一篇文章让你精通:java集合讲解(练习处理)
Posted 韶光不负
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一篇文章让你精通:java集合讲解(练习处理)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
紧跟上文,相信前面文章让你对集合有一定了解,下面让我们对集合进行案例讲解,让你能够更加了解与使用集合。
问题一:找出下面错误的代码,并进行改正
package com.luo_sf.map;
public class Text {
public int gutIndexofArray(float[] f){
int res=0;
float objf=3.4;
List list=null;
for (int i = 0; i <f.size ; i++) {
list.add(f[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i <list.size() ; i++) {
float tmp=(float)list.get(i);
if(objf==tmp){
res=i;
}
}
return res;
}
}
解析:
1,基本数据类型的掌握,在jdk8中float类型是整数时,数字后面可以不用加f,但如果是小数时必须添加f(例如 float f =2.3f)
2,当我们在函数当中定义集合时,要在栈中开辟空间,所以不能使用null;
3,在数组中有length方法,没有size方法。
答案:
package com.luo_sf.map;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Text {
public int gutIndexofArray(float[] f){
int res=0;
float objf=3.4f;//小数加f
ArrayList list=new ArrayList(); //不能使用null
for (int i = 0; i <f.length ; i++) {
//数组当中没有size方法
list.add(f[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i <list.size() ; i++) {
