Java Review - 线程池中使用ThreadLocal不当导致的内存泄漏案例&源码分析
Posted 小小工匠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java Review - 线程池中使用ThreadLocal不当导致的内存泄漏案例&源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

概述
ThreadLocal的基本使用我们就不赘述了,可以参考
每日一博 - ThreadLocal VS InheritableThreadLocal VS TransmittableThreadLocal
直接进入主题。 我们今天要聊的是使用ThreadLocal会导致内存泄漏的原因,并给出使用ThreadLocal导致内存泄漏的案例及源码分析。

Why 内存泄露 ?
我们知道 ThreadLocal只是一个工具类,具体存放变量的是线程的threadLocals变量。threadLocals是一个ThreadLocalMap类型的变量
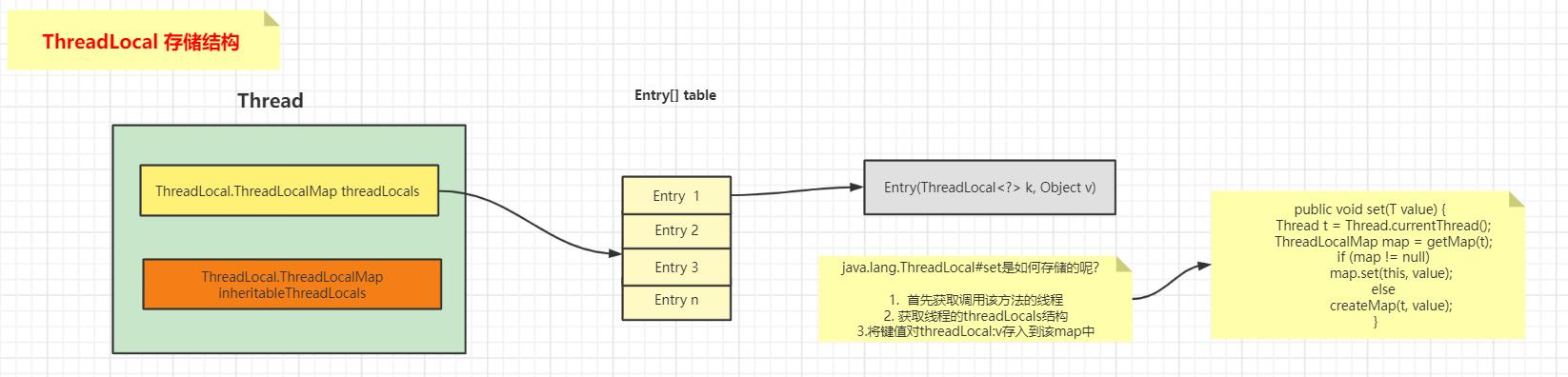
ThreadLocalMap内部是一个Entry数组,Entry继承自WeakReference,Entry内部的value用来存放通过ThreadLocal的set方法传递的值,那么ThreadLocal对象本身存放到哪里了呢?
下面看看Entry的构造函数
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>>
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v)
super(k);
value = v;
继续跟进 super(k);
/**
* Creates a new weak reference that refers to the given object. The new
* reference is not registered with any queue.
*
* @param referent object the new weak reference will refer to
*/
public WeakReference(T referent)
super(referent);
继续 super(referent);
Reference(T referent)
this(referent, null);
Reference(T referent, ReferenceQueue<? super T> queue)
this.referent = referent;
this.queue = (queue == null) ? ReferenceQueue.NULL : queue;
k被传递给WeakReference的构造函数,也就是说ThreadLocalMap里面的key为ThreadLocal对象的弱引用,具体就是referent变量引用了ThreadLocal对象,value为具体调用ThreadLocal的set方法时传递的值。
-
当一个线程调用ThreadLocal的set方法设置变量时,当前线程的ThreadLocalMap里就会存放一个记录,这个记录的key为ThreadLocal的弱引用,value则为设置的值。
-
如果当前线程一直存在且没有调用ThreadLocal的remove方法,并且这时候在其他地方还有对ThreadLocal的引用,则当前线程的ThreadLocalMap变量里面会存在对ThreadLocal变量的引用和对value对象的引用,它们是不会被释放的,这就会造成内存泄漏。
-
考虑这个ThreadLocal变量没有其他强依赖,而当前线程还存在的情况,由于线程的ThreadLocalMap里面的key是弱依赖,所以当前线程的ThreadLocalMap里面的ThreadLocal变量的弱引用会在gc的时候被回收,但是对应的value还是会造成内存泄漏,因为这时候ThreadLocalMap里面就会存在key为null但是value不为null的entry项。
-
其实在ThreadLocal的set、get和remove方法里面可以找一些时机对这些key为null的entry进行清理,但是这些清理不是必须发生的。

