最近公共祖先三种类型汇总(漫画版)
Posted 2021dragon
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了最近公共祖先三种类型汇总(漫画版)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


最近公共祖先定义


查找最近公共祖先

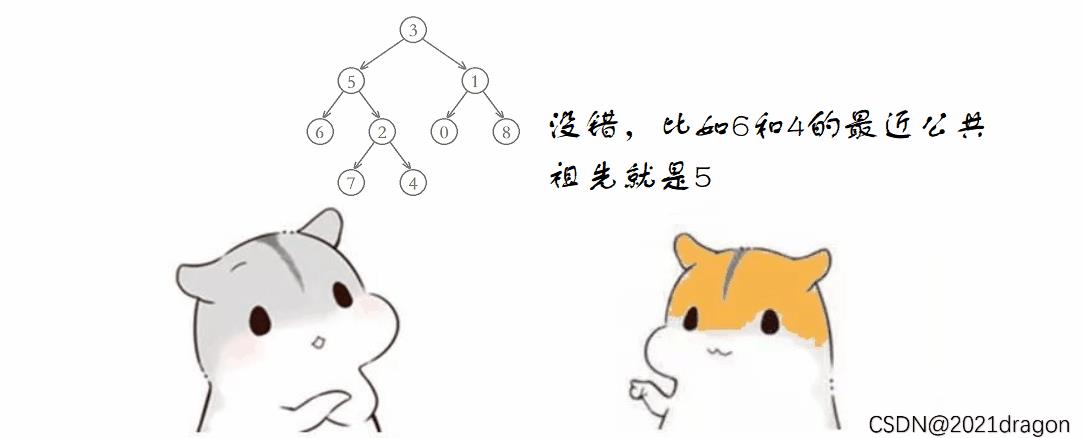



三叉链


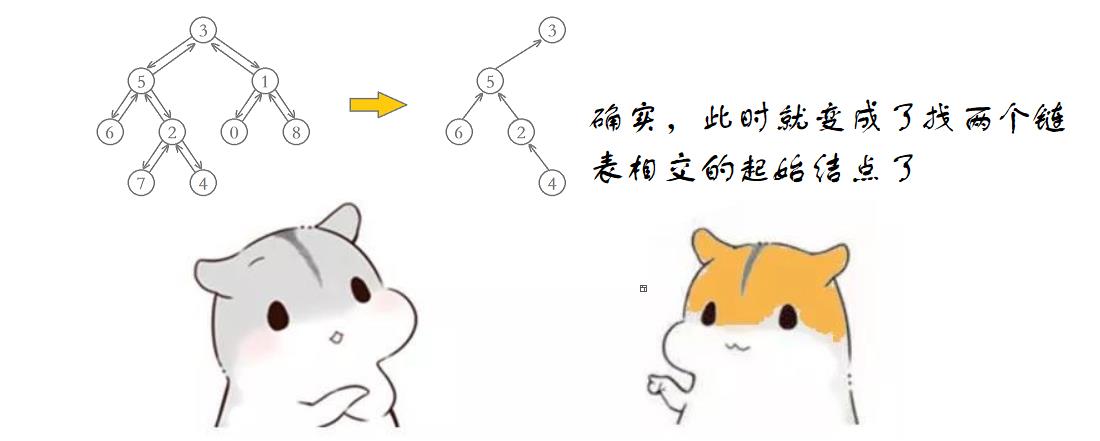

代码如下:
//三叉链
struct TreeNode
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode *parent;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), parent(NULL)
;
class Solution
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
TreeNode* curp = p, *curq = q; //用于遍历p、q结点的祖先结点
int lenp = 0, lenq = 0; //分别记录p、q结点各自的祖先结点个数
//统计p结点的祖先结点个数
while (curp != root)
lenp++;
curp = curp->parent;
//统计q结点的祖先结点个数
while (curq != root)
lenq++;
curq = curq->parent;
//longpath和shortpath分别标记祖先路径较长和较短的结点
TreeNode* longpath = p, *shortpath = q;
if (lenp < lenq)
longpath = q;
shortpath = p;
//p、q结点祖先结点个数的差值
int count = abs(lenp - lenq);
//先让longpath往上走count个结点
while (count--)
longpath = longpath->parent;
//再让longpath和shortpath同时往上走,此时第一个相同的结点便是最近公共祖先结点
while (longpath != shortpath)
longpath = longpath->parent;
shortpath = shortpath->parent;
return longpath; //返回最近公共祖先结点
;
二叉搜索树




