嵌入式linux应用开发之常用shell脚本总结
Posted 特立独行的猫a
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了嵌入式linux应用开发之常用shell脚本总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
总结下日常工作中常用的linux下的shell脚本。
linux的shell脚本很强大,可以用来做一些特殊功能。shell脚本语法虽然很简单,但是有时候把经常忘,还得再写一遍且验证ok才能用,这里总结下留作备忘。
关于shell脚本的学习觉得不需要太刻意,根据需要来。看的多用的多了自然就会了,至少能看懂吧。
目录
启用硬件IO口
enGPIO.sh
#!/bin/sh
mygpioPath1="/sys/class/gpio/gpio115"
mygpioPath2="/sys/class/gpio/gpio116"
buzzGPIO="/sys/class/gpio/gpio15"
qrd_pwr="/sys/class/gpio/gpio121"
power_down="/sys/class/gpio/gpio128"
touch_key="/sys/class/gpio/gpio112"
oth_pwr="/sys/class/gpio/gpio130"
echo "shell exec open..."
#enable voice
if [ ! -d "$mygpioPath1" ]; then
echo 115 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$mygpioPath1" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio115/direction"
echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio115/value"
fi
#enable voice
#if [ ! -d "$mygpioPath2" ]; then
# echo 116 > /sys/class/gpio/export
#fi
#if [ -d "$mygpioPath2" ]; then
# echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio116/direction"
# echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio116/value"
#fi
#enable buzzse
if [ ! -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo 15 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/direction"
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
fi
if [ ! -d "$qrd_pwr" ]; then
echo 121 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$qrd_pwr" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio121/direction"
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio121/value"
fi
#enable power down check
if [ ! -d "$power_down" ]; then
echo 128 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$power_down" ]; then
echo "in" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio128/direction"
fi
#enable touch key check
if [ ! -d "$touch_key" ]; then
echo 112 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$touch_key" ]; then
echo "in" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio112/direction"
fi
#enable oth_pwr
if [ ! -d "$oth_pwr" ]; then
echo 130 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$qrd_pwr" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio130/direction"
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio130/value"
fi开机后应用启动其它应用服务
int main(int argc, char ** argv)
printf("main\\n");
system("../opt/enGPIO.sh");
system("killall -9 monitor");
//启动监控服务monitor进程
system("../opt/startmonitor.sh");
startmonitor.sh
#!/bin/bash
fileName="/app/city_app/opt/monitor"
buzzGPIO="/sys/class/gpio/gpio15"
#enable buzzse for notifying success
function beep_notify()
if [ ! -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo 15 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/direction"
echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
sleep 1
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
fi
function CheckProcess()
PROCESS_NUM=`ps | grep "$1" | grep -v "grep" | wc -l`
return $PROCESS_NUM
if [ ! -f $fileName ]; then
echo "error!monitor exe not exit!"
exit 1
else
echo "find monitor exe,begin start..."
CheckProcess monitor
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "no monitor progress find!"
else
echo "find monitor,..."
killall -9 monitor
sleep 1
fi
cd /app/city_app/opt/
./monitor &
echo "start ok"
beep_notify
exit 0
fi
触发执行其它应用
如uplog.sh,触发ftp应用上传日志文件
#!/bin/sh
echo "upload log to ftp server..."
echo $1
if [ -z $1 ]; then
today=`date +"%Y%m%d"`
else
today=$1
fi
echo $today
function getfname()
echo $1
filename=$(find /log/ -name "$1")
echo $filename
return 0
#filename="find ./ -name "*$today.log""
#echo $filename
getfname *$today.log
echo $filename
../opt/ftp -ftpcfg=/../opt/ftpcfg.ini -fname=$filename
拷贝U盘中的文件到设备中
setconfig.sh,把U盘根目录下的config.ini文件拷贝到设置的指定目录下。
#!/bin/bash
usbPath="/media/usb"
fileName="/media/usb/config_up.ini"
buzzGPIO="/sys/class/gpio/gpio15"
#enable buzzse for notifying success
function beep_notify()
if [ ! -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo 15 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/direction"
echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
sleep 1
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
fi
setconfig()
echo "find usb device,begin copy config_ini..."
if [ ! -f $fileName ]; then
echo "config file not exit!"