float tmp=(float)list.get(i);
if(objf==tmp){
res=i;
break;//改进,查找第一个
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
float [] ft={1.2f,3.4f,6,3.5f,9,3.4f};
Text test=new Text();
int val=test.gutIndexofArray(ft);
System.out.println(val);
}
}
问题二:查看下面代码,打印输出的值是什么?
package com.luo_sf.map;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Text {
public static void print(List<Integer> al){
al.add(2);
al=new ArrayList<Integer>();
al.add(3);
al.add(4);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Integer> al=new ArrayList<>();
al.add(1);
print(al);
System.out.println(al.get(1));
System.out.println(al);
}
}
解析:
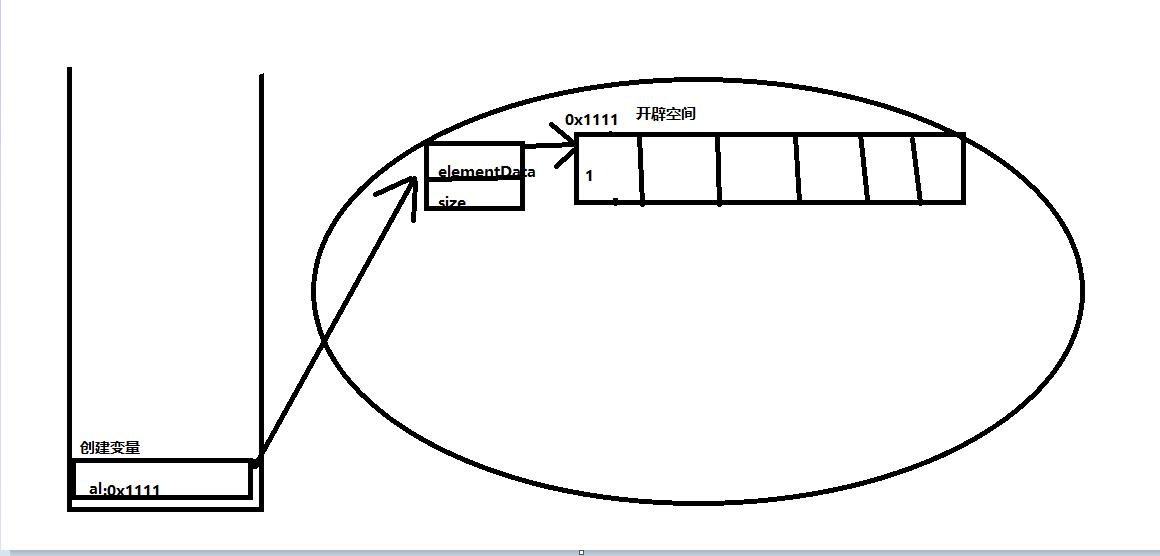
main函数是开始所以我们先找到main函数进行解析,我们可以看到创建了al变量,并创建了一个List空间,添加了元素1(如下图)
在进入到创建print函数当中,因为我们传入al,在al中添加了2,创建了al变量,并开辟了空间(开辟空间的后print中的al指向新的List)(如下图)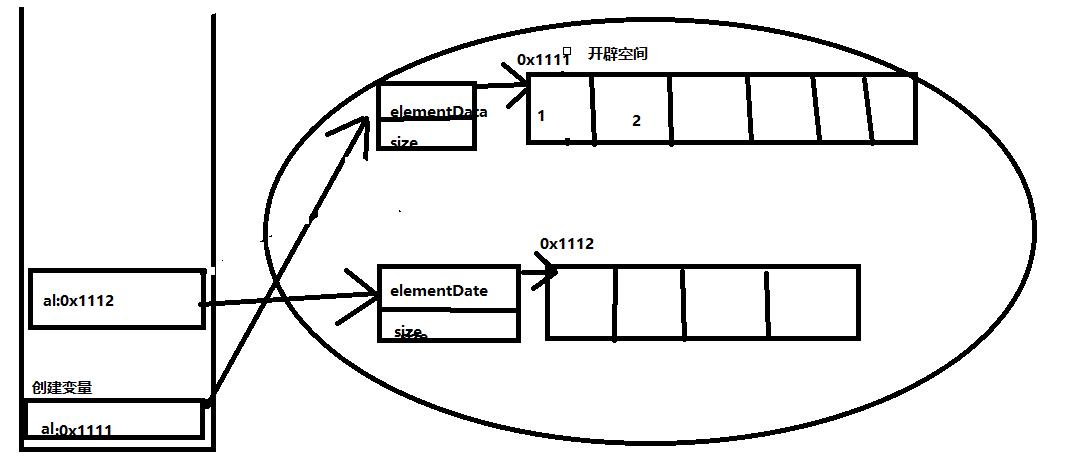
然后在新的List下添加元素3和4.
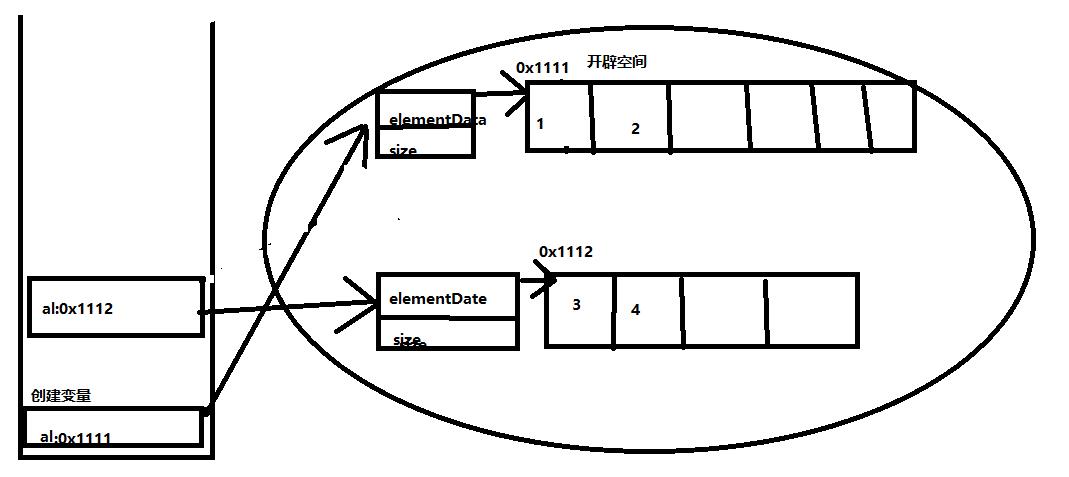
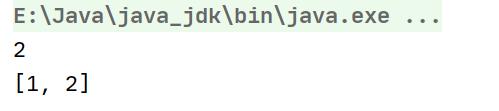
当我们最后输出是一个弹栈的过程,所以输出的应该是2与数组【1,2】.