代码如下:
//搜索二叉树
struct TreeNode
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL)
;
class Solution
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
if (p->val == root->val || q->val == root->val) //p、q结点中某一个结点的值等于根结点的值,则根结点就是这两个结点的最近公共祖先
return root;
if (p->val < root->val&&q->val < root->val) //p、q结点的值都小于根结点的值,说明这两个结点的最近公共祖先在该树的左子树当中
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else if (p->val > root->val&&q->val > root->val) //p、q结点的值都大于根结点的值,说明这两个结点的最近公共祖先在该树的右子树当中
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
else //p、q结点的值一个比根小一个比根大,说明根就是这两个结点的最近公共祖先
return root;
;
普通二叉树
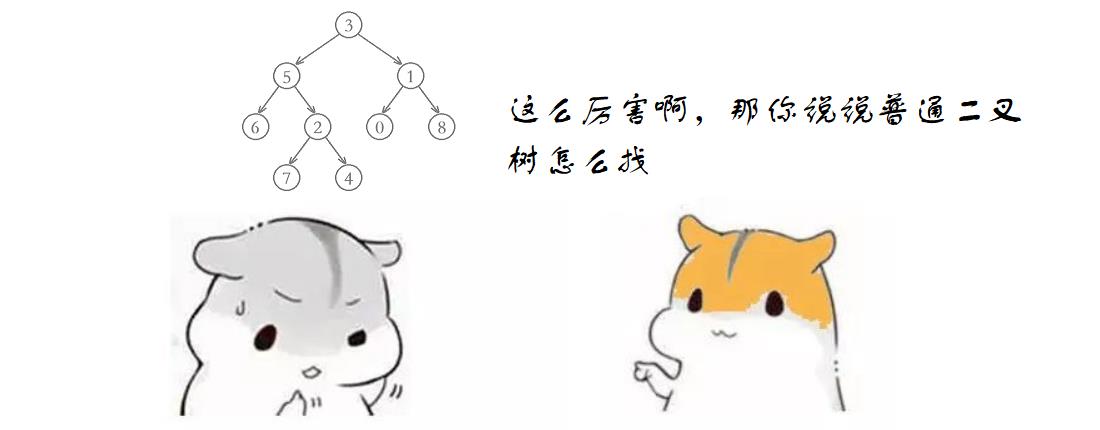


代码如下:
//普通二叉树
struct TreeNode
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL)
;
class Solution
public:
bool Find(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x)
if (root == nullptr) //空树,查找失败
return false;
if (root == x) //查找成功
return true;
return Find(root->left, x) || Find(root->right, x); //在左子树找到了或是右子树找到了,都说明该结点在该树当中
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
if (p == root || q == root) //p、q结点中某一个结点为根结点,则根结点就是这两个结点的最近公共祖先
return root;
//判断p、q结点是否在左右子树
bool IspInLeft, IspInRight, IsqInLeft, IsqInRight;
IspInLeft = Find(root->left, p);
IspInRight = !IspInLeft;
IsqInLeft = Find(root->left, q);
IsqInRight = !IsqInLeft;
if (IspInLeft&&IsqInLeft) //p、q结点都在左子树,说明这两个结点的最近公共祖先也在左子树当中
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else if (IspInRight&&IsqInRight) //p、q结点都在右子树,说明这两个结点的最近公共祖先也在右子树当中
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
else //p、q结点一个在左子树一个在右子树,说明根就是这两个结点的最近公共祖先
return root;
;

