js数据结构学习双链表 集合
Posted lin-fighting
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了js数据结构学习双链表 集合相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
双链表
单链表明显的缺点就是寻找上一个节点的时候太麻烦,需要从头遍历。
双向链表既可以从头遍历到尾也可以从尾遍历到头,也可以解决单向链表的缺点。
缺点:
插入和删除的时候需要处理四个指针,比较复杂。
比起单向链表,占用内存肯定稍微大一点。
但是其与方便程度相比,是微不足道的。
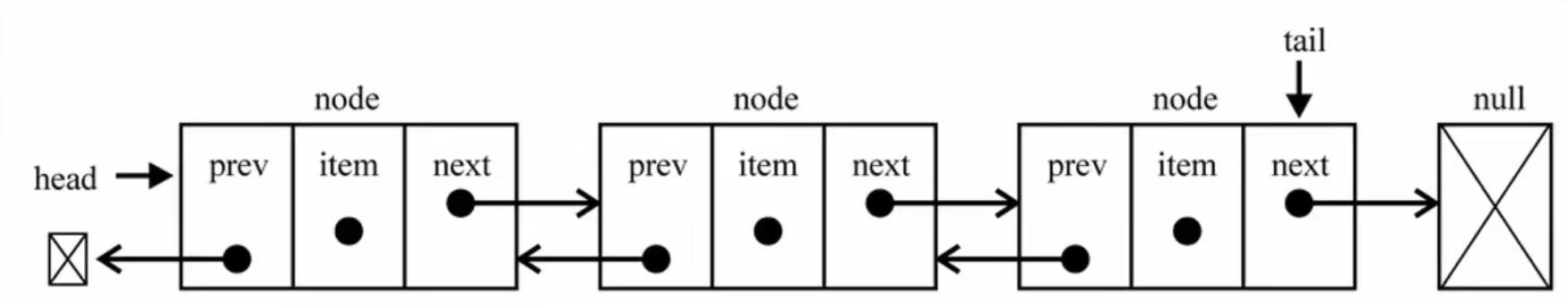
特点:
有头指针和尾指针指向链表的第一个和最后一个节点
每个节点有三部分,data,pre,next
第一个节点的pre为null
最后一个节点的next为null。
实现:
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
//头指针
this.head = null;
//尾指针
this.tail = null;
//链表的长度
this.length = 0;
}
append(data) {
const element = new Node(data);
if (this.head) {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
//双向连接
element.prev = current;
current.next = element;
this.tail = element;
} else {
//第一个
this.head = element;
this.tail = element;
}
this.length++;
}
// //特定位置插入
insert(position, data) {
const element = new Node(data);
if (
typeof position !== "number" ||
position < 0 ||
position > this.length
) {
return false;
}
if (this.length === 0) {
//链表原来为空
this.head = element;
this.tail = element;
} else if (position === 0) {
//第一位
this.head.prev = element;
element.next = this.head;
this.head = element;
} else if (position === this.length) {
//最后一个
this.tail.next = element
element.prev = this.tail
this.tail = element
} else {
let index = 0;
let current = this.head;
//找到插入位置的上一个节点,如postion为2,这个位置的上个节点就是1
while (index++ < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
}
//修改四个节点
let nextElement = current.next; //把原来的第二的节点保存起来
nextElement.prev = element;
element.next = nextElement;
element.prev = current;
current.next = element;
}
this.length++;
return true
}
// //获取对应位置的元素
get(position) {
if (
typeof position !== "number" ||
position < 0 ||
position >= this.length
) {
return false;
}
let index = 0
let current = this.head
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
return current.data
}
// //返回元素在列表中的索引
indexOf(data) {
let index = 0
let current = this.head
