点云配准 4-icp 如何逐步匹配多幅点云(win10)
Posted 行码阁119
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了点云配准 4-icp 如何逐步匹配多幅点云(win10)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、声明
本人作为初学者,才开始接触点云配准这一块,如有错误地方,望大家指出,我将及时修改,共同进步。
二、实验
本例迭代最近点算法的使用,以便逐步地对一系列点云进行两两匹配。它的思想是对所有的点云进行变换,使得都与第一个点云在统一坐标系中。在每个连贯的有重叠的点云之间找到最佳的变换,并累积这些变换到全部的点云。能够进行ICP算法的点云需要粗略的预匹配(如:在一个机器人的量距内或在地图框架内),并且一个点云与另一个点云需要有重叠部分。
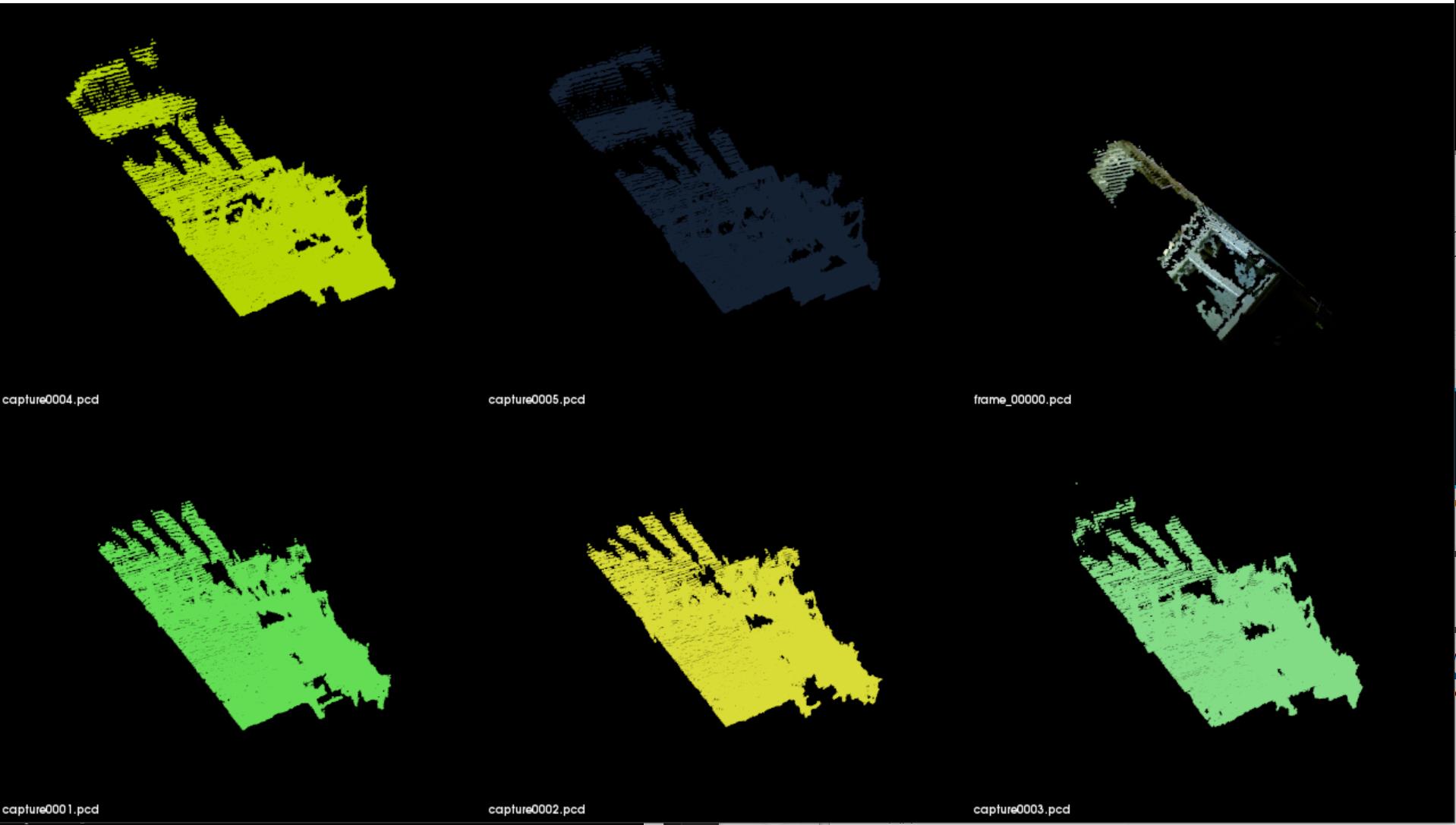
首先看一下,在变换之前的数据分布形状,仔细一看,还是存在一定的差异:
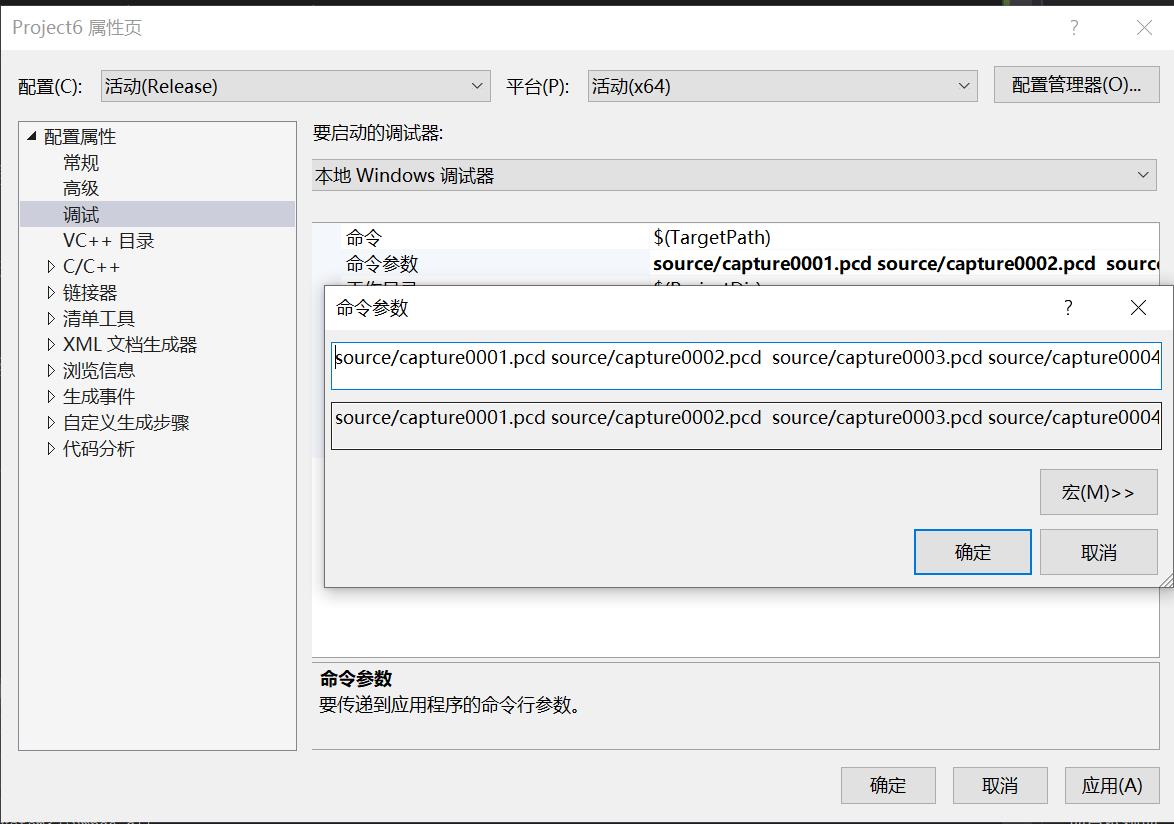
由于,实在win10下,进行了操作,所以,需要提前将项目属性->调式->命令参数中添加如下内容(既不用修改代码),然后点击确认,即可:
运行代码:

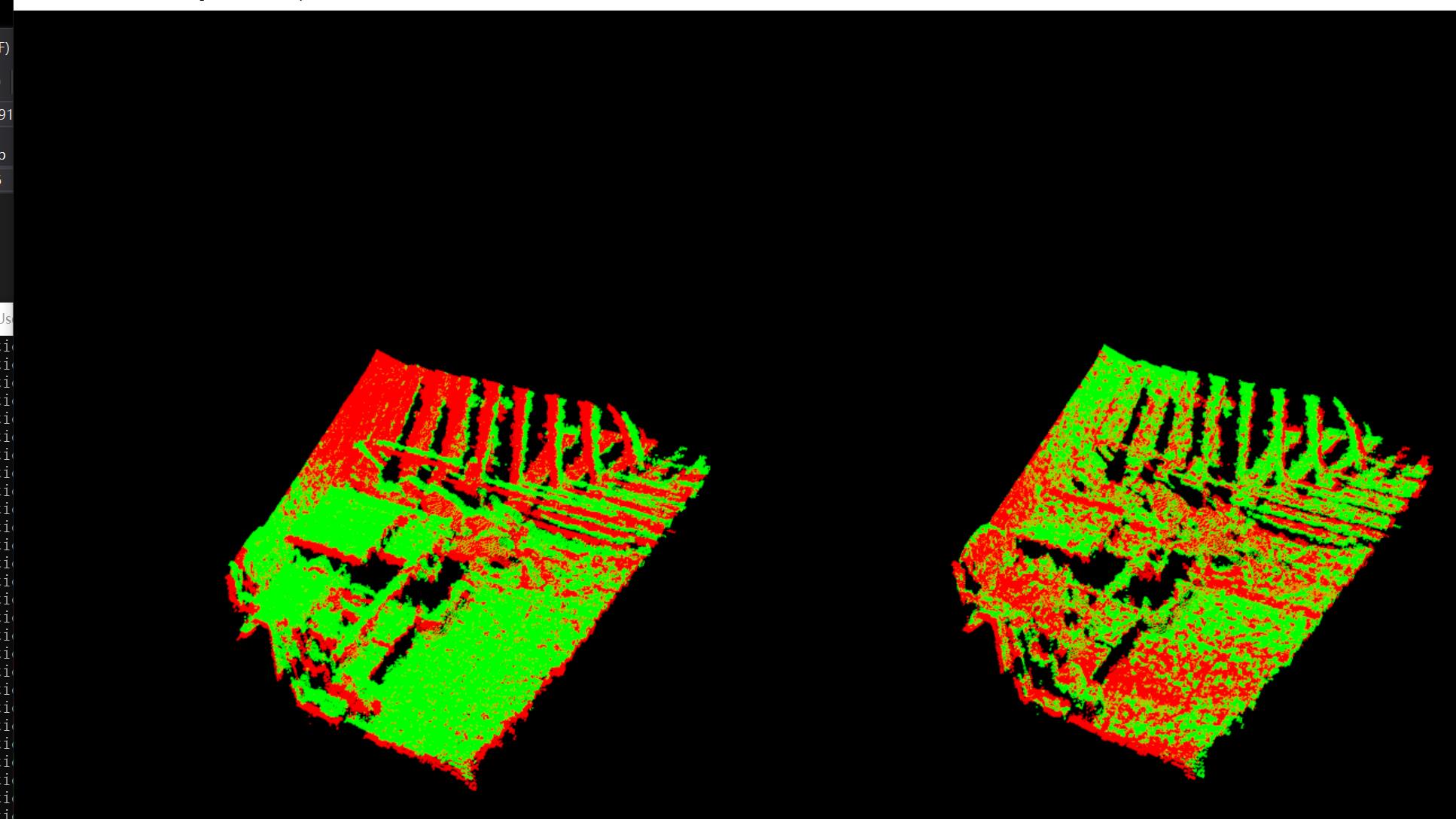
按下q之后,开始匹配第一幅图像:

配准结束:
cmd显示
再次按下q(可以看到第二幅图像和第三幅之间以及第二幅和第一幅之间点云分布不同):
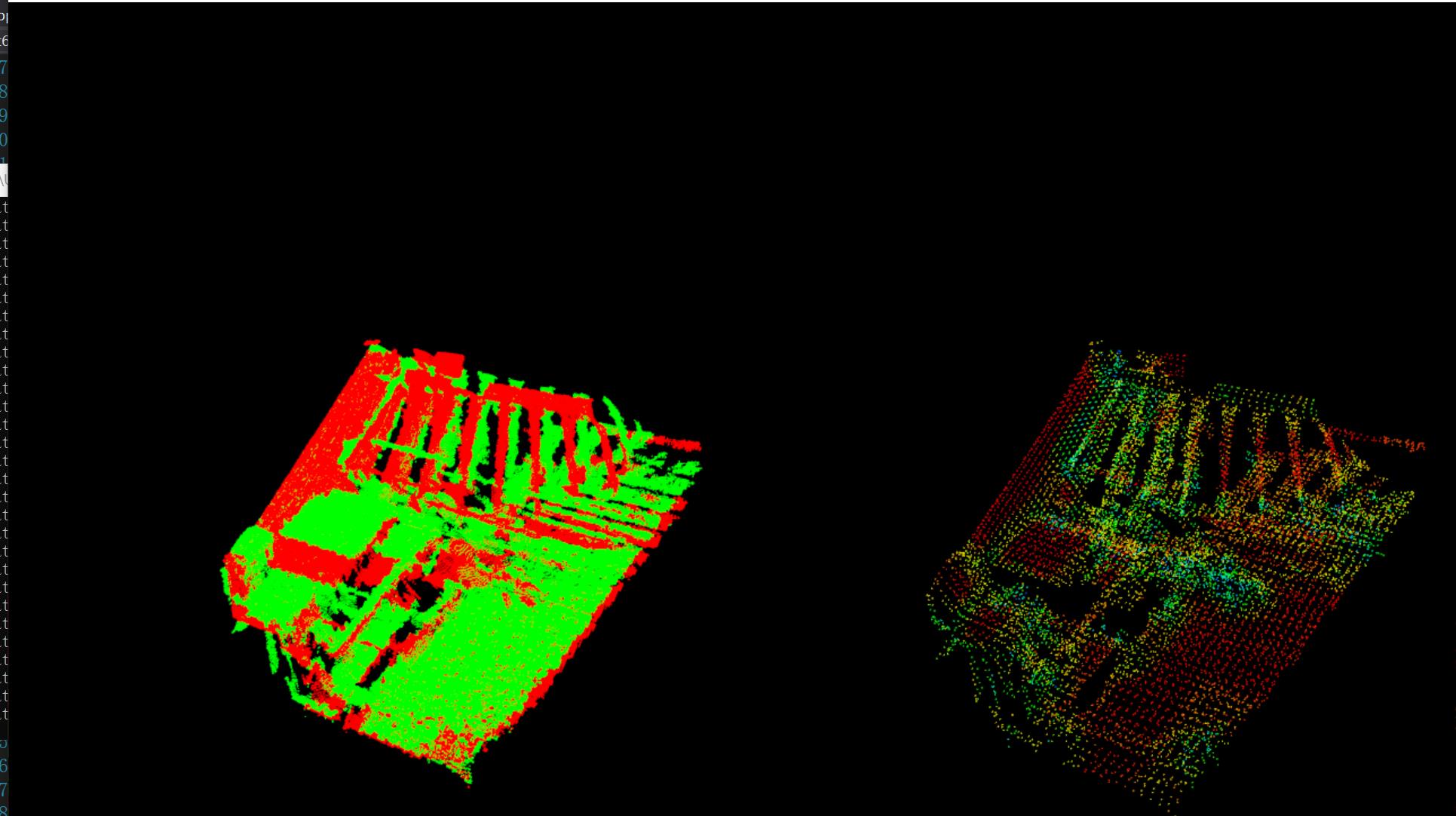
第二幅和第三幅配准后:

然后依次下去,第三幅和第四幅图,配准:
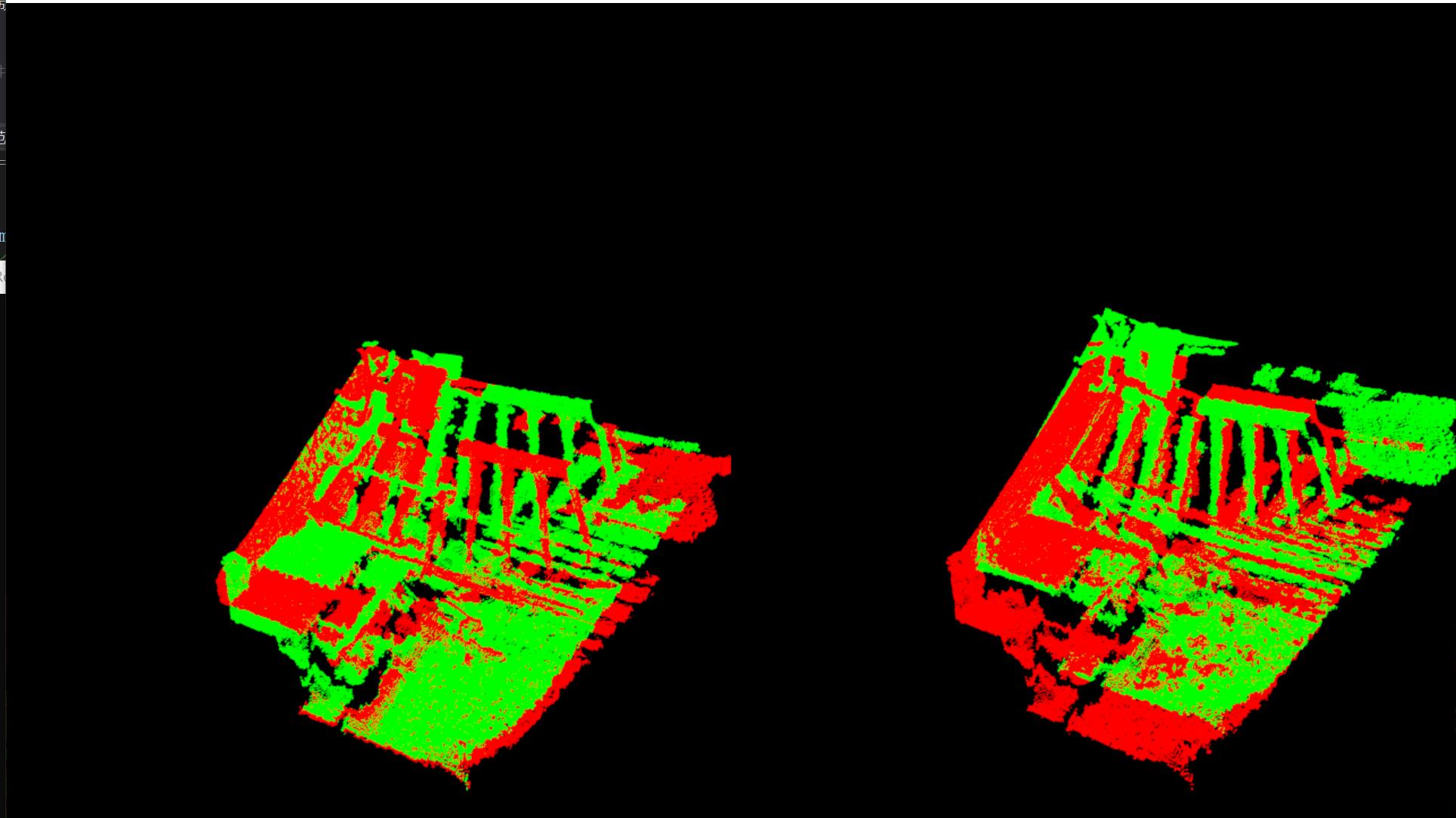
第四幅和第五幅图,配准:
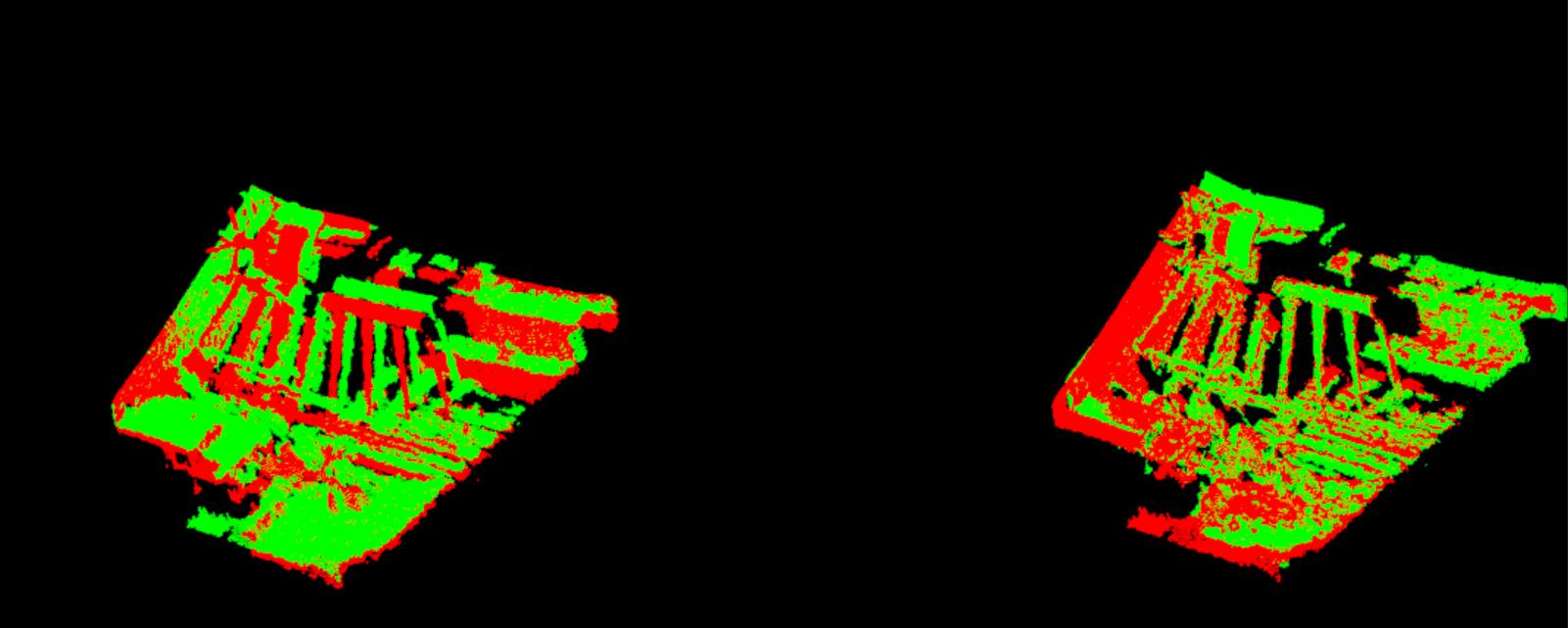
第五附图和第六幅图:

 在工程文件下,会生成
在工程文件下,会生成

然后利用,命令窗口显示:
pcl_viewer -multiview 1.pcd 2.pcd 3.pcd 4.pcd
三、代码(代码无需修改):
/*
* @Description: 如何逐步匹配多幅点云 https://www.cnblogs.com/li-yao7758258/p/6489585.html
