让你学会与理解Java的线程与并发(二,创建运行与常见方法)
Posted 韶光不负
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了让你学会与理解Java的线程与并发(二,创建运行与常见方法)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
线程与进程,并发https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121340716 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121340716创建线程https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121363419
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121340716创建线程https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121363419 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121363419
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121363419
小编相信大家学习前面的二篇文章对线程与线程创建已经有一定的了解,下面就让跟小编一起来知道线程是如何运行的还有一些线程常见的方法吧!
目录
二次执行start的问题(“Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException”)
线程运行
多个线程的运行
测试代码(运行几秒就关闭,需要自己电脑cpu有二核或者以上,小编测试1000以下几乎没有互换)
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args)
new Thread (() ->
int i=0;
while (i<10000)
System.out.println("我是t1号线程");
i++;
,"t1").start();
new Thread (() ->
int i=0;
while (i<10000)
System.out.println("我是t2号线程");
i++;
,"t2").start();

结论:多线程是交替执行的,线程谁先谁后不由人控制
查看进程与杀死进程
Windows:
1,点击菜单栏鼠标右键查看任务管理器(快捷键 ctrl+alt+.)
2,命令提示符(win键+r)——>cmd——>tasklist(查看进程)
3,命令提示符(win键+r)——>cmd——>taskkill 进程id (杀死进程)
Linux:
1, ps -fe 查看所有进程
2,ps -fT -p <PID> 查看id进程下所有线程
3,kill id名称 杀死进程
4,top -H -p <PID> 查看id进程下所有线程
Java:
1,jps 查看所有Java进程
2,jstack <PID> 查看pid进程下所有线程状态
3,jconsole 查看进程中某个线程运行情况(图形化界面显示)
线程运行原理
jvm中由堆,栈,方法区组成,其中的栈内存就是给线程用的,每一个线程启动后,虚拟机就会分配一块栈内存。(可以理解为当我们调用main函数是,就是启动了一个栈,其中的栈帧就对应main函数当中方法的调用)
每一个栈多个栈帧组成,对应着每次方法调用所占内存
每一个线程只有一个活动栈帧,对应这当前正在执行的方法
线程上下文切换
因为下面原因导致cpu不在执行当前的线程,转而执行另一个线程的代码(线程使用cpu到不使用cpu过程)(1~3被动上下文切换,4主动让出cpu)
1,线程的cpu的时间片用完
2,垃圾回收(暂停当前所有的工作线程,垃圾回收的线程回收垃圾)
3,有更高优先级的线程需要执行
4,线程自己调用了sleep,yield,wait等方法
当上下文切换发生时,需要操作系统保存当前线程的状态,并恢复另一个线程的状态,在Java中对应保存线程状态的是“程序记数器”(作用:纪录下一条jvm指令的执行地址(记录栈帧信息),是线程私有的)
常见方法
start() | 启动新线程,并在新线程下运行run()方法下内容(start方法只能调用一次,让线程进入准备状态,运行还要看系统的任务调度器) |
| run() | 线程池启动后调用的方法。(可以常见Tread方法进行覆盖,当存在Runnable,运行Runnable方法) |
| join() | 等待线程运行结束 |
| join(时间) | 设置等待最长时间,过了我就不等了。 |
| get(id) | 获取线程的id(id唯一) |
| getName() | 获取线程名称 |
| setName(new name) | 设置线程的新名称 |
| setPriotity() | 获取线程的优先级 |
| setPriotity(int) | 修改线程优先级(Java中优先级是1~10的整数,优先级大可以提高cpu对线程的调用机率) |
| getState() | 获取线程的状态 |
isInterrupt() | 打断线程,设置打断标记,根据cpu看是否要打断自己 |
isInterrupted() | 判断线程是否被打断(不清除打断标记) |
currentThread() | 获取当前执行的线程 |
| sleep(long n) | 让线程休眠,long n设置的休眠时间(线程休眠时,会让出cpu) |
yield() | 提示线程调度器让出当前线程cpu的使用(主要是测试与调试) |
run()方法的调用与start()方法有什么区别?
有区别,当我们这样调用ran方法时,是在main线程(主线程)下调用,并没有在新线程下调用,并不能实现异步,更不能提高效率。(所有启动线程必须使用start()方法)
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args)
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("张三真是个大帅哥!");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
//t.run(); //有区别,当我们这样调用ran方法时,是在main线程(主线程)下调用,并没有在新线程下调用
//启动线程
t.start();
System.out.println("法外狂徒!");
查看线程状态
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args)
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("张三真是个大帅哥!");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
System.out.println(t.getState());
//启动线程
t.start();
System.out.println(t.getState());

结论:
NEW:表示没有被系统调用 ,表示是新建状态
RUNNABLE:可以被cpu调度执行
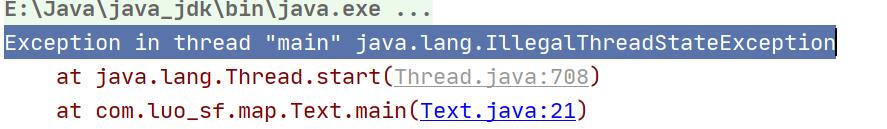
二次执行start的问题(“Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException”)
当我们二次调用start时,会发生下图错误:(解决办法:去掉一个start)
sleep:
1,让线程从运行状态进入有时序的阻塞状态。
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(2000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("张三真是个大帅哥!");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
//启动线程
try
t.start();
System.out.println( t.getState());
Thread.sleep(500);
//查看线程状态
System.out.println( t.getState());
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();

