MySQL基础之子查询
Posted nuist__NJUPT
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL基础之子查询相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
mysql基础之子查询
子查询:出现在其它语句中的select语句,我们都称为子查询或者内查询。
外部的查询语句称为主查询或者外查询。
一、where后面的子查询
1-单行子查询
查询比Abel工资高的员工信息:
#查询比Abel工资高的员工信息
select *
from employees
where salary > (
select salary
from employees
where last_name = 'Abel');
返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比143号员工多的员工姓名,job_id和工资:
#返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比143号员工多的员工姓名,job_id和工资
select last_name, job_id, salary
from employees
where job_id = (
select job_id
from employees
where employee_id = 141)
and salary > (
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 143);
返回工资最少的员工的last_name,job_id,salary:
#返回工资最少的员工的last_name,job_id,salary
select last_name, job_id, salary
from employees
where salary = (
select min(salary)
from employees
);
查询最低工资大于50号部门最低工资的部门id和其最低工资:
#查询最低工资大于50号部门最低工资的部门id和其最低工资
select department_id, min(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
having min(salary) > (
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = 50);
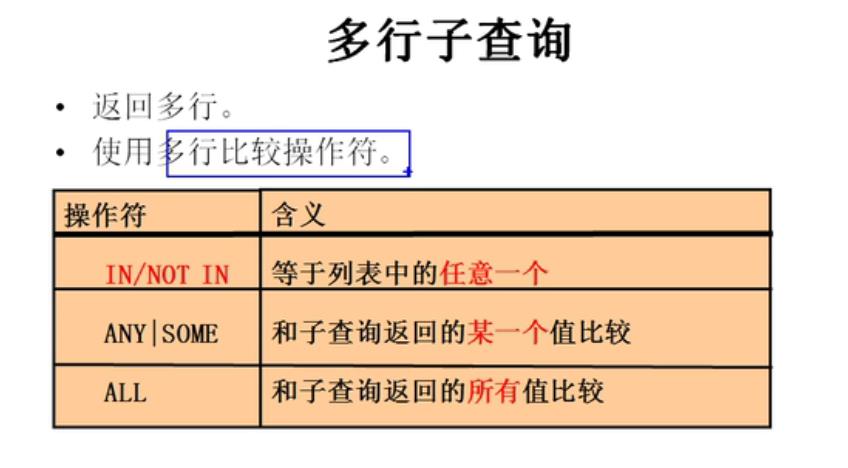
2-多行子查询
多行子查询需要搭配多行操作符来使用
in:等于列表中任意一个
not in:列表中一个都不等于
any/some:列表中任意一个满足就可以
all:列表中的所有的都要满足才可以
in 和 =any一个意思
not in 和 <>all一个意思
返回location_id是1400或者1700的部门中所有员工姓名:
#返回location_id是1400或者1700的部门中所有员工姓名
select last_name
from employees
where department_id in(
select department_id
from departments
where location_id in(1400,1700));
查询其它工种中比job_id为’IT_PROG’工种任一工资低的员工号,姓名,工种,工资:
#查询其它工种中比job_id为'IT_PROG'工种任一工资低的员工号,姓名,工种,工资
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, salary
from employees
where salary < any(
select distinct salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG') and
job_id <> 'IT_PROG';
也可以写成这种:
#查询其它工种中比job_id为'IT_PROG'工种任一工资低的员工号,姓名,工种,工资
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, salary
from employees
where salary < (
select max(salary)
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG') and
job_id <> 'IT_PROG';
3-行子查询
查询员工编号最小且工资最高的员工信息:
#查询员工编号最小且工资最高的员工信息
select *
from employees
where (employee_id,salary)=(
select min(employee_id), max(salary)
from employees);
二、select后面的子查询
仅仅支持标量子查询
#查询每个部门的员工个数
select d.*, (
select count(*)
from employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id)
from departments d;
查询员工号为102的部门名:
#查询员工号为102的部门名
select (
select department_name
from departments d inner join employees e on
d.department_id = e.department_id
where employee_id = 102) 部门名;
三、from后面的子查询
将子查询的结果当作一张表,要求必须起别名。
四、exists后面的子查询()相关子查询
exists(完整查询语句):结果为0或者1
#查询有员工的部门名:
#查询有员工的部门名
select department_name
from departments d
where exists(
select *
from employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id);
查询没有女朋友的男神信息:
#查询没有女朋友的男神信息
select bo.*
from boys bo
where not exists(
select boyfriend_id
from beauty
where beauty.boyfriend_id = bo.id);
测试题
查询和Alotkey相同部门的员工姓名和工资:
#查询和Zlotkey相同部门的员工姓名和工资
select last_name, salary
from employees
where department_id = (
select department_id
from employees
where last_name = 'Zlotkey');
查询比公司平均工资高的员工的员工号,姓名和平均工资:
#查询比公司平均工资高的员工的员工号,姓名和平均工资
select employee_id, last_name, avg(salary)
from employees
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees);
以上是关于MySQL基础之子查询的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章