LeetCode刷题日记精选例题(附代码+链接)
Posted 温文艾尔
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode刷题日记精选例题(附代码+链接)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
精选例题
一、删除链表节点
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接
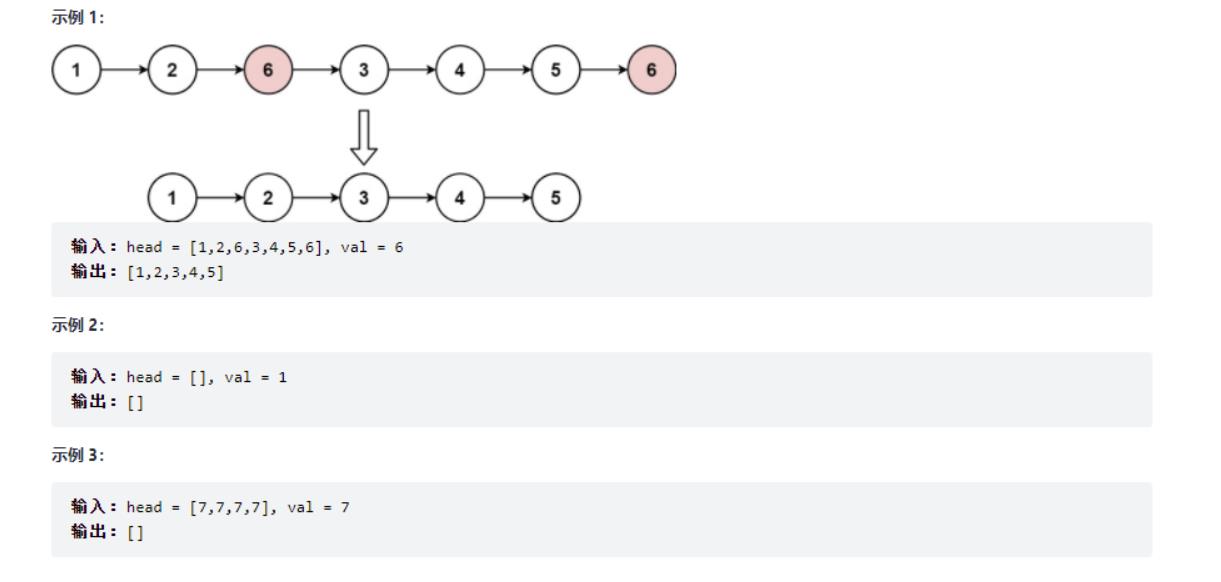
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val)
if (head==null)
return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp!=null)
if (temp.val==val)
pre.next=temp.next;
else
pre=temp;
temp=temp.next;
return dummy.next;
二、设计链表
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。

来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接
单链表实现
class MyLinkedList
//size存储链表元素的个数
int size;
//虚拟头结点
ListNode head;
//初始化链表
public MyLinkedList()
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
//获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1
public int get(int index)
if (index<0||index>=size)
return -1;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i=0;i<=index;i++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.val;
//addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点
public void addAtHead(int val)
addAtIndex(-1,val);
//addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素
public void addAtTail(int val)
addAtIndex(size,val);
//addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val)
if (index>size)
return;
//为负数
if (index<0)
index=0;
size++;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i=0;i<index;i++)
//找到要插入节点的前驱
cur = cur.next;
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
//deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index)
if (index<0||index>=size)
return;