下面分析下ThreadLocalMap的remove方法中的清理过程。
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* @linkplain #get read by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its @link #initialValue method,
* unless its value is @linkplain #set set by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* @code initialValue method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove()
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
继续
/**
* Remove the entry for key.
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key)
// 1 计算当前ThreadLocal变量所在的table数组位置,尝试使用快速定位方法
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
// 2 这里使用循环是为了防止快速定位失败后,遍历table数组
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)])
// 3 找到
if (e.get() == key)
// 4 找到调用WeakReference的clear方法清除对ThreadLocal的弱引用
e.clear();
// 5 清理key为null的元素
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
代码(4)调用了Entry的clear方法,实际调用的是父类WeakReference的clear方法,作用是去掉对ThreadLocal的弱引用。
/**
* Clears this reference object. Invoking this method will not cause this
* object to be enqueued.
*
* <p> This method is invoked only by Java code; when the garbage collector
* clears references it does so directly, without invoking this method.
*/
public void clear()
this.referent = null;
如下代码(6)去掉对value的引用,到这里当前线程里面的当前ThreadLocal对象的信息被清理完毕了。
/**
* Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries
* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges
* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See
* Knuth, Section 6.4
*
* @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key
* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot
* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked
* for expunging).
*/
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot)
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
// 6 去掉对value的引用
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len))
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// 如果key为null。则去掉对value的引用
if (k == null)
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
else
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i)
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
return i;
代码(7)从当前元素的下标开始查看table数组里面是否有key为null的其他元素,有则清理。循环退出的条件是遇到table里面有null的元素。所以这里知道null元素后面的Entry里面key 为null的元素不会被清理。

总结一下:
-
ThreadLocalMap的Entry中的key使用的是对ThreadLocal对象的弱引用,这在避免内存泄漏方面是一个进步,因为如果是强引用,即使其他地方没有对ThreadLocal对象的引用,ThreadLocalMap中的ThreadLocal对象还是不会被回收,而如果是弱引用则ThreadLocal引用是会被回收掉的。
-
但是对应的value还是不能被回收,这时候ThreadLocalMap里面就会存在key为null但是value不为null的entry项,虽然ThreadLocalMap提供了set、get和remove方法,可以在一些时机下对这些Entry项进行清理,但是这是不及时的,也不是每次都会执行,所以在一些情况下还是会发生内存漏,因此在使用完毕后及时调用remove方法才是解决内存泄漏问题的王道。