return 1
else
cp $fileName /app/city_app/etc/
return 0
fi
if [ -d "$usbPath" ]; then
setconfig
if [ $? -ne 0 ] ;then
echo "faild to set config"
exit 1
fi
beep_notify
beep_notify
beep_notify
echo "set ok"
exit 0
else
echo "no usb device found!"
exit 1
fi
拷贝U盘数据
#!/bin/bash
usbPath="/media/usb"
fileName="/media/usb/qrlinux"
dbName="/app/city_app/opt/bus.db"
buzzGPIO="/sys/class/gpio/gpio15"
#enable buzzse for notifying success
function beep_notify()
if [ ! -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo 15 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/direction"
echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
sleep 1
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
fi
function CheckProcess()
PROCESS_NUM=`ps | grep "$1" | grep -v "grep" | wc -l`
return $PROCESS_NUM
copydata()
echo "find usb device,begin copy data..."
if [ ! -f $dbName ]; then
echo "db file not exit!"
return 1
else
cp -v /app/city_app/opt/bus.db /media/usb/
cd /media/usb/
ls -l
return 0
fi
if [ -d "$usbPath" ]; then
copydata
if [ $? -ne 0 ] ;then
echo "faild to copy data"
fi
else
echo "no usb device found!"
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -f $fileName ]; then
echo "qrlinux file not exit!"
else
echo "find qrlinux file,begin updata..."
CheckProcess qrlinux
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "no qrlinux progress find!"
else
echo "find qrlinux,..."
killall -9 qrlinux
sleep 2
fi
cp -v $fileName /app/city_app/opt/
cd /app/city_app/opt/
ls -l
echo "cp ok"
umount /media/usb/
beep_notify
exit 0
fi
Linux应用开机自启动
/etc/init.d/文件夹下放置有很多常用服务的控制脚本和其他的一些脚本。
K开头的脚本文件代表运行级别加载时需要关闭的,S开头的代表需要执行。
因此当我们需要开机启动自己的脚本时,只需要将可执行脚本丢在/etc/init.d目录下,然后在/etc/rc.d/rc*.d中建立软链接即可。如:
[root@localhost ~]# ln -s /etc/init.d/sshd /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S100ssh
sshd是具体服务的脚本文件,S100ssh是其软链接,S开头代表加载时自启动
如果需要在多个运行级别下设置自启动,则需建立多个软链接。
Linux的引导过程
系统启动之后,在进入init.d之前,我们先来看看系统都做了什么工作。系统加电之后,首先进行的硬件自检,然后是bootload对系统的初始化,加载内核。
内核被加载到内存之后,就开始执行了。一旦内核启动运行,对硬件的检测就会决定需要对哪些设备驱动进行初始化。
从这开始内核就能够挂装根文件系统。内核挂装了根文件系统,并已初始化所有的设备驱动程序和数据结构等之后,就通过启动一个叫init的用户级程序,完成引导进程。
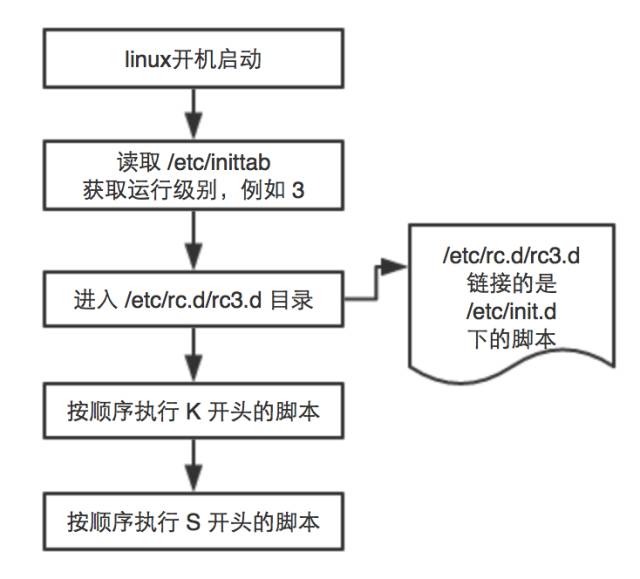
Init进程是系统启动之后的第一个用户进程,所以它的pid(进程编号)始终为1。init进程上来首先做的事是去读取/etc/目录下inittab文件中initdefault id值,这个值称为运行级别(run-level)。它决定了系统启动之后运行于什么级别。运行级别决定了系统启动的绝大部分行为和目的。
这个级别从0到6 ,具有不同的功能。不同的运行级定义如下:
0 – 停机(千万别把initdefault设置为0,否则系统永远无法启动)
1 – 单用户模式,root权限,用于系统维护,禁止远程登陆
2 – 多用户状态,没有 NFS
3 – 标准多用户模式,登陆后进入命令行模式
4 – 系统未使用,保留
5 – 多用户图形模式,登陆后进入图形GUI模式
6 – 重新启动(千万不要把initdefault 设置为6,否则将一直在重启 )
服务器一般都是命令行模式,所以默认运行级别为 3
如何添加自启程序?
