数据结构——双向链表循环链表
Posted 龍弟-idea
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构——双向链表循环链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
双向链表,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。
双链表的实现
结点API设计
| 类名 | Node |
| 构造方法 | Node(T t,Node pre,Node next) |
| 成员变量 | T item :存储数据 Node pre:指向上一个结点 Node next:指向下一个结点 |
双向链表API设计
| 类名 | LoopLinkList |
| 构造方法 | LoopLinkList():创建对象 |
| 成员方法 | 1.public void clear():清空线性表 2.public boolean isEmpty():判断线性表是否为空 3.public int length():获取线性表中元素的个数 4.public T get(int i)获取第i个元素的值 5.public void insert(T t):在线性表中添加一个元素 6.public void insert(int i,T t):在第i个元素之前插入一个值为t的元素 7.public T remove(int i):删除第i个数据元素 8.public int indexOf(T t):返回线性表中首次出现该元素的索引值 10.public T getLast():获取最后一个元素 |
| 成员内部类 | private class Node:结点类 |
| 成员变量 | 1.private Node first:记录首结点 2.private Node last:记录尾结点 3.private int N:记录链表的长度 |
public class LoopLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>
public static void main(String[] args)
// 创建双向链表对象
LoopLinkList<String> sl= new LoopLinkList<>();
// 测试插入
sl.insert("龍弟");
sl.insert("龍龍");
sl.insert("龍哥");
sl.insert(1,"龍帝");
for(String s: sl)
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("-----------------");
// 测试获取
String getResult = sl.get(1);
System.out.println("获取索引1处的结果为:"+getResult);
// 测试删除
String removeResult = sl.remove(0);
System.out.println("删除的元素:" + removeResult);
System.out.println("---------------------");
System.out.println("第一个元素是"+sl.getFirst());
System.out.println("最后一个元素是:" + sl.getLast());
// 测试清空
sl.clear();
System.out.println("清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:"+sl.length());
//首结点
private Node head;
// 最后一个结点
private Node last;
//链表的长度
private int N;
// 结点类
private class Node
public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next)
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
//存储数据
public T item;
// 指向上一个结点
public Node pre;
// 指向下一个结点
public Node next;
public LoopLinkList()
//初始化头节点和尾结点
this.head = new Node(null, null, null);
this.last = null;
// 初始化元素结点
this.N = 0;
// 清空链表
public void clear()
this.head.next = null;
this.head.item = null;
this.last = null;
this.N = 0;
// 获取链表长度
public int length()
return N;
// 判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
return N == 0;
// 获取第一个元素
public T getFirst()
if (isEmpty())
return null;
return head.next.item;
// 获取最后一个元素
public T getLast()
if (isEmpty())
return null;
return last.item;
// 插入元素t
public void insert(T t)
// 如果链表为空
if (isEmpty())
// 创建新的节点
Node newNode = new Node(t, head, null);
// 让新结点成为尾结点
last = newNode;
// 让头结点指向尾结点
head.next = last;
else
// 如果链表不为空
Node oldLast = last;
// 创建新的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, oldLast, null);
// 让当前的尾节点 指向新结点
oldLast.next = newNode;
// 让新结点成为尾结点
last = newNode;
N++;
//向指定位置i处插入元素t
public void insert(int i, T t)
//找到位置i的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++ )
pre = pre.next;
//当前结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//构建新节点
Node newNode = new Node(t, pre, curr);
pre.next = newNode;
curr.pre = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
// 获取指定位i处的元素
public T get(int i)
Node n = head.next;
for(int index = 0; index < i; index++)
n = n.next;
return n.item;
// 找到元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t)
Node n = head;
for(int index = 0; index<N; index++)
n = n.next;
if(n.next.equals(t))
return index;
return -1;
// 删除位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i)
//寻找i位置的前一个元素
Node pre = head;
for(int index = 0; index < i; index++)
pre = pre.next;
//i位置的元素
Node curr = pre.next;
//i位置的下一个元素
Node nextNode = curr.next;
pre.next = nextNode;
nextNode.pre = pre;
// 长度减一
N--;
return curr.item;
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator()
return new TIterator();
private class TIterator implements Iterator
private Node n;
public TIterator()
this.n = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext()
return n.next != null;
@Override
public Object next()
n = n.next;
return n.item;
java中LinkedList实现
java中LinkedList集合也是使用双向链表实现,并提供了增删改查等相关方法
1.底层是否用双向链表实现;
2.结点类是否有三个域
链表的复杂度分析
get(int i):每一次查询,都需要从链表的头部开始,依次向后查找,随着数据元素N的增多,比较的元素越多,时间复杂度为O(n)
insert(int i,T t);每一次插入,需要先找到i位置的前一个元素,然后完成插入操作,随着数据元素N的增多,查找的元素越多,时间复杂度为O(n);
remove(int i):每一次移除,需要先找到i位置的前一个元素,然后完成插入操作,随着数据元素N的增多,查找的元素越多,时间复杂度为O(n)
相比较顺序表,链表插入和删除的时间复杂度虽然一样,但仍然有很大的优势,因为链表的物理地址是不连续的,它不需要预先指定存储空间大小,或者在存储过程中涉及到扩容等操作..同时它并没有涉及的元素的交换。
相比较顺序表,链表的查询操作性能会比较低。因此,如果我们的程序中查询操作比较多,建议使用顺序表;增删操作比较多,建议使用链表。
循环链表
循环链表,也就是链表整体要形成一个圆环状。在单向链表中,最后一个节点的指针为null ,不指向任何结点,因为没有下一个元素了。要实现循环链表,我们只需要让单向链表的最后一个节点的指针指向头结点即可。
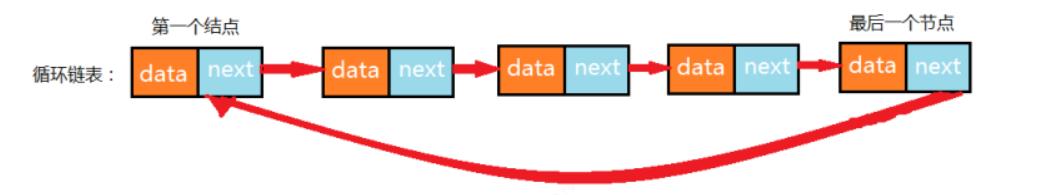
public static void main(String[] args)
//构建结点
Node<Integer> first=new Node<Integer>(5,null);
Node<Integer> second=new Node<Integer>(6,null);
Node<Integer> third=new Node<Integer>(7,null);
Node<Integer> fourth=new Node<Integer>(7,null);
Node<Integer> fifth=new Node<Integer>(7,null);
//生成单链表
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
third.next=fourth;
fourth.next=fifth;
//构成循环链表,让最后一个结点指向第一个结点
fifth.next=first;
以上是关于数据结构——双向链表循环链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章