同的数据会进行合并。如此一来,首先表内的数据行实现了有效的减少,其次度量值被预先聚合,进一步减少了后续计算开销。聚合类MergeTree通常可以和MergeTree表引擎协同使用,如下图所示:
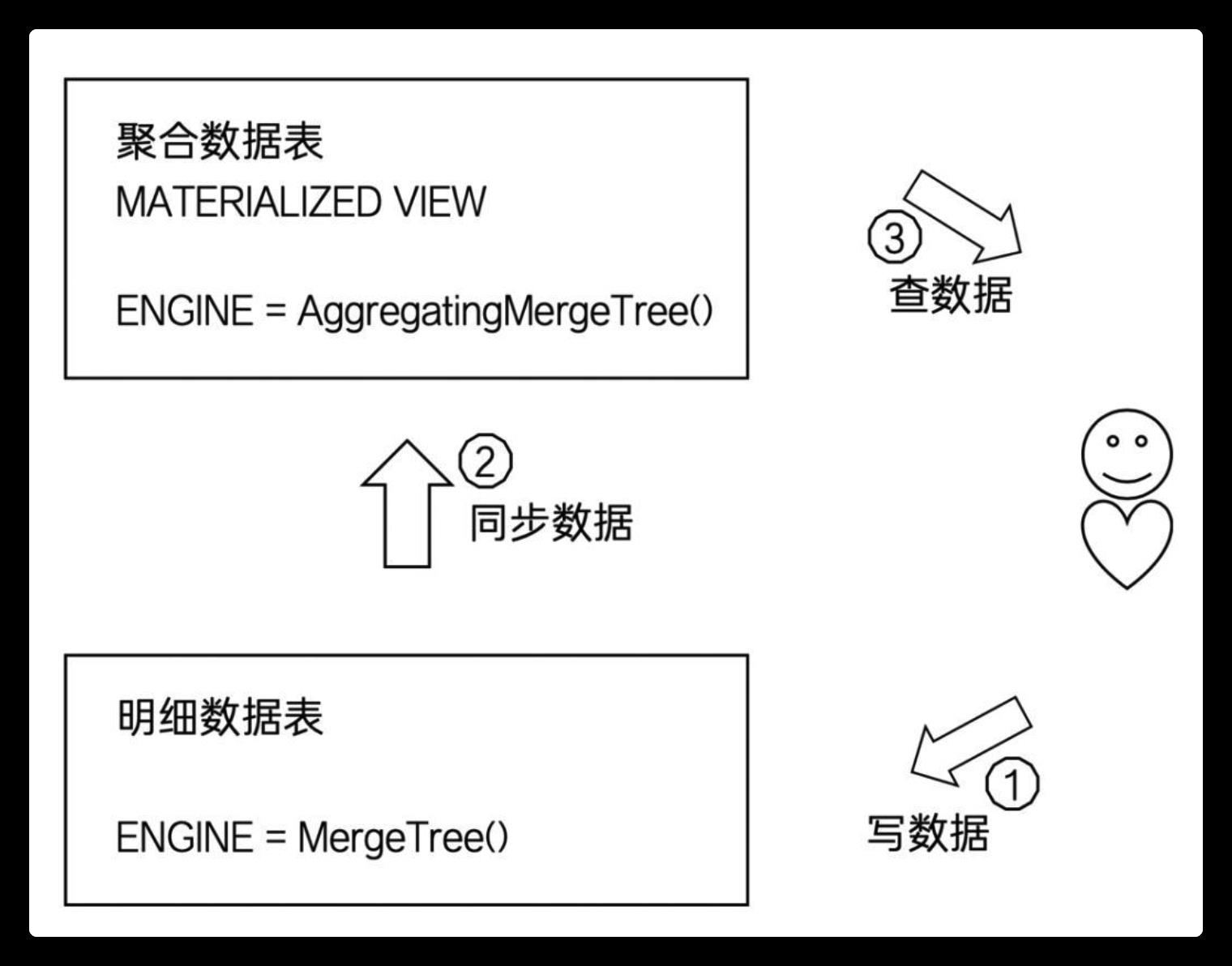
可以将物化视图设置成聚合类MergeTree,将其作为固定主题的查询表使用。
值得一提的是,通常只有在使用SummingMergeTree或AggregatingMergeTree的时候,才需要同时设置ORDER BY与PRIMARY KEY。
显式的设置PRIMARY KEY,是为了将主键和排序键设置成不同的值,是进一步优化的体现。
例如某个场景的查询需求如下:
聚合条件,GROUP BY A,B,C
过滤条件,WHERE A
此时,如下设置将会是一种较优的选择:
GROUP BY A,B,C
PRIMARY KEY A
BTW,如果ORDER BY与PRIMARY KEY不同,PRIMARY KEY必须是ORDER BY的前缀(为了保证分区内数据和主键的有序性)。
SummingMergeTree 引擎测试
该引擎会把索引以为的所有 number 型字段(包含 int 和 double)自动进行聚合。