(1)/etc/init.d 目录中添加
以启动SVN为例
1)在 /etc/init.d 目录下创建启动服务的脚本
vim /etc/init.d/svn
#!/bin/bash
svnserve -d -r /svn仓库路径
设置执行权限
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/svn
2)把这个脚本软链接到 /etc/rc.d/rc3.d
ln -s /etc/init.d/svn /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S101svn
S 代表是要执行这个脚本,101 是执行顺序,通常要大于60,这样可以保证基础服务都已经启动完成
重启linux测试
(2)/etc/rc.local 文件中添加
直接修改 /etc/rc.local
该脚本是在系统初始化级别脚本运行之后再执行的,因此可以在里面添加想在系统启动之后执行的脚本
(3)chkconfig 命令添加
如何禁止自启程序?
(1)直接删除 /etc/rc.d/rcN.d 目录的目标链接文件
(2)删除 /etc/rc.local 文件中定义的启动脚本
(3)查看自启动服务列表,从中选择目标服务执行禁止操作
chkconfig –list
chkconfig –del 服务名
init.d里面放的都是什么东西。这个目录存放的是一些脚本,一般是linux以rpm包安装时设定的一些服务的启动脚本。系统在安装时装了好多rpm包,这里面就有很多对应的脚本。执行这些脚本可以用来启动,停止,重启这些服务。
前面说到,/etc/rc.d/init.d这个目录下的脚本就类似与windows中的注册表,在系统启动的时候执行。程序运行到这里(init进程读取了运行级别),该行/etc/rc.d/init.d里面的脚本,但是并不是直接运行,而是有选择的因为系统并不需要启动所有的服务。
系统是如何选择哪些需要启动哪些不需要启动?运行级别就起作用了。在决定了系统启动的run level之后,/etc/rc.d/rc这个脚本先执行。在有些linux源码中它都是一上来就check_runlevel(),知道了运行级别之后,对于每一个运行级别,在rc.d下都有一个子目录分别是rc0.d,rc1.d ….. rc6.d。每个目录下都是到init.d目录的一部分脚本一些链接。每个级别要执行哪些服务就在相对应的目录下,比如级别5要启动的服务就都放在rc5.d下,但是放在这个rc5.d下的都是一些链接文件,链接到init.d中相对应的文件,真正干活到init.d里的脚本。
/etc/init.d里面还放置了一些脚本可以用来管理服务用。比如:
可以使用start,stop,restart选项。例如,如果你想关闭网络,你可以使用如下形式的命令:
/etc/init.d/networking stop
又比如,你改变了网络设置,并且需要重启网络。你可以使用如下命令:
/etc/init.d/networking restart
rc.local也是经常使用的一个脚本。该脚本是在系统初始化级别脚本运行之后再执行的,因此可以安全地在里面添加你想在系统启动之后执行的脚本。
rc和rcS脚本
#!/bin/sh
#
# rc This file is responsible for starting/stopping
# services when the runlevel changes.
#
# Optimization feature:
# A startup script is _not_ run when the service was
# running in the previous runlevel and it wasn't stopped
# in the runlevel transition (most Debian services don't
# have K?? links in rc1,2,3,4,5 )
#
# Author: Miquel van Smoorenburg <miquels@cistron.nl>
# Bruce Perens <Bruce@Pixar.com>
#
# Version: @(#)rc 2.78 07-Nov-1999 miquels@cistron.nl
#
. /etc/default/rcS
export VERBOSE
startup_progress()
step=$(($step + $step_change))
if [ "$num_steps" != "0" ]; then
progress=$((($step * $progress_size / $num_steps) + $first_step))
else
progress=$progress_size
fi
#echo "PROGRESS is $progress $runlevel $first_step + ($step of $num_steps) $step_change $progress_size"
if type psplash-write >/dev/null 2>&1; then
TMPDIR=/mnt/.psplash psplash-write "PROGRESS $progress" || true
fi
#if [ -e /mnt/.psplash/psplash_fifo ]; then
# echo "PROGRESS $progress" > /mnt/.psplash/psplash_fifo
#fi
#
# Start script or program.
#
startup()
# Handle verbosity
[ "$VERBOSE" = very ] && echo "INIT: Running $@..."