* 编译执行: ./pairwise_incremental_registration ../pairwise/frame_00000.pcd ../pairwise/capture0001.pcd ../pairwise/capture0002.pcd ../pairwise/capture0003.pcd ../pairwise/capture0004.pcd ../pairwise/capture0005.pcd
* @Author: HCQ
* @Company(School): UCAS
* @Email: 1756260160@qq.com
* @Date: 2020-10-22 17:20:55
* @LastEditTime: 2020-10-22 18:23:55
* @FilePath: /pcl-learning/14registration配准/2如何逐步匹配多幅点云/pairwise_incremental_registration.cpp
*/
#include <boost/make_shared.hpp> //boost指针相关头文件
#include <pcl/point_types.h> //点类型定义头文件
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h> //点云类定义头文件
#include <pcl/point_representation.h> //点表示相关的头文件
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> //PCD文件打开存储类头文件
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h> //ply文件打开存储类头文件
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> //用于体素网格化的滤波类头文件
#include <pcl/filters/filter.h> //滤波相关头文件
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> //法线特征头文件
#include <pcl/registration/icp.h>
//ICP类相关头文件
#include <pcl/registration/icp_nl.h> //非线性ICP 相关头文件
#include <pcl/registration/transforms.h> //变换矩阵类头文件
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> //可视化类头文件
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom;
using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField;
//定义
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud; //申明pcl::PointXYZ数据
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNormalT> PointCloudWithNormals;
// 申明一个全局可视化对象变量,定义左右视点分别显示配准前和配准后的结果点云
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p; //创建可视化对象
int vp_1, vp_2; //定义存储 左 右视点的ID
//申明一个结构体方便对点云以文件名和点云对象进行成对处理和管理点云,处理过程中可以同时接受多个点云文件的输入
struct PCD
PointCloud::Ptr cloud; //点云共享指针
std::string f_name; //文件名称
PCD() : cloud(new PointCloud) ;
;
struct PCDComparator //文件比较处理
bool operator()(const PCD& p1, const PCD& p2)
return (p1.f_name < p2.f_name);
;
// 以< x, y, z, curvature >形式定义一个新的点表示
class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation<PointNormalT>
using pcl::PointRepresentation<PointNormalT>::nr_dimensions_;
public:
MyPointRepresentation()
nr_dimensions_ = 4; //定义点的维度
// 重载copyToFloatArray方法将点转化为四维数组
