DataBinding的双向绑定实现原理
Posted 一代小强
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了DataBinding的双向绑定实现原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
“ 悄悄咪咪告诉你,DataBinding是怎么实现双向绑定的“
在讲DataBinding之前,有必要讲讲ViewBinding
1、ViewBinding
1) 配置
要使用ViewBinding,只需要在gradle 添加如下配置即可
android {
...
viewBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
如果需要在生成绑定类时忽略某个布局文件,请将 tools:viewBindingIgnore=“true” 属性添加到相应布局文件的根视图中:
<LinearLayout
...
tools:viewBindingIgnore="true" >
...
</LinearLayout>
2)用法
在创建xml文件后,Android Studio会自动创建对应的类,类名格式为:XML 文件的名称转换为驼峰式大小写,并在末尾添加Binding一词。
比如,创建了一个activity_view.xml
<LinearLayout
...>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/viewBindingView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="20dp" />
</LinearLayout>
生成的绑定类就叫做ActivityViewBinding,然后在对应的activity中使用布局绑定
public class ViewBindingActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActivityViewBinding activityViewBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 初始化布局和view
activityViewBinding = ActivityViewBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
// 设置contentView
setContentView(activityViewBinding.getRoot());
// 获取到id为viewBindingView的textView,并设置文本
activityViewBinding.viewBindingView.setText("你好,我是viewBinding");
}
}
3) 原理
在build之后,会在如下路径生成对应的类
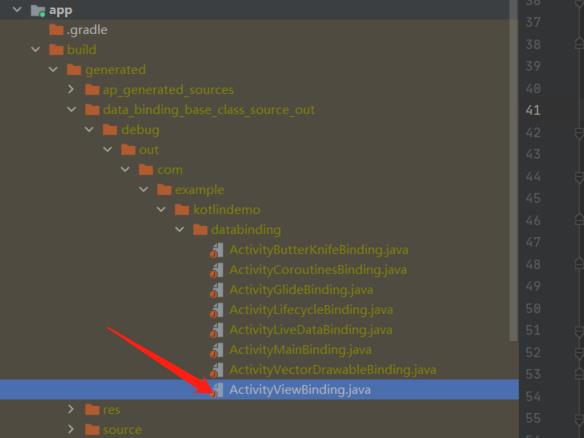
生成如下代码
public final class ActivityViewBinding implements ViewBinding {
@NonNull
private final LinearLayout rootView;
// 通过遍历xml,找到声明id了的view,id作为变量名
@NonNull
public final TextView viewBindingView;
private ActivityViewBinding(@NonNull LinearLayout rootView, @NonNull TextView viewBindingView) {
this.rootView = rootView;
this.viewBindingView = viewBindingView;
}
@Override
@NonNull
public LinearLayout getRoot() {
return rootView;
}
// 传入LayoutInflater,用于获取对应布局的view
@NonNull
public static ActivityViewBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater) {
return inflate(inflater, null, false);
}
@NonNull
public static ActivityViewBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable ViewGroup parent, boolean attachToParent) {
// 通过指定的布局获取到rootView
View root = inflater.inflate(R.layout.activity_view, parent, false);
if (attachToParent) {
parent.addView(root);
}
return bind(root);
}
// 核心代码,通过代码模板,找到对应的view
@NonNull
public static ActivityViewBinding bind(@NonNull View rootView) {
int id;
missingId:
{
id = R.id.viewBindingView;
TextView viewBindingView = rootView.findViewById(id);
if (viewBindingView == null) {
break missingId;
}
return new ActivityViewBinding((LinearLayout) rootView, viewBindingView);
}
String missingId = rootView.getResources().getResourceName(id);
throw new NullPointerException("Missing required view with ID: ".concat(missingId));
}
}
生成的类通过LayoutInflater获取布局,然后依次初始化view。
2、DataBinding
1)配置
DataBinding 跟ViewBinding一样,只需要在gradle中添加如下配置即可
android {
...
dataBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
2)用法
我们先看activity_main.xml布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="video"
type="com.example.databinding.VideoBean" />
</data>
<LinearLayout xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/bind_text1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@{video.title}" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bind_text2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(video.score + 1)}" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
与正常的xml布局不一样的是,DataBinding 以layout作为第一层。第二层分别是 data和view的根布局。
其中data下的name作为对象,type为类路径名
package com.example.databinding;
public class VideoBean {
public String title;
public int score;
public VideoBean(String title, int score) {
this.title = title;
this.score = score;
}
}
然后在布局中就可以把对象的属性值显示到TextView上
<TextView
...