case "$1" in
*.sh)
# Source shell script for speed.
(
trap - INT QUIT TSTP
scriptname=$1
shift
. $scriptname
)
;;
*)
"$@"
;;
esac
startup_progress
# Ignore CTRL-C only in this shell, so we can interrupt subprocesses.
trap ":" INT QUIT TSTP
# Set onlcr to avoid staircase effect.
stty onlcr 0>&1
# Limit stack size for startup scripts
[ "$STACK_SIZE" == "" ] || ulimit -S -s $STACK_SIZE
# Now find out what the current and what the previous runlevel are.
runlevel=$RUNLEVEL
# Get first argument. Set new runlevel to this argument.
[ "$1" != "" ] && runlevel=$1
if [ "$runlevel" = "" ]
then
echo "Usage: $0 <runlevel>" >&2
exit 1
fi
previous=$PREVLEVEL
[ "$previous" = "" ] && previous=N
export runlevel previous
# Is there an rc directory for this new runlevel?
if [ -d /etc/rc$runlevel.d ]
then
# Find out where in the progress bar the initramfs got to.
PROGRESS_STATE=0
#if [ -f /dev/.initramfs/progress_state ]; then
# . /dev/.initramfs/progress_state
#fi
# Split the remaining portion of the progress bar into thirds
progress_size=$(((100 - $PROGRESS_STATE) / 3))
case "$runlevel" in
0|6)
# Count down from -100 to 0 and use the entire bar
first_step=-100
progress_size=100
step_change=1
;;
S)
# Begin where the initramfs left off and use 2/3
# of the remaining space
first_step=$PROGRESS_STATE
progress_size=$(($progress_size * 2))
step_change=1
;;
*)
# Begin where rcS left off and use the final 1/3 of
# the space (by leaving progress_size unchanged)
first_step=$(($progress_size * 2 + $PROGRESS_STATE))
step_change=1
;;
esac
num_steps=0
for s in /etc/rc$runlevel.d/[SK]*; do
case "$s##/etc/rc$runlevel.d/S??" in
gdm|xdm|kdm|reboot|halt)
break
;;
esac
num_steps=$(($num_steps + 1))
done
step=0
# First, run the KILL scripts.
if [ $previous != N ]
then
for i in /etc/rc$runlevel.d/K[0-9][0-9]*
do
# Check if the script is there.
[ ! -f $i ] && continue
# Stop the service.
startup $i stop
done
fi
# Now run the START scripts for this runlevel.
for i in /etc/rc$runlevel.d/S*
do
[ ! -f $i ] && continue
if [ $previous != N ] && [ $previous != S ]
then
#
# Find start script in previous runlevel and
# stop script in this runlevel.
#
suffix=$i#/etc/rc$runlevel.d/S[0-9][0-9]
stop=/etc/rc$runlevel.d/K[0-9][0-9]$suffix
previous_start=/etc/rc$previous.d/S[0-9][0-9]$suffix
#
# If there is a start script in the previous level
# and _no_ stop script in this level, we don't
# have to re-start the service.
#
[ -f $previous_start ] && [ ! -f $stop ] && continue
fi
case "$runlevel" in
0|6)
startup $i stop
;;
*)
startup $i start
;;
esac
done
fi
#!/bin/bash
#myapp application start mechnism
#manu run myapp
#set -e
curdir=$(pwd)
myapp_city_app_name=city_app
#search executable file in bin directory
#and start the file.