virtual void copyToFloatArray(const PointNormalT& p, float* out) const
// < x, y, z, curvature >
out[0] = p.x;
out[1] = p.y;
out[2] = p.z;
out[3] = p.curvature; // 曲率
;
/** \\左视图用来显示未匹配的源和目标点云*/
void showCloudsLeft(const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_source)
p->removePointCloud("vp1_target");
p->removePointCloud("vp1_source");
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> tgt_h(cloud_target, 0, 255, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> src_h(cloud_source, 255, 0, 0);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_target, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_source, src_h, "vp1_source", vp_1);
PCL_INFO("Press q to begin the registration.\\n");
p->spin();
/** \\右边显示配准后的源和目标点云*/
void showCloudsRight(const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_source)
p->removePointCloud("source");
p->removePointCloud("target");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> tgt_color_handler(cloud_target, "curvature");
if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable())
PCL_WARN("Cannot create curvature color handler!");
PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> src_color_handler(cloud_source, "curvature");
if (!src_color_handler.isCapable())
PCL_WARN("Cannot create curvature color handler!");
p->addPointCloud(cloud_target, tgt_color_handler, "target", vp_2);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_source, src_color_handler, "source", vp_2);
p->spinOnce();
/** \\brief Load a set of PCD files that we want to register together
* \\param argc the number of arguments (pass from main ())
* \\param argv the actual command line arguments (pass from main ())
* \\param models the resultant vector of point cloud datasets
*/
void loadData(int argc, char** argv, std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD>>& models)
std::string extension(".pcd");
// 第一个参数是命令本身,所以要从第二个参数开始解析
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++)
std::string fname = std::string(argv[i]);
// PCD文件名至少为5个字符大小字符串(因为后缀名.pcd就已经占了四个字符位置)
if (fname.size() <= extension.size())
continue;