2,其他线程可以使用interrupt()方法打断休眠。
如何打断线程,休眠线程的唤醒(interrupt打断休眠)
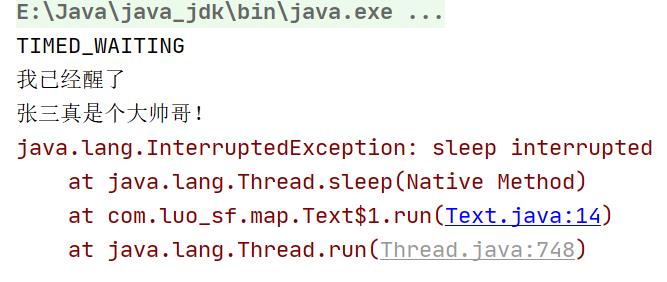
注意:当休眠被打断时,就会报错(如下图)
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(2000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("我已经醒了");
System.out.println("张三真是个大帅哥!");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
//启动线程
try
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
//查看线程状态
t.interrupt(); //打断休眠,唤醒就会抛异常
System.out.println( t.getState());
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3,线程休眠结束后,并不一定能立即执行
yield:
1,调用yield方法会让线程从run状态到runmable(就绪)状态,然后调用其他相同优先级的线程(当没有其他相同优先级的线程时,就不能保证该线程暂停效果)
2,实现依赖操作系统的任务调度器(当你让出cpu时,没有其他线程需要时,任务调度器还是会将cpu还给自己)
sleep()与yield()的区别?
1,(主要)调用sleep是阻塞状态,调用yield是就绪状态,任务调度器可能会给就绪状态分配时间片,不好给就绪状态分配时间片。
2,sleep有等待时间,而yield没有等待时间。
线程优先级(1~10的整数,默认是5,数越大,优先级越高)
1,线程优先级会提示任务调度器,优先执行该线程,但是是提示,任务调度器可以不执行该线程
2,当cpu比较忙,任务优先级会给该线程获取更多的时间片,但cpu不忙时。优先级没有作用。
总结:(yield和优先级都不能真正控制线程的调度,还是系统的任务调度器决定)
实例:防止cpu占到100%
当在服务端进行开发是,会使用while(ture)这样的死循环来一直接收服务端的命令。为了不让while(ture)浪费cpu,这时可以使用 sleep()与yield()来让出cpu的使用权给其他程序。
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
while (true)
try
Thread.sleep(500);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
t.start();
jion方法(等待线程运行完毕)
试一试分析下面代码回答i的值?(线程同步)
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
static int i =0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
test();
public static void test() throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("开始");
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("开始线程");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
i=10;
System.out.println("结束线程");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
t.start();
System.out.println("开始主线程");
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("结束主线程");

结论:为什么i=0?
因为二个线程是并行运行,开始时候完,线程进入休眠1秒,主线程就开始进行获取i的值0,当主线程结束后,才开始进入i=10;但是没有进行获取i。
解决:想要i=10的方法
1,同样休眠一断时间
2,join方法(推荐)
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
static int i =0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
test();
public static void test() throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("开始");
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("开始线程");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
i=10;
System.out.println("结束线程");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
t.start();
t.join();//等待线程结束
System.out.println("开始主线程");
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("结束主线程");

线程同步
从案例分析,调用方法来看:
1,需要等待结果返回,才能进行运行就是同步(当需要多个线程时,Join等待时间为线程最长时间)
2,不需要等待结果返回,才能进行运行就是异步
限时同步
join带参数,当join的等待时间内线程没有返回结果,则就不使用该结果(当参数时间长,还是会等待该时间),
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
static int i =0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
test();
public static void test() throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("开始");
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("开始线程");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
i=10;
System.out.println("结束线程");
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
t.start();
t.join(500);//等待线程结束
System.out.println("开始主线程");
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("结束主线程");

isInterrupt()方法使用
打断sleep ,wite , join线程
当打断sleep(阻塞状态)时,会清空打断状态。并报错!
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
test();
public static void test() throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("开始");
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("开始线程");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r,"t2");
t.start();
t.join(500);//等待线程进入睡眠线程结束
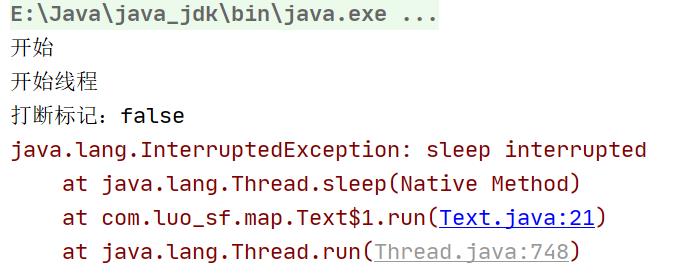
t.interrupt();//打断
System.out.println("打断标记:" + t.isInterrupted());
打断正常线程(当线程打断后,程序并不会停止线程,如果需要停止线程,需要bereak)
package com.luo_sf.map;
/**
* 线程常见方法
*/
public class Text
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("开始");
Runnable r = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
while (true)
//获取打断状态
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
//判断是否停止
if (interrupted)
System.out.println("被打断了,退出循环");
break;
;
//Thread 第一个参数Runnable的名称 ,第二个为线程名称:
Thread t = new Thread(r, "t2");
t.start();
t.join(1000);//等待线程进入睡眠线程结束
t.interrupt();//打断
System.out.println("打断标记:" + t.isInterrupted());

以上是关于让你学会与理解Java的线程与并发(二,创建运行与常见方法)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章