android:text="@{video.title}" />
在对应的activity中,使用的方式与ViewBinding类似
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActivityMainBinding mainBinding;
private VideoBean video;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 获取对应的binding类
mainBinding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
setContentView(mainBinding.getRoot());
video = new VideoBean("小黄人", 8);
// 设置对应的数据
mainBinding.setVideo(video);
// 设置周期监听,可选
mainBinding.setLifecycleOwner(this);
}
}
全程我们没有初始化对应的view,只是获取bean,然后更新一下即可

当然,我们也可以在布局中添加对应的事件响应
<Button
android:id="@+id/bind_text2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:onClick="@{video::increaseScore}"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(video.score + 1)}" />
在类中添加 increaseScore方法,如下所示,即可实现点击button修改score的值,并更新ui。
public class VideoBean extends BaseObservable {
public String title;
// 声明该属性是可绑定监听的
@Bindable
public int score;
public VideoBean(String title, int score) {
this.title = title;
this.score = score;
}
public void increaseScore(View view) {
score++;
// 通知score属性变化了
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.score);
}
}
我们只需要修改少量代码即可实现双向绑定,接下来将会讲解对应的原理。
更多见布局和绑定表达式
3)原理
view的初始化
生成的类路径与ViewBinding一样,直接看看对应的类
// 抽象类
public abstract class ActivityMainBinding extends ViewDataBinding {
@NonNull
public final Button bindText2;
@Bindable
protected VideoBean mVideo;
protected ActivityMainBinding(Object _bindingComponent, View _root, int _localFieldCount,
TextView bindText1, Button bindText2) {
super(_bindingComponent, _root, _localFieldCount);
this.bindText1 = bindText1;
this.bindText2 = bindText2;
}
// 把data下的参数都声明了get/set方法
public abstract void setVideo(@Nullable VideoBean video);
@Nullable
public VideoBean getVideo() {
return mVideo;
}
@NonNull
public static ActivityMainBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater) {
return inflate(inflater, DataBindingUtil.getDefaultComponent());
}
@NonNull
@Deprecated
public static ActivityMainBinding inflate(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable Object component) {
return ViewDataBinding.<ActivityMainBinding>inflateInternal(inflater, R.layout.activity_main, null, false, component);
}
...
}
这里的ActivityMainBinding 继承了ViewDataBinding,但是内部却没有类似ViewBinding那样,直接通过findViewById方式初始化我们需要的view,那这些view是怎么来的?
这个问题我们先放一放,上面的inflate方法调用了ViewDataBinding的inflateInternal 方法
public abstract class ViewDataBinding extends BaseObservable implements ViewBinding {
...
protected static <T extends ViewDataBinding> T inflateInternal(
@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutId, @Nullable ViewGroup parent,
boolean attachToParent, @Nullable Object bindingComponent) {
return DataBindingUtil.inflate(
inflater,
layoutId,
parent,
attachToParent,
checkAndCastToBindingComponent(bindingComponent)
);
}
}
来到DataBindingUtil 这个工具类
public class DataBindingUtil {
private static DataBinderMapper sMapper = new DataBinderMapperImpl();
public static <T extends ViewDataBinding> T inflate(
@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutId, @Nullable ViewGroup parent,
boolean attachToParent, @Nullable DataBindingComponent bindingComponent) {
final boolean useChildren = parent != null && attachToParent;
final int startChildren = useChildren ? parent.getChildCount() : 0;
final View view = inflater.inflate(layoutId, parent, attachToParent);
if (useChildren) {
return bindToAddedViews(bindingComponent, parent, startChildren, layoutId);
} else {
// activity里面传的parent为null ,所以会走这里
return bind(bindingComponent, view, layoutId);
}
}
static <T extends ViewDataBinding> T bind(DataBindingComponent bindingComponent, View root,
int layoutId) {
return (T) sMapper.getDataBinder(bindingComponent, root, layoutId);
}
}
DataBinderMapperImpl 的实现如下
package androidx.databinding;
public class DataBinderMapperImpl extends MergedDataBinderMapper {
DataBinderMapperImpl() {
// 将impl添加到mMappers中
addMapper(new com.example.databinding.DataBinderMapperImpl());
}
}
// 对应的基类
public class MergedDataBinderMapper extends DataBinderMapper {
....
@Override
public ViewDataBinding getDataBinder(DataBindingComponent bindingComponent, View view,
int layoutId) {
// 遍历 mMappers
for(DataBinderMapper mapper : mMappers) {
ViewDataBinding result = mapper.getDataBinder(bindingComponent, view, layoutId);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
if (loadFeatures()) {
return getDataBinder(bindingComponent, view, layoutId);
}
return null;
}
}
那就看看com.example.databinding.DataBinderMapperImpl 的实现
public class DataBinderMapperImpl extends DataBinderMapper {
private static final int LAYOUT_ACTIVITYMAIN = 1;
private static final SparseIntArray INTERNAL_LAYOUT_ID_LOOKUP = new SparseIntArray(1);
static {
// 保存我们创建的layout与 index的映射
INTERNAL_LAYOUT_ID_LOOKUP.put(com.example.databinding.R.layout.activity_main, LAYOUT_ACTIVITYMAIN);
}
@Override
public ViewDataBinding getDataBinder(DataBindingComponent component, View view, int layoutId) {
// 通过layoutId,获取到index,上面传的是R.layout.activity_main,
// 所以这里localizedLayoutId为LAYOUT_ACTIVITYMAIN
int localizedLayoutId = INTERNAL_LAYOUT_ID_LOOKUP.get(layoutId);
if(localizedLayoutId > 0) {
// 获取到TAG,上面的代码没有设置tag的地方,但是通过debug得知对应的tag为"layout/activity_main_0"
final Object tag = view.getTag();
if(tag == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("view must have a tag");
}
switch(localizedLayoutId) {
case LAYOUT_ACTIVITYMAIN: {
if ("layout/activity_main_0".equals(tag)) {
return new ActivityMainBindingImpl(component, view);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The tag for activity_main is invalid. Received: " + tag);
}
}
}
return null;
}
...