该引擎在分布式情况下并不是完全聚合,而是每台机器有一条同纬度的数据。SummingMergeTree 是按 part 纬度来聚合,数据刚导入 clickhouse 可能会产生多个 part,但是 clickhouse 会定期把 part merge,从而实现一台机器只有一条同纬度的数据。
如果将字段设为索引,则不会继续聚合,对于非设为索引的字段,如果是 int 类型会进行聚合,非 int 类型,会随机选取一个字段进行覆盖。
数据更新
数据的更新在ClickHouse中有多种实现手段,例如按照分区Partition重新写入、使用Mutation的DELETE和UPDATE查询。
使用CollapsingMergeTree或VersionedCollapsingMergeTree也能实现数据更新,这是一种使用标记位,以增代删的数据更新方法,如下图所示:
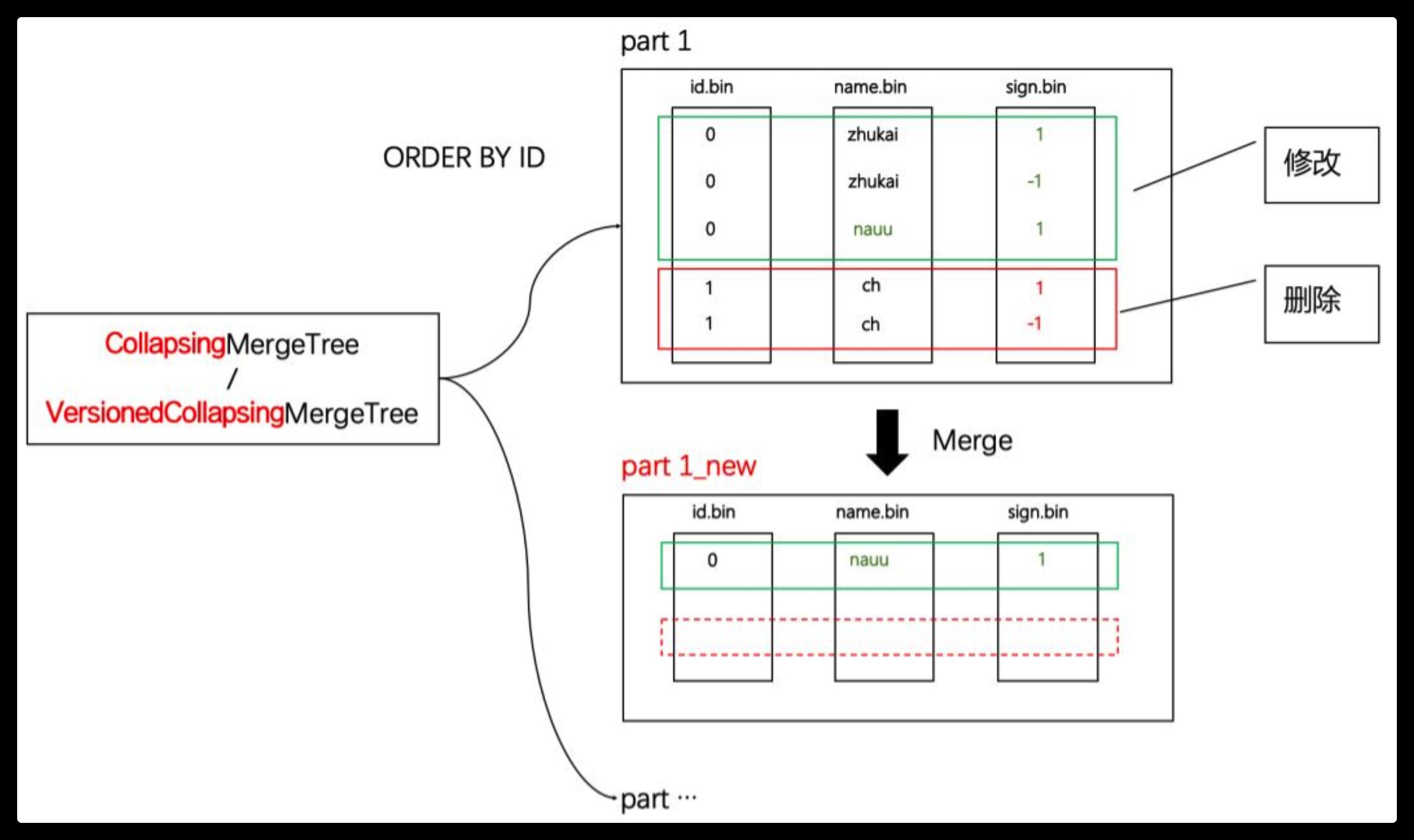
通过增加一个 sign 标志字段(例如图中的sign字段),作为数据有效性的判断依据。
可以看到,在新分区合并后,在同一分区内,ORDER BY条件相同的数据,其标志值为1和-1的数据行会进行抵消。
下图是另外一种便于理解的视角,就如同挤压瓦楞纸一般,数据被抵消了:

VersionedCollapsingMergeTree: 带版本的CollapsingMergeTree
CollapsingMergeTree 和 VersionedCollapsingMergeTree的区别又是什么呢?
