从Servlet开始谈Spring框架的启动原理
Posted Dream_it_possible!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从Servlet开始谈Spring框架的启动原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
目录
1. Web应用的启动监听器ContextLoaderListener
3. Spring-webmvc核心实现DispatcherServlet
在工作中我们往往会用到了Spring框架做后端开发,如果想寻求技术的突破,光学会用是远远不够的,我学习Spring框架有一段时间了,我慢慢地认识了Spring, 例如Spring的核心容器IOC是如何实现的,Aop原理,Web应用启动原理,如何与其他框架整合,包括Spring的一些高级用法,在此记录下来,学习的道路漫长,学的越多不懂的越多,fighting!
学习web容器前,我们先看一个Spring框架的UML类图, 主要是展现DispatcherServlet、FramworkServlet、HttpServletBean和ApplicationContextAware的关系,DispatcherServlet最终实现了Servlet接口。

接着看另外一个核心接口WebApplicationContext的UML类图
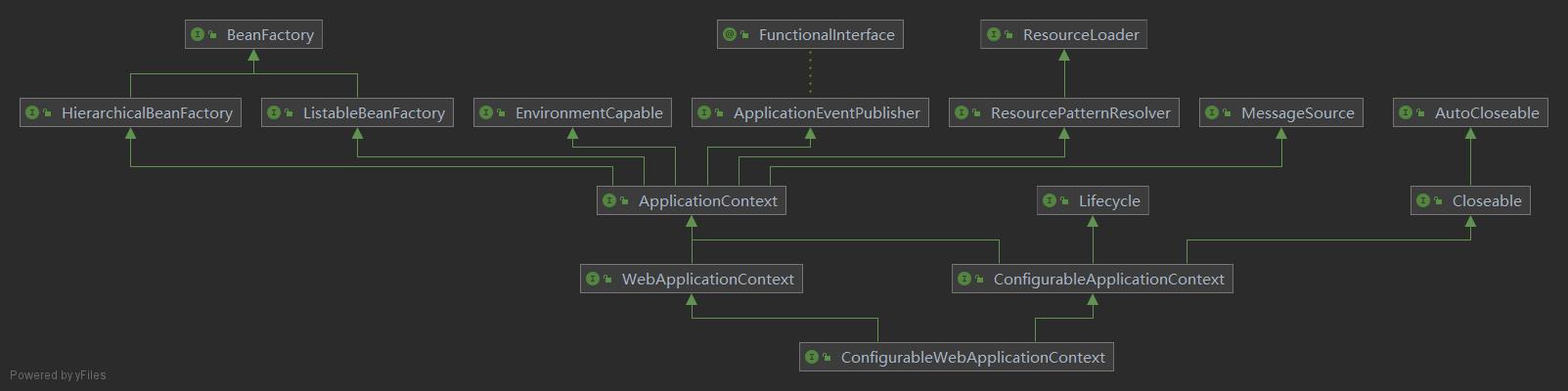
由UML类图可以发现WebApplicationContext有一个父接口ApplicationContext和一个子接口ConfigurableWebApplicationContext子接口, 其中ConfigurableWebApplicationContext有4个实现GenericWebApplicationContext、GroovyWebApplicationContext、StaticWebApplicationContext和XmlWebApplicationContext。

此处实现用到了策略模式,Spring容器默认使用的XmlWebApplicationContext,可以在FrameworkServlet里找到一个静态熟悉DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS, 在没有找到web容器的情况下,那么就使用XmlWebApplicationContext容器。
public static final Class<?> DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;上述的类和接口基本都是Spring框架的核心类,为了掌握启动原理,不光要熟悉这些类,我们可以从Servlet开始追踪溯源,其中ContextLoaderListener是Spring框架提供的一个web应用的实现类, 实现了ServletContextListener接口。
一、web应用启动原理分析
1. Web应用的启动监听器ContextLoaderListener
早期的应用开发者在利用Spring框架开发web应用时,我们需要在web.xml文件里添加一个web监听器的配置 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener, 为什么要添加ContextLoaderListener这个配置呢?
我们可以从Spring源码中找到这个ContextLoaderListener类,查看源码:

