利用卷积神经网络实现手写字识别
Posted Jeaten
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了利用卷积神经网络实现手写字识别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文我们介绍一下卷积神经网络,然后基于pytorch实现一个卷积神经网络,并实现手写字识别
卷积神经网络介绍
传统神经网络处理图片问题的不足
让我们先复习一下神经网络的工作流程:
- 搭建一个神经网络
- 将要训练的数据(如图片)转换为神经网络能够识别的向量
- 训练神经网络并实现预测
然而,以上过程中,如果训练的是图片,而图片非常大(像素),则将图片转换成向量后的向量的维度将会非常大,这样会导致在训练网络的时候所需的神经元非常多,需要涉及到非常多参数的更新,也就导致了训练效果不好。
计算机中,图片是以矩阵的形式存的,以我们实验数据集mnist中的手写字为例:
一张手写字 0 的图片为:
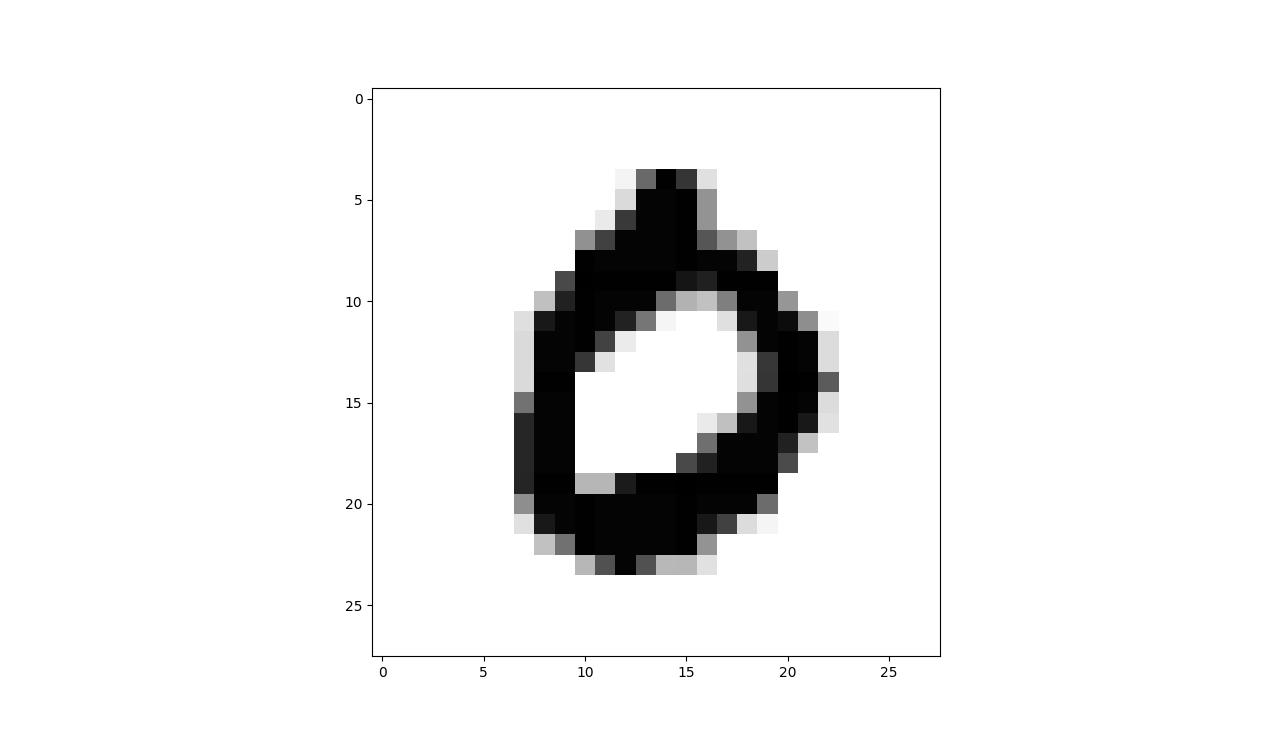
与其对应的像素矩阵(其中每个位置的值表示像素值)为:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 11 150 253 202 31 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 251 251 253 107 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 21 197 251 251 253 107 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 110 190 251 251 251 253 169 109 62 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 253 251 251 251 251 253 251 251 220 51 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 182 255 253 253 253 253 234 222 253 253 253 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 63 221 253 251 251 251 147 77 62 128 251 251 105 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32 231 251 253 251 220 137 10 0 0 31 230 251 243 113 5 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 251 251 253 188 20 0 0 0 0 0 109 251 253 251 35 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 251 251 201 30 0 0 0 0 0 0 31 200 253 251 35 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37 253 253 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32 202 255 253 164 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 140 251 251 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 