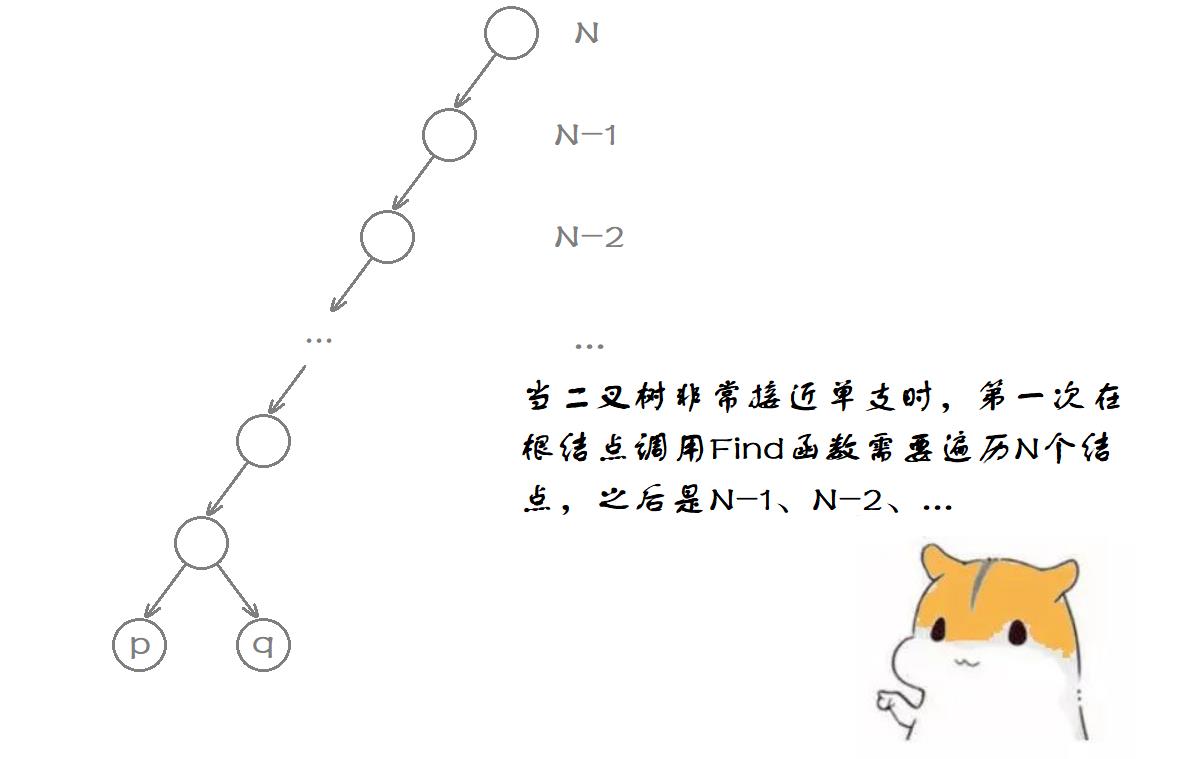





看着似乎不太好理解,来看看下面的动图演示:
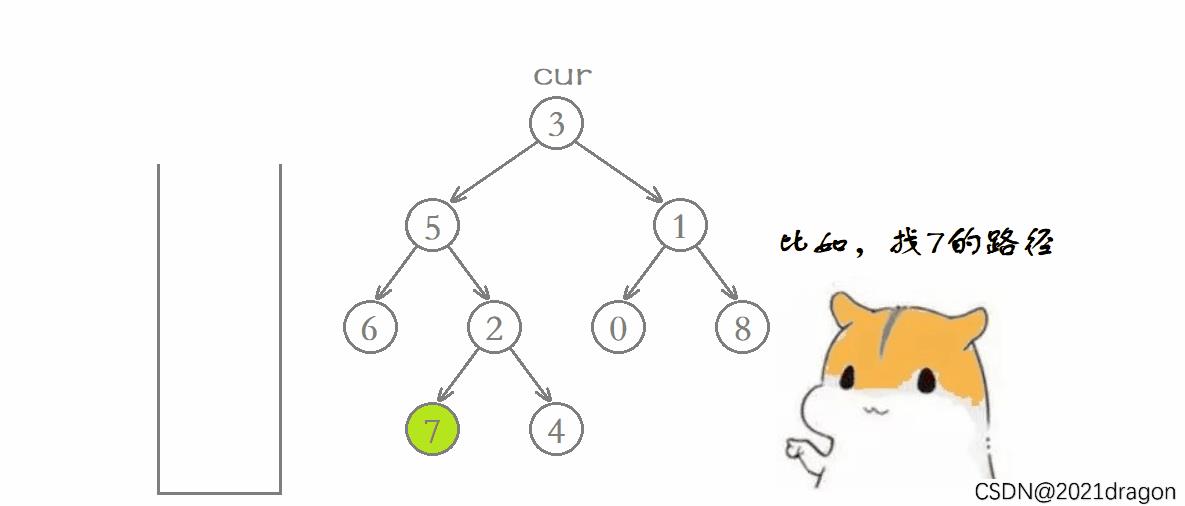
代码如下:
//普通二叉树
struct TreeNode
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL)
;
class Solution
public:
bool FindPath(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x, stack<TreeNode*>& path)
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
path.push(root); //该结点可能是路径当中的结点,先入栈
if (root == x) //该结点是最终结点,查找结束
return true;
if (FindPath(root->left, x, path)) //在该结点的左子树找到了最终结点,查找结束
return true;
if (FindPath(root->right, x, path)) //在该结点的右子树找到了最终结点,查找结束
return true;
path.pop(); //在该结点的左右子树均没有找到最终结点,该结点不可能是路径当中的结点,该结点出栈
return false; //在该结点处查找失败
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
stack<TreeNode*> pPath, qPath;
FindPath(root, p, pPath); //将从根到p结点的路径存放到pPath当中
FindPath(root, q, qPath); //将从根到q结点的路径存放到qPath当中
//longpath和shortpath分别标记长路径和短路径
stack<TreeNode*>* longPath = &pPath, *shortPath = &qPath;
if (pPath.size() < qPath.size())
longPath = &qPath;
shortPath = &pPath;
//让longPath先弹出差值个数据
int count = longPath->size() - shortPath->size();
while (count--)
longPath->pop();
//longPath和shortPath一起弹数据,直到两个栈顶的结点相同
while (longPath->top() != shortPath->top())
longPath->pop();
shortPath->pop();
return longPath->top(); //返回这个相同的结点,即最近公共祖先
;

以上是关于最近公共祖先三种类型汇总(漫画版)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章