C++初阶string(上)
Posted Huang_ZhenSheng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++初阶string(上)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文中的string类的常用接口可以查询相关的文档进行查看:文档查询,暂不做具体的介绍
目录
一,string类对象的访问及遍历操作
template<class T>
class basic_string
{
public:
private:
T* _a;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello");
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
//第一种遍历方式
for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
s2[i] += 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i] << endl;
}
//第二种遍历方式
for (auto& ch : s2)
{
ch -= 1;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s2)
{
cout << ch << "";
}
cout << endl;
//第三种遍历方式
//迭代器的方式
string::iterator it = s2.begin();
while (it != s2.end())
{
*it += 1;
it++;
}
it = s2.begin();
while (it != s2.end())
{
cout << *it << "";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}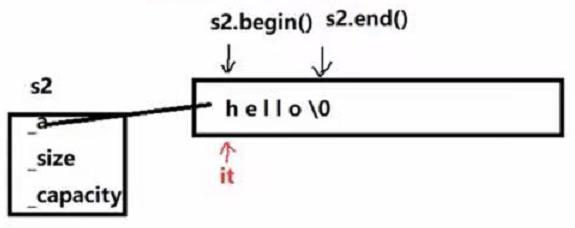
begin()返回第一个有效数据位置的迭代器
end()返回最后一个有效数据的下一个位置的迭代器
迭代器是一个像指针一样的东西,有可能是指针,也有可能不是指针!
迭代器的好处:可以统一类似的方式去访问修改容器
vector迭代器:
int main() { vector<int>v = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin(); while (vit != v.end()) { cout << *vit << ""; vit++; } cout << endl; }
所以容器都支持用你迭代器,所以迭代器才是容器通用的访问方式
vector/string这种结构支持下标+[]去访问,像list,map就不支持了
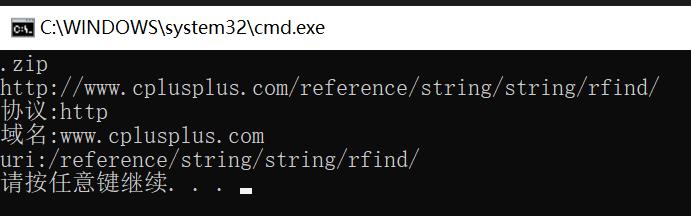
取文件的后缀
void test_string()
{
string file1("test.txt.zip");
string file2("test.c");
size_t pos1 = file1.rfind('.');
if (pos1 != string::npos)
{
//string sub1 = file1.substr(pos1,file1.size()-pos1);
string sub1 = file1.substr(pos1);
cout << sub1 << endl;
}
string url("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rfind/");
cout << url << endl;
//取出url中协议,域名,uri
size_t i1 = url.find("://");
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
string p = url.substr(0, i1 - 0);
cout << "协议:" << p << endl;
}
size_t i2 = url.find('/',i1+3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
string d = url.substr(i1+3,i2-(i1+3));
cout << "域名:" << d << endl;
}
string uri = url.substr(i2);
cout << "uri:" << uri << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
三,经典习题
字符串中的第一个唯一字符OJ

计数排序的思想:
class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s)
{
int count[26] = {0};
//统计出每个字符出现的次数
for(auto ch:s)
{
count[ch-'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();i++)
{
if(count[s[i]-'a'] == 1)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};仅仅反转字母OJ

class Solution {
public:
bool isLetter(char ch)
{
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
return true;
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')
return true;
return false;
}
string reverseOnlyLetters(string S) {
auto begin = S.begin();
auto end = S.end() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
while (begin < end && !isLetter(*begin))
++begin;
while (begin < end && !isLetter(*end))
--end;
swap(*begin, *end);
++begin;
--end;
}
return S;
}
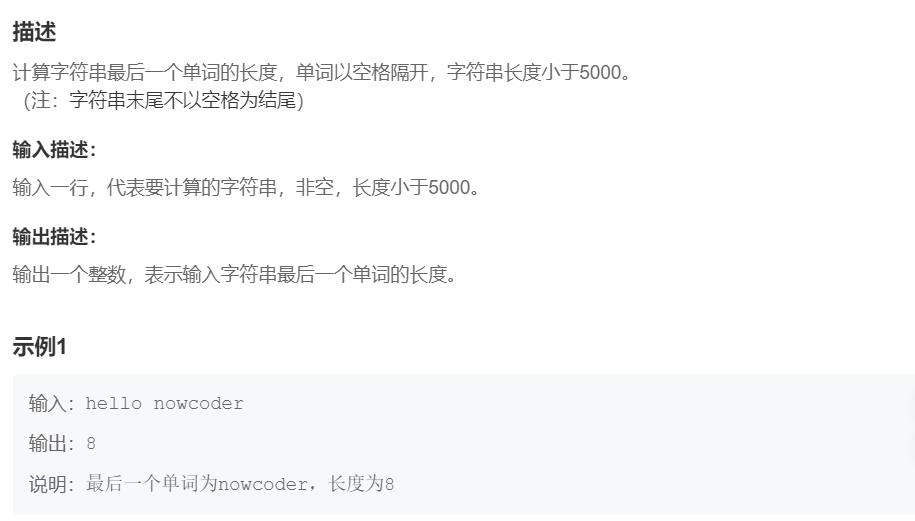
};字符串最后一个单词的长度OJ
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
size_t pos = s.rfind(' ');
if(pos != string::npos)
{
cout <<s.size()-(pos+1)<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<s.size()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}验证回文串OJ
class Solution
{
public:
bool IsletterOrNun(char ch)
{
if ((ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')
|| (ch >= 'a'&& ch <= 'z')
|| (ch >= '0'&& ch <= '9'))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool isPalindrome(string s)
{
int begin = 0;
int end = s.size() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
while (begin < end && !IsletterOrNun(s[begin]))
{
begin++;
}
while (begin < end && !IsletterOrNun(s[end]))
{
end--;
}
if (s[begin] != s[end])
{
//有一个是数字,就不存在大小写比较问题
if (s[begin] < 'A' || s[end] < 'A')
{
return false;
}
//忽略字母的大小写
else if (s[begin] < s[end] && s[begin] + 32 == s[end])
{
begin++;
end--;
}
else if (s[end] < s[begin] && s[end] + 32 == s[begin])
{
begin++;
end--;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
begin++;
end--;
}
}
return true;
}
};字符串相加OJ