109 251 253 251 35 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 217 251 251 0 0 0 0 0 0 21 63 231 251 253 230 30 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 217 251 251 0 0 0 0 0 0 144 251 251 251 221 61 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 217 251 251 0 0 0 0 0 182 221 251 251 251 180 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 218 253 253 73 73 228 253 253 255 253 253 253 253 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 113 251 251 253 251 251 251 251 253 251 251 251 147 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 31 230 251 253 251 251 251 251 253 230 189 35 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 62 142 253 251 251 251 251 253 107 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 72 174 251 173 71 72 30 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
mnist数据集是一个非常小的数据集,每个图片的像素仅有28*28维,而我们经常遇到的图片比这个可大了多了。
同时,还有一个问题不容忽视:一张图片中的像素并不是每个像素点都是一样的,以我们图中的手写体0为例,仅仅黑的有手写的部分是有用的,而别的白的地方是没有用的。
给一张高清图,即使把它压缩到非常小也不影响我们对图中信息的判断。
因此,我们可否让计算机像人一样,只去处理一些关键的信息,而不用把所有的信息全处理了呢。
答案当然是肯定的,不过我们先不着急去想怎么做,而是看一下下一部分的趣图 —— 矩阵运算。
卷积神经网络
矩阵运算 —— 卷积运算
我们都知道矩阵可以相乘,给定一个大矩阵,我们可以用其中的子矩阵与给定的矩阵做内积(矩阵相乘后相加),将会得到一个较小的矩阵,如下图所示:
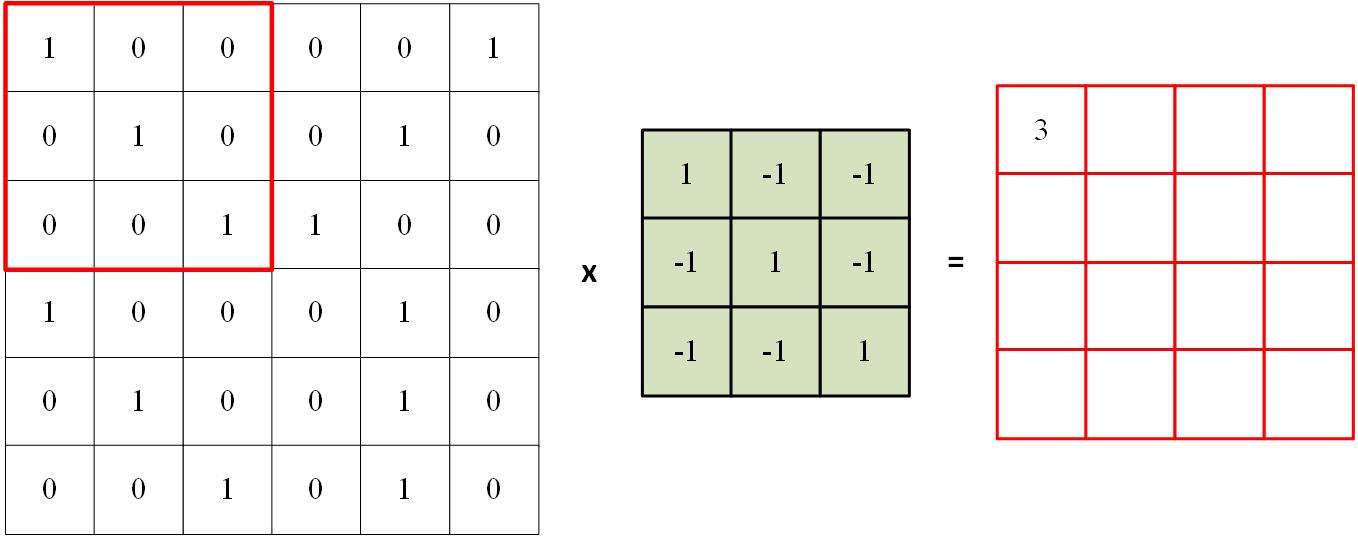
通过以上的处理,一个很大的矩阵变为较为小的矩阵。当然,给定一个非常大图片的像素矩阵,我们同样可以进行这样的操作,这样就能使得原始较大的矩阵得到压缩。
我们可以将这种操作操作叫卷积或特征提取
数据降维—— 池化操作
虽然经过以上的操作,原始较大的矩阵被处理为了较小的矩阵,但还是相对比较大,毫无疑问,我们可以将其继续进行卷积操作以得到维度更小的矩阵。但这样显得太麻烦了,我们可以采取更简单的方法:
将矩阵分成几大块,取其中大块中小块值中的最大值或所有小块值的平均值作为更小矩阵的值:
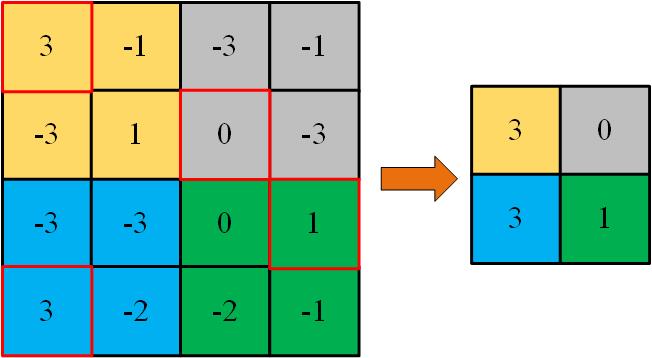
- 取最大值的叫最大池化
- 取平均值的叫平均池化
其实,就是在做降维操作,也许子采样(Subsampling)的名字更适合
输入神经网络 —— flatten
经过以上两步的处理,原始高维度数据的信息将会得到降低,实在不行,多进行以上两种操作就行了。