#the file number must be only one!!!!
function searchBinAndRun()
# echo "searchBinAndRun...enter"
path=$1
cd $path
if [ ! -d bin ];
then
echo "no bin directory ..."
return 1
fi
cd bin
files=$(ls $path/bin)
echo "path= $path"
for filename in $files
do
echo $filename
if [ ! -d $filename ];
then
chmod 777 $filename
#./$filename &
./$filename
return 0
fi
done
return 1
#set env variable for application
function setAppEnv()
# echo "setAppEnv...enter"
path=$1
echo "path= $path"
if [ -d lib ];
then
cd lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$(pwd)
#echo "LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
fi
#start myapp specified application
#after opkg the app ipk
function startmyappApp()
echo "startmyappApp...start"
if [ $# -lt 1 ] ;
then
echo "para is not enough!!,quit"
return 1
fi
appname=$1
cd /app
#echo "---->$appname"
if [ -d $appname ];
then
cd $appname
#echo "pwd = $(pwd)"
setAppEnv /app/$appname
if searchBinAndRun /app/$appname ;
then
echo "$appname starts success"
return 0
else
echo "$appname starts error"
return 1
fi
else
echo "$appname dir isnot exist!!"
return 1
fi
#
###myapp start main
#
#######try to start myapp customersized app########
####monitor myapp-app,may be restarted!!############
echo "2--->try to start customersized app....."
startmyappApp $myapp_city_app_name
exit 0
简化常用指令操作,写个脚本
比如设置环境变量和scp往机器中拷贝文件,整个脚本简化下操作,省得重复敲不少命令
#!/bin/bash
source /opt/myir-imx-fb-qt5/4.1.15-2.0.1/environment-setup-cortexa7hf-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi
scp myapp root@192.168.79.1:/app/my_app/bin或者是启动应用,手动执行可能还得进入某个目录或设置环境变量,写一个脚本搞定:
run_app.sh
#!/bin/bash
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/app/city_app/lib/
echo $LD_LIBRARY_PATH
cd /app/city_app/bin/
./b503_app
查找应用并设置应用的环境变量并运行
run_app.sh
应用升级脚本
start_remoteupdate.sh
#!/bin/bash
singelName="remoteupdate"
fileName="/usr/bin/remoteupdate"
configFile="/app/update.conf"
function CheckProcess()
PROCESS_NUM=`ps | grep "$1" | grep -v "grep" | wc -l`
return $PROCESS_NUM
function startProcess()
echo "check process run status"
CheckProcess $singelName
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "progress is not run"
else
echo "process is running"
#killall -9 $singelName
#sleep 1
exit 0
fi
echo "start remoteupdate ..."
$singelName &
echo "start end"
#copy config file
if [ -f $configFile ];then
echo "config file exist"
else
echo "copy update.conf file"
cp /app/city_app/opt/update.conf /app/
sync
if [ -f $configFile ];then
echo "copy ok"
fi
fi
#start process remoteupdate
if [ ! -f $fileName ];then
echo "copy remoteupdate process to /usr/bin"
cp /app/city_app/opt/$singelName /usr/bin/
sync
if [ -f $fileName ];then
echo "copy ok"
startProcess
exit 0
else
echo "copy fail"
exit 1
fi
else
echo "remoteupdate file exsit"
startProcess
exit 0
fi
应用监控和升级服务脚本
app_monitor.sh
#!/bin/bash
#######city app monitor deamon ########
function checkAppRun()
flag=0
val=0
cnt=0
max=$2
#echo "checkApprun...$1"
while [ $val -lt $max ]
do
cnt=$(ps | grep $1 | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -le 1 ];
then
let flag+=1
sleep 1
let val+=1
else
break
fi
done
if [ $flag -ge $max ];
then
return 0
#$1 app is not running
else
return 1
#$1 app has been run
fi
function CheckProcess()
PROCESS_NUM=`ps | grep "$1" | grep -v "grep" | wc -l`
return $PROCESS_NUM
function monitor_app()
while true
do
CheckProcess b503_app
if [ $? -ne 1 ] ;
then
if [ $? -ne 0 ];
then
killall -9 b503_app
fi
source /etc/init.d/app_update_b503_app.sh
fi
# CheckProcess remoteupdate
# if [ $? -ne 1 ] ;
# then
# if [ $? -ne 0 ];
# then
# killall -9 remoteupdate
# fi
# source /etc/init.d/app_start_remoteupdate.sh
# fi
done
function monitor_b503_ft()
while true
do
CheckProcess b503_ft
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;
then
break
else
sleep 1
fi
done
function monitor_ft_app()
while true
do
checkAppRun b503_ft 2
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;
then
break
fi
done
################main#####################
####synchronize date and rtc time#######
#date
#hwclock -w --local
########################################
source /etc/init.d/app_update_b503_ft.sh
#monitor_ft_app &
checkAppRun b503_ft 2
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;