在线程池中使用ThreadLocal导致的内存泄漏
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2021/11/21 8:55
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest
static class LocalVariable
// 模拟大对象
private Long[] variable = new Long[1024 * 1024];
// byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10];
// 1
final static ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 5, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
// 2
final static ThreadLocal<LocalVariable> tl = new ThreadLocal<LocalVariable>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
// 3
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
tpe.submit(()->
// 4
tl.set(new LocalVariable());
// 5
System.out.println("ThreadLocal set完毕");
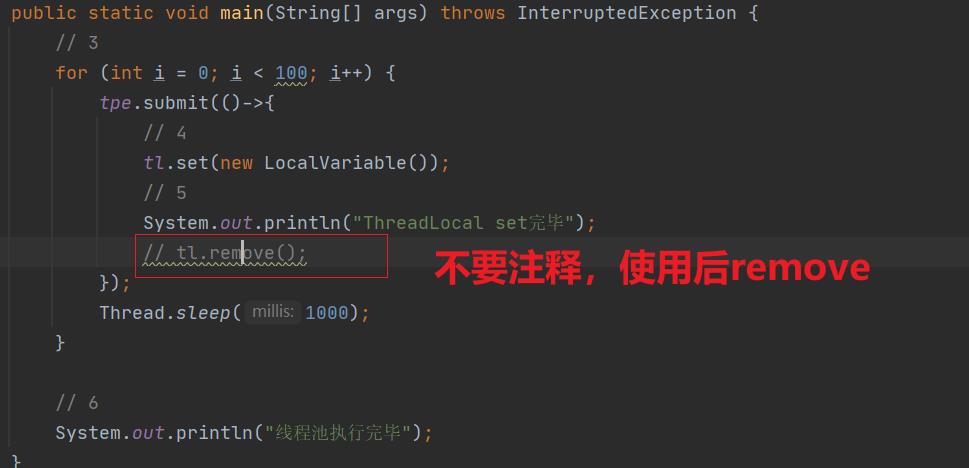
// tl.remove();
);
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 6
System.out.println("线程池执行完毕");
- 代码(1)创建了一个核心线程数和最大线程数都为5的线程池。
-代码(2)创建了一个ThreadLocal的变量,泛型参数为LocalVariable,LocalVariable内部是一个Long数组。
-代码(3)向线程池里面放入100个任务。
-代码(4)设置当前线程的localVariable变量,也就是把new的LocalVariable变量放入当前线程的threadLocals变量中。
由于没有调用线程池的shutdown或者shutdownNow方法,所以线程池里面的用户线程不会退出,进而JVM进程也不会退出。
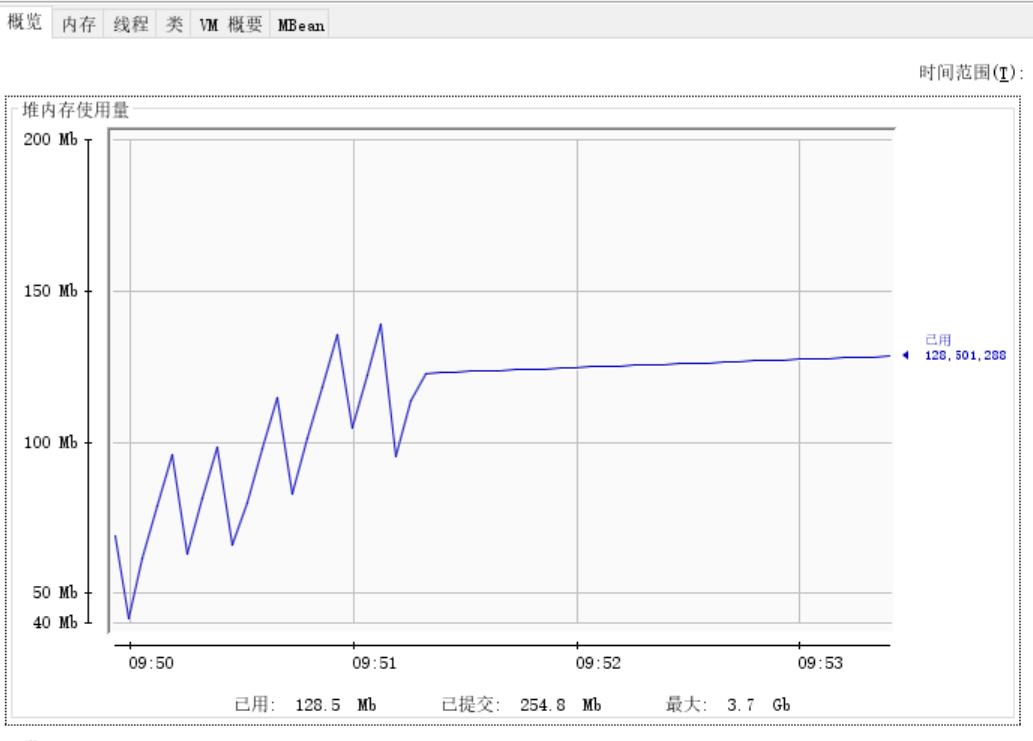
通过jconsle来看一下内存的状态
然后去掉localVariable.remove()注释,
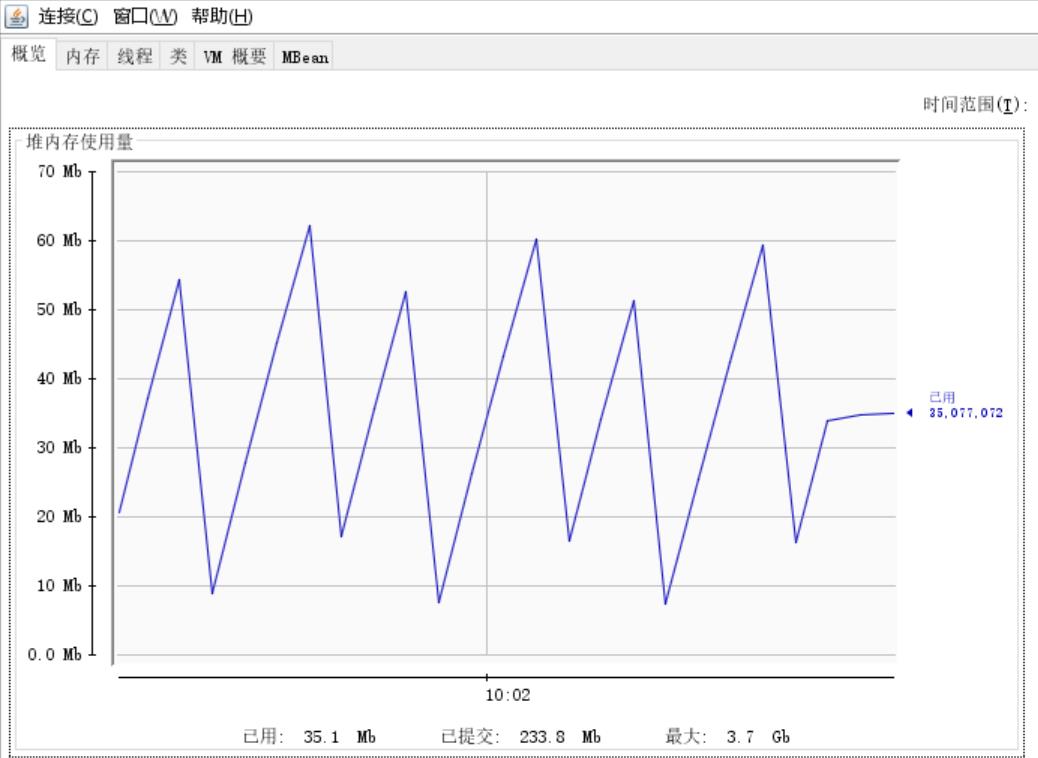
再运行,观察堆内存变化
从运行结果一 可知,当主线程处于休眠时,