CollapsingMergeTree 对数据写入的顺序是敏感的,它要求标志位需要按照正确的顺序排序。例如按照1,-1的写入顺序是正确的; 而如果按照-1,1的错误顺序写入,CollapsingMergeTree就无法正确抵消。
试想,如果在一个多线程并行的写入场景,我们是无法保证这种顺序写入的,此时就需要使用VersionedCollapsingMergeTree了。
VersionedCollapsingMergeTree 在 CollapsingMergeTree基础之上,额外要求指定一个version字段,在分区Merge合并时,它会自动将version字段追加到ORERY BY的末尾,从而保证了标志位的有序性。
ENGINE=VersionedCollapsingMergeTree(sign,ver) ORDER BY id //等效于ORDER BY id,ver
监控集成
GraphiteMergeTree可以与Graphite集成,如果你使用了Graphite作为系统的运行监控系统, 则可以通过GraphiteMergeTree存储指标数据,加速查询性能、降低存储成本。
高可用
Replicated* 拥有数据副本的能力,如下图所示:
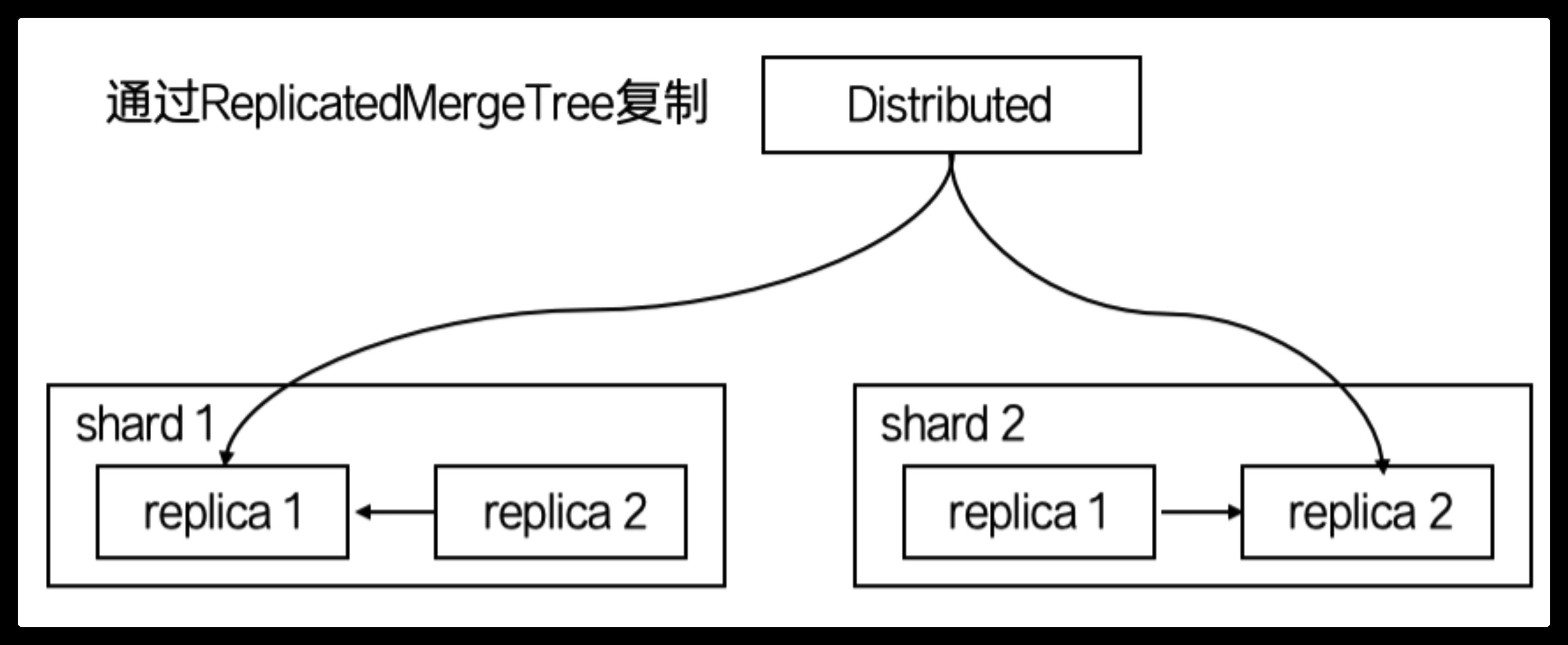
结合刚才的5类场景,如果进一步需要高可用的需求,选择一种MergeTree和Replicated组合即可,例如 ReplicatedMergeTree、ReplicatedReplacingMergeTree 等等。
合并算法概述 Overview of the merge algorithm
每个合并按块顺序执行。
Each merge is executed sequentially block by block.
合并算法的主要思想是,确保合并操作不是一个在线程池中执行的子例程(因为它可能会占用一段时间的线程),而是使合并操作在一个协程中完成。它可以在某些点暂停执行,然后从该点恢复执行。
The main idea is to make a merge not a subroutine which is executed in a thread pool and may occupy a thread for a period of time, but to make a merge a coroutine which can suspend the execution in some points and then resume the execution from this point.
挂起执行的最佳点是在一个块上的工作完成之后。
任务本身将通过 BackgroundJobExecutor 执行。