}
至于view的tag是怎么来的,笔者猜测是Android Studio自动添加的
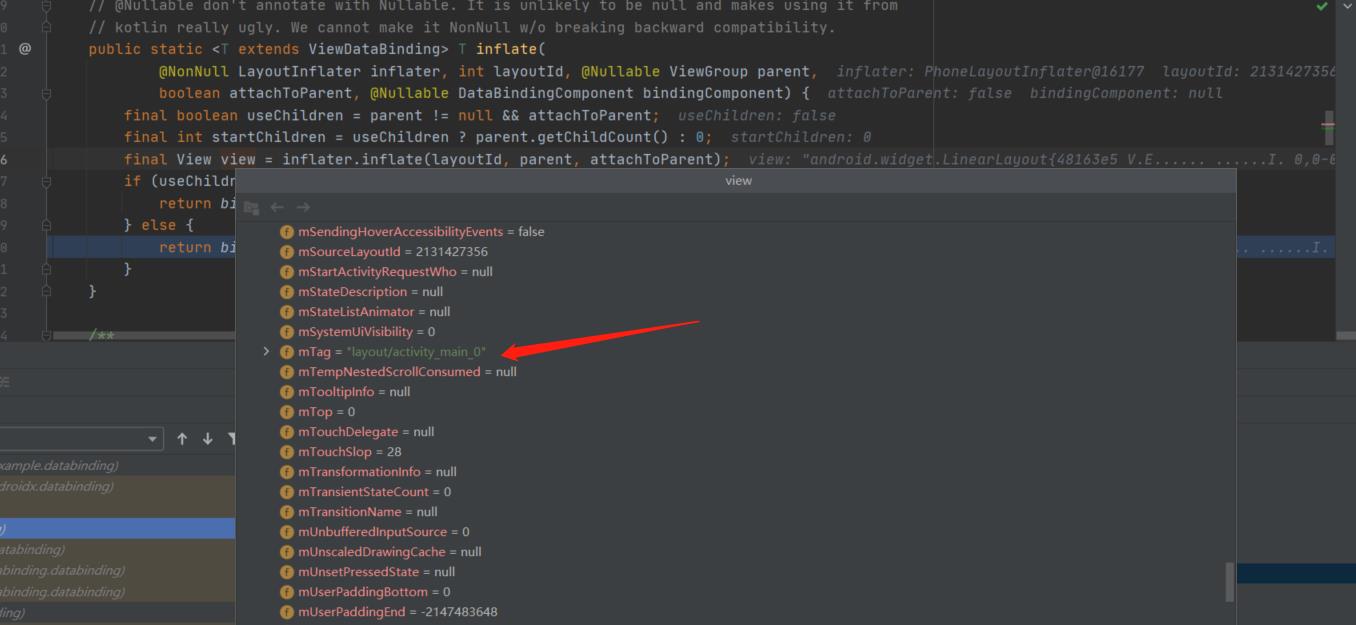
最终我们获取到了ActivityMainBindingImpl的实例,对应实现如下
public class ActivityMainBindingImpl extends ActivityMainBinding {
@Nullable
private static final androidx.databinding.ViewDataBinding.IncludedLayouts sIncludes;
@Nullable
private static final android.util.SparseIntArray sViewsWithIds;
static {
sIncludes = null;
sViewsWithIds = null;
}
// views
@NonNull
private final android.widget.LinearLayout mboundView0;
// listeners
private OnClickListenerImpl mVideoIncreaseScoreAndroidViewViewOnClickListener;
// Inverse Binding Event Handlers
public ActivityMainBindingImpl(@Nullable androidx.databinding.DataBindingComponent bindingComponent, @NonNull View root) {
// 通过mapBindings方法获取view的数组
this(bindingComponent, root, mapBindings(bindingComponent, root, 3, sIncludes, sViewsWithIds));
}
private ActivityMainBindingImpl(androidx.databinding.DataBindingComponent bindingComponent, View root, Object[] bindings) {
// 调用super即ActivityMainBinding的构造函数初始化view
super(bindingComponent, root, 0
, (android.widget.TextView) bindings[1]
, (android.widget.Button) bindings[2]
);
this.bindText1.setTag(null);
this.bindText2.setTag(null);
this.mboundView0 = (android.widget.LinearLayout) bindings[0];
this.mboundView0.setTag(null);
setRootTag(root);
invalidateAll();
}
...
public void setVideo(@Nullable com.example.databinding.VideoBean Video) {
this.mVideo = Video;
synchronized(this) {
mDirtyFlags |= 0x1L;
<以上是关于DataBinding的双向绑定实现原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章