std::transform(fname.begin(), fname.end(), fname.begin(), (int (*)(int))tolower);
//检查参数是否为一个pcd后缀的文件
if (fname.compare(fname.size() - extension.size(), extension.size(), extension) == 0)
//加载点云并保存在总体的点云列表中
PCD m;
m.f_name = argv[i];
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[i], *m.cloud);
//从点云中移除NAN点也就是无效点
std::vector<int> indices;
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*m.cloud, *m.cloud, indices);
models.push_back(m);
/** \\brief Align a pair of PointCloud datasets and return the result
* \\param cloud_src the source PointCloud
* \\param cloud_tgt the target PointCloud
* \\param output the resultant aligned source PointCloud
* \\param final_transform the resultant transform between source and target
*/
///实现匹配,其中参数有输入一组需要配准的点云,以及是否需要进行下采样,其他参数输出配准后的点云以及变换矩阵
void pairAlign(const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt, PointCloud::Ptr output, Eigen::Matrix4f& final_transform, bool downsample = false)
// Downsample for consistency and speed
// \\note enable this for large datasets
PointCloud::Ptr src(new PointCloud); //存储滤波后的源点云
PointCloud::Ptr tgt(new PointCloud); //存储滤波后的目标点云
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> grid; //滤波处理对象
if (downsample)
grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05); //设置滤波时采用的体素大小
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
grid.filter(*src);
grid.setInputCloud(cloud_tgt);
grid.filter(*tgt);
else
src = cloud_src;
tgt = cloud_tgt;
// 计算表面的法向量和曲率
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src(new PointCloudWithNormals);
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt(new PointCloudWithNormals);
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, PointNormalT> norm_est; //点云法线估计对象
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
norm_est.setSearchMethod(tree);
norm_est.setKSearch(30);
norm_est.setInputCloud(src);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_src);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);
norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);
norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);
//
// Instantiate our custom point representation (defined above) ...