任务的接口很简单。主要方法是' execute() ',如果任务想要再次执行,它将返回true,否则返回false。
A perfect point where to suspend the execution is after the work over a block is finished.
The task itself will be executed via BackgroundJobExecutor.
The interface of the task is simple. The main method is `execute()` which will return true, if the task wants to be executed again and false otherwise.
对于这种任务,我们可以给合并一个优先级。 优先级很简单:
合并的大小越小,优先级越高。
By default priority queue will have max element at top。
所以,如果ClickHouse想要将一些真正大的部分合并成一个更大的部分,那么它将被执行很长一段时间,因为合并的结果并不是真正需要立即。 最好尽快合并小部分。
With this kind of task we can give a merge a priority. A priority is simple :
the lower the size of the merge, the higher priority.
So, if ClickHouse wants to merge some really big parts into a bigger part, then it will be executed for a long time, because the result of the merge is not really needed immediately. It is better to merge small parts as soon as possible.
合并任务后台执行器:MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor
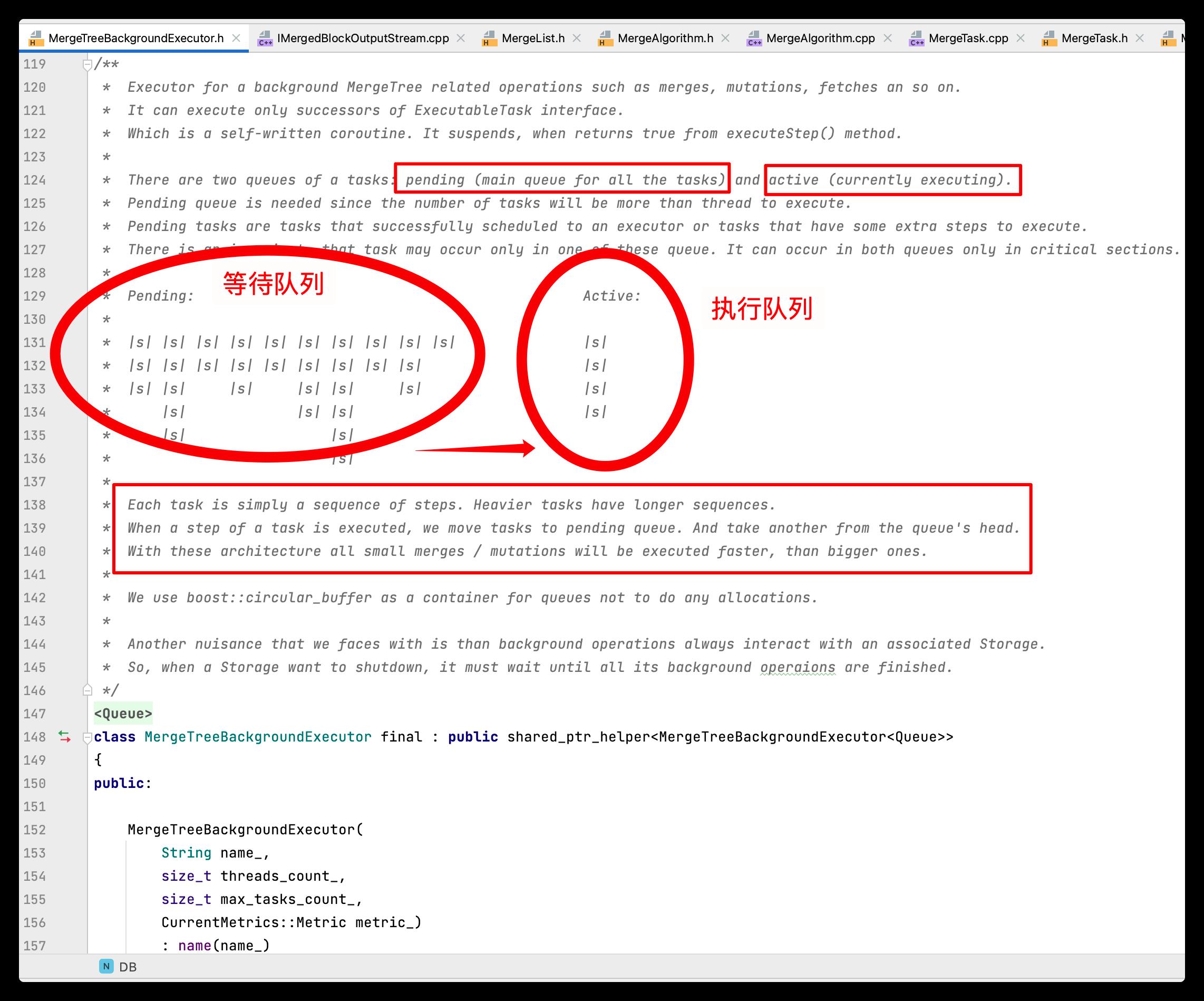
一个 MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor 任务有两个队列:Pending 挂起队列(所有任务的主队列)和 Active 活动队列(当前正在执行)。
Pending 挂起队列是需要的,因为任务的数量将超过线程执行。
MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor.h 代码:
#pragma once
#include <deque>
#include <functional>
#include <atomic>
#include <mutex>
#include <future>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <base/shared_ptr_helper.h>
#include <base/logger_useful.h>
#include <Common/ThreadPool.h>
#include <Common/Stopwatch.h>
#include <Storages/MergeTree/IExecutableTask.h>
namespace DB
namespace ErrorCodes
extern const int LOGICAL_ERROR;
struct TaskRuntimeData;
using TaskRuntimeDataPtr = std::shared_ptr<TaskRuntimeData>;
/**
* Has RAII class to determine how many tasks are waiting for the execution and executing at the moment.
* Also has some flags and primitives to wait for current task to be executed.
*/
struct TaskRuntimeData
TaskRuntimeData(ExecutableTaskPtr && task_, CurrentMetrics::Metric metric_)
: task(std::move(task_))
, increment(std::move(metric_))
ExecutableTaskPtr task;
CurrentMetrics::Increment increment;
std::atomic_bool is_currently_deletingfalse;
/// Actually autoreset=false is needed only for unit test
/// where multiple threads could remove tasks corresponding to the same storage
/// This scenario in not possible in reality.