size--;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i=0;i<index;i++)
cur = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
//遍历链表
public void list()
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null)
System.out.println(cur);
cur = cur.next;
双向链表实现
class MyLinkedList
int size;
ListNode head,tail;//Sentinel node
class ListNode
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode pre;
ListNode()
ListNode(int val)
this.val = val;
@Override
public String toString()
return "ListNode" +
"val=" + val +
'';
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyLinkedList()
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
//获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1
public int get(int index)
if (index<0||index>=size)
return -1;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i=0;i<=index;i++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.val;
//addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点
public void addAtHead(int val)
addAtIndex(-1,val);
//addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素
public void addAtTail(int val)
addAtIndex(size,val);
//addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val)
if (index>size)
return;
if (index<0)
index=0;
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
//到达要插入节点的前驱节点
for (int i=0;i<index;i++)
cur=cur.next;
node.next = cur.next;
node.pre = cur;
cur.next.pre=node;
cur.next=node;
size++;
//deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index)
if (index<0||index>=size)
return;
ListNode cur = head;
//到达要删除节点的前驱节点
for (int i=0;i<index;i++)
cur=cur.next;
cur.next.next.pre=cur;
cur.next=cur.next.next;
size--;
//遍历链表
public void list()
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null)
System.out.println(cur);
cur = cur.next;
三、反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接



public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head)
if (head==null)
return null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode reverseNode = new ListNode();
ListNode temp = null;
ListNode pre = new ListNode();
pre.next=head;
while (cur!=null)
temp = cur.next;//将其下一个先记录下来
cur.next = reverseNode.next;
reverseNode.next=cur;
cur=temp;
pre.next=reverseNode.next;
return pre.next;
四、两两交换链表中的节点
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接
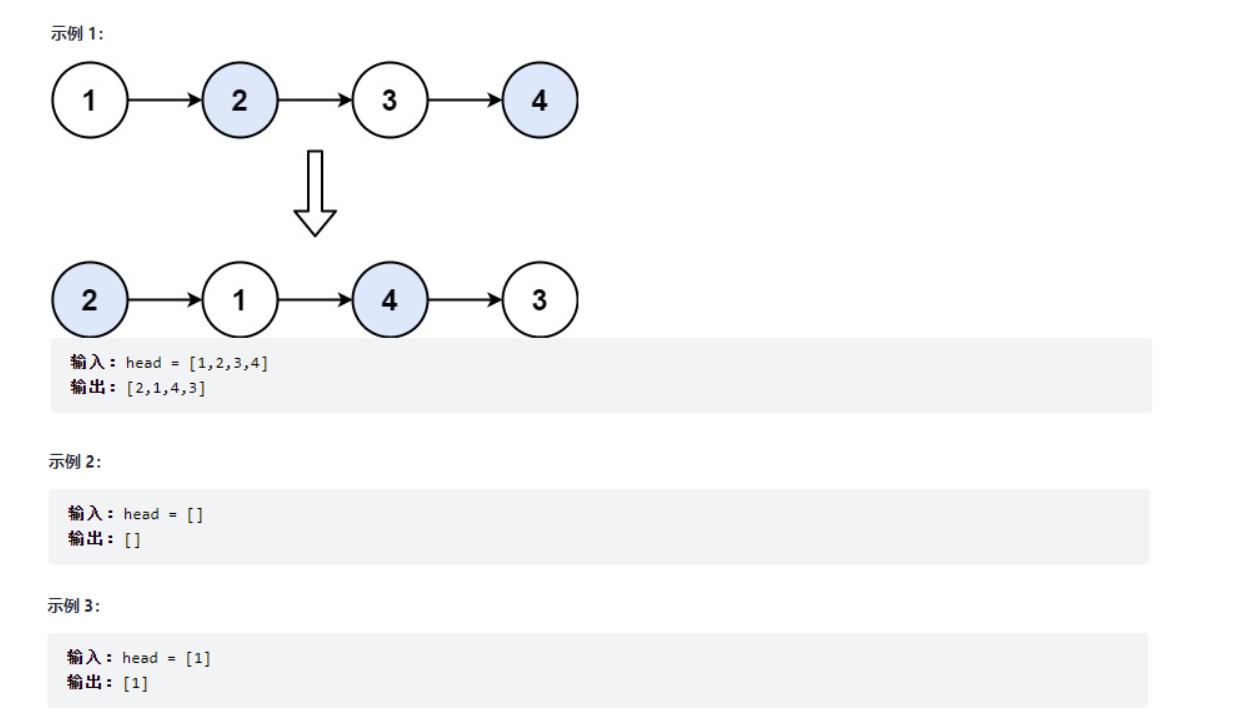
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head)
if (head==null)
return null;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp.next=head;
ListNode prev = temp;
while (prev.next!=null&&prev.next.next!=null)
ListNode p = head.next.next;
prev.next=head.next;
head.next.next=head;
head.next = p;
prev=head;
head=head.next;
return temp.next;
五、删除链表的倒数第N个节点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接
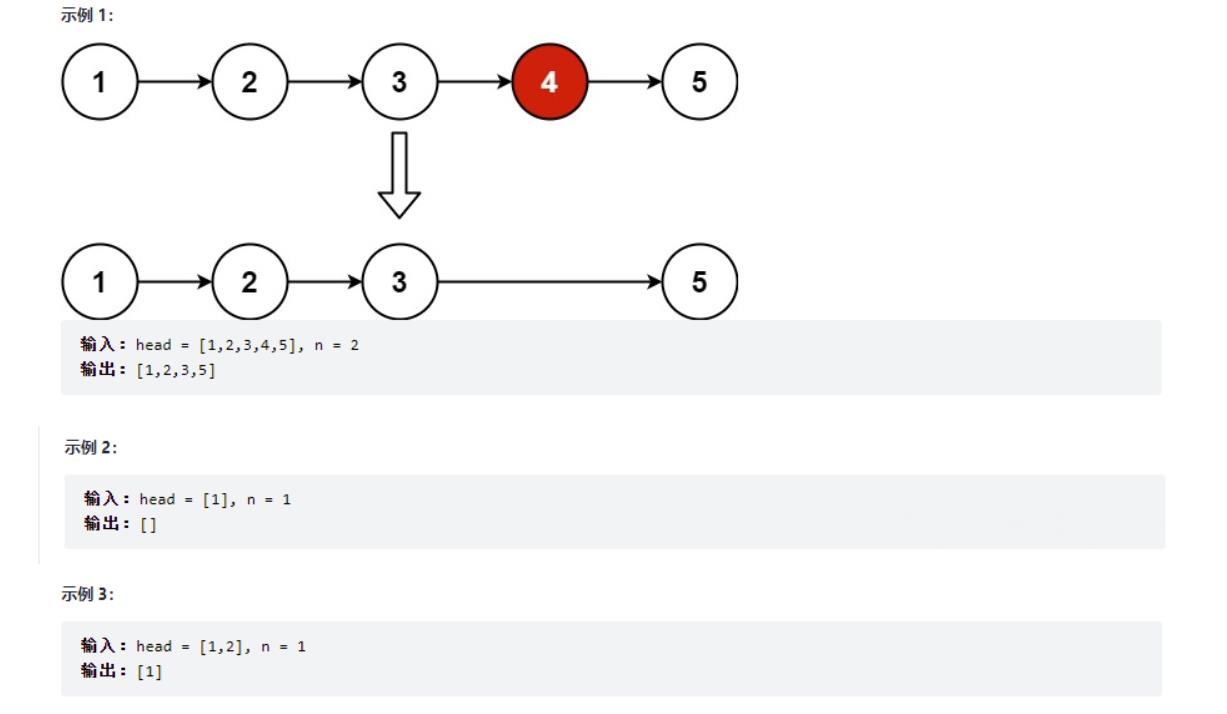
六、链表相交
给定两个(单向)链表,判定它们是否相交并返回交点。请注意相交的定义基于节点的引用,而不是基于节点的值。换句话说,如果一个链表的第k个节点与另一个链表的第j个节点是同一节点(引用完全相同),则这两个链表相交。
示例 1:
输入:listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5]
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接



public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
//思路,计算A链表和B链表的长度,并计算出长度的差值n,让长链表的指针向后移动n位
//比较节点大小,相等则返回,否则向后移动
int lengthA = getLength(headA);
int lengthB = getLength(headB);
ListNode curA=headA;