class Solution
{
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2)
{
string retStr;
int end1 = num1.size() - 1;
int end2 = num2.size() - 1;
int carry = 0;//进位
while (end1 >= 0 || end2 >= 0)
{
int val1 = 0;
int val2 = 0;
if (end1 >= 0)
{
val1 = num1[end1] - '0';//转换成整数
end1--;
}
if (end2 >= 0)
{
val2 = num2[end2] - '0';//转换成整数
}
int ret = val1 + val2 + carry;
if (ret > 9)
{
ret -= 10;
carry = 1;
}
else
{
carry = 0;
}
retStr.insert(retStr.begin(), '0' + ret);
//retStr += ('0' + ret);
}
if (carry == 1)
{
retStr.insert(retStr.begin(), '1');
//retStr += '1';
}
reverse(retStr.begin(), retStr.end());
return retStr;
}
};四,深浅拷贝
深拷贝的传统写法:
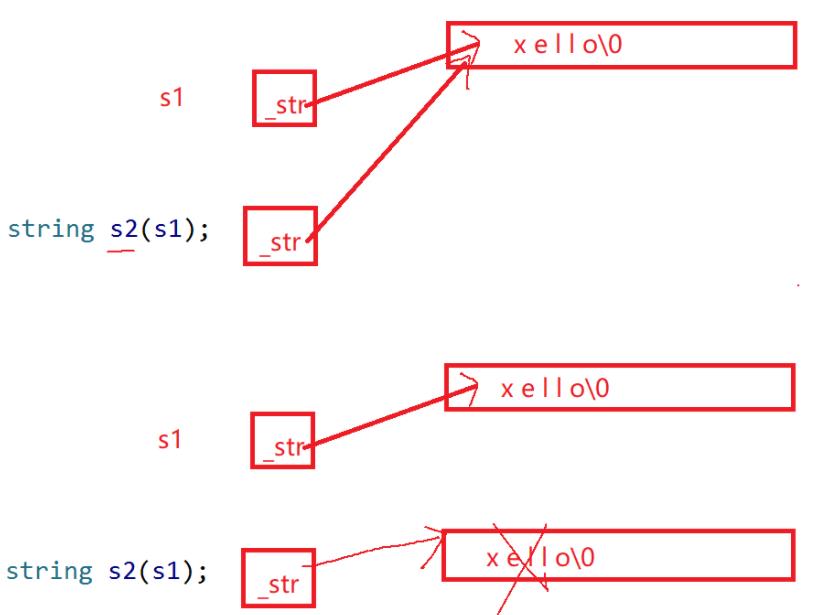
浅拷贝:
指向同一块空间
第一:析构两次空间
第二:其中一个去修改值,会影响另一个
深拷贝:
拷贝构造,新开一块跟原对象一样大的空间,再把原对象空间上的值拷贝过来
namespace bit
{
class string
{
public:
string(char* str)
:_str(new char[strlen(str)+1])
{
strcpy(_str, str);
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _str[pos];
}
//s2(s1)深拷贝
string(const string& s)
:_str(new char[strlen(s._str)+1])
{
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
private:
char* _str;
};
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello");
s1[0] = 'x';
string s2(s1);
s2[0] = 'y';
}
}赋值:
思考:下面这段代码的问题??? 有何缺陷?
——>>>万一假设new失败了,那么把s1对象给释放了
//s1 = s3
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
}——>改造:
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
char* tmp = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
return *this;
}深拷贝的现代写法:
//深拷贝的现代写法
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
赋值:
//s1=s3
string &operator = (const string &s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
return *this;
}
最简洁的现代写法:
string& operator = (string s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
return *this;
}以上是关于C++初阶string(上)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章