Poco::Event is_done/*autoreset=*/false;
/// This is equal to task->getPriority() not to do useless virtual calls in comparator
UInt64 priority0;
/// By default priority queue will have max element at top
static bool comparePtrByPriority(const TaskRuntimeDataPtr & lhs, const TaskRuntimeDataPtr & rhs)
return lhs->priority > rhs->priority;
;
class OrdinaryRuntimeQueue
public:
TaskRuntimeDataPtr pop()
auto result = std::move(queue.front());
queue.pop_front();
return result;
void push(TaskRuntimeDataPtr item) queue.push_back(std::move(item));
void remove(StorageID id)
auto it = std::remove_if(queue.begin(), queue.end(),
[&] (auto item) -> bool return item->task->getStorageID() == id; );
queue.erase(it, queue.end());
void setCapacity(size_t count) queue.set_capacity(count);
bool empty() return queue.empty();
private:
boost::circular_buffer<TaskRuntimeDataPtr> queue0;
;
/// Uses a heap to pop a task with minimal priority
class MergeMutateRuntimeQueue
public:
TaskRuntimeDataPtr pop()
std::pop_heap(buffer.begin(), buffer.end(), TaskRuntimeData::comparePtrByPriority);
auto result = std::move(buffer.back());
buffer.pop_back();
return result;
void push(TaskRuntimeDataPtr item)
item->priority = item->task->getPriority();
buffer.push_back(std::move(item));
std::push_heap(buffer.begin(), buffer.end(), TaskRuntimeData::comparePtrByPriority);
void remove(StorageID id)
auto it = std::remove_if(buffer.begin(), buffer.end(),
[&] (auto item) -> bool return item->task->getStorageID() == id; );
buffer.erase(it, buffer.end());
std::make_heap(buffer.begin(), buffer.end(), TaskRuntimeData::comparePtrByPriority);
void setCapacity(size_t count) buffer.reserve(count);
bool empty() return buffer.empty();
private:
std::vector<TaskRuntimeDataPtr> buffer;
;
/**
* Executor for a background MergeTree related operations such as merges, mutations, fetches an so on.
* It can execute only successors of ExecutableTask interface.
* Which is a self-written coroutine. It suspends, when returns true from executeStep() method.
*
* There are two queues of a tasks: pending (main queue for all the tasks) and active (currently executing).
* Pending queue is needed since the number of tasks will be more than thread to execute.
* Pending tasks are tasks that successfully scheduled to an executor or tasks that have some extra steps to execute.
* There is an invariant, that task may occur only in one of these queue. It can occur in both queues only in critical sections.
*
* Pending: Active:
*
* |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s|
* |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s|
* |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s| |s|
* |s| |s| |s| |s|
* |s| |s|
* |s|
*
* Each task is simply a sequence of steps. Heavier tasks have longer sequences.
* When a step of a task is executed, we move tasks to pending queue. And take another from the queue's head.
* With these architecture all small merges / mutations will be executed faster, than bigger ones.
*
* We use boost::circular_buffer as a container for queues not to do any allocations.
*
* Another nuisance that we faces with is than background operations always interact with an associated Storage.
* So, when a Storage want to shutdown, it must wait until all its background operaions are finished.
*/
template <class Queue>
class MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor final : public shared_ptr_helper<MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>>
public:
MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor(
String name_,
size_t threads_count_,
size_t max_tasks_count_,
CurrentMetrics::Metric metric_)
: name(name_)
, threads_count(threads_count_)
, max_tasks_count(max_tasks_count_)
, metric(metric_)
if (max_tasks_count == 0)
throw Exception(ErrorCodes::LOGICAL_ERROR, "Task count for MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor must not be zero");
pending.setCapacity(max_tasks_count);
active.set_capacity(max_tasks_count);
pool.setMaxThreads(std::max(1UL, threads_count));
pool.setMaxFreeThreads(std::max(1UL, threads_count));
pool.setQueueSize(std::max(1UL, threads_count));
for (size_t number = 0; number < threads_count; ++number)
pool.scheduleOrThrowOnError([this] threadFunction(); );
~MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor()
wait();
bool trySchedule(ExecutableTaskPtr task);
void removeTasksCorrespondingToStorage(StorageID id);
void wait();
private:
String name;
size_t threads_count0;
size_t max_tasks_count0;
CurrentMetrics::Metric metric;
void routine(TaskRuntimeDataPtr item);
void threadFunction();
/// Initially it will be empty
Queue pending; // 等待队列
boost::circular_buffer<TaskRuntimeDataPtr> active0; // 执行队列