但还有一个事实,处理后我们的数据还是图片或者其他维的矩阵,并不能直接输入到神经网络中加以运算。
一个可以的操作:将最终的低维矩阵转换成一维的数据(掰平 – flatten)。
然后就可以输入到神经网络中进行运算运算了。关于神经网络的运算,不懂得可以看博主之前得博客。
所以,总结一下:
- 卷积神经网络是卷积加神经网络的结合,卷积部分主要包括卷积、池化、flatten等操作 —— 提取特征,然后供神经网络进行运算
关于神经网络部分,这里不再赘述,不懂的可以看机器学习专栏关于神经网络的文章
卷积神经网络实现及手写字识别
- 从http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/下载,下载后将文件解压
- 将
main函数中的path改为下载文件的存储路径即可
如果对数据集有问题,可以私信博主
关于实现:
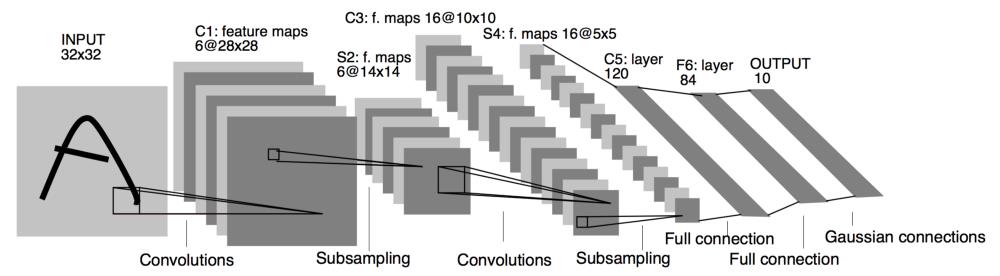
- 使用经典的
LeNet-5结构(激活函数等有所不同):
- 基于
pytorch实现,包括神经网络的构建,激活函数的选择 - 归一化使用了像素值
/255的方式实现,可以尝试用别的方式进行归一化处理
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch import nn
class Data:
'''
this class is about data module
'''
def __init__(self):
self.start_loc_image=16 # the start location of image data
self.start_loc_label=8 # the start location of label data
self.num_pixel=28*28 # the number of pixels
self.choice={'train-image':'train-images.idx3-ubyte','train-label':'train-labels.idx1-ubyte',
'test-image':'t10k-images.idx3-ubyte','test-label':'t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte'} # the specific file name
def get(self,path,train_test='',image_label=''):
'''
get the data from the file whose path is "path"
:param path: the saving path of given files, default is "./file/"
:param train_test: the data category("train" or "test")
:param image_label: the data information("image" or "label")
:return: the data you want
'''
if train_test not in ['train','test'] or image_label not in ['image','label']:raise NameError(
'please check you spelling,"train_test" can be "train/test", "image_label" can be "image/label"')
ch=train_test+'-'+image_label
data=[]
if image_label=='image':
print('loading images ...')
