C语言中 static 和 extern 的用法详解
Posted 我想月薪过万
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C语言中 static 和 extern 的用法详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在 C 语言中变量存在两种 :
- 全局变量
- 局部变量
所以下面我们就以这两种变量为引展开对 static 和 extern 的讲解
extern
其实啊,我们所定义的全局变量默认就是 带 extern 的。如
int g_x = 10; ==>等价==> extern int g_x = 10;这是什么意思呢?,就是说这种全局变量 在整个源程序中 所有 源文件 里都可以访问和修改。
只是访问方式有所不同,下面我就详细说一下在各个地方的访问方式:
- 在声明全局变量的源文件中使用
#include <stdio.h>
void demo();
int g_x = 10;
int main()
g_x = 20;
printf("main => %d\\n", g_x);
demo();
printf("main => %d\\n", g_x);
return 0;
- 在其他源文件中使用
#include <stdio.h>
void demo()
extern int g_x; //声明一个变量 加上 extern 之后表示使用全局的,你不加就是局部变量了
g_x = 30;
printf("other => %d\\n", g_x);
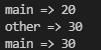
- 运行结果
static
static 如果修饰全局变量,则会 对其他源文件隐藏该全局变量。
我们还是用上面的的代码示例,就简单修改一个地方,在 int g_x = 10 前面加上一个修饰符 static
如下:
int g_x = 10; ==>修改为==> static int g_x = 10;这个时候你再编译这个代码,你就会发现报错,说demo01.c中找不到该变量。
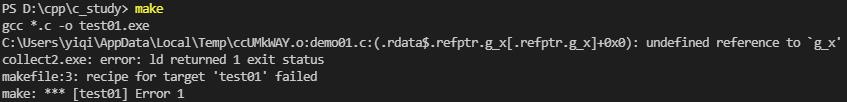
现在你能明白这个道理了吧:即 static 如果修饰全局变量,则会 对其他源文件隐藏该全局变量。
static 如果修饰局部变量,则会使该局部变量获得持久化能力,示例代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
void test_static()
static int num = 10;
num += 10;
printf("test => %d\\n", num);
int main()
test_static();
test_static();
return 0;
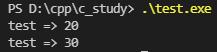
运行结果展示
以上是关于C语言中 static 和 extern 的用法详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章