std::mutex mutex; // 互斥锁
std::condition_variable has_tasks;
std::atomic_bool shutdownfalse;
ThreadPool pool;
;
extern template class MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<MergeMutateRuntimeQueue>;
extern template class MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<OrdinaryRuntimeQueue>;
using MergeMutateBackgroundExecutor = MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<MergeMutateRuntimeQueue>;
using OrdinaryBackgroundExecutor = MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<OrdinaryRuntimeQueue>;
MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor.cpp 源代码:
#include <Storages/MergeTree/MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <Common/setThreadName.h>
#include <Storages/MergeTree/BackgroundJobsAssignee.h>
namespace DB
template <class Queue>
void MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>::wait() // 等待执行
std::lock_guard lock(mutex);
shutdown = true;
has_tasks.notify_all();
pool.wait();
template <class Queue>
// 调度任务执行
bool MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>::trySchedule(ExecutableTaskPtr task)
std::lock_guard lock(mutex); // 上锁
if (shutdown)
return false;
auto & value = CurrentMetrics::values[metric];
if (value.load() >= static_cast<int64_t>(max_tasks_count))
return false;
pending.push(std::make_shared<TaskRuntimeData>(std::move(task), metric));
has_tasks.notify_one();
return true;
template <class Queue>
void MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>::removeTasksCorrespondingToStorage(StorageID id)
std::vector<TaskRuntimeDataPtr> tasks_to_wait;
std::lock_guard lock(mutex); // 上锁
/// Erase storage related tasks from pending and select active tasks to wait for
pending.remove(id);
/// Copy items to wait for their completion
std::copy_if(active.begin(), active.end(), std::back_inserter(tasks_to_wait),
[&] (auto item) -> bool return item->task->getStorageID() == id; );
for (auto & item : tasks_to_wait)
item->is_currently_deleting = true;
/// Wait for each task to be executed
for (auto & item : tasks_to_wait)
item->is_done.wait();
item.reset();
template <class Queue>
void MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>::routine(TaskRuntimeDataPtr item)
DENY_ALLOCATIONS_IN_SCOPE;
/// All operations with queues are considered no to do any allocations
auto erase_from_active = [this, item]
active.erase(std::remove(active.begin(), active.end(), item), active.end());
;
bool need_execute_again = false;
try
ALLOW_ALLOCATIONS_IN_SCOPE;
need_execute_again = item->task->executeStep();
catch (...)
tryLogCurrentException(__PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
if (need_execute_again)
std::lock_guard guard(mutex); // 上锁
if (item->is_currently_deleting)
erase_from_active();
/// This is significant to order the destructors.
item->task.reset();
item->is_done.set();
item = nullptr;
return;
/// After the `guard` destruction `item` has to be in moved from state
/// Not to own the object it points to.
/// Otherwise the destruction of the task won't be ordered with the destruction of the
/// storage.
pending.push(std::move(item));
erase_from_active();
has_tasks.notify_one();
item = nullptr;
return;
std::lock_guard guard(mutex); // 上锁
erase_from_active();
has_tasks.notify_one();
try
ALLOW_ALLOCATIONS_IN_SCOPE;
/// In a situation of a lack of memory this method can throw an exception,
/// because it may interact somehow with BackgroundSchedulePool, which may allocate memory
/// But it is rather safe, because we have try...catch block here, and another one in ThreadPool.
item->task->onCompleted();
catch (...)
tryLogCurrentException(__PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
/// We have to call reset() under a lock, otherwise a race is possible.
/// Imagine, that task is finally completed (last execution returned false),
/// we removed the task from both queues, but still have pointer.
/// The thread that shutdowns storage will scan queues in order to find some tasks to wait for, but will find nothing.
/// So, the destructor of a task and the destructor of a storage will be executed concurrently.
item->task.reset();
item->is_done.set();
item = nullptr;
template <class Queue>
void MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<Queue>::threadFunction()
setThreadName(name.c_str());
DENY_ALLOCATIONS_IN_SCOPE;
while (true) // MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor 常驻线程池
try
TaskRuntimeDataPtr item;
std::unique_lock lock(mutex); // 上锁
has_tasks.wait(lock, [this]() return !pending.empty() || shutdown; );
if (shutdown)
break;
item = std::move(pending.pop());
active.push_back(item);
routine(std::move(item));
catch (...)