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
return index
}
current = current.next
index++
}
return -1
}
// //修改某个位置的元素
update(position, data) {
if (
typeof position !== "number" ||
position < 0 ||
position >= this.length
) {
return false;
}
let index = 0
let current = this.head
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
current.data = data
return true
}
// //从列表的特定位置移除一项
removeAt(position) {
if (
typeof position !== "number" ||
position < 0 ||
position >= this.length
) {
return false;
}
if (this.length === 1) {
//只有一个
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else if (position === 0) {
//删除第一个
this.head.next.prev = null
this.head = this.head.next
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {
//删最后一个
this.tail.prev.next = null
this.tail = this.tail.prev
} else {
let index = 0
let current = this.head
while (index++ < position) { //找到当前位置的节点
current = current.next
}
current.prev.next = current.next
current.next.prev = current.prev
}
this.length--
return true
}
// 从列表移除一项
remove(element) {
if (!this.length) {
return false
} else if (this.length === 1) {
//列表只有一个,且相等
if (this.head.data === element) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
return false
}
} else if (this.tail.data === element) {
//最后一个相等
this.tail.prev.next = null
this.tail = this.tail.prev
} else {
let current = this.head
let isRemove = false
while (current) {
if (current.data === element) {
current.prev.next = current.next
current.next.prev = current.next
isRemove = true
break;
}
current = current.next
}
if (!isRemove) {
return false
}
}
this.length--
return true
}
isEmpty() {
return !!this.length;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
forwardString() {
let current = this.head;
let str = "";
while (current) {
str += `,${current.data.toString()}`;
current = current.next;
}
return str.slice(1);
}
backwardString() {
let current = this.tail;
let str = "";
while (current) {
str += `,${current.data.toString()}`;