由上图可以发现ContextLoaderListener类继承了ContextLoader类并实现了ServletContextListener接口,如果对servlet比较熟悉的话,该接口也是sevlet的监听器,主要的作用在于监听容器的启动,初始化容器,tomcat就是一个很好的例子,可以从javax.servlet-api-3.1.0.jar里找到源代码,ServletContextListener接口包含2个方法 ContextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce)和contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce),主要的功能是初始化ServletContext 容器和销毁ServletContext容器。
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener
/**
* Receives notification that the web application initialization
* process is starting.
*
* <p>All ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* initialization before any filters or servlets in the web
* application are initialized.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being initialized
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce);
/**
* Receives notification that the ServletContext is about to be
* shut down.
*
* <p>All servlets and filters will have been destroyed before any
* ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* destruction.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being destroyed
*/
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce);
contextInitialized放发在Servlet容器启动时,就会执行我们可以在ContextLoaderListener类的源代码里找到实现,找到了initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext())方法
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
包含了Spring容器的初始化逻辑:
2. Web应用初始化入口init()
如果对servlet足够熟悉,那么你一定知道servlet接口里的init()方法是servlet容器初始化的入口,也就是说我们可以在Servlet接口里定义我们自己实现的初始化逻辑。 接着看Spring框架里的org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean, HttpServletBean是一个抽象类,实现了servlet接口里的Init()方法, 源码如下:
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty())
try
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
catch (BeansException ex)
if (logger.isErrorEnabled())
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// web 应用的启动入口 initServletBean()
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
...
该方法的作用是容器初始化的入口,从代码里可以找到一个方法initServletBean(),该方法在FrameWorkServlet类里实现,代码如下:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware
/**
* Overridden method of @link HttpServletBean, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
* web 容器启动入口
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled())
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try
// 初始化web容器
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
catch (ServletException ex)
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
catch (RuntimeException ex)
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled())
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
// 其他代码用...表示
...
如果足够细心,我们就会发现FrameworkServlet类实现了一个ApplicationContextAware接口,该接口里只包含一个方法setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext),在Spring中,我们知道如果有类实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,那么我们可以通过setApplicationContext(AppicationContext applicationContext)方法拿到applicationContext容器, WebApplicationContext接口是ApplicationContext的子接口,他们俩是一个父子容器的关系。
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
if (this.webApplicationContext == null && applicationContext instanceof WebApplicationContext)
this.webApplicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) applicationContext;
this.webApplicationContextInjected = true;
从上述代码,我们可以发现webApplicationContext容器先通过setApplicationContext方法初始化赋值。
为什么在FramworkServlet的initServletBean方法里又做了一次初始webApplicationContext
的动作呢?

接着看initWebApplicationContext()方法,里面判断了一下wac能否转为ConfigurableWebApplciationContext, 如果能的话,那就继续判断是否需要设置父容器,如果需要的父容器那么设置父容器WebApplicationContext。
if (this.webApplicationContext != null)
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive())
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null)
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
从上述代码中我们可以找到问题的答案,Web应用需要通过parent属性将各容器之间关联起来,如果出现找不到容器的情况下,那么会去创建一个默认的web容器, 该默认的容器是XmlWebApplicationContext。
if (wac == null)
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
一切初始化好后,那么就开始初始化mvc所有相关的策略,前提是没有收到refresh事件
if (!this.refreshEventReceived)
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
接着看DispatcherServlet!
3. Spring-webmvc核心实现DispatcherServlet
MVC是现在非常流行一种web应用架构,Spring框架在启动IOC容器时在DispatcherSevlet类里的Onrefresh()方法实现了MVC的九大组件的初始化策略:
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context)
initStrategies(context);
....
初始化策略如下: 多文件上传、国际化、主题、处理器映射、处理器适配器、处理器异常解决方案、请求转换为视图转换器、视图解析器、Flashmap管理器。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context)
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
上述流程执行完毕后,Web应用的启动流程就基本结束了,最后把WebApplicationContext放入到ServletContext上下文里使用。
if (this.publishContext)
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled())
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
也就是在初始化的时候,先去找从ServletContext里去拿WebApplicationContext,如果没有拿到,那么再去createWebApplicationContext。

web容器初始化完毕后,WebApplicationContext也具有了Servlet相关的特性。
二、 Spring IOC容器的启动原理分析
从上述代码中可以发现,在启动web应用时,会伴随着IOC容器的启动,我们都知道Spring框架的核心是IOC,IOC简单的讲就是讲对象的管理和依赖交给Spring去管理,其实Spring的IOC容器真正启动的时候是在调用AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()方法结束后,refresh()方法包含了Spring IOC容器启动的所有流程。
 refresh()方法在AbstractApplicationContext类里有具体的实现:
refresh()方法在AbstractApplicationContext类里有具体的实现:
 refresh()方法源代码:
refresh()方法源代码:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
catch (BeansException ex)
if (logger.isWarnEnabled())
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
finally
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
IOC容器的启动是也就意味着Spring应用的启动成功,我们才能从IOC容器中拿到Bean。
二、Spring Boot 应用启动原理分析
Spring本身是一个低侵入、可扩展的轻量级框架,现在最流行的Springboot 框架也是基于Spring实现的。
可以从main()方法找到boot的启动路线以及原理, 进入到SpringApplication.run(String... args)方法:

我们可以发现最终调用到了AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()方法, 如下:

由此可见,Springboot一方面帮我们的开发简化了很多配置上的工作,另一方面具备Spring 框架所有的功能。
以上是关于从Servlet开始谈Spring框架的启动原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章