ListNode curB=headB;
//让A链表为长度最长的链表
if (lengthB-lengthA>0)
ListNode t = curA;
curA=curB;
curB=t;
int tN = lengthA;
lengthA=lengthB;
lengthB=tN;
int X = lengthA-lengthB;
//curA代表的为长度最长的链表
for (int i=0;i<X;i++)
curA = curA.next;
//开始逐个比较大小
while (curA!=null)
if (curA==curB)
return curA;
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
return null;
//获得链表长度
public int getLength(ListNode node)
int length = 0;
ListNode cur = node;
while (cur!=null)
length++;
cur=cur.next;
return length;
七、环形链表II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目链接
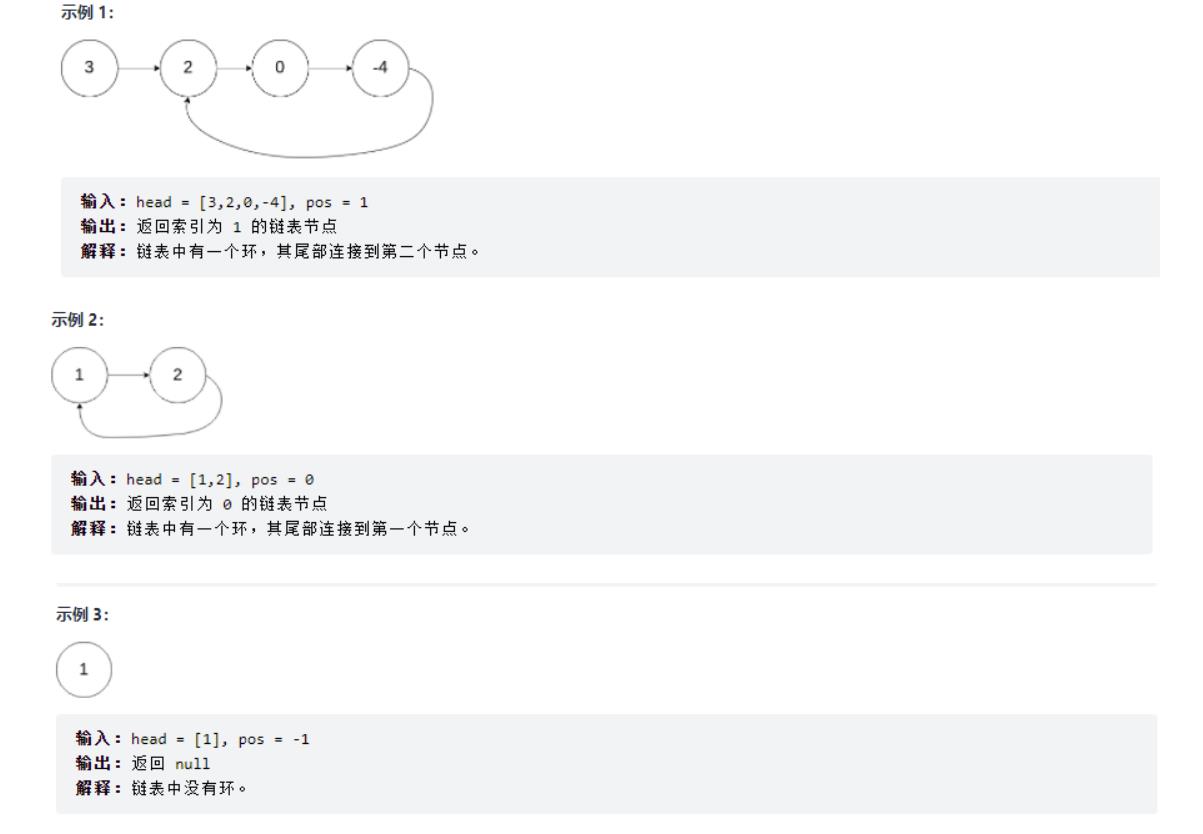
题目解析
我们可以采用快慢指针算法,在这个问题中我们必须要解决两个重要的问题‘
- 链表是否成环
- 环形的起始位置在哪里
我们设置两个指针,快指针fast一次走两步,慢指针slow一次走一步,这样fast的行进速度比slow块,虽然fast先走,但只要链表成环,则必有一次fast==slow
此时我们可以得到slow指针的行动路程为(进入环形之前的路程X+进入链表之后的路程Y)
fast指针必须至少要走完环形链表一圈才能与slow遇见,
我们设X为进入环形前的长度,设Y为进入环形后到slow与fast相遇的长度,设Z为slow与fast相遇的位置离环形起点的长度

此时有slow位置=X+Y,fast位置=X+2Y+Z,因为fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步,所以slow所走路程为fast的1/2
可得方程式
2(X+Y)=X+2Y+Z
解得
X=Z
故我们在slow与fast相遇后设置temp指针指向head,fast=fast.next,temp=temp.next,直到fast==temp位置,此时temp便是入口节点
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head)
if (head==null||head.next==null)
return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
fast=head;
//判断是否成环
int length = 0;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null)
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast==slow)
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp!=fast)
fast=fast.next;
temp=temp.next;
return temp;
return null;
以上是关于LeetCode刷题日记精选例题(附代码+链接)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章