current = current.prev;
}
return str.slice(1);
}
}
const test = new LinkedList();
test.append("FBA");
test.append("CBA");
test.insert(0, "NBA");
test.insert(0, "DDD");
test.insert(0, "EEE");
test.remove('CBA')
test.remove('NBA')
console.log(test.forwardString());
跟单链表的实现流程差不多,不同的是要兼顾this.tail的处理,如增加或者删除的时候,要注意this.tail是否需要变化。而且处理的指针也多了两个左右。但是实现思路不是很难,如上。
集合
集合是由一组无序的,不能重复的元素构成。
es6其实已经实现了Set集合类。(js中的Set是有序集合)
具体可以了解:集合
这里我们从头简单封装下Set集合类。
这里基于object封装。
class Set{
constructor(){
this.items = {}
}
add(val){
if(this.has(val)){
return false
}
this.items[val] = val
return true
}
remove(val){
if(!this.has(val)){
return false
}
delete this.items[val]
return true
}
has(val){
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(val)
}
clear(){
this.items = {}
return true
}
size(){
return Object.keys(this.items).length
}
values(){
return Object.values(this.items)
}
}
const test = new Set()
test.add('NBA')
test.add('CBA')
test.add('FBA')
console.log(test.values());
test.remove('CBA')
test.add('MBA')
console.log(test.items);
set的封装完成。这里是基于对象封装的。
集合间操作
并集 A+B
交集 A跟B共有
差集 A有B没有
子集
实现
//并集
//并集
union(otherSet){
const newSet = new Set()
//将老集合的加到新集合中
this.values().forEach(item=>{
newSet.add(item)
})
console.log(newSet);
// 将其他集合加到集合中
otherSet.values().forEach(item=>{
if(!newSet.has(item)){
newSet.add(item)
}
})
return newSet
}
//交集
intersection(otherSet){
const newSet = new Set()
// 遍历1,判断存在2吗,存在即交集
this.values().forEach(item=>{
if(otherSet.has(item)){
newSet.add(item)
}
})
return newSet
}
//差集
difference(otherSet){
const newSet = new Set()
// 遍历1,判断存在2吗,存在即交集
this.values().forEach(item=>{
if(!otherSet.has(item)){
newSet.add(item)
}
})
return newSet
}
son(otherSet){
let isSon = true
//遍历子集合,判断是否有一个没在父集合中
otherSet.values().forEach(item=>{
if(!this.has(item)){
isSon = false
}
})
return isSon
}
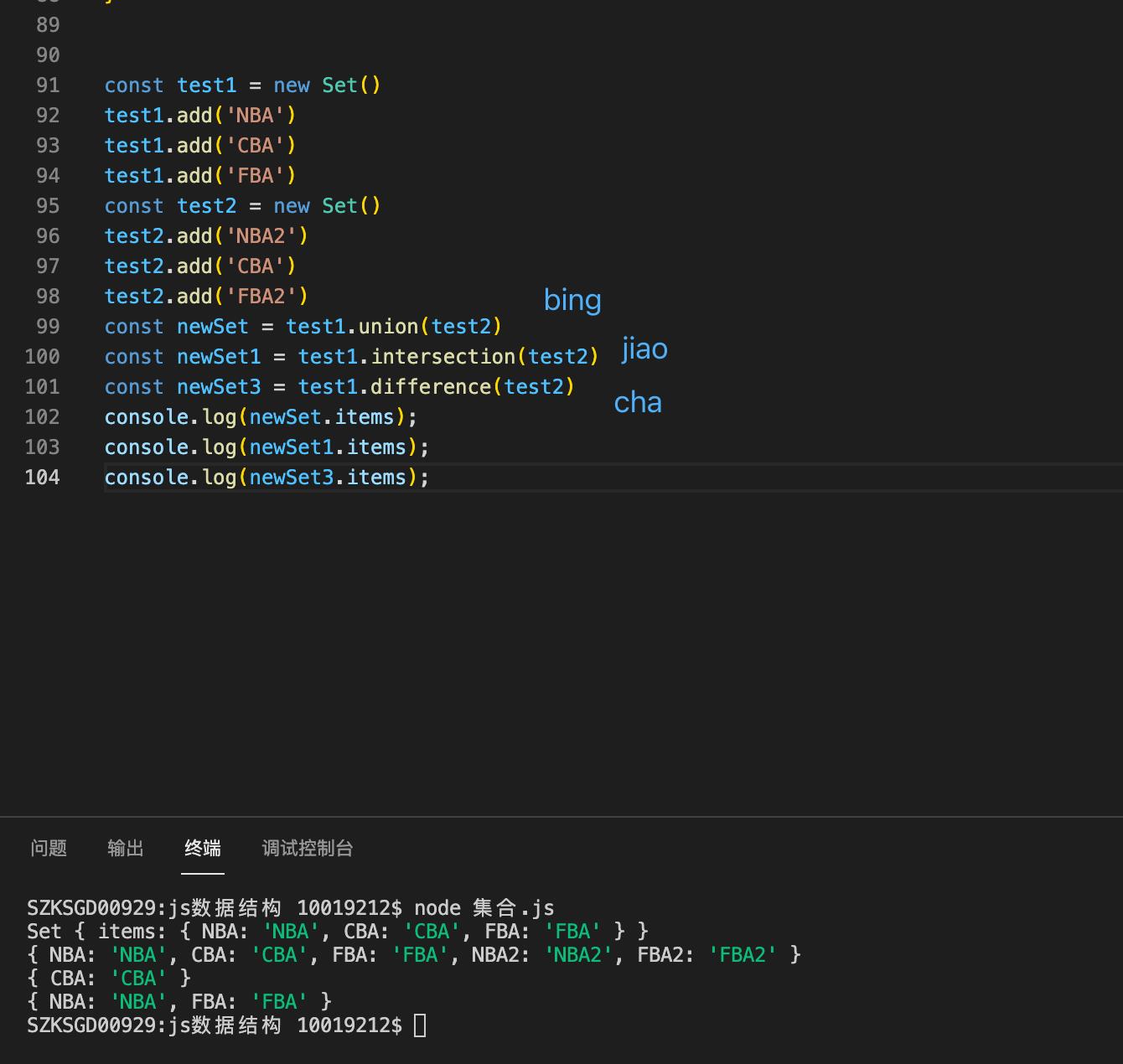
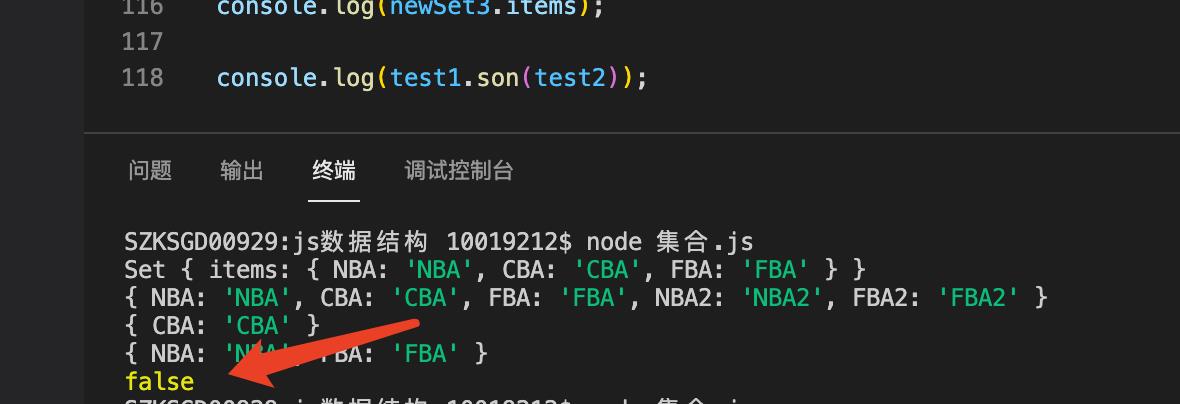
集合就实现完毕了。
以上是关于js数据结构学习双链表 集合的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章