进程占用了大概128.5MB内存,
运行结果二 显示占用了大概35.1Mb内存,

由此可知运行代码一时发生了内存泄漏,

下面分析泄露的原因
-
第一次运行代码时,在设置线程的localVariable变量后没有调用
localVariable.remove()方法,这导致线程池里面5个核心线程的threadLocals变量里面的new LocalVariable()实例没有被释放。 -
虽然线程池里面的任务执行完了,但是线程池里面的5个线程会一直存在直到JVM进程被杀死。这里需要注意的是,由于localVariable被声明为了static变量,虽然在线程的ThreadLocalMap里面对localVariable进行了弱引用,但是localVariable不会被回收。
-
第二次运行代码时,由于线程在设置
localVariable变量后及时调用了localVariable.remove()方法进行了清理,所以不会存在内存泄漏问题。
总结:如果在线程池里面设置了ThreadLocal变量,则一定要记得及时清理,因为线程池里面的核心线程是一直存在的,如果不清理,线程池的核心线程的threadLocals变量会一直持有ThreadLocal变量。

以上是关于Java Review - 线程池中使用ThreadLocal不当导致的内存泄漏案例&源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java Review - 并发编程_ThreadPoolExecutor原理&源码剖析
Java Review - 并发编程_ThreadPoolExecutor原理&源码剖析