答案:
练习1:完成下面要求
1,实现List到Map的转化具体要求如下
2,定义public void listtoMap方法,把list中Student元素封装到Map中
3,使用构造方法1创建多个学生信息并加入list
4,遍历List,输出全部学生信息
5,将list中学生信息放入到map当中
6,遍历map,输出Entry的key与value
一,创建学生类
package com.luo_sf.map;
//创建测试用的学生类
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private Double scpre;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age, Double scpre) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.scpre = scpre;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Double getScpre() {
return scpre;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setScpre(Double scpre) {
this.scpre = scpre;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\\'' +
", age=" + age +
", scpre=" + scpre +
'}';
}
}
二,书写方法
package com.luo_sf.map;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 实现List到Map的转化具体要求如下
* 定义public void listtoMap方法,把list中Student元素封装到Map中
* 使用构造方法1创建多个学生信息并加入list
* 遍历List,输出全部学生信息
* 将list中学生信息放入到map当中
* 遍历map,输出Entry的key与value
*/
public class Text {
public static Map lsittoMap(List<Student> list){
Map<Integer,Student> map=new HashMap<>();
for (Student stu: list) {
map.put(stu.getId(),stu);
}
return map;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建多个学生对象
Student stu1=new Student(1,"xiaoming",18,78.5);
Student stu2=new Student(2,"zhangsan",19,88.5);
Student stu3=new Student(3,"lishi",20,67.5);
Student stu4=new Student(4,"wangwu",18,88.5);
Student stu5=new Student(5,"xiaobai",17,98.5);
//添加入List
List<Student> list= new ArrayList<>();
list.add(stu1);
list.add(stu2);
list.add(stu3);
list.add(stu4);
list.add(stu5);
//遍历数组
for (Student stu: list) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
//list转化为Map
Map map=lsittoMap(list);
//遍历map
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet =map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Student> entry:entrySet){
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
功能2:定义mapToList()将Map映射信息封装到List中
创建一个实体类StudentEntry,可以存储Map中每一个Entry的信息
使用构造方法Student创建学生信息,并使用学生作为key
创建List对象,每一个元素都是StudrentEntry
将Map中每一个Entry信息放入List对象
创建一个实体类StudentEntry并加入List中
package com.luo_sf.map;
//创建StudentEntry类
public class StudentEntry {
private int key;
private Student value;
public StudentEntry() {
}
public StudentEntry(int key, Student value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public int getKey() {
return key;
}
public Student getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setKey(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public void setValue(Student value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentEntry{" +
"key=" + key +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
package com.luo_sf.map;
import com.sun.deploy.util.SyncAccess;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 实现List到Map的转化具体要求如下
* 定义public void listtoMap方法,把list中Student元素封装到Map中
* 使用构造方法1创建多个学生信息并加入list
* 遍历List,输出全部学生信息
* 将list中学生信息放入到map当中
* 遍历map,输出Entry的key与value
*/
/**
* 功能2:定义mapToList()将Map映射信息封装到List中
* 创建一个实体类StudentEntry,可以存储Map中每一个Entry的信息
* 使用构造方法Student创建学生信息,并使用学生作为key
* 创建List对象,每一个元素都是StudrentEntry
* 将Map中每一个Entry信息放入List对象
* 说明Comparable作用,并提过分数对学生进行排序
*/
public class Text {
public static List<StudentEntry> mapToList(Map<Integer,Student> map){
//创建List
List<StudentEntry> list =new ArrayList<>();
//遍历Map并存储到List中
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet=map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Student> entry: entrySet){
Integer key=entry.getKey();
Student value=entry.getValue();
StudentEntry studentEntry =new StudentEntry(key,value);
list.add(studentEntry);
}
//返回List
return list;
}
public static Map lsittoMap(List<Student> list){
Map<Integer,Student> map=new HashMap<>();
for (Student stu: list) {
map.put(stu.getId(),stu);
}
return map;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建多个学生对象
Student stu1=new Student(1,"xiaoming",18,78.5);
Student stu2=new Student(2,"zhangsan",19,88.5);
Student stu3=new Student(3,"lishi",20,67.5);
Student stu4=new Student(4,"wangwu",18,88.5);
Student stu5=new Student(5,"xiaobai",17,98.5);
//添加入List
List<Student> list= new ArrayList<>();
list.add(stu1);
list.add(stu2);
list.add(stu3);
list.add(stu4);
list.add(stu5);
//遍历数组
for (Student stu: list) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
//list转化为Map
Map map=lsittoMap(list);
//遍历map
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet =map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Student> entry:entrySet){
System.out.println(entry);
}
List<StudentEntry> list2=mapToList(map);
list2.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
以上是关于一篇文章让你精通:java集合讲解(练习处理)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章