then
source /etc/init.d/app_update_b503_app.sh
monitor_app &
else
monitor_b503_ft
source /etc/init.d/app_update_b503_app.sh
monitor_app &
fi
应用ipk包安装脚本
#!/bin/bash
#b503 application update mechnism
#search directory in order, /update,/media/usb/
#set -e
buzzGPIO="/sys/class/gpio/gpio15"
curdir=$(pwd)
#b503_city_app_name=city_app
#enable buzzse for notifying success
function beep_notify()
if [ ! -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo 15 > /sys/class/gpio/export
fi
if [ -d "$buzzGPIO" ]; then
echo "out" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/direction"
echo "1" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
sleep 1
echo "0" > "/sys/class/gpio/gpio15/value"
fi
#install all ipks in specified directory
function install_ipks()
path=$1
files=$(ls $path)
for filename in $files
do
if [ "$filename##*."x = "ipk"x ];
then
echo $filename
cd $path
opkg install --force-reinstall --force-downgrade --force-overwrite $filename
# sleep 1
fi
done
#check and create directory by specified path
function check_and_mkdir()
result_path=$1
result_name=$2
cd $result_path
# echo "$result_path"
if [ ! -d $result_name ];
then
#echo "mkdir $result_name"
mkdir -p $result_name
#else
# echo "$result_name is exit!!"
fi
#check if updating from update directory
function isUpdateIpkFromUpdir()
#echo "1--->search update ipk directory."
cd /update
#cnt=$(find -name "*.ipk" | wc -l)
if [ -d ipk ];
then
cnt=$(ls ipk | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ] ;
then
echo "1.1--->check update flag !"
cnt=$(find -name "update.txt" | wc -l )
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ];
then
var=$(cat update.txt)
if [[ $var -eq 1 ]];
then
echo "1.2--->update-flag is 1!"
return 0
else
echo "1.3--->update flag is 0"
return 1
fi
else
echo "1.8--->no update.txt.."
return 1
fi
else
echo "1.9--->there is no ipk files in update directory!"
return 1
fi
fi
return 1
#check if updating bin from update directory
function isUpdateBinFromUpdir()
#echo "1--->search update bin directory."
cd /update
if [ -d bin ];
then
cnt=$(ls bin | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ] ;
then
cnt=$(find -name "update.txt" | wc -l )
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ];
then
var=$(cat update.txt)
if [[ $var -eq 2 ]];
then
return 0
else
return 1
fi
else
return 1
fi
fi
fi
return 1
#check if updating lib from update directory
function isUpdateLibFromUpdir()
#echo "1--->search update lib directory."
cd /update i
if [ -d lib ];
then
cnt=$(ls lib | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ] ;
then
cnt=$(find -name "update.txt" | wc -l )
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ];
then
var=$(cat update.txt)
if [[ $var -eq 3 ]];
then
return 0
else
return 1
fi
else
return 1
fi
fi
fi
return 1
#check if updating audio from update directory
function isUpdateAudioFromUpdir()
#echo "1--->search update audio directory."
cd /update
if [ -d audio ];
then
cnt=$(ls audio | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ] ;
then
cnt=$(find -name "update.txt" | wc -l )
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ];
then
var=$(cat update.txt)
if [[ $var -eq 4 ]];
then
return 0
else
return 1
fi
else
return 1
fi
fi
fi
return 1
#check if updating form udisk
function isUpdateFromUdisk()
#echo "2--->search u disk directory."
cd /media
cnt=$(find -name "usb" | wc -l )
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ];
then
cd /media/usb
cnt=$(find -name "*.ipk" | wc -l)
if [ $cnt -ge 1 ] ;
then
echo "2.1--->udisk,find ipk files"
return 0
else
echo "2.2--->udisk,no b503-app.ipk......"
return 1
fi
else
#echo "2.9:no udisk is inserted......."
return 1
fi
服务管理,启动或停止服务
service.sh
#!/usr/bin/env sh
export ALIPAY_ROOT=$(cd `dirname $0`; cd ../../; pwd)
# define the global value
pid=
start_service()
cd $ALIPAY_ROOT/iotsdk/bin
nohup ./alipay_iotd >/dev/null 2>&1 &
PS_LINE=`ps |grep alipay_iotd|grep -v grep`
if [ ! -z "$PS_LINE" ]; then
#pids=($PS_LINE// / )
pid=`echo $PS_LINE | cut -d ' ' -f 1`
#pid=$pids[0]
echo "snapshot pid is $pid"
fi
case $1 in
"keepalive")
if [ -z "$pid" ]; then
start_service
fi
;;
"startup")
if [ -z "$pid" ]; then
start_service
else
echo "Service was already started!"