with open(path+self.choice[ch],'rb',) as f:
file=f.read()
for i in range(self.start_loc_image,file.__len__(),self.num_pixel):
item=[]
pixel=file[i:i+self.num_pixel].hex()
for p in range(0,pixel.__len__(),2):
item.append(int(pixel[p:p+2],16)) # decode -> get the pixel information from original file
data.append(self.transform2image(item))
f.close()
elif image_label=='label':
print('load labels ...')
with open(path+self.choice[ch],'rb',) as f:
file=f.read()
for i in range(self.start_loc_label,file.__len__()):
data.append(file[i]) # decode -> get the label from original file
f.close()
return data
def transform2image(self,data:list):
'''
transform pixel point to image
:param data: the original 1D pixel points
:return: transformed image(28*28)
'''
assert data.__len__()==784
import numpy as np
return [np.reshape(data,(28,-1))]
def transfer_tensor(self,data):
'''
transfer data to tensor format
:param data: the original input data
:return: transferred data
'''
return torch.tensor(data)
def normalize(self,data,maximum=255):
'''
normalize the data with maximum
:param data: the input data
:param maximum: the maximum of pixel(is 255)
:return: normalized data
'''
return torch.div(data,maximum)
class Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
'''
the corresponding parameters
'''
self.channel_input = 1 # the channel of input data
self.size_kernel=5 # the size of kernel
self.len_padding=2 # the length of kernel
self.channel_c1=6 # the channel of convolution1
self.channel_c2=16 # the channel of convolution2
self.len_flatten=120 # the length of flatten data
self.len_hidden=84 # the length of hidden layer
self.len_out=10 # the length of final output
super(Network, self).__init__()
self.c1=nn.Conv2d(self.channel_input,self.channel_c1,kernel_size=self.size_kernel,padding=self.len_padding)
self.c2=nn.Conv2d(self.channel_c1,self.channel_c2,kernel_size=self.size_kernel)
self.fc1=nn.Linear(self.channel_c2*5*5,self.len_flatten)
self.fc2=nn.Linear(self.len_flatten,self.len_hidden)
self.fc3=nn.Linear(self.len_hidden,self.len_out)
### other parameters
self.learning_rate=0.01 # learning rate
self.optimizer=optim.SGD(self.parameters(),lr=self.learning_rate)
def forward(self,x):
'''
calculate the output
:param x: input vector
:return: output
'''
out_c1=self.c1(x)
out_sub1=nn.MaxPool2d(2)(out_c1)
out_c2=self.c2(out_sub1)
out_sub2=nn.MaxPool2d(2)(out_c2)
out_flatten=out_sub2.view(x.size(0), -1)
out_full_con1=self.fc1(out_flatten)
out_full_con2=self.fc2(out_full_con1)
out=self.fc3(out_full_con2)
return out
def accuracy(self,act,pre):
'''
calculate the accuracy
:param act: actual value
:param pre: predicted value
:return: accuracy
'''
assert act.__len__()==pre.__len__()
return round((act==pre).sum().item()/act.__len__(),3)
def pre_process(self,feature,label):
'''
pre processing
:param feature: feature
:param label: label
:return: preprocessed feature and label
'''
### transform to the format of tensor
feature=dat.transfer_tensor(feature)
feature=dat.normalize(feature)
label=dat.transfer_tensor(label)
return feature,torch.tensor(label,dtype=torch.int64)
def per_train(self,epoch,feature,label,validation=0.2,batch=50,verbose=True,num_view=5):
'''
train neural network
:param epoch: training times
:param feature: feature
:param label: label
:param validation: for using evaluation
:param batch: batch size
:param verbose: whether view the training process or not
:param num_view: view via training "num_view" times
:return: none
'''
assert feature.__len__()==label.__len__()
print('training neural network ...')
fea,lab=self.pre_process(feature,label)
len_train=int(feature.__len__()*(1-validation))
data_train,label_train=fea[:len_train+1],lab[:len_train+1]
data_train=[data_train[i:i+batch]for i in range(0,len_train,batch)]
label_train=[label_train[i:i+batch]for i in range(0,len_train,batch)<以上是关于利用卷积神经网络实现手写字识别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章