MyPointRepresentation point_representation;
// ... and weight the 'curvature' dimension so that it is balanced against x, y, and z
float alpha[4] = 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 ;
point_representation.setRescaleValues(alpha);
//
// 配准
pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear<PointNormalT, PointNormalT> reg; // 配准对象
reg.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);
//设置收敛判断条件,越小精度越大,收敛也越慢
// Set the maximum distance between two correspondences (src<->tgt) to 10cm大于此值的点对不考虑
// Note: adjust this based on the size of your datasets
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(0.1);
// 设置点表示
reg.setPointRepresentation(pcl::make_shared<const MyPointRepresentation>(point_representation));
reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src); // 设置源点云
reg.setInputTarget(points_with_normals_tgt); // 设置目标点云
//
// Run the same optimization in a loop and visualize the results
Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(), prev, targetToSource;
PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src;
reg.setMaximumIterations(2); 设置最大的迭代次数,即每迭代两次就认为收敛,停止内部迭代
std::cout << "下来了" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3000; ++i) //手动迭代,每手动迭代一次,在配准结果视口对迭代的最新结果进行刷新显示
PCL_INFO("Iteration Nr. %d.\\n", i);
// 存储点云以便可视化
points_with_normals_src = reg_result;
// Estimate
reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src);
reg.align(*reg_result);
//accumulate transformation between each Iteration
Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation() * Ti;
//if the difference between this transformation and the previous one
//is smaller than the threshold, refine the process by reducing
//the maximal correspondence distance
if (fabs((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation() - prev).sum()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon())
reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance() - 0.001);
prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation();
// visualize current state
showCloudsRight(points_with_normals_tgt, points_with_normals_src);
//
// Get the transformation from target to source
targetToSource = Ti.inverse(); //deidao
//
// Transform target back in source frame
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud_tgt, *output, targetToSource);
p->removePointCloud("source");
p->removePointCloud("target");
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tgt_h(output, 0, 255, 0);
PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_src_h(cloud_src, 255, 0, 0);
p->addPointCloud(output, cloud_tgt_h, "target", vp_2);
p->addPointCloud(cloud_src, cloud_src_h, "source", vp_2);
PCL_INFO("Press q to continue the registration.\\n");
p->spin();
p->removePointCloud("source");
p->removePointCloud("target");
//add the source to the transformed target
*output += *cloud_src;
final_transform = targetToSource;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
// 存储管理所有打开的点云
std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD>> data;
loadData(argc, argv, data); // 加载所有点云到data
// 检查输入
if (data.empty())
PCL_ERROR("Syntax is: %s <source.pcd> <target.pcd> [*]", argv[0]);
PCL_ERROR("[*] - multiple files can be added. The registration results of (i, i+1) will be registered against (i+2), etc");
return (-1);
PCL_INFO("Loaded %d datasets.", (int)data.size());
// 创建PCL可视化对象
p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer(argc, argv, "Pairwise Incremental Registration example");
p->createViewPort(0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1); //用左半窗口创建视口vp_1
p->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2); //用右半窗口创建视口vp_2
PointCloud::Ptr result(new PointCloud), source, target;
Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(), pairTransform;
for (size_t i = 1; i < data.size(); ++i) //循环处理所有点云================重点======================================
source = data[i - 1].cloud; //连续配准
target = data[i].cloud; // 相邻两组点云
showCloudsLeft(source, target); //可视化为配准的源和目标点云
//调用子函数完成一组点云的配准,temp返回配准后两组点云在第一组点云坐标下的点云
PointCloud::Ptr temp(new PointCloud);
PCL_INFO("Aligning %s (%d) with %s (%d).\\n", data[i - 1].f_name.c_str(), source->points.size(), data[i].f_name.c_str(), target->points.size());
// pairTransform返回从目标点云target到source的变换矩阵
pairAlign(source, target, temp, pairTransform, true); // ===================重点=========================
//把当前两两配准后的点云temp转化到全局坐标系下返回result
pcl::transformPointCloud(*temp, *result, GlobalTransform);
//用当前的两组点云之间的变换更新全局变换
GlobalTransform = GlobalTransform * pairTransform;
//保存转换到第一个点云坐标下的当前配准后的两组点云result到文件i.pcd
std::stringstream ss;
ss << i << ".pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFile(ss.str(), *result, true);
/* ]--- */四、注意事项(关于q):

你有可能发现在命令窗口怎么按q程序都不往下运行,那么这需要你在生成显示图右边侧,右击一下,按q即可。

如图所示:

以上是关于点云配准 4-icp 如何逐步匹配多幅点云(win10)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章