fi
;;
"shutdown")
if [ -n "$pid" ]; then
kill -9 "$pid"
echo "Service was terminated!"
fi
;;
"restart")
if [ -n "$pid" ]; then
echo "Stop service..."
kill -9 "$pid"
echo "Service was terminated!"
fi
sleep 3
start_service
;;
"status")
echo "Service is running on proc: $pid"
;;
*)
echo "Unsupported command!"
;;
esac统一改写目录下的文件属性
#!/bin/bash
#查找当前目录下(递归级数1)的所有目录文件
SRC_DIR=$(find ./ -maxdepth 1 -type d)
#变量SRC_DIR可以用$引用,可以$直接引用,但不可以用$()引用
echo $SRC_DIR
#将当前目录下所有一级目录文件的Other写属性去掉
chmod o-w $SRC_DIR
自动下载并构建freetype脚本
#!/bin/bash
set -x
set -o errexit -o nounset
# 22.0.16 is the libtool version of 2.9.0
if pkg-config --atleast-version 22.0.16 freetype2; then exit; fi
pushd $HOME
wget http://download.savannah.gnu.org/releases/freetype/freetype-2.9.tar.bz2
tar xf freetype-2.9.tar.bz2
pushd freetype-2.9
./autogen.sh
./configure --prefix=$HOME/.local
make -j4 install
popd
popd
首次安装脚本install.sh
#!/usr/bin/env sh
#SOURCE_DIR=`pwd`
SOURCE_DIR=/app/city_app/alipay
TARGET_DIR=/app/alipay
if [ ! -d $TARGET_DIR ]; then
mkdir $TARGET_DIR
fi
if [ ! -d $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk ]; then
mkdir $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk
fi
if [ ! -d $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin ]; then
mkdir $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin
fi
if [ ! -d $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/conf ]; then
mkdir $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/conf
fi
if [ ! -d $TARGET_DIR/runtime ]; then
mkdir $TARGET_DIR/runtime
fi
if [ -e $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/alipay_iotd ]; then
cp $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/alipay_iotd $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin
fi
if [ -e $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/alipay_iotmd ]; then
cp $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/alipay_iotmd $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin
fi
if [ -e $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/monitor.sh ]; then
cp $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/monitor.sh $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin
fi
if [ -e $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/service.sh ]; then
cp $SOURCE_DIR/iotsdk/bin/service.sh $TARGET_DIR/iotsdk/bin
fiautogen.sh
#!/bin/sh
# Run this to generate all the initial makefiles, etc.
test -n "$srcdir" || srcdir=`dirname "$0"`
test -n "$srcdir" || srcdir=.
olddir=`pwd`
cd $srcdir
#echo -n "checking for ragel... "
#which ragel ||
# echo "You need to install ragel... See http://www.complang.org/ragel/"
# exit 1
#
echo -n "checking for pkg-config... "
which pkg-config ||
echo "*** No pkg-config found, please install it ***"
exit 1
echo -n "checking for libtoolize... "
which glibtoolize || which libtoolize ||
echo "*** No libtoolize (libtool) found, please install it ***"
exit 1
echo -n "checking for gtkdocize... "
if which gtkdocize ; then
gtkdocize --copy || exit 1
else
echo "*** No gtkdocize (gtk-doc) found, skipping documentation ***"
echo "EXTRA_DIST = " > gtk-doc.make
fi
echo -n "checking for autoreconf... "
which autoreconf ||
echo "*** No autoreconf (autoconf) found, please install it ***"
exit 1
echo "running autoreconf --force --install --verbose"
autoreconf --force --install --verbose || exit $?
cd $olddir
test -n "$NOCONFIGURE" ||
echo "running configure $@"
"$srcdir/configure" "$@"
引用
linux系统中开机自启的三种方式_灬紫荆灬-CSDN博客_linux开机自启动
linux /etc/init.d和/etc/rc/init.d联系,运行级别,/etc/rc.d/init.d执行流程_mengzuchao的专栏-CSDN博客
以上是关于嵌入式linux应用开发之常用shell脚本总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章