tryLogCurrentException(__PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
template class MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<MergeMutateRuntimeQueue>;
template class MergeTreeBackgroundExecutor<OrdinaryRuntimeQueue>;
附录:ClickHouse SQL 表达式语法
参考:ASTSelectQuery.h
#pragma once#include
#include
namespace DB
struct ASTTablesInSelectQueryElement;
struct StorageID;
/** SELECT query
*/
class ASTSelectQuery :public IAST
public:
enum class Expression : uint8_t
WITH,
SELECT,
TABLES,
PREWHERE,
WHERE,
GROUP_BY,
HAVING,
WINDOW,
ORDER_BY,
LIMIT_BY_OFFSET,
LIMIT_BY_LENGTH,
LIMIT_BY,
LIMIT_OFFSET,
LIMIT_LENGTH,
SETTINGS
;
static String expressionToString(Expression expr)
switch (expr)
case Expression::WITH:
return "WITH";
case Expression::SELECT:
return "SELECT";
case Expression::TABLES:
return "TABLES";
case Expression::PREWHERE:
return "PREWHERE";
case Expression::WHERE:
return "WHERE";
case Expression::GROUP_BY:
return "GROUP BY";
case Expression::HAVING:
return "HAVING";
case Expression::WINDOW:
return "WINDOW";
case Expression::ORDER_BY:
return "ORDER BY";
case Expression::LIMIT_BY_OFFSET:
return "LIMIT BY OFFSET";
case Expression::LIMIT_BY_LENGTH:
return "LIMIT BY LENGTH";
case Expression::LIMIT_BY:
return "LIMIT BY";
case Expression::LIMIT_OFFSET:
return "LIMIT OFFSET";
case Expression::LIMIT_LENGTH:
return "LIMIT LENGTH";
case Expression::SETTINGS:
return "SETTINGS";
return "";
/** Get the text that identifies this element. */
String getID(char)const override return "SelectQuery";
ASTPtr clone()const override;
bool distinct =false;
bool group_by_with_totals =false;
bool group_by_with_rollup =false;
bool group_by_with_cube =false;
bool group_by_with_constant_keys =false;
bool limit_with_ties =false;
ASTPtr & refSelect() return getExpression(Expression::SELECT);
ASTPtr & refTables() return getExpression(Expression::TABLES);
ASTPtr & refPrewhere() return getExpression(Expression::PREWHERE);
ASTPtr & refWhere() return getExpression(Expression::WHERE);
ASTPtr & refHaving() return getExpression(Expression::HAVING);
const ASTPtr with()const return getExpression(Expression::WITH);
const ASTPtr select()const return getExpression(Expression::SELECT);
const ASTPtr tables()const return getExpression(Expression::TABLES);
const ASTPtr prewhere()const return getExpression(Expression::PREWHERE);
const ASTPtr where()const return getExpression(Expression::WHERE);
const ASTPtr groupBy()const return getExpression(Expression::GROUP_BY);
const ASTPtr having()const return getExpression(Expression::HAVING);
const ASTPtr window()const return getExpression(Expression::WINDOW);
const ASTPtr orderBy()const return getExpression(Expression::ORDER_BY);
const ASTPtr limitByOffset()const return getExpression(Expression::LIMIT_BY_OFFSET);
const ASTPtr limitByLength()const return getExpression(Expression::LIMIT_BY_LENGTH);
const ASTPtr limitBy()const return getExpression(Expression::LIMIT_BY);
const ASTPtr limitOffset()const return getExpression(Expression::LIMIT_OFFSET);
const ASTPtr limitLength()const return getExpression(Expression::LIMIT_LENGTH);
const ASTPtr settings()const return getExpression(Expression::SETTINGS);
bool hasFiltration()const return where() || prewhere() || having();
/// Set/Reset/Remove expression.
void setExpression(Expression expr, ASTPtr && ast);
ASTPtr getExpression(Expression expr,bool clone =false)const
auto it = positions.find(expr);
if (it != positions.end())
return clone ? children[it->second]->clone() : children[it->second];
return ;
/// Compatibility with old parser of tables list. TODO remove
ASTPtr sampleSize()const;
ASTPtr sampleOffset()const;
std::pair arrayJoinExpressionList()const;
const ASTTablesInSelectQueryElement * join()const;
bool final()const;
bool withFill()const;
void replaceDatabaseAndTable(const String & database_name,const String & table_name);
void replaceDatabaseAndTable(const StorageID & table_id);
void addTableFunction(ASTPtr & table_function_ptr);
void updateTreeHashImpl(SipHash & hash_state)const override;
void setFinal();
const char * getQueryKindString()const override return "Select";
protected:
void formatImpl(const FormatSettings & settings, FormatState & state, FormatStateStacked frame)const override;
private:
std::unordered_mappositions;
ASTPtr & getExpression(Expression expr);
;
参考资料
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1604965
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361622782
https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/
以上是关于ClickHouse为什么这么快?MergeTree 表存储引擎图文实例详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章